算法刷题-Excel表列序号、单词拆分 II、排序链表

Excel表列序号(数学、字符串)
给你一个字符串 columnTitle ,表示 Excel 表格中的列名称。返回该列名称对应的列序号。
例如,
A -> 1 B -> 2 C -> 3 … Z -> 26 AA -> 27 AB -> 28 …
示例 1:
输入: columnTitle = “A” 输出: 1
示例 2:
输入: columnTitle = “AB” 输出: 28
示例 3:
输入: columnTitle = “ZY” 输出: 701
示例 4:
输入: columnTitle = “FXSHRXW” 输出: 2147483647
提示:
- 1 <= columnTitle.length <= 7
- columnTitle 仅由大写英文组成
- columnTitle 在范围 [“A”, “FXSHRXW”] 内
解答:
class Solution {public int titleToNumber(String s) {char[] charArray = s.toCharArray();int res = 0;for (int i = 0; i < charArray.length; i++) {res = res * 26 + (charArray[i] - 'A' + 1);}return res;}
}
单词拆分 II(字典树、记忆化搜索)
给定一个非空字符串 s 和一个包含非空单词列表的字典 wordDict,在字符串中增加空格来构建一个句子,使得句子中所有的单词都在词典中。返回所有这些可能的句子。
说明:
- 分隔时可以重复使用字典中的单词。
- 你可以假设字典中没有重复的单词。
示例 1:
输入: s = “catsanddog” wordDict = [“cat”, “cats”, “and”, “sand”, “dog”]
输出: [ “cats and dog”, “cat sand dog” ]
示例 2:
输入: s = “pineapplepenapple” wordDict = [“apple”, “pen”, “applepen”, “pine”, “pineapple”]
输出: [ “pine apple pen apple”, “pineapple pen apple”, “pine applepen apple” ]
解释: 注意你可以重复使用字典中的单词。
示例 3:
输入: s = “catsandog” wordDict = [“cats”, “dog”, “sand”, “and”, “cat”]
输出: []
解答:
class Solution {public List<String> wordBreak(String s, List<String> wordDict) {List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();int max = 0, min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();for (String word : wordDict) {set.add(word);max = Integer.max(max, word.length());min = Integer.min(min, word.length());}boolean f[] = new boolean[s.length() + 1];f[0] = true;for (int i = 1; i < s.length() + 1; i++) {for (int j = Math.max(i - max, 0); j <= i - min; j++) {if (f[j] && set.contains(s.substring(j, i))) {f[i] = true;break;}}}if (f[s.length()]) {dfs(s, res, new StringBuilder(), set, 0, max, min);}return res;}private void dfs(String s, List<String> res, StringBuilder sb, Set<String> set, int index, int max, int min) {if (index == s.length()) {sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1);res.add(sb.toString());return;}String str;int size;for (int i = index + min; i <= s.length() && i <= index + max; i++) {if (set.contains(str = s.substring(index, i))) {size = sb.length();sb.append(str).append(' ');dfs(s, res, sb, set, i, max, min);sb.delete(size, sb.length());}}}
}
排序链表(链表、双指针)
给你链表的头结点 head ,请将其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的链表 。
进阶:
- 你可以在 O(n log n) 时间复杂度和常数级空间复杂度下,对链表进行排序吗?
示例 1:
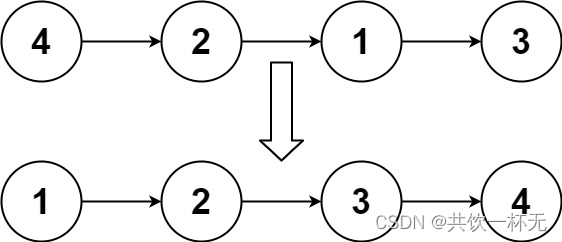
输入:head = [4,2,1,3] 输出:[1,2,3,4]
示例 2:
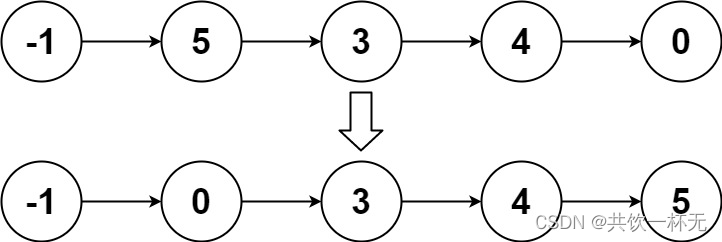
输入:head = [-1,5,3,4,0] 输出:[-1,0,3,4,5]
示例 3:
输入:head = [] 输出:[]
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目在范围 [0, 5 * 104] 内
- -105 <= Node.val <= 105
public class ListNode {int val;ListNode next;ListNode(int x) {val = x;}
}
class Solution {public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {if (head == null)return head;return mergeSort(head);}public ListNode mergeSort(ListNode head) {if (head.next == null)return head;ListNode p1 = head;ListNode p2 = head.next;if (p2 != null && p2.next != null) {p1 = p1.next;p2 = p2.next.next;}ListNode left = head;ListNode right = p1.next;p1.next = null;left = mergeSort(left);right = mergeSort(right);return merge(left, right);}public ListNode merge(ListNode left, ListNode right) {ListNode head = null;if (left.val < right.val) {head = left;left = left.next;} else {head = right;right = right.next;}ListNode tmp = head;while (left != null && right != null) {if (left.val < right.val) {tmp.next = left;left = left.next;} else {tmp.next = right;right = right.next;}tmp = tmp.next;}tmp.next = left != null ? left : right;return head;}
}
本文内容到此结束了,
如有收获欢迎点赞👍收藏💖关注✔️,您的鼓励是我最大的动力。
如有错误❌疑问💬欢迎各位指出。
主页:共饮一杯无的博客汇总👨💻保持热爱,奔赴下一场山海。🏃🏃🏃
