【Leetcode】队列实现栈和栈实现队列



目录
一.【Leetcode225】队列实现栈
1.链接
2.题目再现
3.解法
二.【Leetcode232】栈实现队列
1.链接
2.题目再现
3.解法
一.【Leetcode225】队列实现栈
1.链接
队列实现栈
2.题目再现
3.解法
这道题给了我们两个队列,要求去实现栈;
首先,我们要知道栈和队列的特征:
栈:后进先出,只能从栈顶入数据和出数据;
队列:先进先出,从队尾入数据,队头出数据;
根据这些特点,我们可以采用两边倒的方法来实现;
具体来说:
1.入栈时就是在不为空的队列插入数据,若两个队列都为空,就随便插入到一个队列中;
2.出栈时将不为空的队列的数据倒入为空的队列中,当不为空的队列就剩一个数据时,就停止向空队列倒数据,然后再删点那最后一个数据;
3.判空时,需要两个队列都为空,才算栈为空;
4.取栈顶元素即取不为空的队列的队尾元素,在取栈顶元素前要判断栈是否为空;
5.销毁栈时,要先销毁其中的两个队列,然后再销毁栈。
因为是用C语言实现的,所以得自己手搓个队列。
typedef int Qdatatype;typedef struct QueueNode
{struct QueeuNode* next;Qdatatype data;
}QueueNode;typedef struct Queue
{QueueNode* head;QueueNode* tail;
}Queue;
void Queueinit(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);pq->head = NULL;pq->tail = NULL;
}void Queuedestroy(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);QueueNode* cur = pq->head;while (cur != pq->tail){QueueNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}void Queuepush(Queue* pq, Qdatatype x)
{assert(pq);QueueNode* newnode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;if (pq->head == NULL){pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;}else{pq->tail->next = newnode;pq->tail = newnode;}
}void Queuepop(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(pq->head);QueueNode* next = pq->head->next;if (pq->head->next == NULL){free(pq->head);pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;}else{free(pq->head);pq->head = next;}
}Qdatatype Queuefront(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(pq->head);return pq->head->data;
}Qdatatype Queueback(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(Queuesize(pq) > 0);return pq->tail->data;
}int Queuesize(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);int size = 0;QueueNode* cur = pq->head;while (cur != pq->tail->next){size++;cur = cur->next;}return size;
}bool Queueempty(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->head == NULL;
}typedef struct
{Queue q1;Queue q2;
} MyStack;MyStack* myStackCreate() {MyStack*obj=(MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));if(obj==NULL)exit(-1);Queueinit(&obj->q1);Queueinit(&obj->q2);return obj;
}void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x)
{if(!Queueempty(&obj->q1)){Queuepush(&obj->q1,x);}else{Queuepush(&obj->q2,x);}
}int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {Queue*empty=&obj->q1;Queue*noempty=&obj->q2;if(!Queueempty(&obj->q1)){empty=&obj->q2;noempty=&obj->q1;}while(Queuesize(noempty)>1){Queuepush(empty,Queuefront(noempty));Queuepop(noempty);}int front=Queuefront(noempty);Queuepop(noempty);return front;
}int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {if(!Queueempty(&obj->q1)){return Queueback(&obj->q1);}else{return Queueback(&obj->q2);}
}
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {return Queueempty(&obj->q1)&&Queueempty(&obj->q2);
}void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {Queuedestroy(&obj->q1);Queuedestroy(&obj->q2);free(obj);
}
二.【Leetcode232】栈实现队列
1.链接
栈实现队列
2.题目再现

3.解法
这个的解法和上面的类似,只不过这个不用总是来回倒;
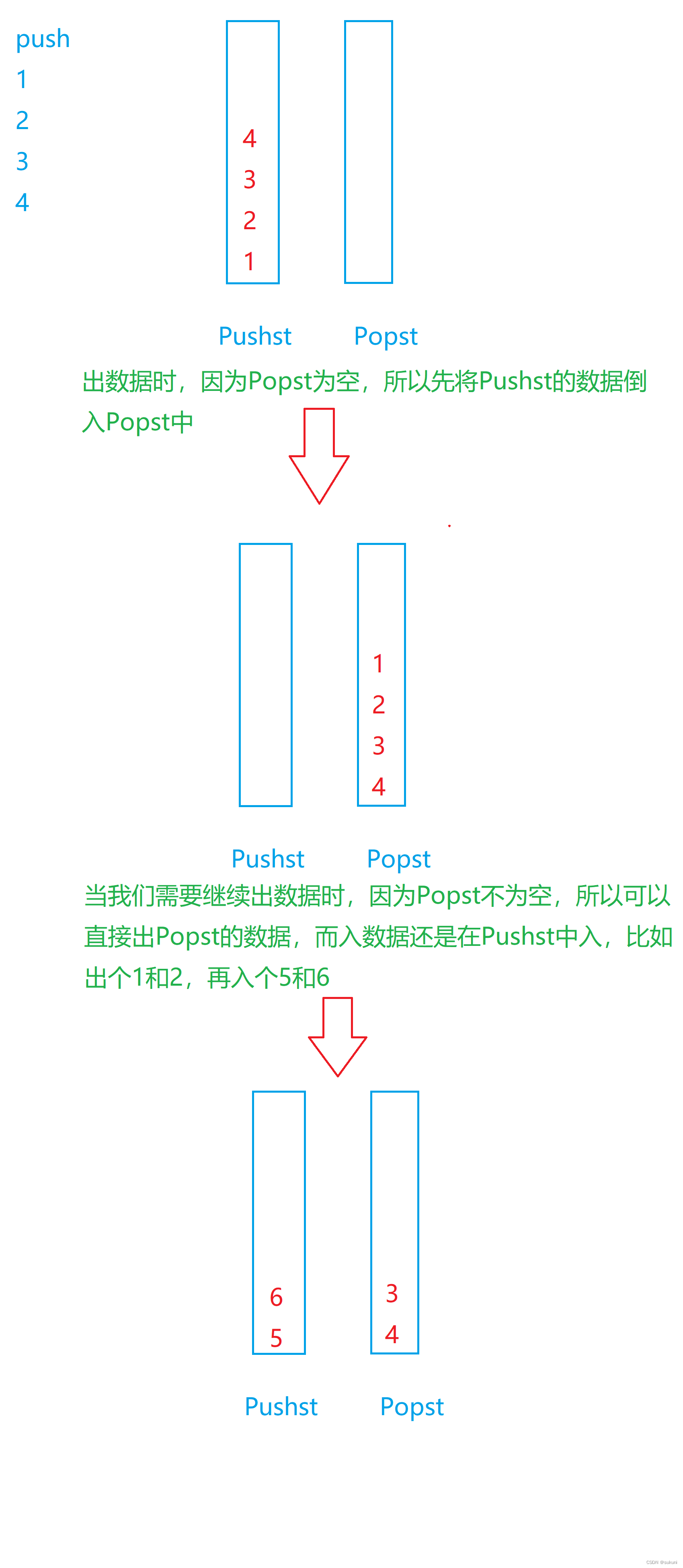
根据栈和队列的特征,我们会发现将一个栈中的数据倒入另一个栈时,数据的顺序刚好符合队列的要求,不需要再重复地倒数据,所以我们可以让一个栈专门用来入数据(Pushst),一个栈专门用来出数据(Popst),当我们要出数据而这个栈为空时,我们才将用来入数据的栈中的数据倒入用来出数据的栈 。
如图:
1.判空时,需要两个栈都为空,队列才为空;
2.返回队头数据时,和出数据的操作类似,只是不需要删除队头的数据,还有在之前要判断队列是否为空;
3.销毁队列前,要先销毁两个栈。
同样,因为是C语言,得先手搓个栈。
#define MR_CAP 5
typedef int STdatatype;typedef struct Stack
{STdatatype* arr;int top;int capacity;
}ST;void Stackinit(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);ps->arr = (STdatatype*)malloc(MR_CAP * sizeof(STdatatype));if (ps->arr == NULL){perror("Stackinit malloc");exit(-1);}ps->top = 0;ps->capacity = MR_CAP;
}void Stackdestroy(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);free(ps->arr);ps->arr = NULL;ps->top = 0;ps->capacity = 0;
}void Stackpush(ST* ps, STdatatype x)
{assert(ps);if (ps->top == ps->capacity){STdatatype* tmp = (STdatatype*)realloc(ps->arr, ps->capacity * 2 * sizeof(STdatatype));if (tmp == NULL){perror("Stackpush realloc");exit(-1);}else{ps->arr = tmp;ps->capacity *= 2;}}ps->arr[ps->top] = x;ps->top++;
}void Stackpop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(ps->top > 0);ps->top--;
}STdatatype Stacktop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->arr[ps->top - 1];
}int Stacksize(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top;}bool Stackempty(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);if (ps->top == 0){return true;}elsereturn false;}typedef struct {ST Pushst;ST Popst;
} MyQueue;MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {MyQueue*obj=(MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));if(obj==NULL)exit(-1);Stackinit(&obj->Pushst);Stackinit(&obj->Popst);return obj;
}void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {Stackpush(&obj->Pushst,x);
}int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {if(Stackempty(&obj->Popst)){while(!Stackempty(&obj->Pushst)){Stackpush(&obj->Popst,Stacktop(&obj->Pushst));Stackpop(&obj->Pushst);}}return Stacktop(&obj->Popst);}int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {int front=myQueuePeek(obj);Stackpop(&obj->Popst);return front;
}bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {return Stackempty(&obj->Pushst)&&Stackempty(&obj->Popst);
}void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {Stackdestroy(&obj->Pushst);Stackdestroy(&obj->Popst);free(obj);
}
🐲👻这两道题的讲解就到这里了,若有错误或是建议欢迎小伙伴们指出。🐯🤖
🥰🤩希望小伙伴们可以多多支持博主哦。😍😃
😁😄谢谢你的阅读。😼😸