【C++】vector的模拟实现

文章目录
-
- 1.查看STL源码
- 2.vector的模拟实现
-
- 1. 构造函数
-
- 无参构造
- 构造n个 val
- 迭代器模板
- 2. reserve
- 3. 迭代器
- 4.pop_back 尾删
- 5.resize
- 6.push_back
- 7.insert
-
- 迭代器失效—— pos为野指针
- 迭代器失效——修改迭代器位置
- 8. erase
-
- 对于VS和Linux环境测试
- 3.深浅拷贝问题
- 4. 整体代码实现
1.查看STL源码
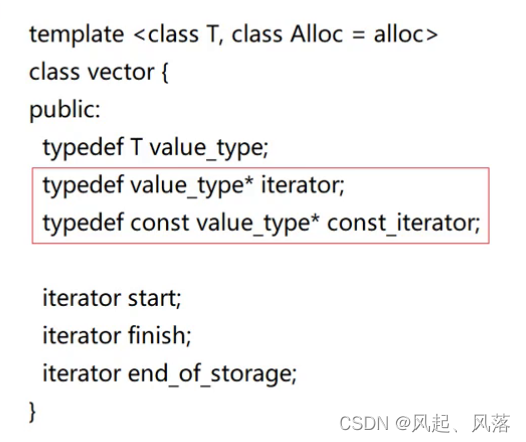
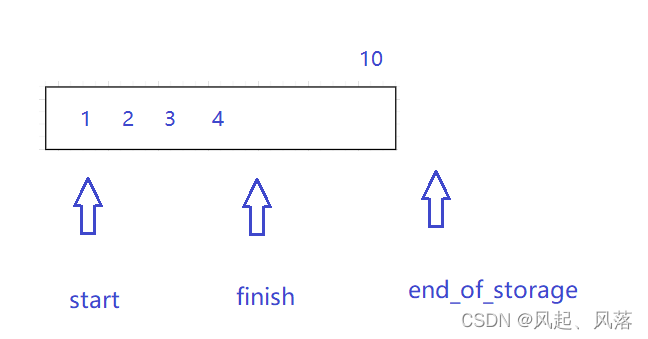
start、finish、end_of_storage 都是指针

通过观察函数的实现过程,可以得知 start与begin等价 ,end与finish等价
2.vector的模拟实现
为了模拟实现vector,所以使用自己的名空间包含vector类
1. 构造函数
无参构造
vector()//构造函数:_start(nullptr), _finish(nullptr), _end_of_storage(nullptr){}
只是将_start 、_finish 、_end_of_storage 初始化为nullptr
构造n个 val
vector(size_t n, const T& val = T()):_start(nullptr), _finish(nullptr), _end_of_storage(nullptr){reserve(n);//扩容for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){push_back(val);}}
正常来说匿名对象生命周期只有这一行,因为这行之后没有会用它了
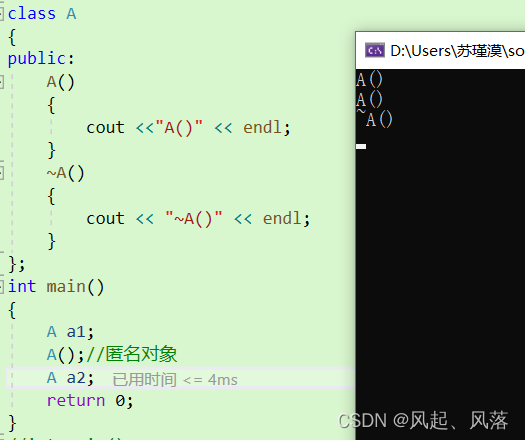
当调用完匿名对象后,会调用析构函数
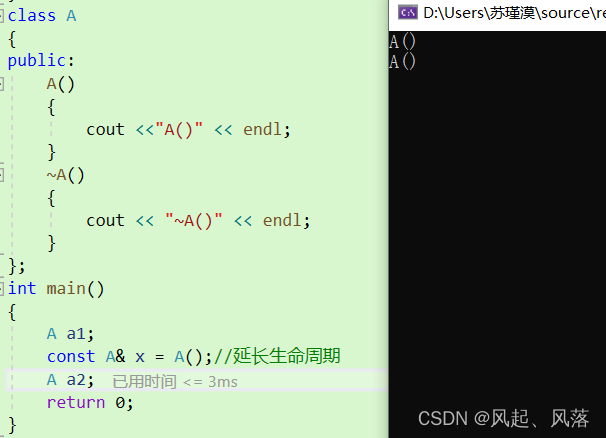
引用会延长匿名对象的生命周期到引用对象域结束,因为后面用xx就是用匿名对象
由于匿名对象具有常性,所以需要用const修饰
此时调用完匿名对象,并不会调用析构函数释放
迭代器模板
template <class InputIterator>//随机迭代器vector(InputIterator first, InputIterator last):_start(nullptr), _finish(nullptr), _end_of_storage(nullptr){//[first,last)while (first != last){push_back(*first);first++;}}
template <class InputIterator>//随机迭代器vector(InputIterator first, InputIterator last):_start(nullptr), _finish(nullptr), _end_of_storage(nullptr){//[first,last)while (first != last){push_back(*first);first++;}}
提供迭代器模板,可以使用任意类型迭代器
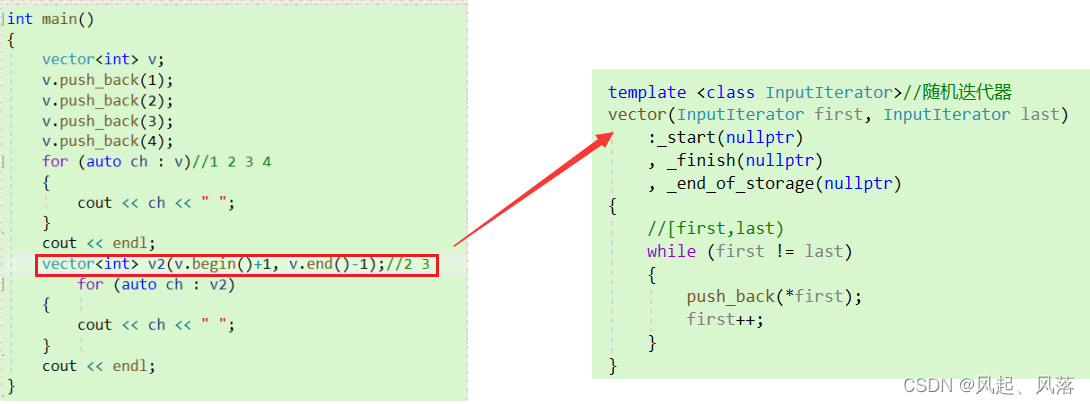
调用vector本身迭代器

对于数组和string类型也同样适用
2. reserve
void reserve(size_t n)//开辟空间{if (n > capacity())//避免缩容{size_t sz = size();T* tmp = new T[n];if (_start != NULL)//为NULL时没有意义{memcpy(tmp, _start, sizeof(T)*size());//拷贝数据delete[]_start;//释放旧空间}_start = tmp;//指向新空间_finish = tmp + sz;_end_of_storage = tmp + n;//容量变大了}}
为了避免缩容的情况,所以使用 n>capacity() , 开辟一块空间tmp,将start中的数据拷贝到新空间,释放旧空间,指向新空间,同时更新_finish 和_end_of_storage
在计算_finish的大小时,由于size里面的_start改变了,所以需要提前储存原来的size
3. 迭代器
typedef T* iterator;
typedef const T* const_iterator;
iterator begin(){return _start;}iterator end(){return _finish;}const_iterator begin()const {return _start;}const_iterator end()const{return _finish;}
正向迭代器的应用
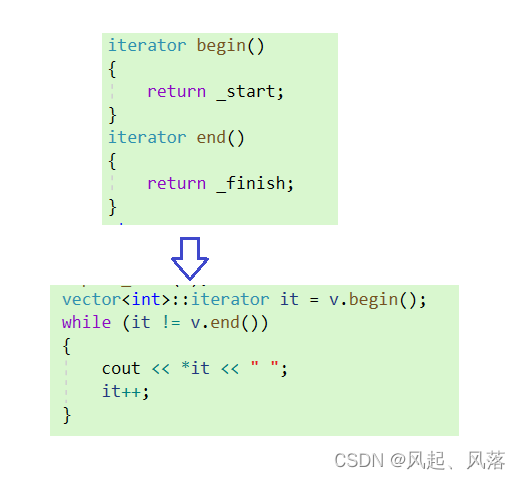
反向迭代器的应用

此时v由const修饰,所以需要const_iterator类型的迭代器
4.pop_back 尾删
为了防止没有数据继续删除,使用断言报错
bool empty(){return _start = _finish;}void pop_back()//尾删{assert(!empty());_finish--;}

5.resize
void resize(size_t n ,T val=T())//扩容+初始化{if (n < size())//删除数据{_finish = _start + n;}else{if (n > capacity()){reserve(n);//扩容}while (_finish != _start + n)//将剩余空间初始化{*_finish = val;_finish++;}}}
T val= T() ,T()是匿名对象,因为T模板泛型,所以有可能是内置类型int char,也有可能是自定义类型,为了两者都可以使用,所以使用匿名对象调用默认构造函数

内置类型也是有构造函数的
6.push_back
void push_back(const T& x)//尾插{if (_finish == _end_of_storage)//扩容{reserve(capacity() == 0 ? 4 : 2 * capacity());}*_finish = x;_finish++;}
需要考虑扩容问题,而若capacity本身为0的情况也要考虑
7.insert
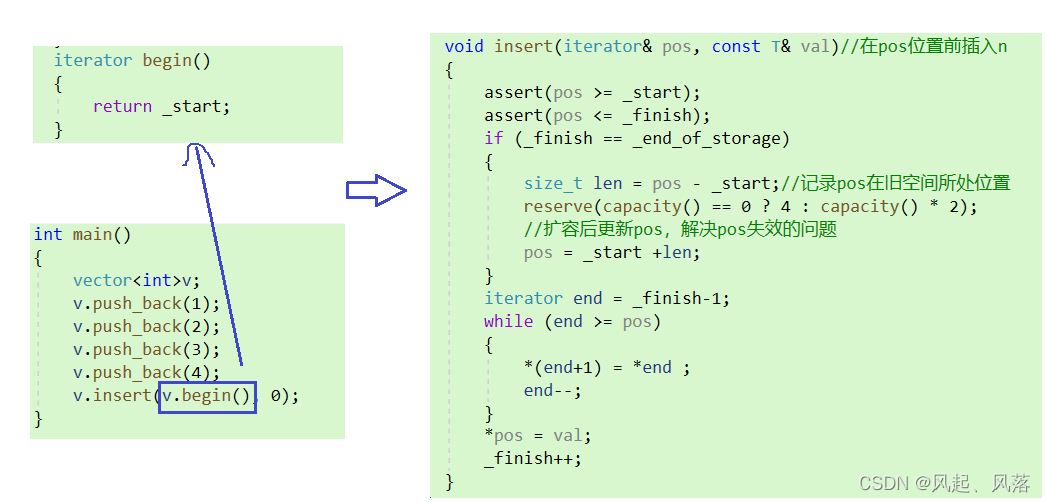
void insert(iterator pos, const T& val)//在pos位置前插入n{assert(pos >= _start);assert(pos <= _finish);if (_finish == _end_of_storage){size_t len = pos - _start;//记录pos在旧空间所处位置reserve(capacity() == 0 ? 4 : capacity() * 2);//扩容后更新pos,解决pos失效的问题pos = _start +len;}iterator end = _finish-1;while (end >= pos){*(end+1) = *end ;end--;}*pos = val;_finish++;}
迭代器失效—— pos为野指针

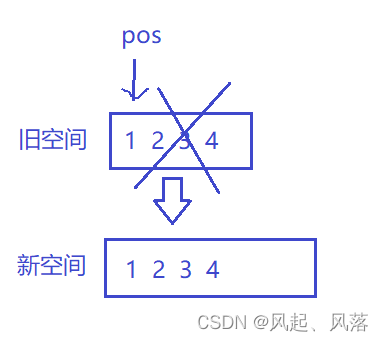
扩容时出现了问题,由于pos指向原来的空间,但是扩容时将释放了旧空间,但是pos依旧指向原来的空间,所以pos变成了野指针
所以需要记录pos在旧空间所处位置,再更新pos在新空间的位置
迭代器失效——修改迭代器位置
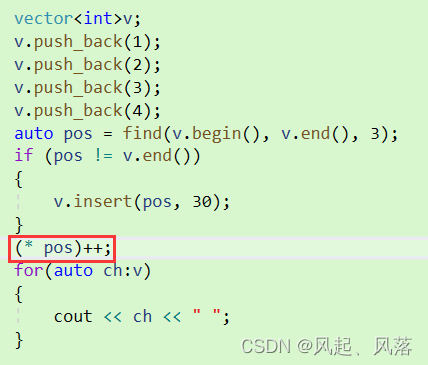
加入修改迭代器位置后,会直接报错
形参pos位置的改变不会影响实参,所以pos依旧指向旧空间
若将形参pos加入引用,会报错,当调用begin时,因为是传值返回,所以返回临时对象,而临时对象具有常性,所以不能直接传给引用

为了解决这个问题,将修改指向的pos返回
8. erase
void erase(iterator pos)//删除pos位置数据{assert(pos >= _start);assert(pos < _finish);iterator start = pos + 1;while (start != _finish){*(start - 1) = *start;start++;}_finish--;}
对于VS和Linux环境测试
 VS做了强制检查,只要使用了erase,迭代器就失效了,所以会报错
VS做了强制检查,只要使用了erase,迭代器就失效了,所以会报错
而同样的代码在Linux下会就能正常运行
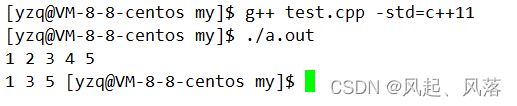
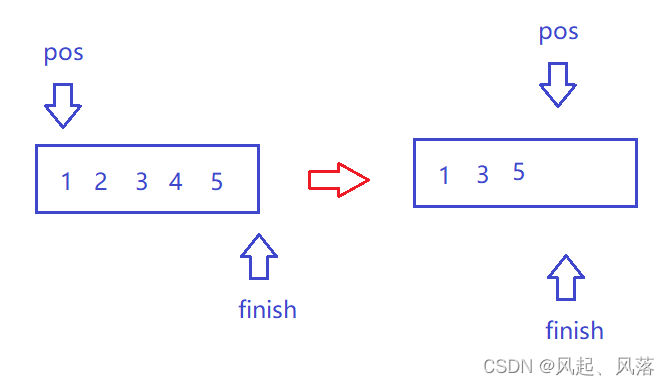
遇到偶数就删除,并且每次结尾pos都会++,运行结束时正好pos位置等于finish
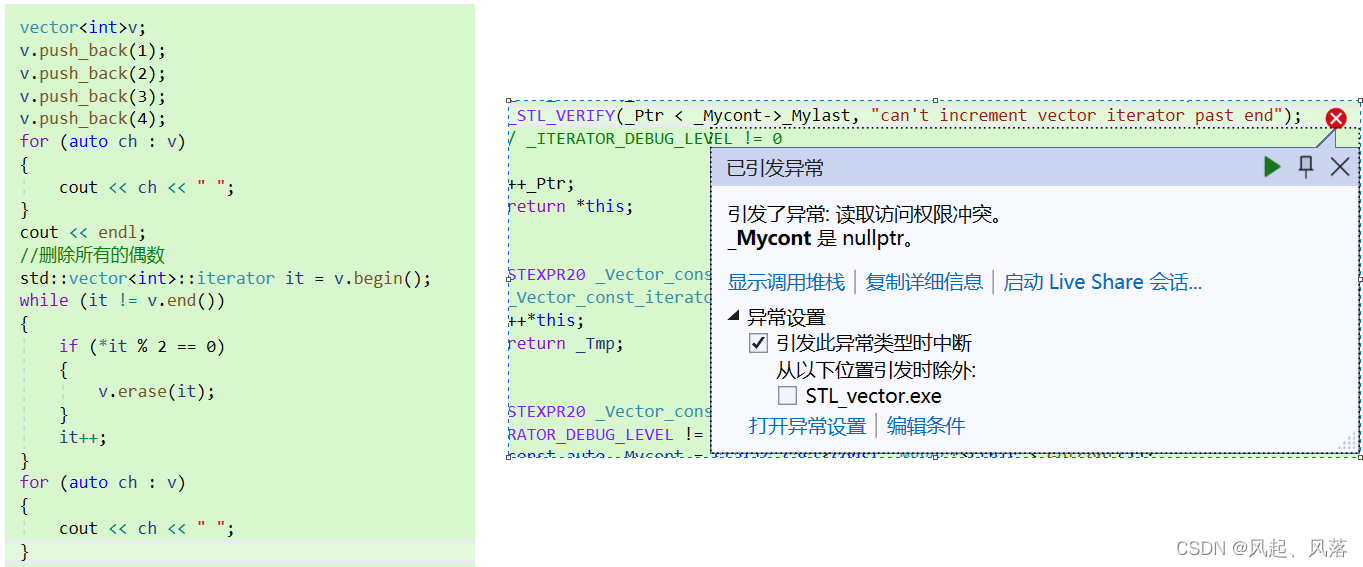
VS做了强制检查,使用erase后,迭代器失效了,所以会报错

同样的代码在Linux下就会发生段错误
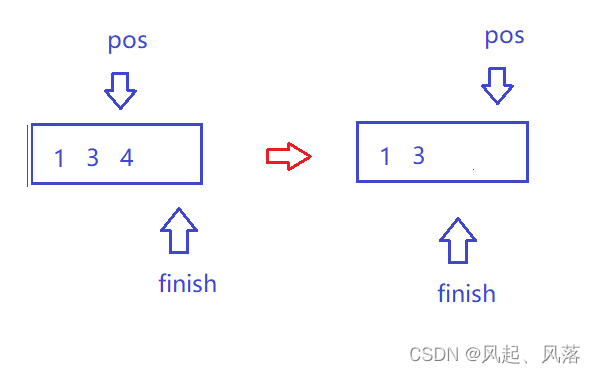
假设为最后一个位置被删除,finish会移动到到最后到3位置的后面,同时pos++,此时pos位置已经在finish位置后面,就会造成一直循环下去
说明g++没有强制类型检查,具体问题具体分析,结果未定义
3.深浅拷贝问题
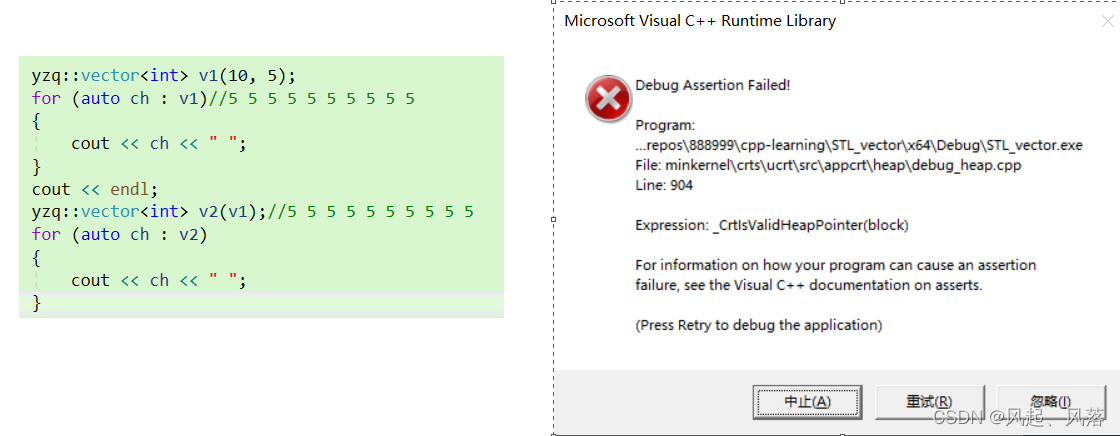
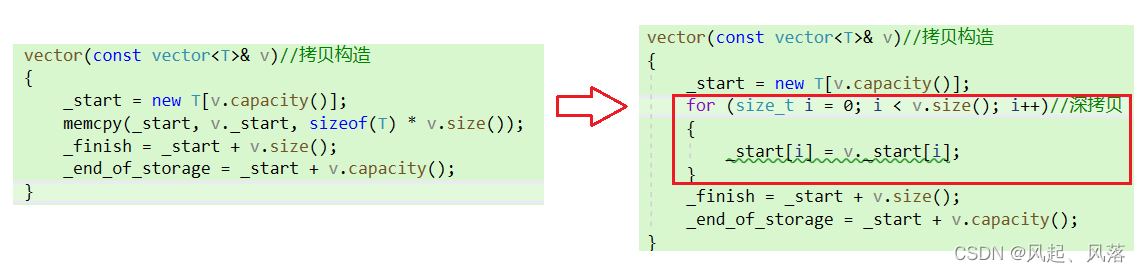
对内置类型调用默认拷贝构造函数会进行浅拷贝,所以需要我们自己来实现深拷贝
vector(const vector<T>& v)//拷贝构造{_start = new T[v.capacity()];memcpy(_start, v._start, sizeof(T) * v.size());_finish = _start + v.size();_end_of_storage = _start + v.capacity();}
若为上面内置类型,那报错的问题就可以解决了,但若为自定义类型依旧会报错
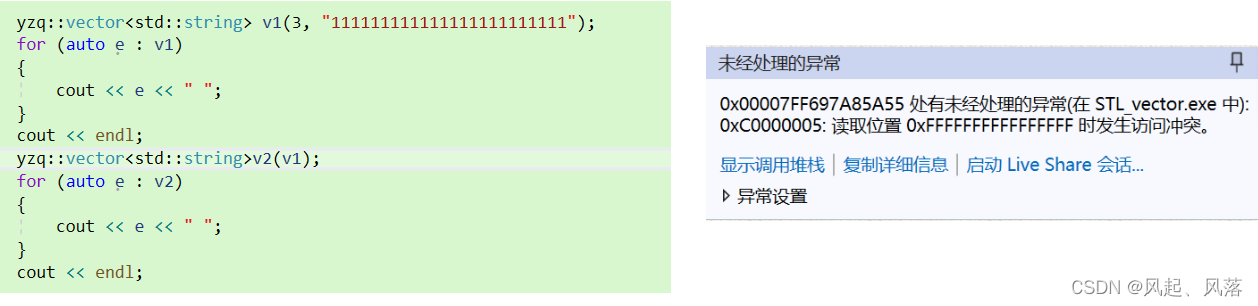
因为自己实现的拷贝构造中memcpy也是一种浅拷贝(按字节拷贝)
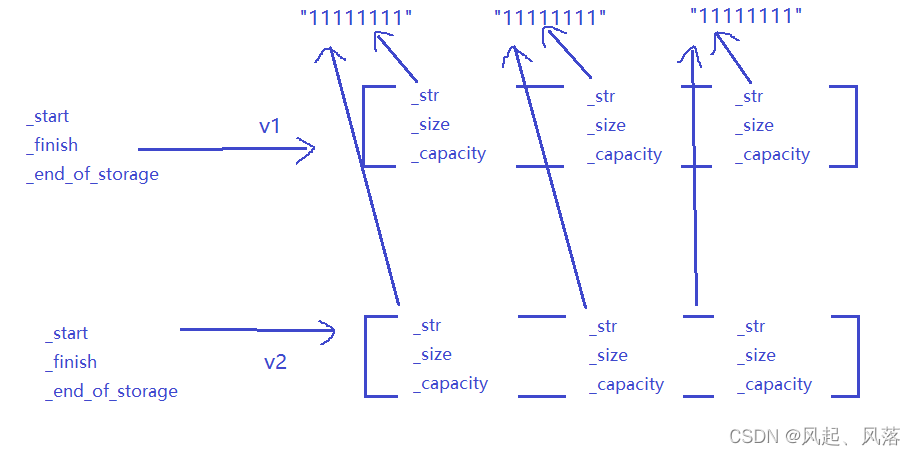
深拷贝是重新开辟一块与原空间大小相同的新空间,并将原空间的数据拷贝给新空间,但是若为string 类型,本身的_str指向字符串,而新空间只是将_str拷贝过去了,依旧指向同一字符串
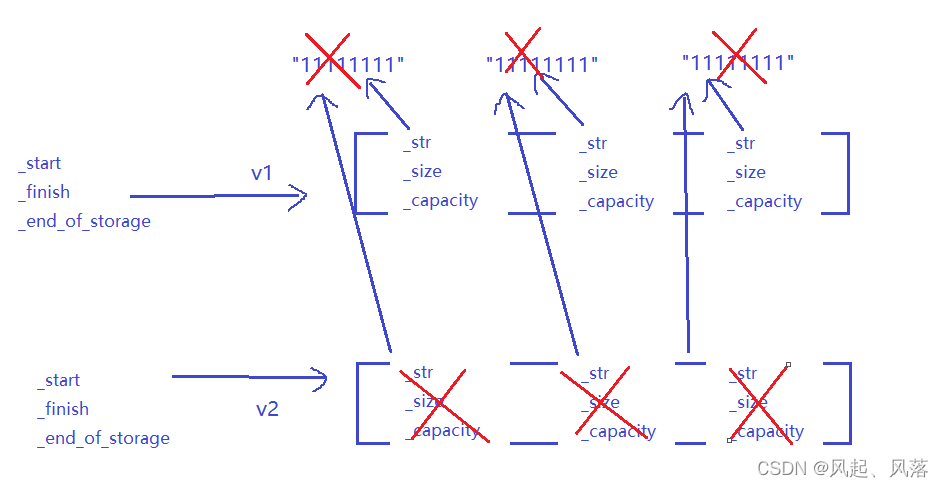
v2先进行析构,会调用delete[ ] ,会对数组上每个成员依次调用析构函数,此时指向的字符串旧全部被析构了,
再次使v1析构,依旧会析构字符串,所以会报错
属于深拷贝内的浅拷贝
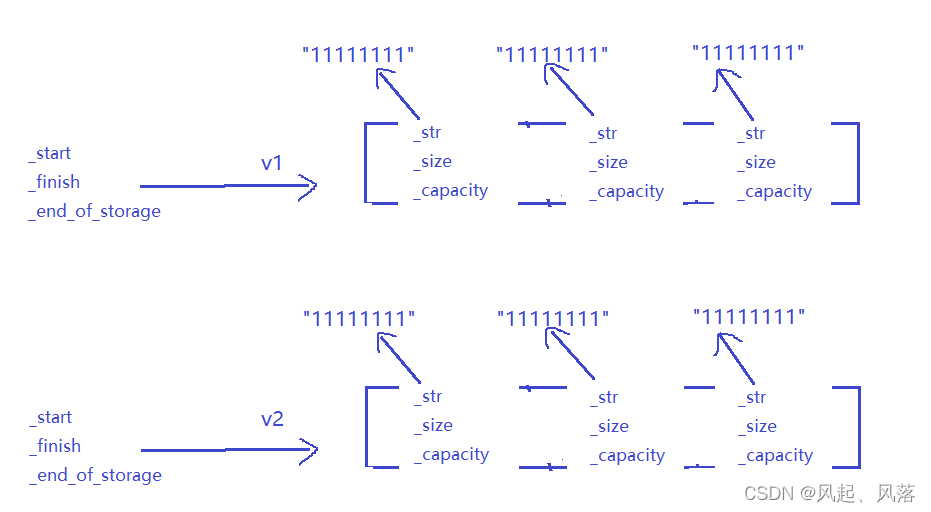
这样v1与v2中的_str都指向自己的字符串,不会发生析构两次的问题了
同样reserve也存在使用memcp造成浅拷贝的问题
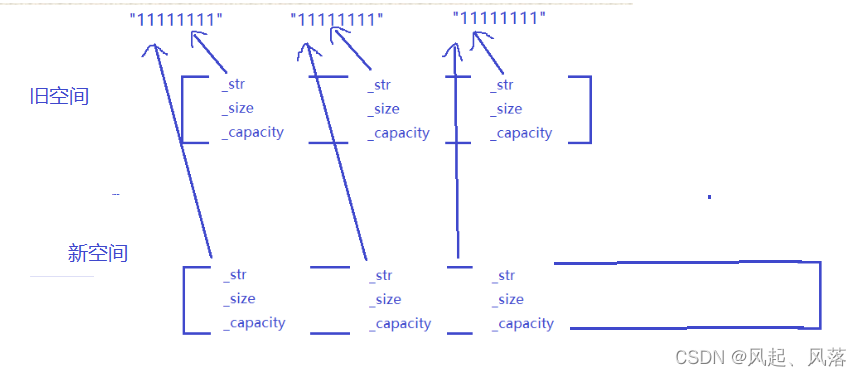
将旧空间上的_str等拷贝到新空间上,释放旧空间就导致_str所指向的字符串析构
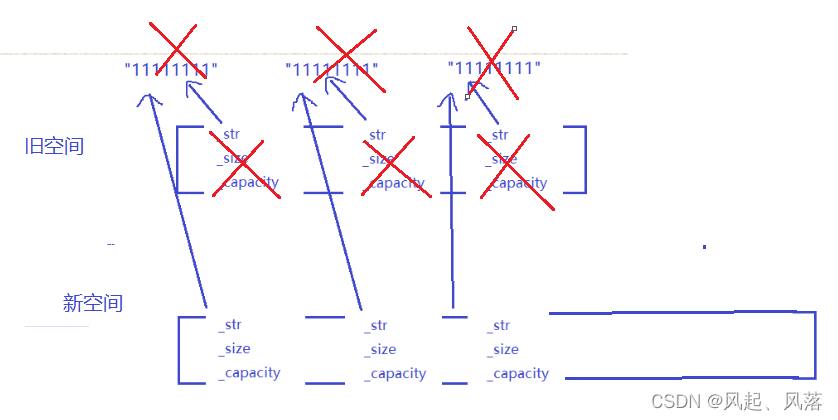
当新空间析构时,_str所指向的字符串就会造成二次析构,从而报错

4. 整体代码实现
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<assert.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<functional>
using namespace std;
namespace yzq
{template <class T>class vector{public:typedef T* iterator;typedef const T* const_iterator;vector()//构造函数:_start(nullptr), _finish(nullptr), _end_of_storage(nullptr){}vector(size_t n, const T& val = T()):_start(nullptr), _finish(nullptr), _end_of_storage(nullptr){reserve(n);//扩容for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){push_back(val);}}vector(const vector<T>& v)//拷贝构造{reserve(v.capacity());for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); i++){_start[i] = v._start[i];}_finish = _start + v.size();}~vector(){delete[] _start;_start = _finish = _end_of_storage = nullptr;}void push_back(const T& x)//尾插{if (_finish == _end_of_storage)//扩容{reserve(capacity() == 0 ? 4 : 2 * capacity());}*_finish = x;_finish++;}size_t capacity()const{return _end_of_storage - _start;}size_t size() const{return _finish - _start;}void reserve(size_t n)//开辟空间{if (n > capacity())//避免缩容{size_t sz = size();T* tmp = new T[n];if (_start != NULL)//为NULL时没有意义{for (size_t i = 0; i < sz; i++)//深拷贝{tmp[i] = _start[i];}delete[]_start;//释放旧空间}_start = tmp;//指向新空间_finish = tmp + sz;_end_of_storage = tmp + n;//容量变大了}}T& operator[](size_t pos){assert(pos < size());//防止越界return _start[pos];}iterator begin(){return _start;}iterator end(){return _finish;}private:iterator _start;iterator _finish;iterator _end_of_storage;};
}int main()
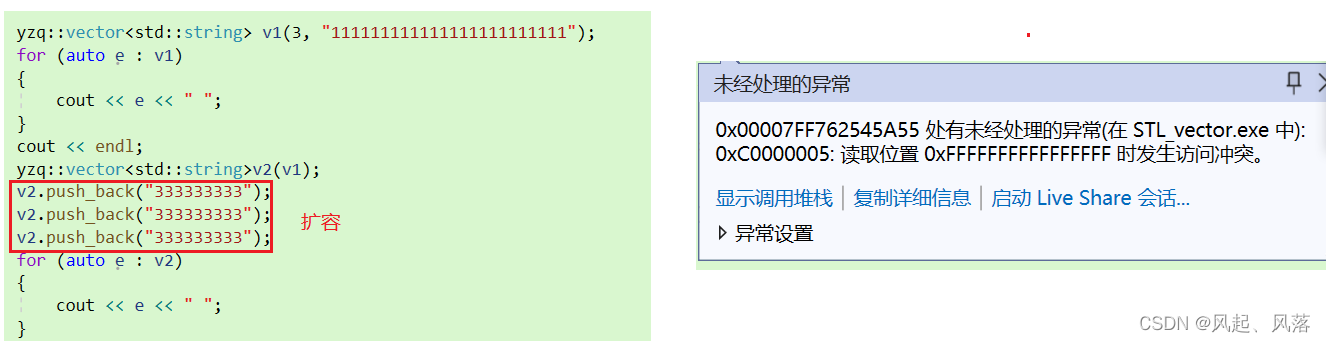
{yzq::vector<std::string> v1(3, "111111111111111111111111");for (auto e : v1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;yzq::vector<std::string>v2(v1);v2.push_back("333333333"); v2.push_back("333333333");v2.push_back("333333333");for (auto e : v2){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;
}

