Linux内核之网络协议栈以及套接字sk_buff分析

网络协议栈以及套接字sk_buff分析
一、Linux 内核网络协议栈构架
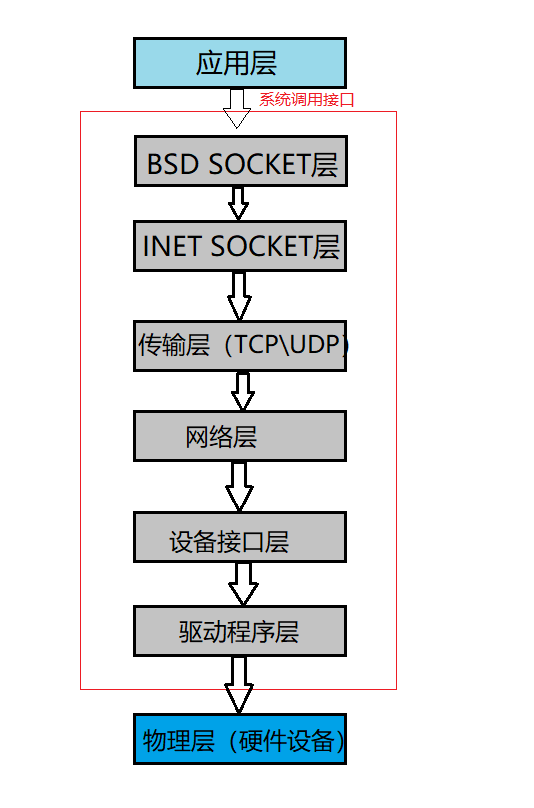
网络协议在传输数据的过程中,数据要进入内核的网络协议栈,通过协议族(TCP、UDP等),每一层之间当作比特流传输到网络中,而且,每一层收到数据都会封装相应的协议首部。比如TCP协议传给IP协议时,称为TCP报文段或者TCP segment;IP协议传给链路层时,称为数据单元或IP数据报;最后通过以太网传输比特流(帧 frame)。
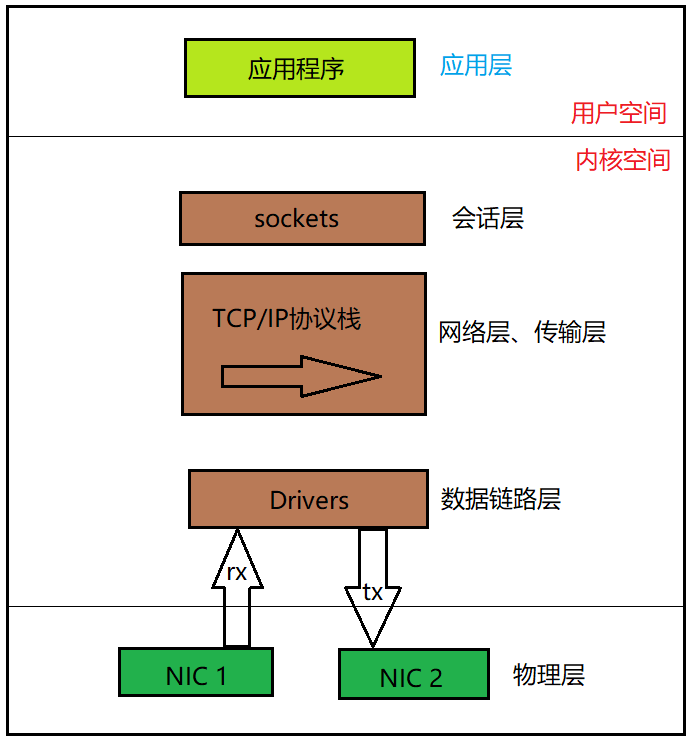
分用:当目标主机收到以太网数据帧时,数据信息开始从内核网络协议栈中由底向上进行操作,同时要去掉各个层次协议上的报文首部,每一层协议都会检查报文首部当中的协议标识(比如IP有IP首部、TCP有TCP首部),确保接收数据信息能上上层协议。
物理层:连接的硬件设备,比如网卡。
链路层:针对物理层进行访问的接口,比如驱动程序。
网络层:负责将网络数据包传输到正确的位置,比如IP协议、ARP协议。
传输层:为应用程序之间提供点到点的连接,比如UDP、TCP协议。
应用层:应用程序。
二、网络协议栈常见的数据结构
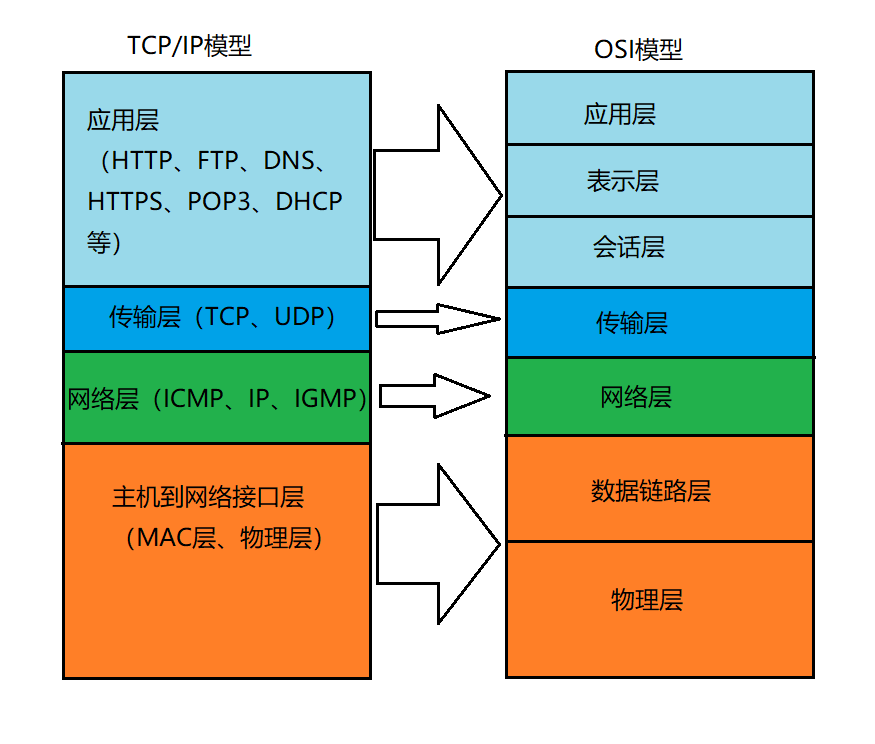
2.1、TCP/IP 参考模型及 ISO/OSI 参考模型
2.2、套接字 sk_buff 分析
在内核分析(收到)网络分组时,底层协议的数据将传递到更高的层。发送数据时顺序相反,各种协议产生的数据(首部和净荷)依次向更低的层传递,直至最终发送。
这些操作的速度对网络子系统的性能有决定性的影响,因此内核使用一种特殊的结构,称为套接字缓冲区(socket buffer),具体源码分析如下(include/linux/skbuff.h):
struct sk_buff {union {struct {/* These two members must be first. 双向链表存储*/struct sk_buff *next;struct sk_buff *prev;union {struct net_device *dev;//与SKB相关的网络接口设备(NIC,网络接口卡)/* Some protocols might use this space to store information,* while device pointer would be NULL.* UDP receive path is one user.*/unsigned long dev_scratch;};};struct rb_node rbnode; /* used in netem, ip4 defrag, and tcp stack */struct list_head list;};union {struct sock *sk;int ip_defrag_offset;};union {//存储时间戳相对参考时间的偏移量ktime_t tstamp;u64 skb_mstamp_ns; /* earliest departure time */};/ This is the control buffer. It is free to use for every* layer. Please put your private variables there. If you* want to keep them across layers you have to do a skb_clone()* first. This is owned by whoever has the skb queued ATM.*/char cb[48] __aligned(8);//重点,控制缓冲区,用于存储专用信息union {struct {unsigned long _skb_refdst;//可能指向目标对象的引用计数void (*destructor)(struct sk_buff *skb);};struct list_head tcp_tsorted_anchor;};#if defined(CONFIG_NF_CONNTRACK) || defined(CONFIG_NF_CONNTRACK_MODULE)unsigned long _nfct;//连接跟踪数据信息,主要让Linux内核能够跟踪所有的网络连接和传话操作
#endifunsigned int len,//数据包总字节数data_len;//非线性数据长度,有分页数据__u16 mac_len,//MAC数据包头长度hdr_len;/* Following fields are _not_ copied in __copy_skb_header()* Note that queue_mapping is here mostly to fill a hole.*/__u16 queue_mapping;/* if you move cloned around you also must adapt those constants */
#ifdef __BIG_ENDIAN_BITFIELD
#define CLONED_MASK (1 << 7)
#else
#define CLONED_MASK 1
#endif
#define CLONED_OFFSET() offsetof(struct sk_buff, __cloned_offset)/* private: */__u8 __cloned_offset[0];/* public: */__u8 cloned:1,//使用_skb_clone()克隆数据时,被克隆和克隆得到的数据包中,这个字段设为1nohdr:1,//只考虑有效负载,禁止修改包头fclone:2,peeked:1,head_frag:1,pfmemalloc:1;
#ifdef CONFIG_SKB_EXTENSIONS__u8 active_extensions;
#endif/* fields enclosed in headers_start/headers_end are copied* using a single memcpy() in __copy_skb_header()*//* private: */__u32 headers_start[0];/* public: *//* if you move pkt_type around you also must adapt those constants */
#ifdef __BIG_ENDIAN_BITFIELD
#define PKT_TYPE_MAX (7 << 5)
#else
#define PKT_TYPE_MAX 7
#endif
#define PKT_TYPE_OFFSET() offsetof(struct sk_buff, __pkt_type_offset)/* private: */__u8 __pkt_type_offset[0];//广播、组播/* public: */__u8 pkt_type:3;__u8 ignore_df:1;__u8 nf_trace:1;__u8 ip_summed:2;__u8 ooo_okay:1;__u8 l4_hash:1;__u8 sw_hash:1;__u8 wifi_acked_valid:1;__u8 wifi_acked:1;__u8 no_fcs:1;/* Indicates the inner headers are valid in the skbuff. 指向SKB是用于封装的*/__u8 encapsulation:1;__u8 encap_hdr_csum:1;__u8 csum_valid:1;#ifdef __BIG_ENDIAN_BITFIELD
#define PKT_VLAN_PRESENT_BIT 7
#else
#define PKT_VLAN_PRESENT_BIT 0
#endif
#define PKT_VLAN_PRESENT_OFFSET() offsetof(struct sk_buff, __pkt_vlan_present_offset)/* private: */__u8 __pkt_vlan_present_offset[0];/* public: */__u8 vlan_present:1;__u8 csum_complete_sw:1;__u8 csum_level:2;__u8 csum_not_inet:1;__u8 dst_pending_confirm:1;
#ifdef CONFIG_IPV6_NDISC_NODETYPE__u8 ndisc_nodetype:2;
#endif__u8 ipvs_property:1;__u8 inner_protocol_type:1;__u8 remcsum_offload:1;
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_SWITCHDEV__u8 offload_fwd_mark:1;__u8 offload_l3_fwd_mark:1;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_CLS_ACT__u8 tc_skip_classify:1;__u8 tc_at_ingress:1;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_REDIRECT__u8 redirected:1;__u8 from_ingress:1;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_TLS_DEVICE__u8 decrypted:1;
#endif#ifdef CONFIG_NET_SCHED__u16 tc_index; /* traffic control index */
#endifunion {__wsum csum;struct {__u16 csum_start;__u16 csum_offset;};};__u32 priority;//数据包排队优先级int skb_iif;//数据包到达的网络设备__u32 hash;__be16 vlan_proto;//使用vlan协议__u16 vlan_tci;//标志控制信息(ID和优先级组成)
#if defined(CONFIG_NET_RX_BUSY_POLL) || defined(CONFIG_XPS)union {unsigned int napi_id;unsigned int sender_cpu;};
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NETWORK_SECMARK__u32 secmark;//安全标记,该操作由iptables secmask目标设置
#endifunion {__u32 mark;//通过此标识来标识SKB,在iptables使用MARK目标和mangle表来设置mark字段__u32 reserved_tailroom;};union {__be16 inner_protocol;__u8 inner_ipproto;};__u16 inner_transport_header;__u16 inner_network_header;__u16 inner_mac_header;__be16 protocol;//协议字段__u16 transport_header;__u16 network_header;__u16 mac_header;/* private: */__u32 headers_end[0];/* public: *//* These elements must be at the end, see alloc_skb() for details. */sk_buff_data_t tail;//数据尾sk_buff_data_t end;//缓冲区尾部unsigned char *head,//缓冲区头部*data;//数据unsigned int truesize;//为SKB分配的空间refcount_t users;#ifdef CONFIG_SKB_EXTENSIONS/* only useable after checking ->active_extensions != 0 */struct skb_ext *extensions;
#endif
};
2.3、套接字缓冲区管理数据
套接字缓冲区的基本思想是,通过操作指针来增删协议首部。
- head 和 end 指向数据在内存中的起始和结束位置。
- data 和 tail 指向协议数据区域的起始和结束位置。
- mac_header 指向 MAC 协议首部的起始。
- network_header 和 transport_header 分别指向网络层和传输层协议首部的起始。
在32 位的系统上,数据类型 sk_buff_data_t 用来表示各种类型为简单指针的数据,具体结构 sk_buff_data_t 如下所示(include/linux/skbuff.h):
#if BITS_PER_LONG > 32
#define NET_SKBUFF_DATA_USES_OFFSET 1
#endif#ifdef NET_SKBUFF_DATA_USES_OFFSET
typedef unsigned int sk_buff_data_t;
#else
typedef unsigned char *sk_buff_data_t;
#endif
从套接字缓冲区获取 TCP 首部(include/linux/tcp.h):
static inline struct tcphdr *tcp_hdr(const struct sk_buff *skb)
{return (struct tcphdr *)skb_transport_header(skb);
}
从套接字缓冲区获取 UDP 首部(include/linux/udp.h):
static inline struct udphdr *udp_hdr(const struct sk_buff *skb)
{return (struct udphdr *)skb_transport_header(skb);
}
2.4、Linux 内核提供套接字缓冲区标准 API 函数
(include/linux/skbuff.h)
/* alloc_skb - allocate a network buffer* @size: size to allocate* @priority: allocation mask This function is a convenient wrapper around __alloc_skb().*/
static inline struct sk_buff *alloc_skb(unsigned int size,gfp_t priority)
{return __alloc_skb(size, priority, 0, NUMA_NO_NODE);
}static inline struct sk_buff *__pskb_copy(struct sk_buff *skb, int headroom,gfp_t gfp_mask)
{return __pskb_copy_fclone(skb, headroom, gfp_mask, false);
}/* alloc_skb_fclone - allocate a network buffer from fclone cache* @size: size to allocate* @priority: allocation mask This function is a convenient wrapper around __alloc_skb().*/
static inline struct sk_buff *alloc_skb_fclone(unsigned int size,gfp_t priority)
{return __alloc_skb(size, priority, SKB_ALLOC_FCLONE, NUMA_NO_NODE);
}struct sk_buff *skb_morph(struct sk_buff *dst, struct sk_buff *src);
void skb_headers_offset_update(struct sk_buff *skb, int off);
int skb_copy_ubufs(struct sk_buff *skb, gfp_t gfp_mask);
struct sk_buff *skb_clone(struct sk_buff *skb, gfp_t priority);
void skb_copy_header(struct sk_buff *new, const struct sk_buff *old);
struct sk_buff *skb_copy(const struct sk_buff *skb, gfp_t priority);
struct sk_buff *__pskb_copy_fclone(struct sk_buff *skb, int headroom,gfp_t gfp_mask, bool fclone);
static inline struct sk_buff *__pskb_copy(struct sk_buff *skb, int headroom,gfp_t gfp_mask)
{return __pskb_copy_fclone(skb, headroom, gfp_mask, false);
}/* skb_headroom - bytes at buffer head* @skb: buffer to check Return the number of bytes of free space at the head of an &sk_buff.*/
static inline unsigned int skb_headroom(const struct sk_buff *skb)
{return skb->data - skb->head;
}/* skb_tailroom - bytes at buffer end* @skb: buffer to check Return the number of bytes of free space at the tail of an sk_buff*/
static inline int skb_tailroom(const struct sk_buff *skb)
{return skb_is_nonlinear(skb) ? 0 : skb->end - skb->tail;
}/* skb_availroom - bytes at buffer end* @skb: buffer to check Return the number of bytes of free space at the tail of an sk_buff* allocated by sk_stream_alloc()*/
static inline int skb_availroom(const struct sk_buff *skb)
{if (skb_is_nonlinear(skb))return 0;return skb->end - skb->tail - skb->reserved_tailroom;
}
- skb_put()
- kfree_skb()
- skb_push()
- skb_pull()
- 等等
2.5、使用一个表头来实现套接字缓冲区的等待队列
struct sk_buff_head {/* These two members must be first. */struct sk_buff *next;struct sk_buff *prev;__u32 qlen;spinlock_t lock;
};
sk_buff会被双向链表进行管理。
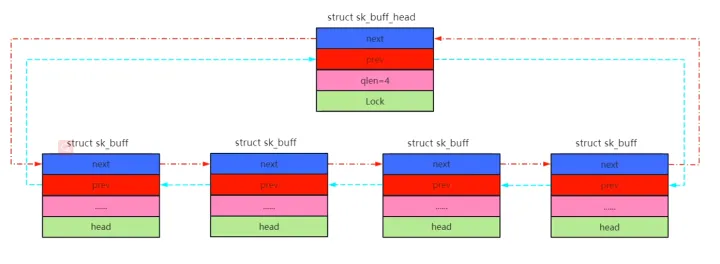
- next:指向链表下一个成员。
- prev:指向链表上一个成员。
- sk_buff_head:表示链表头。
- qlen:表示链表长度。
- lock:表示双向链表操作的保护锁,防止并发访问链表。
操作:直接在链表头部插入一个新的节点sk_buff。
2.6、net_device 数据结构分析
net_device 结构体存储着网络设备的所有信息,每个设备都有这种结 构 。 所 有 设 备 的 net_device 结 构 放 在 一 个 全 局 变 量dev_base 所有全局列表中。和 sk_buff 一样,整体结构相当庞大的。
结构体中有一个 next 指针,用来连接系统中所有网络设备。内核把这些连接起来的设备组成一个链表,并由全局变量 dev_base 指向链表的第一个元素。
net_device数据结构类型存储网络设备的所有数据信息(包含物理设备和虚拟设备);可以流量管理、设备状态管理、设备信息统计等等。
net_device 结构体具体源码如下(include/linux/netdevice.h):
struct net_device {char name[IFNAMSIZ];struct netdev_name_node *name_node;struct dev_ifalias __rcu *ifalias;/ I/O specific fields* FIXME: Merge these and struct ifmap into one*/unsigned long mem_end;unsigned long mem_start;unsigned long base_addr;int irq;/ Some hardware also needs these fields (state,dev_list,* napi_list,unreg_list,close_list) but they are not* part of the usual set specified in Space.c.*/unsigned long state;struct list_head dev_list;struct list_head napi_list;struct list_head unreg_list;struct list_head close_list;struct list_head ptype_all;struct list_head ptype_specific;// ...
}
name:网络设备名称。
mem_end、mem_start:共享内存的结束地址、起始地址。
base_addr:网络设备IO地址。
irq:网络设备的中断号。
dev_list:全局网络设备列表。
napi_list:NAPI机制,NAPI设备的列表入口。
unreg_list:注销网络设备的列表入口。
close_list:关闭网络设备列表的入口。
netdev_ops:网络设置操作集函数。
ethtool_ops:网络管理工具相关函数集。
header_ops:头部相关操作函数,比如解析、缓冲等。
flags:网络接口标志。
if_port:指定接口的端口类型。
dma:网络设备所有使用DMA通道。
max_mtu:最大传输单元。
min_mtu:最小传输单元。
type:指向ARP模块类型。
perm_addr:永久硬件地址。
addr_len:硬件地址长度。
_rx:接收队列。
_tx:发送队列。
num_tx_queues:发送队列数量。
real_num_tx_queues:当前有效的发送队列数量。
trans_start:数据包发送的时间戳,记录的是jiffiles。
ney_device_ops:网络设备相关操作的函数集合。ndo_poll_controller函数是轮询网卡数据的收发。



