Servlet的详细使用

文章目录
- Servlet体系结构
- Servlet urlPattern配置
- Request和Response介绍
-
- Request
-
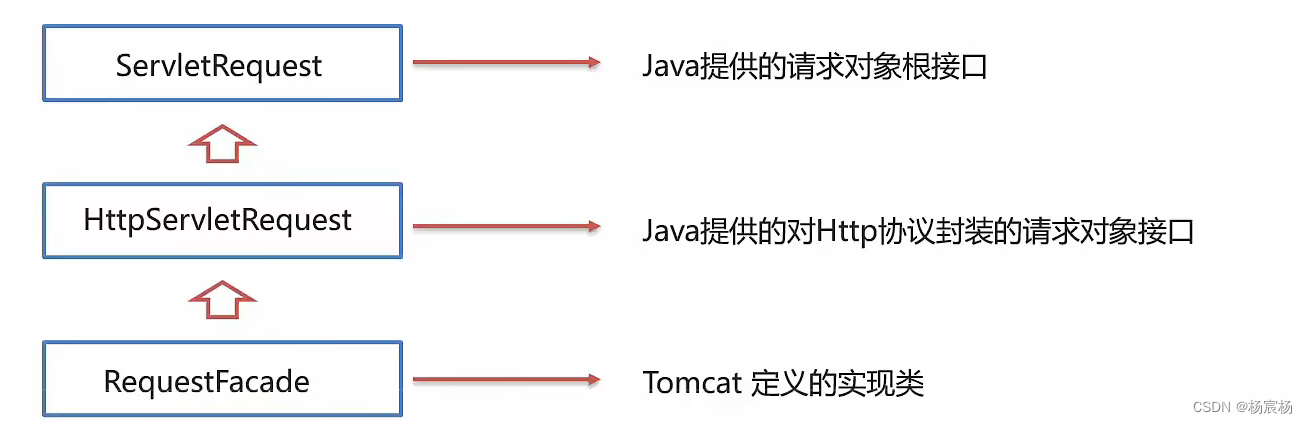
- Request继承体系
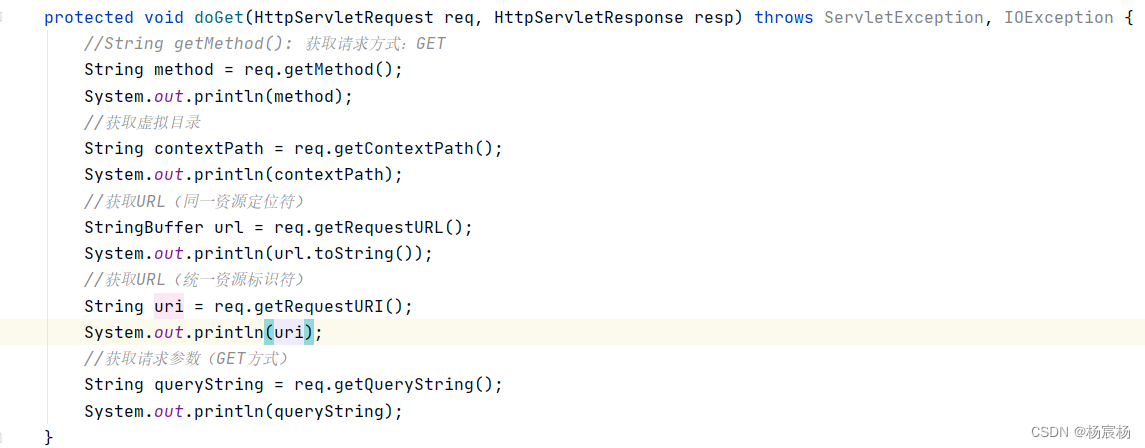
- Request获取请求数据
- Request通用方式获取请求参数
- 请求参数中文乱码--post解决方案
- 请求参数中文乱码--get解决方案
- Request请求转发
- 请求转发间共享数据
- Response
-
- Response设置响应数据功能&完成重定向
- Response 响应字符数据
- Response 响应字节数据
Servlet体系结构
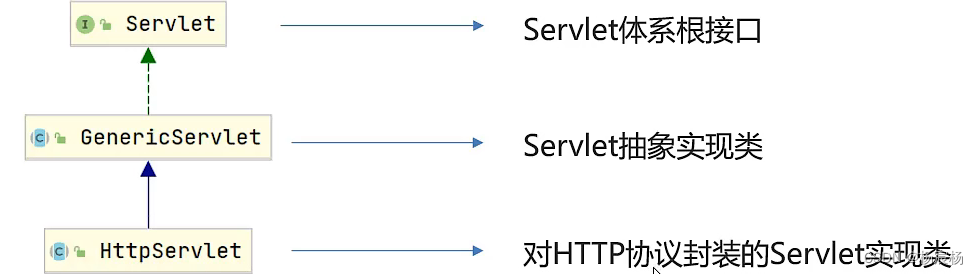
我们将来开发B/S架构的web项目,都是针对HTTP协议,所以我们自定义Servlet,会继承HttpServlet
@WebServlet("/demo4")public class ServletDemo2 extends HttpServlet {@Overrideprotected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {System.out.println("get......");}@Overrideprotected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {System.out.println("post......");}}
运行之后我们访问请求路径,从代码可以看出我们这个Servlet里面有两个方法,一个doGet()和doPost()方法,当我们直接输入访问路径,默认的是执行get方法
运行结果:
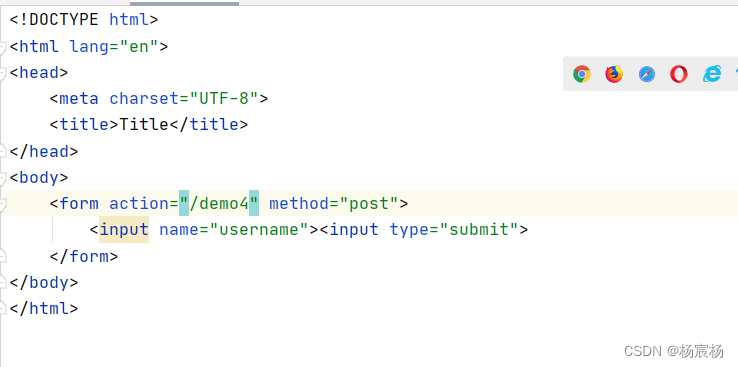
对于post请求来说,我们得写一个表单来请求当前Servlet资源
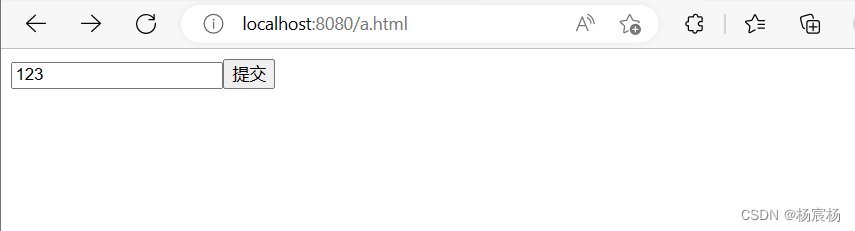
运行结果:
1)页面跳转
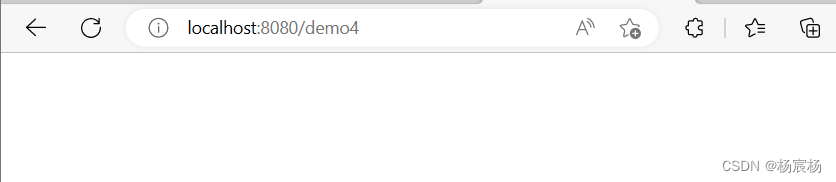
2)
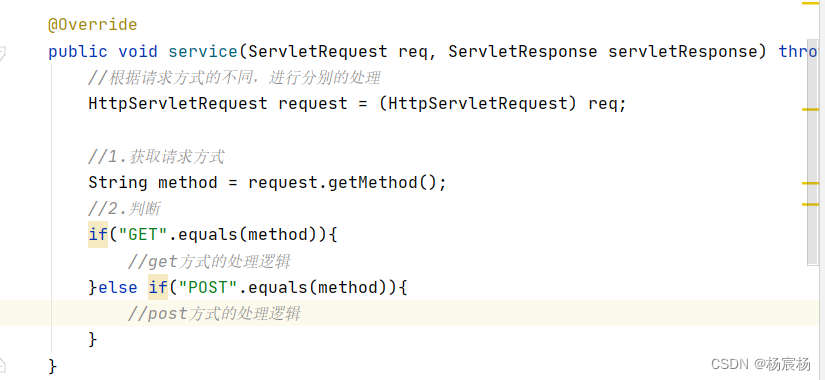
HttpServlet中为什么要根据请求方式的不同,调用不同方法?
post和get请求参数的位置不一样,post请求参数的位置在请求体里面,get请求参数在请求行里面,当我们继承Servlet接口里面,需要根据请求的方式不同,来进行分别的处理,需要在service方法里面先获取请求方式
Servlet urlPattern配置
Servlet想要被访问,必须配置其访问路径(urlPattern)
1.一个Servlet,可以配置多个urlPattern
WebServlet(urlPatterns = {"/demo4","/demo5"})public class ServletDemo4 extends HttpServlet {@Overrideprotected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {System.out.println("demo4 get......");}}
2.urlPattern配置规则
1)精确匹配
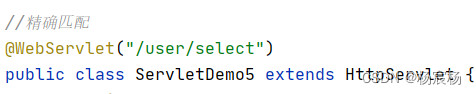
2)目录匹配
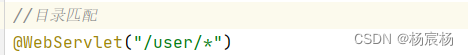
*
注意:当一个路径同时满足精确匹配和目录匹配的时候,精确匹配的优先级大于目录匹配*
3)扩展名匹配
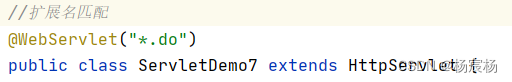
4)任意匹配
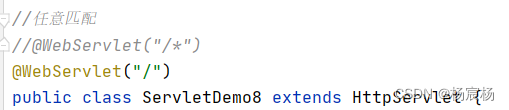
/*的优先级高于/
/和/的区别
当我们项目中的Servlet配置了“/”会覆盖掉tomcat中的DefaultServlet,当其他的url-pattern都匹配不上时都会走这个Servlet
当我们的项目中配置了“/”,意味着匹配任意访问路径
配置任意访问路径会导致我们的任意访问资源无法使用,所以一般不要去配置它
优先级:精确路径>目录路径>扩展名路径>/>/
Request和Response介绍
Request:获取请求数据
Response:设置响应数据
示例代码:
@WebServlet("/demo2")public class ServletDemo2 extends HttpServlet {@Overrideprotected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {System.out.println("get......");}@Overrideprotected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {//使用request对象,获取请求数据String name = req.getParameter("name");//使用response对象,设置响应数据resp.setHeader("content-type","text/html;charaset=utf-8");resp.getWriter().write("<h1>"+name+",欢迎您!</h1>");System.out.println("post......");}}
Request
Request继承体系
Request获取请求数据
请求数据分为3部分:
1.请求行:
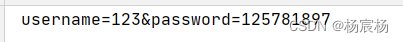
2.请求体:

字符输入流:一般用于文本的情况下
字节输入流:一般用于文件和图片的情况下
示例代码:
第一步:创建表单
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title></head><body><form action="/req1" method="post"><input type="text" name="username"><input type="password" name="password"><input type="submit"></form></body>
</html>
第二步:编写dopost请求
@Overrideprotected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {//获取post 请求体:请求参数//1.获取字符输入流BufferedReader br = req.getReader();//2.读取数据String line = br.readLine();System.out.println(line);}
运行结果:
3.请求头:

Request通用方式获取请求参数
GET请求方式和POST请求方式 区别主要在于获取请求参数的方式不一样,可以提供一种获取请求参数的方式,从而同一doGet和doPost方法
假设我们现在按原来的方法接收到了数据,但是数据时一条长长的字符串,我们还要拆分,这样是不是,有些麻烦
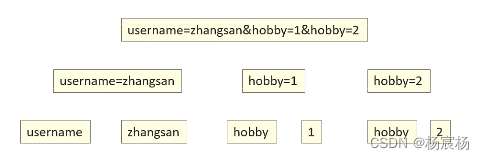
于是request就很贴心的为我们提供了一种方法

示例代码:
@Overrideprotected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {//GET请求限制System.out.println("get....");//1.获取所有参数的Map集合Map<String,String[]> map = req.getParameterMap();for(String key:map.keySet()){System.out.print(key+":");//获取值String[] values = map.get(key);for (String value:values){System.out.print(value+" ");}System.out.println();}//根据key获取参数值,数组String[] hobbies = req.getParameterValues("hobby");for(String hobby:hobbies){System.out.println(hobby);}//根据key,获取单个参数值String username = req.getParameter("username");String password = req.getParameter("password");System.out.println(username);System.out.println(password);}
同样的方法也能在doPost里面,我们完全可以在post请求里面填写一句this.doGet(req,resp);
请求参数中文乱码–post解决方案
当我们从表单post发送请求提交表单后的时候,request接收数据会乱码

(tomcat8及以后的版本,get方式不会乱码,post方式会乱码)
原因:post底层是通过getReader获取一个字符输入流,通过流的方式读取信息,该流的编码形式不是utf-8,但页面是utf-8的
解决方案:在请求里设置字符输入流的编码为UTF-8
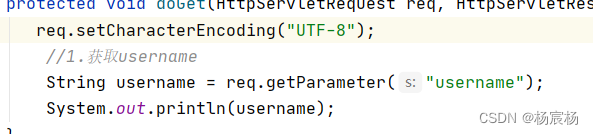
请求参数中文乱码–get解决方案
get请求方式乱码不能用post乱码方式解决
乱码原因:
编码和解码不一致
拿一个代码举例
public class URLDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {String username = "张三";//1.URL编码String encode = URLEncoder.encode(username, "utf-8");System.out.println(encode);//URL解码String decode = URLDecoder.decode(encode,"gbk");System.out.println(decode);}
}
运行结果:
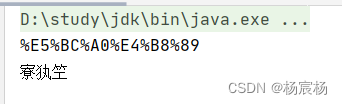
*
由此可以看出因为编码和解码的不一致,导致我们运行结果不是我们想看到的
解决办法:
因为tomcat底层的方法是写死的,我们没有办法改变,但是我们可以想到它两个数据间的字节是一样的(二进制),我们可以把乱码数据转成二进制数据,再把二进制字节数据变成我们想要的数据*
public class URLDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {String username = "张三";//1.URL编码String encode = URLEncoder.encode(username, "utf-8");System.out.println(encode);//URL解码String decode = URLDecoder.decode(encode,"ISO-8859-1");System.out.println(decode);//3.转为字节数据byte[] bytes = decode.getBytes("ISO-8859-1");for(byte b:bytes){System.out.print(b+" ");}System.out.println();//4.将字节数组转为字符串String s = new String(bytes, "utf-8");System.out.println(s);}
}
运行结果:
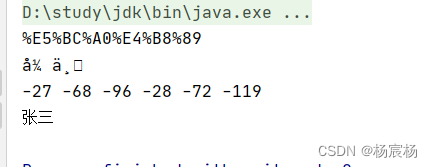
Request请求转发
服务器内部资源跳转方式
示例代码
假设我们在执行req4请求的时候要跳转到req5上
@WebServlet("/req4")public class RequestDemo4 extends HttpServlet {@Overrideprotected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {this.doGet(req,resp);}@Overrideprotected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {System.out.println("demo4...");//请求代码req.getRequestDispatcher("/req5").forward(req,resp);}}
@WebServlet("/req5")public class RequestDemo5 extends HttpServlet {@Overrideprotected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {this.doGet(req,resp);}@Overrideprotected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {System.out.println("demo5...");}}
运行结果:

请求转发间共享数据

请求转发特点:
1.浏览器地址栏路径不发生变化
2.只能转发到当前服务器的内部资源
3.一次请求,可以在转发的资源间使用request共享数据
Response
Response设置响应数据功能&完成重定向
响应数据分为3部分:
1.响应行
2.响应头
3.响应体
什么是重定向?
一种资源跳转方式
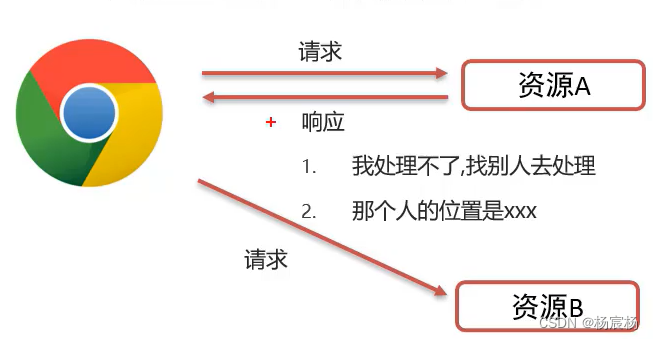
示例代码:
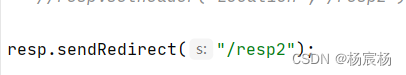
@WebServlet("/resp1")public class ResponseDemo1 extends HttpServlet {@Overrideprotected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {System.out.println("resp1.....");//重定向//1.设置响应状态码resp.setStatus(302);//2.设置响应头 locationresp.setHeader("Location","/resp2");}@Overrideprotected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {this.doPost(req,resp);}}
@WebServlet("/resp2")public class ResponseDemo2 extends HttpServlet {@Overrideprotected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {this.doGet(req,resp);}@Overrideprotected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {System.out.println("resp2.....");}}
重定向简化方法:
重定向特点:
1.浏览器地址栏路径发生变化
2.可以重定向到任意位置的资源(服务器内部,外部均可)
3.两次请求,不能在多个资源中使用request共享数据
路径问题
什么时候路径需要加虚拟目录?
首先你得明确这个路径给谁使用,如果是给浏览器使用,需要加虚拟目录,如果是给服务器使用,不需要加虚拟目录。
例如:

Response 响应字符数据
示例代码:
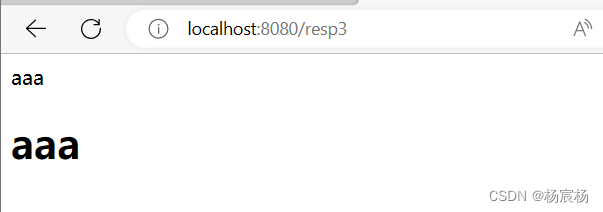
@WebServlet("/resp3")
public class ResponseDemo3 extends HttpServlet {@Overrideprotected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {this.doGet(req,resp);}@Overrideprotected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {//1.获取字符输出流PrintWriter writer = resp.getWriter();//content-typeresp.setHeader("content-type","text/html");writer.write("aaa");writer.write("<h1>aaa</h1>");}
}
运行结果:
1.writer流不要关闭,因为这个流是随着response对象获取出来的,等这次请求响应完毕后,response对象会被销毁,销毁的时候,writer也会被关闭
2.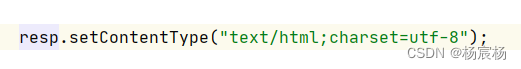
这样的话就可以响应中文了
Response 响应字节数据
示例代码:
@WebServlet("/resp4")public class ResponseDemo4 extends HttpServlet {@Overrideprotected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {this.doGet(req,resp);}@Overrideprotected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {//1.读取文件FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("C://Users//Administrator//Desktop//1.jpg");//2.获取response字节输出流ServletOutputStream os = resp.getOutputStream();//完成流的copybyte[] buff = new byte[1024];int len = 0;while((len=fis.read(buff))!=-1){os.write(buff,0,len);}fis.close();}}
