【数据结构入门】-链表之单链表(1)

个人主页:平行线也会相交
欢迎 点赞👍 收藏✨ 留言✉ 加关注💓本文由 平行线也会相交 原创
收录于专栏【数据结构初阶(C实现)】
文章标题
回顾
在讲解链表之前我们先来看看顺序表有哪些缺陷呢?
1.空间不够需要增容,而增容就需要付出代价,realloc增容(一种是原地扩容,另一种是异地扩容)时会容易产生内存碎片(异地扩容时)。
2.顺序表为了频繁扩容,所以空间一旦满了基本上就是扩2倍,可能会存在空间的浪费(因为扩出来的空间可能用不了那么多)。
3.顺序表要求数据从头开始位置连续存储,那么我们在头部或者中间位置插入删除数据就需要挪动数据,效率不高。
realloc原地扩容:
int main()
{int* p1 = (int*)malloc(10 * sizeof(int));int* p2 = (int*)realloc(p1, 11 * sizeof(int));return 0;
}

realloc(异地扩容):
#include<stdlib.h>int main()
{int* p1 = (int*)malloc(10 * sizeof(int));int* p2 = (int*)realloc(p1, 1000 * sizeof(int));return 0;
}

链表
针对顺序表存在的一些缺陷,所以就设计出来了链表。然而顺序表也并不是一无是处,对于顺序表是一块连续的空间,只需要存储第一个空间的地址,就可以找到所有的数据(对于这种物理上是连续的好处,比如a[i]等价于*(a+i))。
而对于链表倘若要遍历所有的数据,就需要通过指针来进行链接(第一个存第二个的地址、第二个存第三个的地址、第三个存第四个的地址…),所以这也是链表的代价,每存储一个数据就需要伴随一个指针,即每个数据都要存一个指针去链接后面数据节点不支持随机访问(用下标直接访问第i个)。
同时链表一定程度上也更好的解决了顺序表头部、中间插入数据时还需要挪动数据。链表就不需要这么麻烦,只需要改指针的链接,不需要挪动数据。
这里指的是单链表,当然链表不仅仅只是这一种结构,我们先从最简单的单链表开始,循序渐进。
链表的概念及结构
概念:链表是一种物理存储结构上非连接、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的,可以根据自己的需要按需申请空间。
typedef int SLTDateType;struct SListNode
{SLTDateType data;//data就是我们要存储的数据struct SListNode* next;
};
各种节点
void SListPrint(SLTNode* phead);void SListPushBack(SLTNode** pphead,SLTDateType x);void SListPustFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDateType x);void SListPopBack(SLTNode** pphead);void SListPopFront(SLTNode** pphead);SLTNode* SListFind(SLTNode* phead, SLTDateType x);//查找//在pos位置之前去插入一个节点
void SListInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDateType x);//某个位置插入
//void SListInsert(SLTNode* phead, int pos, SLTDateType x);//某个位置插入void SListInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, SLTDateType x);void SListErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos);
//void SListErase(SLTNode phead, int pos);void SListEraseAfter( SLTNode* pos);void SListDestory(SLTNode** pphead);//销毁链表打印链表
首先,phead是一个结构体指针指向第一个节点,cur也是如此,循环打印每个节点的数据就是通过cur = cur->next;走下去的,直到cur为空指针为止。
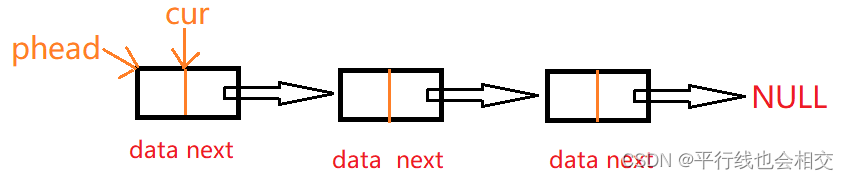
void SListPrint(SLTNode* phead)
{SLTNode* cur = phead;while (cur != NULL){printf("%d->", cur->data);cur = cur->next;}printf("NULL\\n");
}
尾插
//尾插
void SListPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDateType x)
{assert(pphead);SLTNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);//起初链表中是啥也没有的if (*pphead == NULL){*pphead = newnode;}else{//找到尾部=节点SLTNode* tail = *pphead;while (tail->next != NULL){tail = tail->next;}tail->next = newnode;}
}
注意:第一种情况:倘若链表中起初啥也没有的,所以就需要我们先创建一个节点。
第二种情况:此时链表中是有数据的,此时我们要想尾插一个尾节点,就需要先找到尾。找到尾部节点的空指针后,直接把此空指针置为新节点的指针(即tail->next = newnode;)。
我们发现,即使链表是否为空,我们都需要新创建一个节点。所以我们专门分装一个专门创建一个节点的函数,并把这个节点的地址返回就好了。这样我们也方便以后头插等情况时候创建新节点。
还有一个点需要注意,请看这里:void SListPushBack(SLTNode pphead, SLTDateType x),我们在进行尾插的时候为什么要传二级指针过去呢?这的确是一个值得思考的问题。当我们想要进行尾插即SListPushBack(&plist, 1); SListPushBack(&plist, 2);的时候,如果我们不传plist的地址的话,那么在尾插函数(SListPushBack)内部pphead的改变是无法改变外部的plist的。所以我们就需要传plist的地址过去,此时我们也就需要二级指针来进行接收(因为plist本身就是一个指针)。
总之我们如果想改变plist的值的话,就需要将其地址传过去,否则形参就是实参的一份临时拷贝,形参的改变是无法改变实参的。
创建节点
SLTNode* BuyListNode(SLTDateType x)
{SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));//检查是否开辟成功if (newnode == NULL){printf("malloc fail\\n");//内存申请失败的话说明已经没有多少空间了exit(-1);//申请失败则直接结束程序}newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;return newnode;
}
尾删
void SlistPopBack(SLTNode** pphead)
{//温柔一点if (*pphead == NULL){return;}//粗暴一点//assert(*pphead != NULL);//走到这里意味着一定有一个节点if ((*pphead)->next == NULL){free(*pphead);*pphead = NULL;}else{SLTNode* prev = NULL;SLTNode* tail = *pphead;//while (tail->next != NULL)while (tail->next){prev = tail;tail = tail->next;}free(tail);tail = NULL;prev->next = NULL;}
}
进行尾删时总共三种情况:第一,链表为空;第二,链表只要一个节点;第三,链表有1个以上的节点。
这里我们来看一下最复杂的情况(第三种):当链表有一个以上的节点时,当我们尾删链表的最后一个节点时,我们还需要把最后一个链表的前一个链表的next置为空指针,否则其就变成了野指针。但是由于单链表是无法找到前一个节点的next指针的。所以我们定义一个prev,在tail往下走(即tail = tail->next;)之前先进行prev = tail;。另外tail置不置空无所谓,因为出了tail的作用域其就被销毁了。
头插
void SListPustFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDateType x)
{SLTNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);newnode->next = *pphead;*pphead = newnode;
}
头删
void SListPopFront(SLTNode** pphead)
{//空//一个节点//一个以上节点assert(pphead);//处理一个或者多个节点都可以,但是唯独不能处理节点为空/*if (*pphead == NULL){return;}*/assert(*pphead != NULL);//节点为空直接报错SLTNode* next = (*pphead)->next;free(*pphead);*pphead = next;//实际上我们可以把一个节点或者一个以上节点进行统一处理。
}
这里我们先明确一个问题,问题1:free()释放的是指针呢?还是释放的是内存呢?应该是这样的:free释放的是指针指向的内存。
问题2:内存泄漏是内存丢了还是指针丢了?应该是这样的:内存泄漏是指针丢了,我们直到如果指针在的话(可以找到)我们依然可以随时释放指针指向的空间;但是如果指针真的丢了(找不到了)那我们连哪些内存没有释放都不知道。内存是不会丢的,因为内存一直是在那个位置,free只是把这块空间的使用权还给系统,同时把这块空间置为随机值。
查找
查找返回的是一个指针。
SLTNode* SListFind(SLTNode* phead, SLTDateType x)
{SLTNode* cur = phead;while (cur){if (cur->data == x){return cur;}else{cur = cur->next;}}return NULL;//来到这里说明到最后都没有找到,返回空
}
在pos之前去插入
void SListInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDateType x)
{assert(pphead);assert(pos);SLTNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);if (*pphead == pos){//相当于头插了,可以调用其函数newnode->next = *pphead;*pphead = newnode;}else{//找到pos的前一个位置SLTNode* posPrev = *pphead;while (posPrev->next != pos){posPrev = posPrev->next;}posPrev->next = newnode;newnode->next = pos;}
}
在pos之后去插入
void SListInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, SLTDateType x)
{assert(pos);SLTNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);newnode->next = pos->next;pos->next = newnode;
}
注意:顺序不要颠倒()newnode->next = pos->next; pos->next = newnode;。
删除pos位置的值
void SListErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos)
{assert(pphead);assert(pos);if (*pphead == pos){//相当于头删/pphead = pos->next;free(pos);*/SListPopFront(pphead);}else{SLTNode* prev = *pphead;while (prev->next != pos){prev = prev->next;}prev->next = pos->next;free(pos);}
}
销毁链表
void SListDestory(SLTNode** pphead)//销毁链表
{assert(pphead);SLTNode* cur = *pphead;while (cur){SLTNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}*pphead = NULL;
}
总代码
test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"SList.h"void TestSList1()
{SLTNode* plist = NULL;SListPushBack(&plist, 1);SListPushBack(&plist, 2);SListPushBack(&plist, 3);SListPushBack(&plist, 4);SListPrint(plist);SListPushFront(&plist, 1);SListPushFront(&plist, 2);SListPushFront(&plist, 3);SListPushFront(&plist, 4);SListPrint(plist);}void TestSList2()
{SLTNode* plist = NULL;SListPushFront(&plist, 1);SListPushFront(&plist, 2);SListPushFront(&plist, 3);SListPushFront(&plist, 4);SlistPopBack(&plist);SListPrint(plist);}void TestSList3()//测试头删
{SLTNode* plist = NULL;SListPushFront(&plist, 1);SListPushFront(&plist, 2);SListPushFront(&plist, 3);SListPushFront(&plist, 4);SListPopFront(&plist);SListPrint(plist);SListPopFront(&plist);SListPrint(plist);SListPrint(plist);SListPopFront(&plist);SListPrint(plist);
}void TestSList4()//测试查找
{SLTNode* plist = NULL;SListPushFront(&plist, 1);SListPushFront(&plist, 2);SListPushFront(&plist, 3);SListPushFront(&plist, 2);SListPushFront(&plist, 4);SListPushFront(&plist, 2);SListPushFront(&plist, 2);SListPushFront(&plist, 4);SListPrint(plist);//找SLTNode* pos = SListFind(plist, 2);int i = 1;while (pos){printf("第%d个pos节点:%p->%d\\n", i++, pos, pos->data);pos = SListFind(pos->next, 2);}//修改3->30pos = SListFind(plist, 3);if (pos){pos->data = 30;}SListPrint(plist);
}void TestSList5()//测试查找
{SLTNode* plist = NULL;SListPushFront(&plist, 1);SListPushFront(&plist, 2);SListPushFront(&plist, 3);SListPushFront(&plist, 4);SListPrint(plist);SLTNode* pos = SListFind(plist, 3);if (pos){SListInsert(&plist, pos, 30);}SListPrint(plist);pos = SListFind(plist, 1);if (pos){SListInsert(&plist, pos, 10);}SListPrint(plist);pos = SListFind(plist, 4);if (pos){SListInsert(&plist, pos, 40);}SListPrint(plist);}
TestSList6()
{SLTNode* plist = NULL;SListPushBack(&plist, 1);SListPushBack(&plist, 2);SListPushBack(&plist, 3);SListPushBack(&plist, 4);SListPrint(plist);SListDestory(&plist);//销毁链表}
int main()
{//TestSList1();//TestSList2();//TestSList3();//TestSList4();//TestSList5();TestSList6();return 0;
}
Slist.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include"SList.h"SLTNode* BuyListNode(SLTDateType x)
{SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));//检查是否开辟成功if (newnode == NULL){printf("malloc fail\\n");//内存申请失败的话说明已经没有多少空间了exit(-1);//申请失败则直接结束程序}newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;return newnode;
}void SListPrint(SLTNode* phead)
{SLTNode* cur = phead;while (cur != NULL){printf("%d->", cur->data);cur = cur->next;}printf("NULL\\n");
}//尾插
void SListPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDateType x)
{assert(pphead);SLTNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);//起初链表中是啥也没有的if (*pphead == NULL){*pphead = newnode;}else{//找到尾部=节点SLTNode* tail = *pphead;while (tail->next != NULL){tail = tail->next;}tail->next = newnode;}
}//头插
void SListPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDateType x)
{SLTNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);newnode->next = *pphead;*pphead = newnode;
}//头删
void SlistPopBack(SLTNode** pphead)
{//温柔一点if (*pphead == NULL){return;}//粗暴一点//assert(*pphead != NULL);//走到这里意味着一定有一个节点if ((*pphead)->next == NULL){free(*pphead);*pphead = NULL;}else{SLTNode* prev = NULL;SLTNode* tail = *pphead;//while (tail->next != NULL)while (tail->next){prev = tail;tail = tail->next;}free(tail);tail = NULL;prev->next = NULL;}
}void SListPopFront(SLTNode** pphead)
{//空//一个节点//一个以上节点assert(pphead);//处理一个或者多个节点都可以,但是唯独不能处理节点为空/*if (*pphead == NULL){return;}*/assert(*pphead != NULL);//节点为空直接报错SLTNode* next = (*pphead)->next;free(*pphead);*pphead = next;
}SLTNode* SListFind(SLTNode* phead, SLTDateType x)
{SLTNode* cur = phead;while (cur){if (cur->data == x){return cur;}else{cur = cur->next;}}return NULL;//来到这里说明到最后都没有找到,返回空
}//在pos位置之前去插入一个节点
void SListInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDateType x)
{assert(pphead);assert(pos);SLTNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);if (*pphead == pos){//相当于头插了,可以调用其函数newnode->next = *pphead;*pphead = newnode;}else{//找到pos的前一个位置SLTNode* posPrev = *pphead;while (posPrev->next != pos){posPrev = posPrev->next;}posPrev->next = newnode;newnode->next = pos;}
}//在pos之后去插入,更合适,也更简单
void SListInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, SLTDateType x)
{assert(pos);SLTNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);newnode->next = pos->next;pos->next = newnode;
}void SListErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos)
{assert(pphead);assert(pos);if (*pphead == pos){//相当于头删/pphead = pos->next;free(pos);*/SListPopFront(pphead);}else{SLTNode* prev = *pphead;while (prev->next != pos){prev = prev->next;}prev->next = pos->next;free(pos);}
}//删除后一个
void SListEraseAfter(SLTNode* pos)
{assert(pos);assert(pos->next);//报错就说明你用错来SLTNode* next = pos->next;pos->next = next->next;free(next);//next = NULL;//置不置空没有意义
}void SListDestory(SLTNode** pphead)//销毁链表
{assert(pphead);SLTNode* cur = *pphead;while (cur){SLTNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}*pphead = NULL;
}
Slist.h
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>typedef int SLTDateType;typedef struct SListNode
{SLTDateType data;//data就是我们要存储的数据struct SListNode* next;
}SLTNode;void SListPrint(SLTNode* phead);void SListPushBack(SLTNode** pphead,SLTDateType x);void SListPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDateType x);void SListPopBack(SLTNode** pphead);void SListPopFront(SLTNode** pphead);SLTNode* SListFind(SLTNode* phead, SLTDateType x);//查找//在pos位置之前去插入一个节点
void SListInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDateType x);//某个位置插入
//void SListInsert(SLTNode* phead, int pos, SLTDateType x);//某个位置插入void SListInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, SLTDateType x);void SListErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos);
//void SListErase(SLTNode phead, int pos);void SListEraseAfter( SLTNode* pos);void SListDestory(SLTNode** pphead);//销毁链表
以上就是单链表的基本操作,就到这里吧,再见啦!!!




