接口自动化测试——必须掌握二


文章目录
- 一、接口请求体-文件
-
- 1、第一种方法
- 2、第二种方法
- 二、接口请求体-form表单
-
- 1、什么是 form 请求
- 三、接口请求体 - XML
- 四、xml 响应断言
-
- 1、方法一:XMLSession
- 2、方法二:xml.etree.ElementTree
- 五、cookie 处理
-
- 1、Cookie使用场景
- 2、传递Cookie的两种方式
- 六、超时处理
- 七、代理配置
-
- 1、使用代理之前和使用代理之后对比
- 2、代理在接口自动化的使用场景
- 3、如何使用
- 八、多层嵌套响应断言
-
- 1、什么是多层嵌套结构
- 2、复杂场景响应提取
- 3、JSONPath 简介
- 4、JSONPath 语法
- 5、JSONPath 与代码结合
一、接口请求体-文件
files:参数用来解决文件上传接口
key:需要替换为文件名
value:对应的二进制流
1、第一种方法
import requestsr1=requests.post("https://www.baidu.com/post",files={"hogwarts_file":open("1.text",'rb')},)
2、第二种方法
files:参数用来解决文件上传接口
通过value元组传递,实现指定filename的需求
r2=requests.post("https://www.baidu.com/post",files={"file":('kobe.txt',open("1.text",'rb'))},)
二、接口请求体-form表单
1、什么是 form 请求
数据量不大
数据层级不深的情况
通常以键值对传递
form格式传参,用data接收请求参数
import requests
class TestReq:def test_data(self):data={"kobe":"py1"}#通过data参数传入请求体信息r=requests.post("https://www.baidu.com/post",data=data)print(r.json())#区别#print(r.text)json格式传参,用json接收请求参数
import requests
class TestReq:def test_json(self):data = {"kobe": "py1"}# 通过json参数传入请求体信息r = requests.post("https://www.baidu.com/post", json=data)print(r.json())#print(r.text)
三、接口请求体 - XML
用data来接收xml格式的传参
import requestsxml= """<?xml version='1.0'encoding='utf-8'?>
<a>6</a>"""headers = {'Content-Type': 'application/xml'}
r = requests.post('https://www.baidu.com/post', data=xml, headers=headers).textprint(r)
四、xml 响应断言
可扩展标记语言(Extensible Markup Language)的缩写
也是一种结构化的数据
1、方法一:XMLSession
r.text:以xml格式形式,获取响应信息
r.xml.links:获取响应中所有的链接,以列表形式展示
r.xml.raw_xml:以字节格式返回响应内容
r.xml.text:返回各个标签下面的内容
xpath方法
1、获取language标签下的内容
first=True:只返回一条数据
r.xml.xpath(“//language”,first=True)
2、获取link标签下所有的的内容
items = r.xml.xpath('//link')res=[]for item in items:res.append(item.text)print(res)
from requests_xml import XMLSessiondef test_xml():#设置sessionsession=XMLSession()r=session.get("https://www.nasa.gov/rss/dyn/lg_image_of_the_day.rss")#print(r.text)#print(r.xml.links) #links 可以拿到响应中所有的链接,列表#print(r.xml.raw_xml) #raw_xml 以字节格式返回响应内容#print(r.xml.text) #text 返回各个标签下面的内容#通过xpath# 获取language标签下的内容item=r.xml.xpath('//language',first=True) #first=True:只返回一条数据print(item.text)#因为返回的是对象,所以需要调用text属性获取具体的值item1=r.xml.xpath('//link',first=True)print(item1.text)items = r.xml.xpath('//link')res=[]for item in items:res.append(item.text)print(res)assert "http://www.nasa.gov/" in res
2、方法二:xml.etree.ElementTree
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ETdef test_etree():#设置sessionsession=XMLSession()r=session.get("https://www.nasa.gov/rss/dyn/lg_image_of_the_day.rss")# 自己封装xml解析方法root=ET.fromstring(r.text)items=root.findall(".//link")result=[]for i in items:result.append(i.text)print(i.text)assert "http://www.nasa.gov/" in result
五、cookie 处理
1、Cookie使用场景
在接口测试过程中,很多情况下,需要发送的请求附带cookies,才会得到正常的响应的结果。所以使用python+requests进行接口自动化测试也是同理,需要在构造接口测试用例时加入cookie。
2、传递Cookie的两种方式
通过请求头信息传递
import requests
def test_demo():url = 'https://www.baidu.com/cookies'header={"Cookie":"werwr=yu",'User-Agent': 'python'}r=requests.get(url=url,headers=header)print(r.request.headers) #获取请求体信息
通过请求的关键字参数cookies传递
def test_demo1():url = 'https://www.baidu.com/cookies'header={'User-Agent': 'python'}cookie_data={"kobe":"kobe","kobe1": "kobe1",}r=requests.get(url=url,headers=header,cookies=cookie_data)print(r.request.headers) #获取请求体信息
六、超时处理
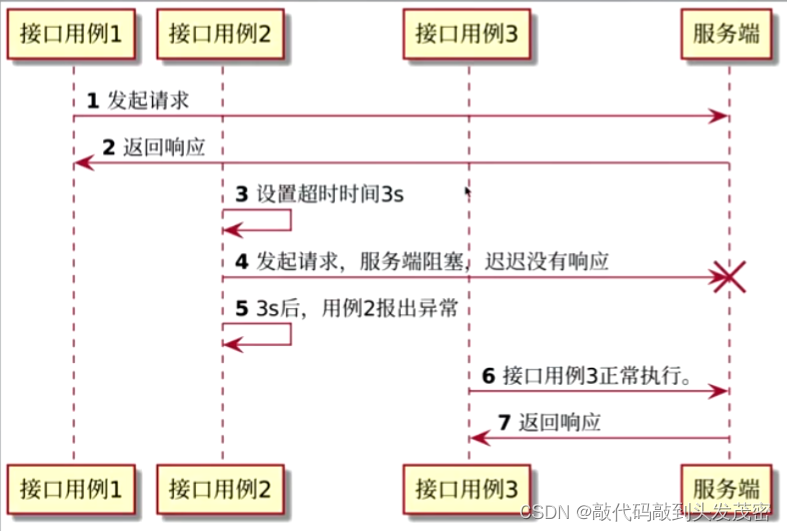
timeout参数设置超时时间,timeout对应的值通常是一个数字类型;提高容错性、健康性
import requestsclass TestReq:def test_timeout(self):#todo timeout参数设置超时时间,timeout对应的值通常是一个数字类型;提高容错性、健康性r=requests.get('https://www.baidu.com/cookies',timeout=3)print(r)七、代理配置
1、使用代理之前和使用代理之后对比

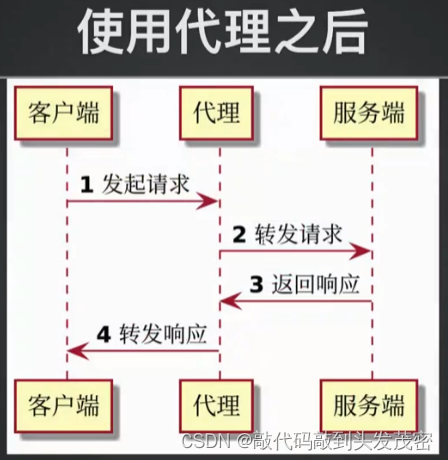
2、代理在接口自动化的使用场景
测试脚本,更直观的排查请求错误,相当于编写代码时的debug
获取没有错误的,真实的接口请求响应信息
通过代理获取自动化测试的请求响应
对比两次请求响应的区别
3、如何使用
a、设定代理格式
b、通过proxies 参数传递代理设置
c、开启代理工具监听请求
verify=False:不会认证https
import requests#定义一个代理的配置信息,key值为协议,value为工具的配置
proxy={"http":"http://127.0.0.1:8080","https":"http://127.0.0.1:8080"
}#通过proxies传递代理配置
#verify=False:不会认证https
data={"a":1}
requests.post(url = 'https://www.baidu.com/post',json=data,proxies=proxy,verify=False)
八、多层嵌套响应断言
1、什么是多层嵌套结构
层级多。
嵌套关系复杂。
{"errcode": 0,"errmsg": "ok","userid": "zhangsan","name": "张三","department": [1, 2],"order": [1, 2],"position": "后台工程师","mobile": "13800000000","gender": "1","email": "zhangsan@gzdev.com","biz_mail": "zhangsan@qyycs2.wecom.work","is_leader_in_dept": [1, 0],"direct_leader": ["lisi", "wangwu"],"avatar": "http://wx.qlogo.cn/mmopen/ajNVdqHZLLA3WJ6DSZUfiakYe37PKnQhBIeOQBO4czqrnZDS79FH5Wm5m4X69TBicnHFlhiafvDwklOpZeXYQQ2icg/0","thumb_avatar": "http://wx.qlogo.cn/mmopen/ajNVdqHZLLA3WJ6DSZUfiakYe37PKnQhBIeOQBO4czqrnZDS79FH5Wm5m4X69TBicnHFlhiafvDwklOpZeXYQQ2icg/100","telephone": "020-123456","alias": "jackzhang","address": "广州市海珠区新港中路","open_userid": "xxxxxx","main_department": 1,"extattr": {"attrs": [{"type": 0,"name": "文本名称","text": {"value": "文本"}},{"type": 1,"name": "网页名称","web": {"url": "http://www.test.com","title": "标题"}}]},"status": 1,"qr_code": "https://open.work.weixin.qq.com/wwopen/userQRCode?vcode=xxx","external_position": "产品经理","external_profile": {"external_corp_name": "企业简称","wechat_channels": {"nickname": "视频号名称","status": 1},"external_attr": [{"type": 0,"name": "文本名称","text": {"value": "文本"}},{"type": 1,"name": "网页名称","web": {"url": "http://www.test.com","title": "标题"}},{"type": 2,"name": "测试app","miniprogram": {"appid": "wx8bd80126147dFAKE","pagepath": "/index","title": "my miniprogram"}}]}
}
2、复杂场景响应提取
提取errcode 对应的值:res[“errcode”]
提取 title 对应的值:res[“extattr”][“external_profile”][“external_attr”][1][“web”][“title”]
3、JSONPath 简介
在 JSON 数据中定位和提取特定信息的查询语言。
JSONPath 使用类似于 XPath 的语法,使用路径表达式从 JSON 数据中选择和提取数据。
相比于传统的提取方式,更加灵活,并且支持定制化。
提取errcode 对应的值:$.errcode
提取 title 对应的值:$..title
4、JSONPath 语法
| 符号 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| $ | 查看的根节点对象,用于表示一个json数据,可以是数组或者对象 |
| @ | 过滤器,处理的当前节点对象 |
* |
通配符 |
. |
获取子节点 |
.. |
递归搜索,筛选所有符合条件的节点 |
?() |
过滤器表达式,筛选操作 |
| [start:end] | 数组片段,区间[start:end],不包含end |
| [A]或[A,B] | 迭代对象下标,表示一个或者多个数组下标 |
{"store": {"book": [{"category": "reference","author": "Nigel Rees","title": "Sayings of the Century","price": 8.95},{"category": "fiction","author": "Evelyn Waugh","title": "Sword of Honour","price": 12.99},{"category": "fiction","author": "Herman Melville","title": "Moby Dick","isbn": "0-553-21311-3","price": 8.99},{"category": "fiction","author": "J. R. R. Tolkien","title": "The Lord of the Rings","isbn": "0-395-19395-8","price": 22.99}],"bicycle": {"color": "red","price": 19.95}},"expensive": 10
}
获取所有书籍的作者:$.book.author
获取所有作者:$..author
获取 store 下面的所有内容: $.store
获取所有的价格: $..price
获取第三本书: $..book[2]
获取所有包含 isbn 的书籍: $..book[?(@.isbn)]
获取所有价格小于 10 的书:$..price[?(@.price<10)]
获取所有书籍的数量:$..book.length
5、JSONPath 与代码结合
环境安装:pip install jsonpath
import jsonpath
import requestsdef test_jsonpath():data = {"kobe": "py1"}r = requests.post("https://www.baidu.com/post", json=data)print(r.json())#todo jsonpath的返回值,如果找到的话,不管找到多少个结果,返回的结果都是列表;如果没有找到返回Falseprint(jsonpath.jsonpath(r.json(),'$..json')) #列表格式

