Flowable从入门到源码分析

什么是工作流?
工作流,是把业务之间的各个步骤以及规则进行抽象和概括性的描述。使用特定的语言为业务流程建模,让其运行在计算机上,并让计算机进行计算和推动。
工作流解决的痛点在于,解除业务宏观流程和微观逻辑的耦合,让熟悉宏观业务流程的人去制定整套流转逻辑,而让专业的人只需要关心他们应当关心的流程节点。
基础概念
BPM:Business Process Management,业务流程管理
BPMN:Business Process Modeling Notation,BPMN是一个广泛接受与支持的,展现流程的注记方法,是一种图形化表示业务流程的标准。它旨在为业务用户、业务分析师、技术开发人员和流程管理系统提供一种通用的、易于理解的方法来描述和执行业务流程。BPMN2.0正式版本于2011年1月3日发布,常见的工作流引擎如:Activiti、Flowable、jBPM 都基于 BPMN 2.0 标准。
附上BPMN官方网站:https://www.bpmn.org/
CMMN:Case Management Model and Notation,CMMN具有与BPMN不同的基本范例,CMMN没有顺序的流程,它以某种状态对案例建模。
DMN:Decision Model and Notation,DMN的目的是提供一个模型决策结构,从而使组织的策略可以用图形清晰的地描绘出来,这个标准可以用于实现规则引擎。
流程元素: BPMN 2.0 定义了许多元素,用于表示业务流程的各个方面。这些元素分为四大类:
- 流程对象(Flow Objects):这是 BPMN 2.0 中的主要元素,包括事件(Event)、活动(Activity)和网关(Gateway)。
- 连接对象(Connecting Objects):这些元素用于表示流程对象之间的关系,包括顺序流(Sequence Flow)、消息流(Message Flow)和关联(Association)。
- 泳道(Swimlanes):泳道表示流程中的组织边界,包括池(Pool)和泳道(Lane)。
- 数据和制品(Data and Artifacts):这些元素用于表示流程中的数据和其他相关信息,包括数据对象(Data Object)、数据存储(Data Store)和注释(Annotation)。
事件:通常用于为流程生命周期中发生的事情建模。事件总是图形化为圆圈。
活动:用于表示需要执行的行为,任务用带有图标的圆角矩形表示。
网关:用于控制执行的流向。网关用其中带有图标的菱形表示。

流程定义(ProcessDefinition):将一个流程 XML 文件部署到 flowable 中,这就是一个定义好的流程
流程实例(ProcessInstance):通过流程定义启动的一个流程,表示一个流程从开始到结束的最大的流程分支,在一个流程中,只存在一个流程实例,流程实例和流程定义的关系就类似于 Java 对象和 Java 类之间的关系
执行实例(Execution):流程实例通常是执行实例的根结点,即在一个流程中,出口和入口可以算是一个流程实例的节点,而中间的过程则是执行实例
流程图
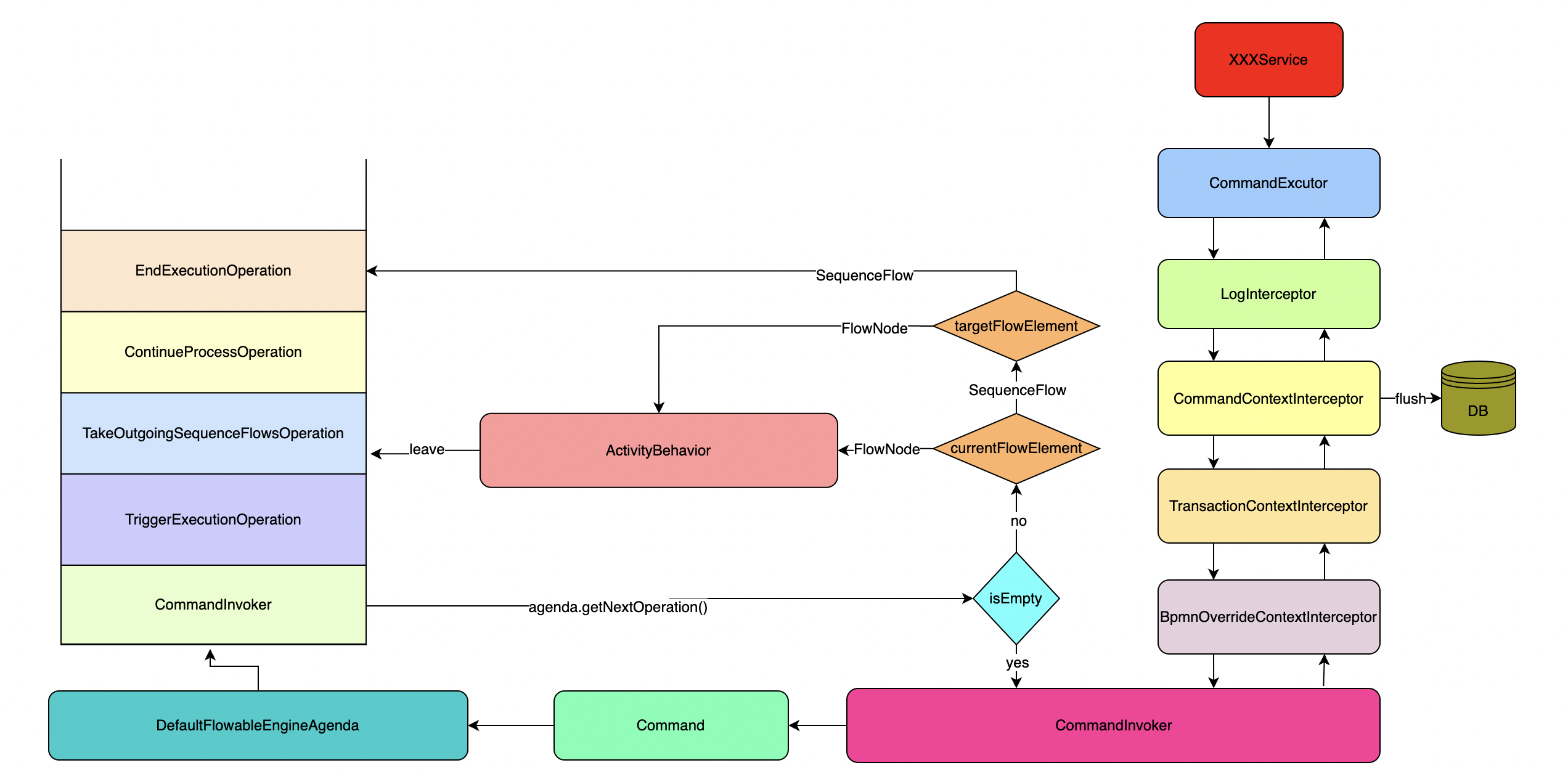
Flowable架构图
表结构
表名的后缀,有一些是通用的后缀名词
- DATABASECHANGELOG:表名中包含这个单词的,表示这个表是 Liquibase 执行的记录,Liquibase 是一个数据库脚本管理的工具,包含 DATABASECHANGELOG 后缀的表一共是 6 张。
- DATABASECHANGELOGLOCK:表名中包含这个单词的,表示这个表记录 Liquibase 执行锁的,用以确保一次只运行一个 Liquibase 实例,包含 DATABASECHANGELOGLOCK 后缀的表也是 6 张。
| 表分类 | 表名 | 解释 |
|---|---|---|
| 一般数据 | ||
| ACT_GE_BYTEARRAY | 通用的流程定义和流程资源 | |
| ACT_GE_PROPERTY | 系统相关属性 | |
| 流程历史记录 | ||
| ACT_HI_ACTINST | 历史的流程实例 | |
| ACT_HI_ATTACHMENT | 历史的流程附件 | |
| ACT_HI_COMMENT | 历史的说明性信息 | |
| ACT_HI_DETAIL | 历史的流程运行中的细节信息 | |
| ACT_HI_ENTITYLINK | 历史参与的人员表 | |
| ACT_HI_IDENTITYLINK | 历史的流程运行过程中用户关系 | |
| ACT_HI_PROCINST | 历史的流程实例 | |
| ACT_HI_TASKINST | 历史的任务实例 | |
| ACT_HI_VARINST | 历史的流程运行中的变量信息 | |
| 流程定义表 | ||
| ACT_RE_DEPLOYMENT | 部署单元信息 | |
| ACT_RE_MODEL | 模型信息 | |
| ACT_RE_PROCDEF | 已部署的流程定义 | |
| 运行实例表 | ||
| ACT_RU_ACTINST | 指示活动的当前状态 | |
| ACT_RU_EVENT_SUBSCR | 运行时事件 | |
| ACT_RU_EXECUTION | 运行时流程执行实例 | |
| ACT_RU_IDENTITYLINK | 运行时用户关系信息,存储任务节点与参与者的相关信息 | |
| ACT_RU_ENTITYLINK | 存储实例的父子关系的信息 | |
| ACT_RU_JOB | 运行时作业 | |
| ACT_RU_TIMER_JOB | 运行时作业 | |
| ACT_RU_SUSPENDED_JOB | 运行时作业 | |
| ACT_RU_EXTERNAL_JOB | 运行时作业 | |
| ACT_RU_HISTORY_JOB | 运行时作业 | |
| ACT_RU_DEADLETTER_JOB | 运行时作业 | |
| ACT_RU_TASK | 运行时任务 | |
| ACT_RU_VARIABLE | 运行时变量表 | |
| 用户用户组表 | ||
| ACT_ID_BYTEARRAY | 二进制数据表,用户组的部署内容 | |
| ACT_ID_GROUP | 用户组信息表 | |
| ACT_ID_INFO | 用户信息详情表 | |
| ACT_ID_MEMBERSHIP | 人与组关系表 | |
| ACT_ID_PRIV | 权限表 | |
| ACT_ID_PRIV_MAPPING | 用户或组权限关系表 | |
| ACT_ID_PROPERTY | 属性表 | |
| ACT_ID_TOKEN | 记录用户的token信息 | |
| ACT_ID_USER | 用户表 | |
| 表单 | ||
| ACT_FO_FORM_DEFINITION | 表单定义表 | |
| ACT_FO_FORM_DEPLOYMENT | 表单部署表 | |
| ACT_FO_FORM_INSTANCE | 表单实例表 | |
| ACT_FO_FORM_RESOURCE | 表单源数据表 | |
| 引擎存储和应用部署 | ||
| ACT_APP_APPDEF | 应用程序定义 | |
| ACT_APP_DEPLOYMENT | 应用程序部署信息 | |
| ACT_APP_DEPLOYMENT_RESOURCE | 应用程序部署资源 | |
| CMMN相关 | ||
| ACT_CMMN_CASEDEF | CMMN的定义 | |
| ACT_CMMN_DEPLOYMENT | CMMN的部署 | |
| ACT_CMMN_DEPLOYMENT_RESOURCE | CMMN相关资源 | |
| ACT_CMMN_HI_CASE_INST | CMMN引擎启动的实例 | |
| ACT_CMMN_HI_MIL_INST | 每个里程碑的数据 | |
| ACT_CMMN_HI_PLAN_ITEM_INST | 计划项的数据 | |
| ACT_CMMN_RU_CASE_INST | 已启动但尚未完成的实例的条目 | |
| ACT_CMMN_RU_MIL_INST | 实例的一部分达到的每个里程碑的条目 | |
| ACT_CMMN_RU_PLAN_ITEM_INST | 实例执行期间创建的每个实例的条目 | |
| ACT_CMMN_RU_SENTRY_PART_INST | 存储哨兵 | |
| DMN相关 | ||
| ACT_DMN_DEPLOYMENT | DMN的部署表 | |
| ACT_DMN_DEPLOYMENT_RESOURCE | DMN的资源表 | |
| ACT_DMN_DECISION | 已部署决策表的元数据,来自其他引擎的定义相对应 | |
| ACT_DMN_HI_DECISION_EXECUTION | 有关 DMN 决策表执行的审计信息 |
Service总览
| service名称 | service作用 |
|---|---|
| RepositoryService | Flowable的资源管理类,部署(deployments)与 流程定义(process definitions) |
| RuntimeService | Flowable的流程运行管理类,启动新流程实例、读取与存储流程变量(process variables) 、查询流程实例与执行(Execution) |
| TaskService | Flowable的任务管理类,查询任务、分配执行用户(assignee) 、认领任务(claim) 、完成任务(complete) |
| HistoryService | Flowable的历史管理类,提供查询历史数据的能力 |
| IdentityService | 用于管理组与用户,可选(引擎运行时并不做用户校验) |
| FormService | 表单相关服务,可选(表单不一定要嵌入流程定义) |
| ManagementService | Flowable的引擎管理类,用于读取数据库表与表原始数据的信息,也提供了对作业(job)的查询与管理操作 |
| DynamicBpmnService | 可用于动态修改流程定义中的部分内容,而不需要重新部署 |
流程分析(附源码)
以下源码基于flowable-6.8.0
画流程图
市面上有3种方式
- 使用官方的
flowable-ui - Flowable提供了名为Flowable Eclipse Designer的Eclipse插件
- 使用IDEA中的插件Flowable BPMN visualizer
这里使用IDEA中的插件,进入setting下载插件
新建项目工程后,在resource下新建BPMN文件
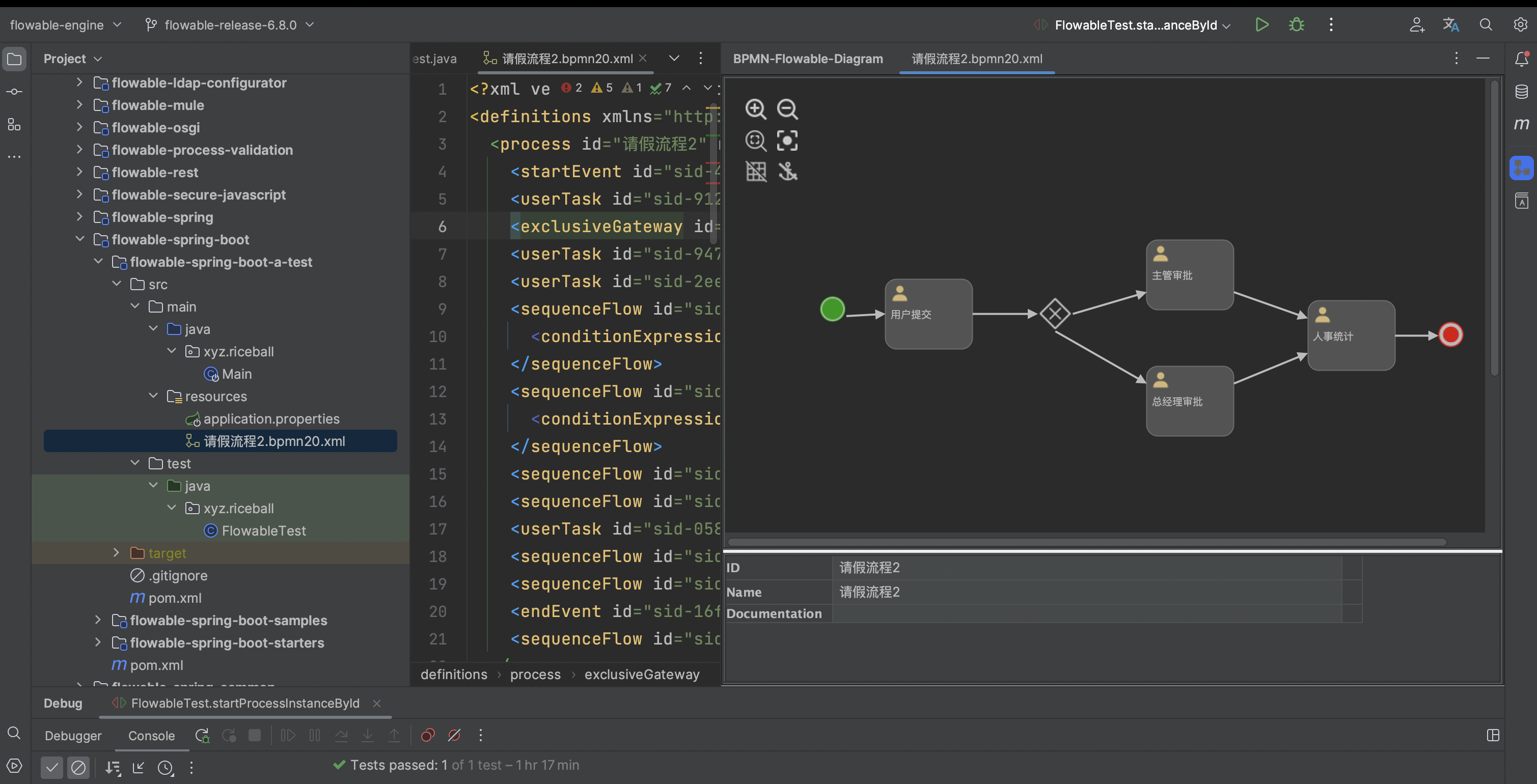
简单描述下文件内容,用户提交一个请假申请,如果不大于3天需要主管审批,如果大于3天需要经历审批,最后由人事处理。生成好的流程文件如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<definitions xmlns="http://www.omg.org/spec/BPMN/20100524/MODEL" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:flowable="http://flowable.org/bpmn" xmlns:bpmndi="http://www.omg.org/spec/BPMN/20100524/DI" xmlns:omgdc="http://www.omg.org/spec/DD/20100524/DC" xmlns:omgdi="http://www.omg.org/spec/DD/20100524/DI" typeLanguage="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" expressionLanguage="http://www.w3.org/1999/XPath" targetNamespace="http://www.flowable.org/processdef"><process id="请假流程2" name="请假流程2" isExecutable="true"><startEvent id="sid-4b49e00f-e468-45d0-90b0-84330a35204a"/><userTask id="sid-9120a0f1-b666-419f-b99f-507f52d2653b" name="用户提交" flowable:assignee="#{user}"/><exclusiveGateway id="sid-f3135f16-d564-4faf-ad90-1de393e7be4d"/><userTask id="sid-9472c76f-3d81-42cf-83f9-ada540b1f70c" name="主管审批" flowable:assignee="#{leader}"/><userTask id="sid-2eef5598-6853-4d2e-a954-bf1f6e635540" name="总经理审批" flowable:assignee="#{manger}"/><sequenceFlow id="sid-a564c466-ba7b-45be-8f2b-7ccbacfaca67" sourceRef="sid-f3135f16-d564-4faf-ad90-1de393e7be4d" targetRef="sid-9472c76f-3d81-42cf-83f9-ada540b1f70c"><conditionExpression xsi:type="tFormalExpression">#{day<=3}</conditionExpression></sequenceFlow><sequenceFlow id="sid-3a113001-c96d-46ed-a568-7f6128cfb6fd" sourceRef="sid-f3135f16-d564-4faf-ad90-1de393e7be4d" targetRef="sid-2eef5598-6853-4d2e-a954-bf1f6e635540"><conditionExpression xsi:type="tFormalExpression">#{day>3}</conditionExpression></sequenceFlow><sequenceFlow id="sid-9da89232-cb03-460b-871c-f1a51d616946" sourceRef="sid-4b49e00f-e468-45d0-90b0-84330a35204a" targetRef="sid-9120a0f1-b666-419f-b99f-507f52d2653b"/><sequenceFlow id="sid-08fc0c8e-3cef-44cf-a35a-45076ab3529c" sourceRef="sid-9120a0f1-b666-419f-b99f-507f52d2653b" targetRef="sid-f3135f16-d564-4faf-ad90-1de393e7be4d"/><userTask id="sid-058f63b5-fe27-49cc-8deb-943cc5509903" name="人事统计" flowable:assignee="#{hr}"/><sequenceFlow id="sid-e5a082e3-b87e-4f24-b328-85385e19b9ca" sourceRef="sid-2eef5598-6853-4d2e-a954-bf1f6e635540" targetRef="sid-058f63b5-fe27-49cc-8deb-943cc5509903"/><sequenceFlow id="sid-4414495e-9471-4721-95ce-c0ee00c6e3e1" sourceRef="sid-9472c76f-3d81-42cf-83f9-ada540b1f70c" targetRef="sid-058f63b5-fe27-49cc-8deb-943cc5509903"/><endEvent id="sid-16f9f49b-d761-4b5e-80ca-049f47920f7c"/><sequenceFlow id="sid-18c67f5e-fcf8-4e01-b6d3-cb2b1779bfcc" sourceRef="sid-058f63b5-fe27-49cc-8deb-943cc5509903" targetRef="sid-16f9f49b-d761-4b5e-80ca-049f47920f7c"/></process><bpmndi:BPMNDiagram id="BPMNDiagram_请假流程2"><bpmndi:BPMNPlane bpmnElement="请假流程2" id="BPMNPlane_请假流程2"><bpmndi:BPMNShape id="shape-56e4d266-0600-41e8-ab81-5ff92e484e88" bpmnElement="sid-4b49e00f-e468-45d0-90b0-84330a35204a"><omgdc:Bounds x="455.0" y="-85.0" width="30.0" height="30.0"/></bpmndi:BPMNShape><bpmndi:BPMNShape id="shape-369f073e-dbf3-4c8e-866c-c97780c1cd5f" bpmnElement="sid-9120a0f1-b666-419f-b99f-507f52d2653b"><omgdc:Bounds x="530.0" y="-105.0" width="100.0" height="80.0"/></bpmndi:BPMNShape><bpmndi:BPMNShape id="shape-913d6bb6-f1d7-47eb-9570-4407e13614ab" bpmnElement="sid-f3135f16-d564-4faf-ad90-1de393e7be4d"><omgdc:Bounds x="705.0" y="-85.0" width="40.0" height="40.0"/></bpmndi:BPMNShape><bpmndi:BPMNShape id="shape-b7d0782d-447f-4baa-91a7-871500d02c94" bpmnElement="sid-9472c76f-3d81-42cf-83f9-ada540b1f70c"><omgdc:Bounds x="830.0" y="-150.0" width="100.0" height="80.0"/></bpmndi:BPMNShape><bpmndi:BPMNShape id="shape-948140a9-d1bd-4e03-80ec-9bd02a606055" bpmnElement="sid-2eef5598-6853-4d2e-a954-bf1f6e635540"><omgdc:Bounds x="829.99994" y="-5.0" width="100.0" height="80.0"/></bpmndi:BPMNShape><bpmndi:BPMNEdge id="edge-061c4eeb-dcc7-4f25-ae7d-350ad9258275" bpmnElement="sid-a564c466-ba7b-45be-8f2b-7ccbacfaca67"><omgdi:waypoint x="745.0" y="-65.0"/><omgdi:waypoint x="830.0" y="-90.0"/></bpmndi:BPMNEdge><bpmndi:BPMNEdge id="edge-aa9ce902-d8c0-470d-bcdc-4853422ed5bc" bpmnElement="sid-3a113001-c96d-46ed-a568-7f6128cfb6fd"><omgdi:waypoint x="725.0" y="-45.0"/><omgdi:waypoint x="829.99994" y="15.0"/></bpmndi:BPMNEdge><bpmndi:BPMNEdge id="edge-29627cef-4fcb-4b40-88d1-a86239798978" bpmnElement="sid-9da89232-cb03-460b-871c-f1a51d616946"><omgdi:waypoint x="485.0" y="-62.5"/><omgdi:waypoint x="530.0" y="-65.0"/></bpmndi:BPMNEdge><bpmndi:BPMNEdge id="edge-de1b1a45-6c9f-45c7-9bd3-09c71010a396" bpmnElement="sid-08fc0c8e-3cef-44cf-a35a-45076ab3529c"><omgdi:waypoint x="630.0" y="-65.0"/><omgdi:waypoint x="705.0" y="-65.0"/></bpmndi:BPMNEdge><bpmndi:BPMNShape id="shape-78c592c7-86bf-4d09-9066-a14df0981477" bpmnElement="sid-058f63b5-fe27-49cc-8deb-943cc5509903"><omgdc:Bounds x="1015.0" y="-80.0" width="100.0" height="80.0"/></bpmndi:BPMNShape><bpmndi:BPMNEdge id="edge-8fe353c5-c308-4f60-9091-6f7f554c043e" bpmnElement="sid-e5a082e3-b87e-4f24-b328-85385e19b9ca"><omgdi:waypoint x="929.99994" y="15.0"/><omgdi:waypoint x="1015.0" y="-20.0"/></bpmndi:BPMNEdge><bpmndi:BPMNEdge id="edge-67ac2561-afdb-4d7e-81bb-c3378f28e868" bpmnElement="sid-4414495e-9471-4721-95ce-c0ee00c6e3e1"><omgdi:waypoint x="930.0" y="-90.0"/><omgdi:waypoint x="1015.0" y="-60.0"/></bpmndi:BPMNEdge><bpmndi:BPMNShape id="shape-e86ea582-8024-4ea1-abc9-ff948a54130a" bpmnElement="sid-16f9f49b-d761-4b5e-80ca-049f47920f7c"><omgdc:Bounds x="1165.0" y="-55.0" width="30.0" height="30.0"/></bpmndi:BPMNShape><bpmndi:BPMNEdge id="edge-16cfbe24-44c2-4988-b94c-ea4f68799253" bpmnElement="sid-18c67f5e-fcf8-4e01-b6d3-cb2b1779bfcc"><omgdi:waypoint x="1115.0" y="-40.0"/><omgdi:waypoint x="1165.0" y="-40.0"/></bpmndi:BPMNEdge></bpmndi:BPMNPlane></bpmndi:BPMNDiagram>
</definitions>初始化配置
本文章根据flowable-spring-boot-starter构建,会自动识别配置信息,通过AppEngineFactoryBean、ContentEngineFactoryBean等
启动项目后,会走到创建flowableAppEngine的代码中:
@Bean(name="flowableAppEngine")public AppEngineFactoryBean appEngine(SpringAppEngineConfiguration configuration) throws Exception {AppEngineFactoryBean appEngineFactoryBean = new AppEngineFactoryBean();appEngineFactoryBean.setAppEngineConfiguration(configuration);invokeConfigurers(configuration);return appEngineFactoryBean;}
创建的时候会调用AppEngineFactoryBean.getObject()方法,然后调用buildAppEngine去初始化配置
@Overridepublic AppEngine getObject() throws Exception {configureExternallyManagedTransactions();if (appEngineConfiguration.getBeans() == null) {appEngineConfiguration.setBeans(new SpringBeanFactoryProxyMap(applicationContext));}//初始化配置 this.appEngine = appEngineConfiguration.buildAppEngine();return this.appEngine;}
会进入SpringAppEngineConfiguration调用父类AppEngineConfiguration的buildAppEngine方法
public AppEngine buildAppEngine() {init();return new AppEngineImpl(this);}
App目前看应该是系统级别的配置,再执行init方法的configuratorsAfterInit()这一行后,是调用EngineConfigurator 的 configure() 方法,就是存在有什么模块就去初始化当前模块的内容
- SpringProcessEngineConfigurator
- SpringEventRegistryConfigurator
- SpringIdmEngineConfigurator
- SpringDmnEngineConfigurator
- SpringFormEngineConfigurator
- SpringContentEngineConfigurator
- SpringCmmnEngineConfigurator
以下都以SpringProcessEngineConfigurator模块的初始化为例:
/* 初始化SpringProcessEngineConfigurator */public void init() {//引擎配置initEngineConfigurations();//合并已经加载的和通过spi机制获取到的 EngineConfiguratorinitConfigurators();//调用 EngineConfigurator 的 beforeInit()configuratorsBeforeInit();initClock();initObjectMapper();initProcessDiagramGenerator();initCommandContextFactory();initTransactionContextFactory();//初始化命令执行器相关initCommandExecutors();initIdGenerator();initHistoryLevel();initFunctionDelegates();initAstFunctionCreators();initDelegateInterceptor();//包装 applicationContextinitBeans();initExpressionManager();//异步工厂initAgendaFactory();//初始化数据源if (usingRelationalDatabase) {initDataSource();} else {initNonRelationalDataSource();}if (usingRelationalDatabase || usingSchemaMgmt) {initSchemaManager();initSchemaManagementCommand();}configureVariableServiceConfiguration();configureJobServiceConfiguration();initHelpers();initVariableTypes();initFormEngines();initFormTypes();initScriptBindingsFactory();initScriptingEngines();initBusinessCalendarManager();//初始化操作数据的serviceinitServices();initWsdlImporterFactory();initBehaviorFactory();initListenerFactory();initBpmnParser();initProcessDefinitionCache();initProcessDefinitionInfoCache();initAppResourceCache();initKnowledgeBaseCache();initJobHandlers();initHistoryJobHandlers();// 事务 ManagedTransactionFactoryinitTransactionFactory();if (usingRelationalDatabase) {initSqlSessionFactory();}initSessionFactories();initDataManagers();initEntityManagers();initProcessDefinitionDeploymentDeletionManager();initCandidateManager();initVariableAggregator();initDependentScopeTypes();initHistoryConfigurationSettings();initHistoryManager();initChangeTenantIdManager();initDynamicStateManager();initProcessInstanceMigrationValidationManager();initIdentityLinkInterceptor();initJpa();initDeployers();initEventHandlers();initFailedJobCommandFactory();initEventDispatcher();initProcessValidator();initFormFieldHandler();initDatabaseEventLogging();initFlowable5CompatibilityHandler();initVariableServiceConfiguration();initIdentityLinkServiceConfiguration();initEntityLinkServiceConfiguration();initEventSubscriptionServiceConfiguration();initTaskServiceConfiguration();initJobServiceConfiguration();initBatchServiceConfiguration();initAsyncTaskInvoker();initAsyncExecutor();initAsyncHistoryExecutor();//调用 EngineConfigurator 的 configure() 方法configuratorsAfterInit();afterInitTaskServiceConfiguration();afterInitEventRegistryEventBusConsumer();initHistoryCleaningManager();initLocalizationManagers();}
初始化命令执行器
/* 初始化命令执行器*/public void initCommandExecutors() {initDefaultCommandConfig();initSchemaCommandConfig();//CommandInvokerinitCommandInvoker();initCommandInterceptors();initCommandExecutor();}
主要看初始化拦截器:
/* 初始化拦截器 commandInterceptors = {ArrayList@10293} size = 6* 0 = {LogInterceptor@10297}* 1 = {SpringTransactionInterceptor@10287}* 2 = {CommandContextInterceptor@10298}* 3 = {TransactionContextInterceptor@10299}* 4 = {BpmnOverrideContextInterceptor@10300}* 5 = {CommandInvoker@10292} 这个在外面设置*/public void initCommandInterceptors() {if (commandInterceptors == null) {commandInterceptors = new ArrayList<>();if (customPreCommandInterceptors != null) {commandInterceptors.addAll(customPreCommandInterceptors);}commandInterceptors.addAll(getDefaultCommandInterceptors());if (customPostCommandInterceptors != null) {commandInterceptors.addAll(customPostCommandInterceptors);}commandInterceptors.add(commandInvoker);}}
获取拦截器:
- 先加入
LogInterceptor, - 如果数据库类型值
cockroachdb,再加入CrDbRetryInterceptor, - 创建spring的事务管理
SpringTransactionInterceptor, - 增加执行器上下文拦截器
CommandContextInterceptor, - 增加事务上下文拦截器
TransactionContextInterceptor, - 其他拦截器,
BpmnOverrideContextInterceptor有且仅有SpringProcessEngineConfigurator的时候存在这个。 CommandInterceptor执行器拦截器,这个在getDefaultCommandInterceptors外设置的
/* 获取默认的拦截器* @return*/public Collection<? extends CommandInterceptor> getDefaultCommandInterceptors() {if (defaultCommandInterceptors == null) {List<CommandInterceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>();interceptors.add(new LogInterceptor());if (DATABASE_TYPE_COCKROACHDB.equals(databaseType)) {interceptors.add(new CrDbRetryInterceptor());}CommandInterceptor transactionInterceptor = createTransactionInterceptor();if (transactionInterceptor != null) {interceptors.add(transactionInterceptor);}if (commandContextFactory != null) {String engineCfgKey = getEngineCfgKey();CommandContextInterceptor commandContextInterceptor = new CommandContextInterceptor(commandContextFactory, classLoader, useClassForNameClassLoading, clock, objectMapper);engineConfigurations.put(engineCfgKey, this);commandContextInterceptor.setEngineCfgKey(engineCfgKey);commandContextInterceptor.setEngineConfigurations(engineConfigurations);interceptors.add(commandContextInterceptor);}if (transactionContextFactory != null) {interceptors.add(new TransactionContextInterceptor(transactionContextFactory));}List<CommandInterceptor> additionalCommandInterceptors = getAdditionalDefaultCommandInterceptors();if (additionalCommandInterceptors != null) {interceptors.addAll(additionalCommandInterceptors);}defaultCommandInterceptors = interceptors;}return defaultCommandInterceptors;}
初始化责任链,顺序就是前面设置到list的顺序
/* 初始化整个责任链*/public void initCommandExecutor() {if (commandExecutor == null) {CommandInterceptor first = initInterceptorChain(commandInterceptors);commandExecutor = new CommandExecutorImpl(getDefaultCommandConfig(), first);}}public CommandInterceptor initInterceptorChain(List<CommandInterceptor> chain) {if (chain == null || chain.isEmpty()) {throw new FlowableException("invalid command interceptor chain configuration: " + chain);}for (int i = 0; i < chain.size() - 1; i++) {chain.get(i).setNext(chain.get(i + 1));}return chain.get(0);}
部署流程
/* 部署流程*/@Testpublic void createDeployment() {repositoryService.createDeployment().name("员工请假").addClasspathResource("请假流程2.bpmn20.xml").deploy();}
查看deploy的源码发现走RepositoryServiceImpl的deploy方法,通过观察源码,发现这个类里面很多commandExecutor.execute(new Cmd())格式的代码,只是传入的Cmd指令不同,这里传入的是DeployCmd
public Deployment deploy(DeploymentBuilderImpl deploymentBuilder) {return commandExecutor.execute(new DeployCmd<Deployment>(deploymentBuilder));}
继续深入后走到CommandExecutorImpl里面,这里就开始进入责任链,以此执行前面设置的拦截器,first为LogInterceptor
@Overridepublic <T> T execute(CommandConfig config, Command<T> command) {return first.execute(config, command, this);}
LogInterceptor拦截器内部实现比较简单,只是判断是否开启debug模式,继续next.execute(config, command, commandExecutor)进入SpringTransactionInterceptor,
如果事务类型是required,当事务已经处于活动状态时,不使用transactionTemplate,原因是transactionTemplate try-catches 捕获异常并将其标记为回滚。这将中断通过同一个拦截器堆栈的嵌套服务调用。这里意思就是已经存在事务了,跟随之前的事务就好了,没有事务的情况需要启用事务
public <T> T execute(final CommandConfig config, final Command<T> command, CommandExecutor commandExecutor) {LOGGER.debug("Running command with propagation {}", config.getTransactionPropagation());// If the transaction is required (the other two options always need to go through the transactionTemplate),// the transactionTemplate is not used when the transaction is already active.// The reason for this is that the transactionTemplate try-catches exceptions and marks it as rollback.// Which will break nested service calls that go through the same stack of interceptors.//如果事务类型是required,当事务已经处于活动状态时,不使用transactionTemplate// 原因是transactionTemplate try-catches 捕获异常并将其标记为回滚。这将中断通过同一个拦截器堆栈的嵌套服务调用int transactionPropagation = getPropagation(config);if (transactionPropagation == TransactionTemplate.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED && TransactionSynchronizationManager.isActualTransactionActive()) {return next.execute(config, command, commandExecutor);} else {TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate = new TransactionTemplate(transactionManager);transactionTemplate.setPropagationBehavior(transactionPropagation);return transactionTemplate.execute(status -> next.execute(config, command, commandExecutor));}}
执行next.execute(config, command, commandExecutor)进入下一个拦截器CommandContextInterceptor,这个拦截器的主要作用就是生成一个CommandContext,并设置值。这个上下文对象比较重要,特别是commandContext -> sessionFactories -> key=org.flowable.common.engine.impl.db.DbSqlSession,这里会存储数据流转的所有数据。入库操作是commandContext.close();
@Overridepublic <T> T execute(CommandConfig config, Command<T> command, CommandExecutor commandExecutor) {CommandContext commandContext = Context.getCommandContext();/ This flag indicates whether the context is reused for the execution of the current command.* If a valid command context exists, this means a nested service call is being executed.* If so, this flag will change to 'true', with the purpose of closing the command context in the finally block.*/boolean contextReused = false;/ Commands can execute service calls, even deeply nested service calls.* This flag stores the 'reused' flag on the command context as it was when starting to execute the command.* For a nested command, this will be 'true'. Only for the root command context usage, this will be false.* When the nested command is done, the original state is restored, which allows to detect at the CommandInvoker* level which command context is the actual root.*/boolean originalContextReusedState = false;// We need to check the exception, because the transaction can be in a// rollback state, and some other command is being fired to compensate (eg. decrementing job retries)if (!config.isContextReusePossible() || commandContext == null || commandContext.getException() != null) {commandContext = commandContextFactory.createCommandContext(command);commandContext.setEngineConfigurations(engineConfigurations);commandContext.setCommandExecutor(commandExecutor);commandContext.setClassLoader(classLoader);commandContext.setUseClassForNameClassLoading(useClassForNameClassLoading);commandContext.setClock(clock);commandContext.setObjectMapper(objectMapper);} else {LOGGER.debug("Valid context found. Reusing it for the current command '{}'", command.getClass().getCanonicalName());contextReused = true;originalContextReusedState = commandContext.isReused();commandContext.setReused(true);}try {// Push the current engine configuration key to a stack// shared between nested calls that reuse the command contextcommandContext.pushEngineCfgToStack(engineCfgKey);// Push on command stackContext.setCommandContext(commandContext);return next.execute(config, command, commandExecutor);} catch (Exception e) {commandContext.exception(e);} finally {try {if (!contextReused) {//刷新dbsession 真正入库commandContext.close();}commandContext.setReused(originalContextReusedState);} finally {// Pop from stackscommandContext.popEngineCfgStack();Context.removeCommandContext();}}// Rethrow exception if neededif (contextReused && commandContext.getException() != null) {// If it's reused, we need to throw the exception again so it propagates upwards,// but the exception needs to be reset again or the parent call can incorrectly be marked// as having an exception (the nested call can be try-catched for example)Throwable exception = commandContext.getException();commandContext.resetException();// Wrapping it to avoid having 'throws throwable' in all method signaturesif (exception instanceof FlowableException) {throw (FlowableException) exception;} else {throw new FlowableException("Exception during command execution", exception);}}return null;}
刷新入库的操作主要看DbSqlSession中的几个字段:insertedObjects、deletedObjects、bulkDeleteOperations、updatedObjects
这个操作是业务处理完之后才进行的,这里主要提前了解下
public void close() {// The intention of this method is that all resources are closed properly, even if exceptions occur// in close or flush methods of the sessions or the transaction context.try {try {try {executeCloseListenersClosing();if (exception == null) {//刷新session 入数据库flushSessions();}} catch (Throwable exception) {exception(exception);} finally {try {if (exception == null) {executeCloseListenersAfterSessionFlushed();}} catch (Throwable exception) {exception(exception);}if (exception != null) {logException();executeCloseListenersCloseFailure();} else {executeCloseListenersClosed();}}} catch (Throwable exception) {// Catch exceptions during rollbackexception(exception);} finally {// Sessions need to be closed, regardless of exceptions/commit/rollbackcloseSessions();}} catch (Throwable exception) {// Catch exceptions during session closingexception(exception);}if (exception != null) {rethrowExceptionIfNeeded();}}
执行next.execute(config, command, commandExecutor)后进入TransactionContextInterceptor拦截器中,新建一个spring的事务上下文,之后进入``BpmnOverrideContextInterceptor`拦截器,
public <T> T execute(CommandConfig config, Command<T> command, CommandExecutor commandExecutor) {CommandContext commandContext = Context.getCommandContext();// Storing it in a variable, to reference later (it can change during command execution)boolean openTransaction = !config.getTransactionPropagation().equals(TransactionPropagation.NOT_SUPPORTED)&& transactionContextFactory != null && !commandContext.isReused();boolean isContextSet = false;try {if (openTransaction) {TransactionContext transactionContext = transactionContextFactory.openTransactionContext(commandContext);Context.setTransactionContext(transactionContext);isContextSet = true;commandContext.addCloseListener(new TransactionCommandContextCloseListener(transactionContext));}//进入下一个拦截器return next.execute(config, command, commandExecutor);} finally {if (openTransaction && isContextSet) {Context.removeTransactionContext();}}}
BpmnOverrideContextInterceptor拦截器中没有任何处理,直接CommandInvoker拦截器中
CommandInvoker是一个非常重要的拦截器,在这个拦截器中循环处理所有的任务
第一次进入推入一个Runnable进入FlowableEngineAgenda,旨在执行指令,目前还未执行
new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {//执行指令commandContext.setResult(command.execute(commandContext));}
放置好Runnable之后,开始循环从agenda中捞取数据执行
/* 循环执行 Operations,第一次只有一个,在执行的过程中,会继续放入ContinueProcessOperation* 直到agenda内部维护的operations 没有数据为止* @param commandContext*/protected void executeOperations(final CommandContext commandContext) {FlowableEngineAgenda agenda = CommandContextUtil.getAgenda(commandContext);while (!agenda.isEmpty()) {Runnable runnable = agenda.getNextOperation();executeOperation(commandContext, runnable);}}public void executeOperation(CommandContext commandContext, Runnable runnable) {//如果是第二次或者以后进入的就是AbstractOperation,第一次进入是runable,直接runif (runnable instanceof AbstractOperation) {AbstractOperation operation = (AbstractOperation) runnable;// Execute the operation if the operation has no execution (i.e. it's an operation not working on a process instance)// or the operation has an execution and it is not endedif (operation.getExecution() == null || !operation.getExecution().isEnded()) {if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {LOGGER.debug("Executing operation {}", operation.getClass());}agendaOperationRunner.executeOperation(commandContext, operation);}} else {if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {LOGGER.debug("Executing operation {}", runnable.getClass());}runnable.run();}}
执行runnable.run();之后,启动了前面所说的command.execute(commandContext),执行指令中的execute方法
这里第一次执行的是DeployCmd,
public Deployment execute(CommandContext commandContext) {// 省略部分代码 。。。return executeDeploy(commandContext);
} protected Deployment executeDeploy(CommandContext commandContext) {DeploymentEntity deployment = deploymentBuilder.getDeployment();ProcessEngineConfigurationImpl processEngineConfiguration = CommandContextUtil.getProcessEngineConfiguration(commandContext);deployment.setDeploymentTime(processEngineConfiguration.getClock().getCurrentTime());// 省略部分代码 。。。deployment.setNew(true);// Save the data//这里只是把数据保存在缓存中,DbSqlSession中的insertedObjects,数据刷新到数据库在CommandContextInterceptor拦截器中processEngineConfiguration.getDeploymentEntityManager().insert(deployment);// 省略部分代码。。。。// Deployment settingsMap<String, Object> deploymentSettings = new HashMap<>();deploymentSettings.put(DeploymentSettings.IS_BPMN20_XSD_VALIDATION_ENABLED, deploymentBuilder.isBpmn20XsdValidationEnabled());deploymentSettings.put(DeploymentSettings.IS_PROCESS_VALIDATION_ENABLED, deploymentBuilder.isProcessValidationEnabled());// Actually deploy//真正的部署服务processEngineConfiguration.getDeploymentManager().deploy(deployment, deploymentSettings);// 省略部分代码。。。。return deployment;}
真正的部署服务的时候,调用到了``BpmnDeployer`的deploy方法
启动流程实例
以张三请假5天为例:
/* 张三请假5天* 启动流程实例*/@Testpublic void startProcessInstanceByKey() {Map<String, Object> variables = new HashMap<>();variables.put("user", "zhangsan");variables.put("day", "5");variables.put("leader", "lisi");variables.put("manger", "wangwu");variables.put("hr", "zhaoliu");ProcessInstance processInstance = runtimeService.startProcessInstanceByKey("请假流程2", variables);System.out.println("processInstance.getProcessInstanceId():" + processInstance.getProcessInstanceId());System.out.println("processInstance.getProcessDefinitionKey() = " + processInstance.getProcessDefinitionKey());System.out.println("processInstance.getBusinessKey() = " + processInstance.getBusinessKey());System.out.println("processInstance.getActivityId() = " + processInstance.getActivityId());}
调用的是commandExecutor.execute(),新建的指令为StartProcessInstanceCmd
public ProcessInstance startProcessInstanceByKey(String processDefinitionKey, Map<String, Object> variables) {return commandExecutor.execute(new StartProcessInstanceCmd<ProcessInstance>(processDefinitionKey, null, null, variables));}
指令执行的逻辑还是如上一节所写的,通过一大串拦截器,最后执行传入的指令,这次我们直接去看指令的execute方法
public ProcessInstance execute(CommandContext commandContext) {ProcessEngineConfigurationImpl processEngineConfiguration = CommandContextUtil.getProcessEngineConfiguration(commandContext);processInstanceHelper = processEngineConfiguration.getProcessInstanceHelper();ProcessDefinition processDefinition = getProcessDefinition(processEngineConfiguration, commandContext);ProcessInstance processInstance = null;if (hasFormData()) {//表单走这里processInstance = handleProcessInstanceWithForm(commandContext, processDefinition, processEngineConfiguration);} else {//普通的开始流程processInstance = startProcessInstance(processDefinition);}return processInstance;}
最终的插入数据的逻辑在ProcessInstanceHelper的createAndStartProcessInstanceWithInitialFlowElement方法中,当然这里的插入还只是在Dbsession中。如果是开始的节点,会构造当前的节点放入命令运行栈中
public ProcessInstance createAndStartProcessInstanceWithInitialFlowElement() {CommandContext commandContext = Context.getCommandContext();// Create the process instanceString initiatorVariableName = null;if (initialFlowElement instanceof StartEvent) {initiatorVariableName = ((StartEvent) initialFlowElement).getInitiator();}String tenantId;if (overrideDefinitionTenantId != null) {tenantId = overrideDefinitionTenantId;} else {tenantId = processDefinition.getTenantId();}StartProcessInstanceBeforeContext startInstanceBeforeContext = new StartProcessInstanceBeforeContext(businessKey, businessStatus, processInstanceName,callbackId, callbackType, referenceId, referenceType,variables, transientVariables, tenantId, ownerId, assigneeId, initiatorVariableName, initialFlowElement.getId(),initialFlowElement, process, processDefinition, overrideDefinitionTenantId, predefinedProcessInstanceId);ProcessEngineConfigurationImpl processEngineConfiguration = CommandContextUtil.getProcessEngineConfiguration(commandContext);if (processEngineConfiguration.getStartProcessInstanceInterceptor() != null) {processEngineConfiguration.getStartProcessInstanceInterceptor().beforeStartProcessInstance(startInstanceBeforeContext);}//插入 ACT_RU_EXECUTIONExecutionEntity processInstance = processEngineConfiguration.getExecutionEntityManager().createProcessInstanceExecution(startInstanceBeforeContext.getProcessDefinition(), startInstanceBeforeContext.getPredefinedProcessInstanceId(),startInstanceBeforeContext.getBusinessKey(), startInstanceBeforeContext.getBusinessStatus(),startInstanceBeforeContext.getProcessInstanceName(), startInstanceBeforeContext.getCallbackId(),startInstanceBeforeContext.getCallbackType(), startInstanceBeforeContext.getReferenceId(),startInstanceBeforeContext.getReferenceType(), stageInstanceId, startInstanceBeforeContext.getTenantId(),startInstanceBeforeContext.getInitiatorVariableName(), startInstanceBeforeContext.getInitialActivityId());//插入 ACT_HI_PROCINSTprocessEngineConfiguration.getHistoryManager().recordProcessInstanceStart(processInstance);if (processEngineConfiguration.isLoggingSessionEnabled()) {BpmnLoggingSessionUtil.addLoggingData(LoggingSessionConstants.TYPE_PROCESS_STARTED, "Started process instance with id " + processInstance.getId(), processInstance);}// add owner and assignee identity links, if setif (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(startInstanceBeforeContext.getOwnerId())) {IdentityLinkUtil.createProcessInstanceIdentityLink(processInstance, ownerId, null, IdentityLinkType.OWNER);}if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(startInstanceBeforeContext.getAssigneeId())) {IdentityLinkUtil.createProcessInstanceIdentityLink(processInstance, assigneeId, null, IdentityLinkType.ASSIGNEE);}FlowableEventDispatcher eventDispatcher = processEngineConfiguration.getEventDispatcher();boolean eventDispatcherEnabled = eventDispatcher != null && eventDispatcher.isEnabled();if (eventDispatcherEnabled) {eventDispatcher.dispatchEvent(FlowableEventBuilder.createEntityEvent(FlowableEngineEventType.PROCESS_CREATED, processInstance),processEngineConfiguration.getEngineCfgKey());}//插入ACT_HI_VARINSTprocessInstance.setVariables(processDataObjects(process.getDataObjects()));//插ACT_RU_VARIABLE// Set the variables passed into the start commandif (startInstanceBeforeContext.getVariables() != null) {for (String varName : startInstanceBeforeContext.getVariables().keySet()) {processInstance.setVariable(varName, startInstanceBeforeContext.getVariables().get(varName));}}if (startInstanceBeforeContext.getTransientVariables() != null) {Object eventInstance = startInstanceBeforeContext.getTransientVariables().get(EventConstants.EVENT_INSTANCE);if (eventInstance instanceof EventInstance) {EventInstanceBpmnUtil.handleEventInstanceOutParameters(processInstance, startInstanceBeforeContext.getInitialFlowElement(), (EventInstance) eventInstance);}for (String varName : startInstanceBeforeContext.getTransientVariables().keySet()) {processInstance.setTransientVariable(varName, startInstanceBeforeContext.getTransientVariables().get(varName));}}// Fire eventsif (eventDispatcherEnabled) {eventDispatcher.dispatchEvent(FlowableEventBuilder.createEntityWithVariablesEvent(FlowableEngineEventType.ENTITY_INITIALIZED, processInstance, startInstanceBeforeContext.getVariables(), false), processEngineConfiguration.getEngineCfgKey());}//创建将访问所有流程定义元素的第一个执行,创建出一个子流程// Create the first execution that will visit all the process definition elementsExecutionEntity execution = processEngineConfiguration.getExecutionEntityManager().createChildExecution(processInstance);execution.setCurrentFlowElement(startInstanceBeforeContext.getInitialFlowElement());//插入ACT_HI_ACTINSTprocessEngineConfiguration.getActivityInstanceEntityManager().recordActivityStart(execution);if (startProcessInstance) {//这里就是开始整个流程的流转的开始,构造下一个节点推入运行栈中startProcessInstance(processInstance, commandContext, startInstanceBeforeContext.getVariables());}if (callbackId != null) {callCaseInstanceStateChangeCallbacks(commandContext, processInstance, null, ProcessInstanceState.RUNNING);}if (processEngineConfiguration.getStartProcessInstanceInterceptor() != null) {StartProcessInstanceAfterContext startInstanceAfterContext = new StartProcessInstanceAfterContext(processInstance, execution, startInstanceBeforeContext.getVariables(), startInstanceBeforeContext.getTransientVariables(), startInstanceBeforeContext.getInitialFlowElement(), startInstanceBeforeContext.getProcess(), startInstanceBeforeContext.getProcessDefinition());processEngineConfiguration.getStartProcessInstanceInterceptor().afterStartProcessInstance(startInstanceAfterContext);}return processInstance;}
在startProcessInstance这个方法中,会构造一个节点ContinueProcessOperation放入FlowableEngineAgenda中,
/* 启动流程* @param processInstance* @param commandContext* @param variables*/public void startProcessInstance(ExecutionEntity processInstance, CommandContext commandContext, Map<String, Object> variables) {Process process = ProcessDefinitionUtil.getProcess(processInstance.getProcessDefinitionId());processAvailableEventSubProcesses(processInstance, process, commandContext);ExecutionEntity execution = processInstance.getExecutions().get(0); // There will always be one child execution created//将子流程推入执行栈中CommandContextUtil.getAgenda(commandContext).planContinueProcessOperation(execution);ProcessEngineConfigurationImpl processEngineConfiguration = CommandContextUtil.getProcessEngineConfiguration(commandContext);FlowableEventDispatcher eventDispatcher = processEngineConfiguration.getEventDispatcher();if (eventDispatcher != null && eventDispatcher.isEnabled()) {eventDispatcher.dispatchEvent(FlowableEventBuilder.createProcessStartedEvent(execution, variables, false),processEngineConfiguration.getEngineCfgKey());}}/* 构造一个ContinueProcessOperation节点推入运行栈中* @param execution*/public void planContinueProcessOperation(ExecutionEntity execution) {planOperation(new ContinueProcessOperation(commandContext, execution), execution);}
回到CommandInvoker中,我们发现第一个指令执行完之后,executeOperations又开始循环获取指令
/* 循环执行 Operations,第一次只有一个,在执行的过程中,会继续放入ContinueProcessOperation* 直到agenda内部维护的operations 没有数据为止* @param commandContext*/protected void executeOperations(final CommandContext commandContext) {FlowableEngineAgenda agenda = CommandContextUtil.getAgenda(commandContext);while (!agenda.isEmpty()) {Runnable runnable = agenda.getNextOperation();executeOperation(commandContext, runnable);}}
这一次是获取ContinueProcessOperation,属于AbstractOperation的子类,执行 agendaOperationRunner.executeOperation(commandContext, operation),其实也就是runable.run()。
既然是一个线程,可以直接看ContinueProcessOperation的run方法,可以看到会根据是节点对象还是流程对象来走逻辑,目前是最开始,起始节点是StartEvent,是一个FlowNode类型的,获取当前活动的具体行为。
/* 执行具体任务的行为* @param activityBehavior* @param flowNode*/protected void executeActivityBehavior(ActivityBehavior activityBehavior, FlowNode flowNode) {LOGGER.debug("Executing activityBehavior {} on activity '{}' with execution {}", activityBehavior.getClass(), flowNode.getId(), execution.getId());ProcessEngineConfigurationImpl processEngineConfiguration = CommandContextUtil.getProcessEngineConfiguration();FlowableEventDispatcher eventDispatcher = null;if (processEngineConfiguration != null) {eventDispatcher = processEngineConfiguration.getEventDispatcher();}if (eventDispatcher != null && eventDispatcher.isEnabled()) {if (flowNode instanceof Activity && ((Activity) flowNode).hasMultiInstanceLoopCharacteristics()) {processEngineConfiguration.getEventDispatcher().dispatchEvent(FlowableEventBuilder.createMultiInstanceActivityEvent(FlowableEngineEventType.MULTI_INSTANCE_ACTIVITY_STARTED, flowNode.getId(),flowNode.getName(), execution.getId(), execution.getProcessInstanceId(), execution.getProcessDefinitionId(), flowNode), processEngineConfiguration.getEngineCfgKey());}else {processEngineConfiguration.getEventDispatcher().dispatchEvent(FlowableEventBuilder.createActivityEvent(FlowableEngineEventType.ACTIVITY_STARTED, flowNode.getId(), flowNode.getName(), execution.getId(),execution.getProcessInstanceId(), execution.getProcessDefinitionId(), flowNode), processEngineConfiguration.getEngineCfgKey());}}if (processEngineConfiguration.isLoggingSessionEnabled()) {BpmnLoggingSessionUtil.addExecuteActivityBehaviorLoggingData(LoggingSessionConstants.TYPE_ACTIVITY_BEHAVIOR_EXECUTE, activityBehavior, flowNode, execution);}try {if (migrationContext != null && activityBehavior instanceof ActivityWithMigrationContextBehavior) {ActivityWithMigrationContextBehavior activityWithMigrationContextBehavior = (ActivityWithMigrationContextBehavior) activityBehavior;activityWithMigrationContextBehavior.execute(execution, migrationContext);} else {//真正的执行活动的行为activityBehavior.execute(execution);}} catch (RuntimeException e) {if (LogMDC.isMDCEnabled()) {LogMDC.putMDCExecution(execution);}throw e;}}
默认的活动行为就是直接离开当前活动,并推入一个新的节点TakeOutgoingSequenceFlowsOperation到执行栈里面
@Overridepublic void execute(DelegateExecution execution) {leave(execution);}@Overridepublic void planTakeOutgoingSequenceFlowsOperation(ExecutionEntity execution, boolean evaluateConditions) {planOperation(new TakeOutgoingSequenceFlowsOperation(commandContext, execution, evaluateConditions, false), execution);}
执行完之后,再次回到CommandInvoker的executeOperations方法中,继续经过循环得到TakeOutgoingSequenceFlowsOperation节点,进入TakeOutgoingSequenceFlowsOperation节点的run方法中。这里是节点类型,需要处理节点。
public void run() {FlowElement currentFlowElement = getCurrentFlowElement(execution);// Compensation checkif ((currentFlowElement instanceof Activity) && ((Activity) currentFlowElement).isForCompensation()) {/ If the current flow element is part of a compensation, we don't always want to follow the regular rules of leaving an activity. More specifically, if there are no outgoing sequenceflow,* we simply must stop the execution there and don't go up in the scopes as we usually do to find the outgoing sequenceflow*/cleanupCompensation();return;}// When leaving the current activity, we need to delete any related execution (eg active boundary events)cleanupExecutions(currentFlowElement);FlowNode sourceFlowNode = getFlowNode(currentFlowElement);if (!forcedSynchronous && sourceFlowNode != null && sourceFlowNode.isAsynchronousLeave()) {handleAsynchronousLeave(currentFlowElement, sourceFlowNode);} else if (currentFlowElement instanceof FlowNode) {//处理节点handleFlowNode((FlowNode) currentFlowElement);} else if (currentFlowElement instanceof SequenceFlow) {handleSequenceFlow();} else {throw new FlowableException("Programmatic error: this operation needs either a FlowNode or a SequenceFlow as current FlowElement");}}
最终由leaveFlowNode方法处理离开节点的处理
/* outgoing节点的离开节点方法* @param flowNode*/protected void leaveFlowNode(FlowNode flowNode) {LOGGER.debug("Leaving flow node {} with id '{}' by following it's {} outgoing sequenceflow",flowNode.getClass(), flowNode.getId(), flowNode.getOutgoingFlows().size());// Get default sequence flow (if set)String defaultSequenceFlowId = null;if (flowNode instanceof Activity) {defaultSequenceFlowId = ((Activity) flowNode).getDefaultFlow();} else if (flowNode instanceof Gateway) {defaultSequenceFlowId = ((Gateway) flowNode).getDefaultFlow();}// Determine which sequence flows can be used for leaving//保存离开的出口List<SequenceFlow> outgoingSequenceFlows = new ArrayList<>();for (SequenceFlow sequenceFlow : flowNode.getOutgoingFlows()) {String skipExpressionString = sequenceFlow.getSkipExpression();if (!SkipExpressionUtil.isSkipExpressionEnabled(skipExpressionString, sequenceFlow.getId(), execution, commandContext)) {if (!evaluateConditions|| (evaluateConditions && ConditionUtil.hasTrueCondition(sequenceFlow, execution) && (defaultSequenceFlowId == null || !defaultSequenceFlowId.equals(sequenceFlow.getId())))) {outgoingSequenceFlows.add(sequenceFlow);}} else if (flowNode.getOutgoingFlows().size() == 1 || SkipExpressionUtil.shouldSkipFlowElement(skipExpressionString, sequenceFlow.getId(), execution, commandContext)) {// The 'skip' for a sequence flow means that we skip the condition, not the sequence flow.outgoingSequenceFlows.add(sequenceFlow);}}//检查是否存在默认序列流// Check if there is a default sequence flowif (outgoingSequenceFlows.size() == 0 && evaluateConditions) { // The elements that set this to false also have no support for default sequence flowif (defaultSequenceFlowId != null) {for (SequenceFlow sequenceFlow : flowNode.getOutgoingFlows()) {if (defaultSequenceFlowId.equals(sequenceFlow.getId())) {outgoingSequenceFlows.add(sequenceFlow);break;}}}}//如果没有出去的流了,直接发出停止事件// No outgoing found. Ending the executionif (outgoingSequenceFlows.size() == 0) {if (flowNode.getOutgoingFlows() == null || flowNode.getOutgoingFlows().size() == 0) {LOGGER.debug("No outgoing sequence flow found for flow node '{}'.", flowNode.getId());agenda.planEndExecutionOperation(execution);} else {throw new FlowableException("No outgoing sequence flow of element '" + flowNode.getId() + "' could be selected for continuing the process");}} else {//走到这里就是顺序流连接对象// Leave, and reuse the incoming sequence flow, make executions for all the others (if applicable)ProcessEngineConfigurationImpl processEngineConfiguration = CommandContextUtil.getProcessEngineConfiguration(commandContext);ExecutionEntityManager executionEntityManager = processEngineConfiguration.getExecutionEntityManager();List<ExecutionEntity> outgoingExecutions = new ArrayList<>(flowNode.getOutgoingFlows().size());SequenceFlow sequenceFlow = outgoingSequenceFlows.get(0);//把顺序流对象塞到里面,继续流转// Reuse existing one execution.setCurrentFlowElement(sequenceFlow);execution.setActive(false);outgoingExecutions.add(execution);// Executions for all the other oneif (outgoingSequenceFlows.size() > 1) {for (int i = 1; i < outgoingSequenceFlows.size(); i++) {ExecutionEntity parent = execution.getParentId() != null ? execution.getParent() : execution;ExecutionEntity outgoingExecutionEntity = processEngineConfiguration.getExecutionEntityManager().createChildExecution(parent);SequenceFlow outgoingSequenceFlow = outgoingSequenceFlows.get(i);outgoingExecutionEntity.setActive(false);outgoingExecutionEntity.setCurrentFlowElement(outgoingSequenceFlow);executionEntityManager.insert(outgoingExecutionEntity);outgoingExecutions.add(outgoingExecutionEntity);}}//走到这里说明,还未完成流程,需要继续执行,推入ContinueProcessOperation//只有在执行完所有操作后才执行,因为有些查询依赖于此// Leave (only done when all executions have been made, since some queries depend on this)for (ExecutionEntity outgoingExecution : outgoingExecutions) {agenda.planContinueProcessOperation(outgoingExecution);if (processEngineConfiguration.isLoggingSessionEnabled()) {BpmnLoggingSessionUtil.addSequenceFlowLoggingData(LoggingSessionConstants.TYPE_SEQUENCE_FLOW_TAKE, outgoingExecution);}}}}protected void handleAdhocSubProcess(FlowNode flowNode) {boolean completeAdhocSubProcess = false;AdhocSubProcess adhocSubProcess = (AdhocSubProcess) flowNode.getParentContainer();if (adhocSubProcess.getCompletionCondition() != null) {Expression expression = CommandContextUtil.getProcessEngineConfiguration(commandContext).getExpressionManager().createExpression(adhocSubProcess.getCompletionCondition());Condition condition = new UelExpressionCondition(expression);if (condition.evaluate(adhocSubProcess.getId(), execution)) {completeAdhocSubProcess = true;}}if (flowNode.getOutgoingFlows().size() > 0) {leaveFlowNode(flowNode);} else {CommandContextUtil.getExecutionEntityManager(commandContext).deleteExecutionAndRelatedData(execution, null, false);}if (completeAdhocSubProcess) {boolean endAdhocSubProcess = true;if (!adhocSubProcess.isCancelRemainingInstances()) {List<ExecutionEntity> childExecutions = CommandContextUtil.getExecutionEntityManager(commandContext).findChildExecutionsByParentExecutionId(execution.getParentId());for (ExecutionEntity executionEntity : childExecutions) {if (!executionEntity.getId().equals(execution.getId())) {endAdhocSubProcess = false;break;}}}if (endAdhocSubProcess) {agenda.planEndExecutionOperation(execution.getParent());}}}
执行完之后,再次回到CommandInvoker的executeOperations方法中,继续经过循环得到ContinueProcessOperation节点,进入ContinueProcessOperation节点的run方法中。
方法最终走到了continueThroughSequenceFlow方法中,SequenceFlow中存在当前节点和目标节点,将目标节点设置成当前节点,封装成ContinueProcessOperation后继续流转。
/* 继续通过 顺序流* @param sequenceFlow*/protected void continueThroughSequenceFlow(SequenceFlow sequenceFlow) {// Execution listener. Sequenceflow only 'take' makes sense ... but we've supported all three since the beginningif (CollectionUtil.isNotEmpty(sequenceFlow.getExecutionListeners())) {try {executeExecutionListeners(sequenceFlow, ExecutionListener.EVENTNAME_START);executeExecutionListeners(sequenceFlow, ExecutionListener.EVENTNAME_TAKE);executeExecutionListeners(sequenceFlow, ExecutionListener.EVENTNAME_END);} catch (BpmnError bpmnError) {ErrorPropagation.propagateError(bpmnError, execution);return;}}// Firing event that transition is being takenProcessEngineConfigurationImpl processEngineConfiguration = CommandContextUtil.getProcessEngineConfiguration();FlowableEventDispatcher eventDispatcher = null;if (processEngineConfiguration != null) {eventDispatcher = processEngineConfiguration.getEventDispatcher();}if (eventDispatcher != null && eventDispatcher.isEnabled()) {FlowElement sourceFlowElement = sequenceFlow.getSourceFlowElement();FlowElement targetFlowElement = sequenceFlow.getTargetFlowElement();processEngineConfiguration.getEventDispatcher().dispatchEvent(FlowableEventBuilder.createSequenceFlowTakenEvent(execution,FlowableEngineEventType.SEQUENCEFLOW_TAKEN,sequenceFlow.getId(),sourceFlowElement != null ? sourceFlowElement.getId() : null,sourceFlowElement != null ? sourceFlowElement.getName() : null,sourceFlowElement != null ? sourceFlowElement.getClass().getName() : null,sourceFlowElement != null ? ((FlowNode) sourceFlowElement).getBehavior() : null,targetFlowElement != null ? targetFlowElement.getId() : null,targetFlowElement != null ? targetFlowElement.getName() : null,targetFlowElement != null ? targetFlowElement.getClass().getName() : null,targetFlowElement != null ? ((FlowNode) targetFlowElement).getBehavior() : null), processEngineConfiguration.getEngineCfgKey());}//插入 ACT_HI_ACTINSTCommandContextUtil.getActivityInstanceEntityManager(commandContext).recordSequenceFlowTaken(execution);//将下一个节点设置为当前节点,再次推入到栈中,继续流转FlowElement targetFlowElement = sequenceFlow.getTargetFlowElement();execution.setCurrentFlowElement(targetFlowElement);LOGGER.debug("Sequence flow '{}' encountered. Continuing process by following it using execution {}", sequenceFlow.getId(), execution.getId());execution.setActive(targetFlowElement instanceof FlowNode);agenda.planContinueProcessOperation(execution);}
执行完之后,再次回到CommandInvoker的executeOperations方法中,继续经过循环得到ContinueProcessOperation节点,进入ContinueProcessOperation节点的run方法中。
这一次是开始事件之后的第一个节点类型——用户提交节点,FlowNode的具体类型是UserTask
和之前一样,获取ActivityBehavior,执行真正的节点的行为,这里的实现类是UserTaskActivityBehavior
public void execute(DelegateExecution execution, MigrationContext migrationContext) {CommandContext commandContext = CommandContextUtil.getCommandContext();ProcessEngineConfigurationImpl processEngineConfiguration = CommandContextUtil.getProcessEngineConfiguration();TaskService taskService = processEngineConfiguration.getTaskServiceConfiguration().getTaskService();TaskEntity task = taskService.createTask();task.setExecutionId(execution.getId());task.setTaskDefinitionKey(userTask.getId());task.setPropagatedStageInstanceId(execution.getPropagatedStageInstanceId());String activeTaskName = null;String activeTaskDescription = null;String activeTaskDueDate = null;String activeTaskPriority = null;String activeTaskCategory = null;String activeTaskFormKey = null;String activeTaskSkipExpression = null;String activeTaskAssignee = null;String activeTaskOwner = null;String activeTaskIdVariableName = null;List<String> activeTaskCandidateUsers = null;List<String> activeTaskCandidateGroups = null;ExpressionManager expressionManager = processEngineConfiguration.getExpressionManager();if (processEngineConfiguration.isEnableProcessDefinitionInfoCache()) {ObjectNode taskElementProperties = BpmnOverrideContext.getBpmnOverrideElementProperties(userTask.getId(), execution.getProcessDefinitionId());activeTaskName = DynamicPropertyUtil.getActiveValue(userTask.getName(), DynamicBpmnConstants.USER_TASK_NAME, taskElementProperties);activeTaskDescription = DynamicPropertyUtil.getActiveValue(userTask.getDocumentation(), DynamicBpmnConstants.USER_TASK_DESCRIPTION, taskElementProperties);activeTaskDueDate = DynamicPropertyUtil.getActiveValue(userTask.getDueDate(), DynamicBpmnConstants.USER_TASK_DUEDATE, taskElementProperties);activeTaskPriority = DynamicPropertyUtil.getActiveValue(userTask.getPriority(), DynamicBpmnConstants.USER_TASK_PRIORITY, taskElementProperties);activeTaskCategory = DynamicPropertyUtil.getActiveValue(userTask.getCategory(), DynamicBpmnConstants.USER_TASK_CATEGORY, taskElementProperties);activeTaskFormKey = DynamicPropertyUtil.getActiveValue(userTask.getFormKey(), DynamicBpmnConstants.USER_TASK_FORM_KEY, taskElementProperties);activeTaskSkipExpression = DynamicPropertyUtil.getActiveValue(userTask.getSkipExpression(), DynamicBpmnConstants.TASK_SKIP_EXPRESSION, taskElementProperties);activeTaskAssignee = getAssigneeValue(userTask, migrationContext, taskElementProperties);activeTaskOwner = getOwnerValue(userTask, migrationContext, taskElementProperties);activeTaskCandidateUsers = getActiveValueList(userTask.getCandidateUsers(), DynamicBpmnConstants.USER_TASK_CANDIDATE_USERS, taskElementProperties);activeTaskCandidateGroups = getActiveValueList(userTask.getCandidateGroups(), DynamicBpmnConstants.USER_TASK_CANDIDATE_GROUPS, taskElementProperties);activeTaskIdVariableName = DynamicPropertyUtil.getActiveValue(userTask.getTaskIdVariableName(), DynamicBpmnConstants.USER_TASK_TASK_ID_VARIABLE_NAME, taskElementProperties);} else {activeTaskName = userTask.getName();activeTaskDescription = userTask.getDocumentation();activeTaskDueDate = userTask.getDueDate();activeTaskPriority = userTask.getPriority();activeTaskCategory = userTask.getCategory();activeTaskFormKey = userTask.getFormKey();activeTaskSkipExpression = userTask.getSkipExpression();activeTaskAssignee = getAssigneeValue(userTask, migrationContext, null);activeTaskOwner = getOwnerValue(userTask, migrationContext, null);activeTaskCandidateUsers = userTask.getCandidateUsers();activeTaskCandidateGroups = userTask.getCandidateGroups();activeTaskIdVariableName = userTask.getTaskIdVariableName();}CreateUserTaskBeforeContext beforeContext = new CreateUserTaskBeforeContext(userTask, execution, activeTaskName, activeTaskDescription, activeTaskDueDate, activeTaskPriority, activeTaskCategory, activeTaskFormKey, activeTaskSkipExpression, activeTaskAssignee, activeTaskOwner, activeTaskCandidateUsers, activeTaskCandidateGroups);if (processEngineConfiguration.getCreateUserTaskInterceptor() != null) {processEngineConfiguration.getCreateUserTaskInterceptor().beforeCreateUserTask(beforeContext);}handleName(beforeContext, expressionManager, task, execution);handleDescription(beforeContext, expressionManager, task, execution);handleDueDate(beforeContext, expressionManager, task, execution, processEngineConfiguration, activeTaskDueDate);handlePriority(beforeContext, expressionManager, task, execution, activeTaskPriority);handleCategory(beforeContext, expressionManager, task, execution);handleFormKey(beforeContext, expressionManager, task, execution);//是否跳过用户任务,如果跳过了,直接删除当前任务,离开走到下一个节点boolean skipUserTask = SkipExpressionUtil.isSkipExpressionEnabled(beforeContext.getSkipExpression(), userTask.getId(), execution, commandContext)&& SkipExpressionUtil.shouldSkipFlowElement(beforeContext.getSkipExpression(), userTask.getId(), execution, commandContext);//插入 ACT_RU_TASKTaskHelper.insertTask(task, (ExecutionEntity) execution, !skipUserTask, (!skipUserTask && processEngineConfiguration.isEnableEntityLinks()));//处理分配需要在插入任务后完成,以便具有id// Handling assignments need to be done after the task is inserted, to have an idif (!skipUserTask) {if (processEngineConfiguration.isLoggingSessionEnabled()) {BpmnLoggingSessionUtil.addLoggingData(LoggingSessionConstants.TYPE_USER_TASK_CREATE, "User task '" + task.getName() + "' created", task, execution);}//处理任务受理人handleAssignments(taskService, beforeContext.getAssignee(), beforeContext.getOwner(), beforeContext.getCandidateUsers(), beforeContext.getCandidateGroups(), task, expressionManager, execution, processEngineConfiguration);if (processEngineConfiguration.getCreateUserTaskInterceptor() != null) {CreateUserTaskAfterContext afterContext = new CreateUserTaskAfterContext(userTask, task, execution);processEngineConfiguration.getCreateUserTaskInterceptor().afterCreateUserTask(afterContext);}try {processEngineConfiguration.getListenerNotificationHelper().executeTaskListeners(task, TaskListener.EVENTNAME_CREATE);} catch (BpmnError bpmnError) {ErrorPropagation.propagateError(bpmnError, execution);return;}// All properties set, now firing 'create' eventsFlowableEventDispatcher eventDispatcher = processEngineConfiguration.getTaskServiceConfiguration().getEventDispatcher();if (eventDispatcher != null && eventDispatcher.isEnabled()) {eventDispatcher.dispatchEvent(FlowableTaskEventBuilder.createEntityEvent(FlowableEngineEventType.TASK_CREATED, task),processEngineConfiguration.getEngineCfgKey());}if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(activeTaskIdVariableName)) {Expression expression = expressionManager.createExpression(userTask.getTaskIdVariableName());String idVariableName = (String) expression.getValue(execution);if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(idVariableName)) {execution.setVariable(idVariableName, task.getId());}}} else {TaskHelper.deleteTask(task, null, false, false, false); // false: no events fired for skipped user taskleave(execution);}}
用户任务执行完之后,就等待用户手动执行,就不再继续流转了,所以没有继续推送节点,直接运行完后,返回到CommandInvoker,再通过责任链返回。
值得注意的是,在CommandContextInterceptor中进行实际的入库操作。
用户执行流程
以张三提交申请为例,先查询出张三所需要审批的任务,然后执行taskService.complete方法。
/* 张三提交申请*/@Testpublic void complete_zs() {//查询zhangsan的任务String userId = "zhangsan";//SELECT RES.* from ACT_RU_TASK RES WHERE RES.ASSIGNEE_ = ? order by RES.ID_ ascList<Task> list = taskService.createTaskQuery().taskAssignee(userId).list();for (Task task : list) {System.out.println("=============================================================");System.out.println("task.getProcessInstanceId() = " + task.getProcessInstanceId());System.out.println("task.getFormKey() = " + task.getFormKey());System.out.println("task.getExecutionId() = " + task.getExecutionId());System.out.println("=============================================================");taskService.complete(task.getId());System.out.println(userId + "完成任务");}}
内部执行的是commandExecutor.execute(new CompleteTaskCmd(taskId, (Map<String, Object>) null));这一行,按照前面的理解,我们直接看CompleteTaskCmd的execute方法。这里直接执行到TaskHelper的completeTask方法。
这里ACT_RU_TASK表只存储当前运行到的实例,所以这里用户处理完之后会把这个删掉,这里就是存在删除逻辑,删除完之后再推入一个节点TriggerExecutionOperation。
public static void completeTask(TaskEntity taskEntity, Map<String, Object> variables, Map<String, Object> localVariables,Map<String, Object> transientVariables, Map<String, Object> localTransientVariables, CommandContext commandContext) {//省略部分代码。。。。//task表示当前执行的节点,这个过程需要删除当前的task,新增下一个节点的task。这里属于删除deleteTask(taskEntity, null, false, true, true);// Continue process (if not a standalone task)if (taskEntity.getExecutionId() != null && !bpmnErrorPropagated) {ExecutionEntity executionEntity = processEngineConfiguration.getExecutionEntityManager().findById(taskEntity.getExecutionId());//将执行节点推入运行栈CommandContextUtil.getAgenda(commandContext).planTriggerExecutionOperation(executionEntity);}}
我们直接看TriggerExecutionOperation的run方法中,获取具体的UserTaskActivityBehavior行为,这里不做处理,默认是同步的情况,直接看UserTaskActivityBehavior的trigger方法,逻辑也比较简单,确认当前任务是删除的之后,离开此节点。
public void trigger(DelegateExecution execution, String signalName, Object signalData) {ProcessEngineConfigurationImpl processEngineConfiguration = CommandContextUtil.getProcessEngineConfiguration();List<TaskEntity> taskEntities = processEngineConfiguration.getTaskServiceConfiguration().getTaskService().findTasksByExecutionId(execution.getId()); // Should be only onefor (TaskEntity taskEntity : taskEntities) {if (!taskEntity.isDeleted()) {throw new FlowableException("UserTask should not be signalled before complete");}}leave(execution);}
离开此节点的逻辑同前面的逻辑,新增一个TakeOutgoingSequenceFlowsOperation置入运行栈中。
删除流程实例
@Testpublic void delete() {//SELECT RES.* , P.KEY_ as ProcessDefinitionKey, P.ID_ as ProcessDefinitionId, P.NAME_ as ProcessDefinitionName, P.VERSION_ as ProcessDefinitionVersion, P.DEPLOYMENT_ID_ as DeploymentId// from ACT_RU_EXECUTION RES inner join ACT_RE_PROCDEF P on RES.PROC_DEF_ID_ = P.ID_ WHERE RES.PARENT_ID_ is null and P.KEY_ = ? order by RES.ID_ ascList<ProcessInstance> processInstanceList = runtimeService.createProcessInstanceQuery().processDefinitionKey("请假流程2").list();for (ProcessInstance processInstance : processInstanceList) {System.out.println("================================");System.out.println("processInstance.getProcessInstanceId() = " + processInstance.getProcessInstanceId());System.out.println("processInstance.getProcessDefinitionKey() = " + processInstance.getProcessDefinitionKey());System.out.println("processInstance.getDeploymentId() = " + processInstance.getDeploymentId());runtimeService.deleteProcessInstance(processInstance.getProcessInstanceId(), "没用的删除掉");System.out.println("================================");}System.out.println("完成删除!!!");}
进入deleteProcessInstance方法发现执行commandExecutor.execute(new DeleteProcessInstanceCmd(processInstanceId, deleteReason)),按照之前的经验直接看DeleteProcessInstanceCmd的execute方法
最终走到ExecutionEntityManagerImpl类的deleteProcessInstance方法,删除运行时的表。
会签、或签
会签任务:一个任务需要两个或者两个以上的成员参与进行审批审批条件是多样,并且可配置通过的权重比例。可以理解为投票,但是也有可能 某一个审批者有一票否决权。
会签的内置参数:
- nrOfInstances: 一共多少实例
- nrOfCompletedInstances: 已经完成审批数量(包含审批结果为通过和拒绝的)
- nrOfActiveInstances: 还未完成审批数量
多实例任务类型
- Parallel:并行,指的如果我们配置了3人会签,3人可以同时在待办看到此任务并处理
- sequential:串行,指的是如果我们配置了3人会签,则会需要串行执行,前一个人办理了后一个人才能看到
