Netty核心源码分析(一),Netty的Server端启动过程源码分析

文章目录
- 系列文章目录
- 一、Netty的Server端启动过程源码分析
-
- 1、NioEventLoopGroup的创建
-
- (1)构造方法
- 2、ServerBootstrap的创建
-
- (1)构造方法
- (2)group方法
- (3)channel方法
- (4)option方法
- (5)handler方法
- (6)childHandler方法
- (7)bind方法
- (8)bind方法中——initAndRegister方法
- (9)bind方法中——initAndRegister方法中Channel创建逻辑
- (10)bind方法中——initAndRegister方法中init方法
- (11)Pipeline的addLast方法
- (13)bind方法中——dobind0方法
- 3、启动完毕的事件循环
系列文章目录
Netty核心源码分析(一),Netty的Server端启动过程源码分析
一、Netty的Server端启动过程源码分析
1、NioEventLoopGroup的创建
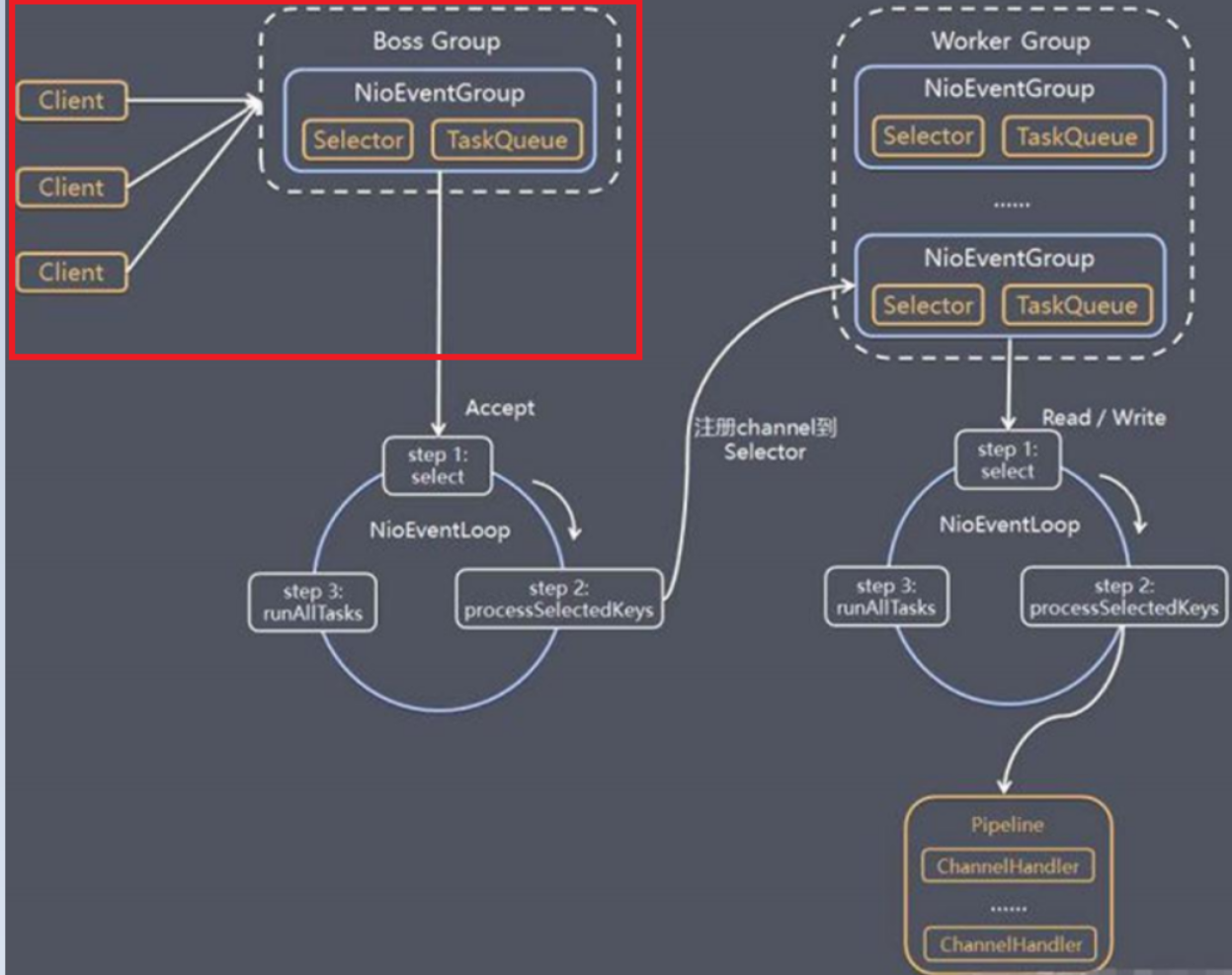
Server端会创建两个EventLoopGroup,我们一般使用NioEventLoopGroup:
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
这两个EventLoopGroup是整个Netty的核心对象。boosGroup用于接收Tcp请求,他会将请求交给workerGroup,workerGroup会获取真正的连接,然后和连接进行通信,比如读写解码编码等操作。
EventLoopGroup 是事件循环组(线程组),内涵多个EventLoop,可以注册channel,用于在事件循环中进行选择(和select相关)。
(1)构造方法
在NioEventLoopGroup的构造方法中,如果不传参的话,默认创建cpu核心数*2个线程:
// io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup#NioEventLoopGroup()
public NioEventLoopGroup() {this(0);
}
// ... 一直往上追
// io.netty.channel.MultithreadEventLoopGroup#MultithreadEventLoopGroup(int, java.util.concurrent.Executor, java.lang.Object...)
protected MultithreadEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor, Object... args) {super(nThreads == 0 ? DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS : nThreads, executor, args);
}
我们发现在父类中,如果nThreads传参为0,就会赋值为DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS :
// MultithreadEventLoopGroup静态代码块
private static final int DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS;static {DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS = Math.max(1, SystemPropertyUtil.getInt("io.netty.eventLoopThreads", NettyRuntime.availableProcessors() * 2)); // 获取cpu核心数 * 2if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("-Dio.netty.eventLoopThreads: {}", DEFAULT_EVENT_LOOP_THREADS);}
}
最终是获取了CPU核心数 * 2,并创建这些线程,我本机CPU是20核,所以创建了40个workerGroup线程。
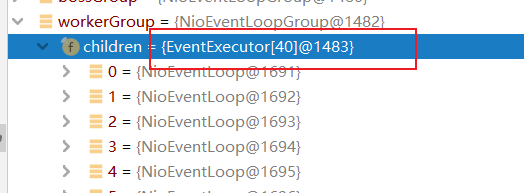
我们在这个构造方法继续往上追:
// nThreads表示使用的线程数
// executor表示执行器如果为null就采用Netty默认的线程工厂和默认的执行器ThreadPerTaskExecutor
// chooserFactory是上一步传入的DefaultEventExecutorChooserFactory
// args表示在创建执行器时传入的固定参数
// io.netty.util.concurrent.MultithreadEventExecutorGroup#MultithreadEventExecutorGroup(int, java.util.concurrent.Executor, io.netty.util.concurrent.EventExecutorChooserFactory, java.lang.Object...)
protected MultithreadEventExecutorGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor,EventExecutorChooserFactory chooserFactory, Object... args) {if (nThreads <= 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("nThreads: %d (expected: > 0)", nThreads));}if (executor == null) { // 为空的话,会创建默认的执行器executor = new ThreadPerTaskExecutor(newDefaultThreadFactory());}// 创建指定线程数的执行器数组children = new EventExecutor[nThreads]; // 40// 初始化线程数组for (int i = 0; i < nThreads; i ++) {boolean success = false;try {// 创建NioEventLoopchildren[i] = newChild(executor, args);success = true;} catch (Exception e) {// TODO: Think about if this is a good exception typethrow new IllegalStateException("failed to create a child event loop", e);} finally {if (!success) {// 如果启动失败,会关闭线程并且停止EventExecutor ,优雅关闭for (int j = 0; j < i; j ++) {children[j].shutdownGracefully();}for (int j = 0; j < i; j ++) {EventExecutor e = children[j];try {while (!e.isTerminated()) {e.awaitTermination(Integer.MAX_VALUE, TimeUnit.SECONDS);}} catch (InterruptedException interrupted) {// Let the caller handle the interruption.Thread.currentThread().interrupt();break;}}}}}chooser = chooserFactory.newChooser(children);final FutureListener<Object> terminationListener = new FutureListener<Object>() {@Overridepublic void operationComplete(Future<Object> future) throws Exception {if (terminatedChildren.incrementAndGet() == children.length) {terminationFuture.setSuccess(null);}}};for (EventExecutor e: children) {// 每个EventExecutor添加监听器e.terminationFuture().addListener(terminationListener);}// 将所有单例线程池添加到HashSet中Set<EventExecutor> childrenSet = new LinkedHashSet<EventExecutor>(children.length);Collections.addAll(childrenSet, children);readonlyChildren = Collections.unmodifiableSet(childrenSet);
}
此时我们知道了,在NioEventLoopGroup的children中,就是包含着这些EventExecutor,而我们默认的就是使用NioEventLoop,
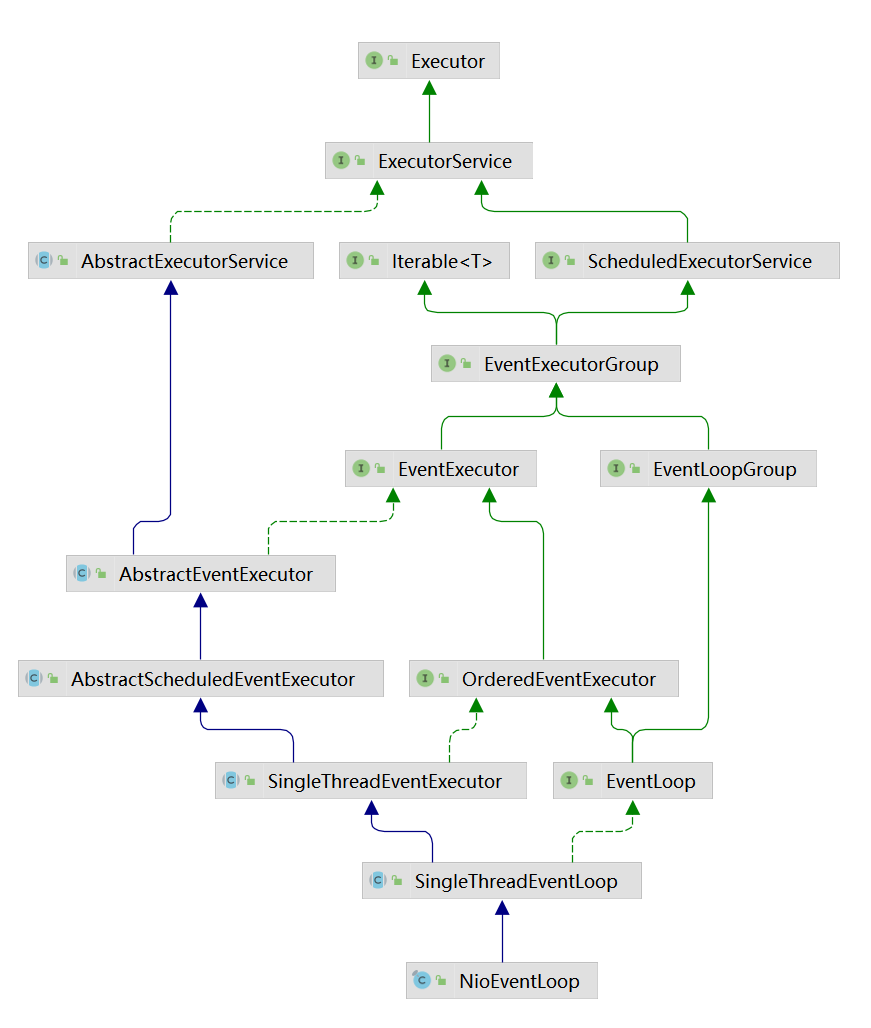
NioEventLoop的父类SingleThreadEventLoop,包含着很多子类:
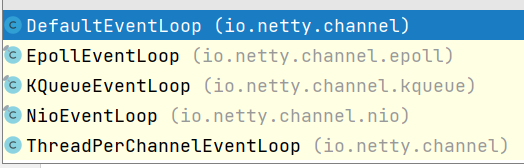
而在我们定义的new NioEventLoopGroup()中,就相当于已经定义好了该实现,通常我们使用NioEventLoop或者EpollEventLoop(linux需支持epoll,提高性能)。
2、ServerBootstrap的创建
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class).option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 100).handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO)).childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {@Overridepublic void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {ChannelPipeline p = ch.pipeline();if (sslCtx != null) {p.addLast(sslCtx.newHandler(ch.alloc()));}p.addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO));//p.addLast(new EchoServerHandler());}});
(1)构造方法
创建的ServerBootstrap是一个引导类,用于启动服务器和引导整个程序的初始化,它和ServerChannel关联,而ServerChannel继承了Channel。
ServerBootstrap包含着ChannelHandler信息以及EventLoopGroup等信息:
public class ServerBootstrap extends AbstractBootstrap<ServerBootstrap, ServerChannel> {private static final InternalLogger logger = InternalLoggerFactory.getInstance(ServerBootstrap.class);private final Map<ChannelOption<?>, Object> childOptions = new LinkedHashMap<ChannelOption<?>, Object>();private final Map<AttributeKey<?>, Object> childAttrs = new LinkedHashMap<AttributeKey<?>, Object>();private final ServerBootstrapConfig config = new ServerBootstrapConfig(this);private volatile EventLoopGroup childGroup;private volatile ChannelHandler childHandler;public ServerBootstrap() { }private ServerBootstrap(ServerBootstrap bootstrap) {super(bootstrap);childGroup = bootstrap.childGroup;childHandler = bootstrap.childHandler;synchronized (bootstrap.childOptions) {childOptions.putAll(bootstrap.childOptions);}synchronized (bootstrap.childAttrs) {childAttrs.putAll(bootstrap.childAttrs);}}
ServerBootstrap的父类还额外包含一些address等信息:
public abstract class AbstractBootstrap<B extends AbstractBootstrap<B, C>, C extends Channel> implements Cloneable {volatile EventLoopGroup group;@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")private volatile ChannelFactory<? extends C> channelFactory;private volatile SocketAddress localAddress;private final Map<ChannelOption<?>, Object> options = new LinkedHashMap<ChannelOption<?>, Object>();private final Map<AttributeKey<?>, Object> attrs = new LinkedHashMap<AttributeKey<?>, Object>();private volatile ChannelHandler handler;AbstractBootstrap() {// Disallow extending from a different package.}AbstractBootstrap(AbstractBootstrap<B, C> bootstrap) {group = bootstrap.group;channelFactory = bootstrap.channelFactory;handler = bootstrap.handler;localAddress = bootstrap.localAddress;synchronized (bootstrap.options) {options.putAll(bootstrap.options);}synchronized (bootstrap.attrs) {attrs.putAll(bootstrap.attrs);}}
(2)group方法
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
将boosGroup和workerGroup传入参数中:
// io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap#group(io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup, io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup)
public ServerBootstrap group(EventLoopGroup parentGroup, EventLoopGroup childGroup) {super.group(parentGroup); // 将bossGroup放入父类AbstractBootstrapif (childGroup == null) {throw new NullPointerException("childGroup");}if (this.childGroup != null) {throw new IllegalStateException("childGroup set already");}this.childGroup = childGroup; // workerGroup放入ServerBootstrap 中return this;
}// io.netty.bootstrap.AbstractBootstrap#group(io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup)
public B group(EventLoopGroup group) {if (group == null) {throw new NullPointerException("group");}if (this.group != null) {throw new IllegalStateException("group set already");}this.group = group; // 将bossGroup放入AbstractBootstrapreturn self();
}我们发现,ServerBootstrap和其父类AbstractBootstrap对于EventLoopGroup似乎有着层级关系,其中bossGroup放入了父类中,workerGroup放入了子类。
(3)channel方法
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
添加了一个Channel的class对象,引导类将通过这个Class对象反射创建ChannelFactory
// io.netty.bootstrap.AbstractBootstrap#channel
public B channel(Class<? extends C> channelClass) {if (channelClass == null) {throw new NullPointerException("channelClass");}// 创建ReflectiveChannelFactoryreturn channelFactory(new ReflectiveChannelFactory<C>(channelClass));
}
在ReflectiveChannelFactory中,重写着newChannel方法,通过反射创建Channel:
// io.netty.channel.ReflectiveChannelFactory#newChannel
@Override
public T newChannel() {try {return clazz.getConstructor().newInstance();} catch (Throwable t) {throw new ChannelException("Unable to create Channel from class " + clazz, t);}
}
注意!Channel的创建在bind方法中,调用了ChannelFactory的newChannel方法。
(4)option方法
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 100)
设置一些配置选项:
// io.netty.bootstrap.AbstractBootstrap#option
public <T> B option(ChannelOption<T> option, T value) {if (option == null) {throw new NullPointerException("option");}if (value == null) {synchronized (options) {options.remove(option);}} else {synchronized (options) {options.put(option, value);}}return self();
}
(5)handler方法
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))
添加一些服务请求专用的处理器:
// io.netty.bootstrap.AbstractBootstrap#handler(io.netty.channel.ChannelHandler)
public B handler(ChannelHandler handler) {if (handler == null) {throw new NullPointerException("handler");}this.handler = handler;return self();
}
实际上handler方法中传入的Handler,是交给boosGroup处理的Handler,因为handler方法是ServerBootstrap的父类AbstractBootstrap中的。
(6)childHandler方法
// io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap#childHandler(io.netty.channel.ChannelHandler)
public ServerBootstrap childHandler(ChannelHandler childHandler) {if (childHandler == null) {throw new NullPointerException("childHandler");}this.childHandler = childHandler;return this;
}
添加workerGroup的处理类,该方法是ServerBootstrap的,添加的handler也是为workerGroup服务的。
(7)bind方法
ChannelFuture f = b.bind(PORT).sync();
绑定端口并进行阻塞,bind方法执行成功之后,server端就算启动成功了。
// io.netty.bootstrap.AbstractBootstrap#bind(int)
public ChannelFuture bind(int inetPort) {return bind(new InetSocketAddress(inetPort));
}
// io.netty.bootstrap.AbstractBootstrap#bind(java.net.SocketAddress)
public ChannelFuture bind(SocketAddress localAddress) {validate();if (localAddress == null) {throw new NullPointerException("localAddress");}return doBind(localAddress);
}// io.netty.bootstrap.AbstractBootstrap#doBind
private ChannelFuture doBind(final SocketAddress localAddress) {// 初始化和注册,Channel的创建和初始化pipeline就是在这做的final ChannelFuture regFuture = initAndRegister();final Channel channel = regFuture.channel();if (regFuture.cause() != null) {return regFuture;}if (regFuture.isDone()) {// At this point we know that the registration was complete and successful.ChannelPromise promise = channel.newPromise();// 完成对端口的绑定doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);return promise;} else {// Registration future is almost always fulfilled already, but just in case it's not.final PendingRegistrationPromise promise = new PendingRegistrationPromise(channel);regFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {@Overridepublic void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {Throwable cause = future.cause();if (cause != null) {// Registration on the EventLoop failed so fail the ChannelPromise directly to not cause an// IllegalStateException once we try to access the EventLoop of the Channel.promise.setFailure(cause);} else {// Registration was successful, so set the correct executor to use.// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2586promise.registered();doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);}}});return promise;}
}
(8)bind方法中——initAndRegister方法
// io.netty.bootstrap.AbstractBootstrap#initAndRegister
final ChannelFuture initAndRegister() {Channel channel = null;try {// 真正创建Channel的方法,ServerBootstrap的channel方法传入的class,在此处通过工厂进行了实例化channel = channelFactory.newChannel();init(channel);} catch (Throwable t) {if (channel != null) {// channel can be null if newChannel crashed (eg SocketException("too many open files"))channel.unsafe().closeForcibly();// as the Channel is not registered yet we need to force the usage of the GlobalEventExecutorreturn new DefaultChannelPromise(channel, GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE).setFailure(t);}// as the Channel is not registered yet we need to force the usage of the GlobalEventExecutorreturn new DefaultChannelPromise(new FailedChannel(), GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE).setFailure(t);}ChannelFuture regFuture = config().group().register(channel);if (regFuture.cause() != null) {if (channel.isRegistered()) {channel.close();} else {channel.unsafe().closeForcibly();}}// If we are here and the promise is not failed, it's one of the following cases:// 1) If we attempted registration from the event loop, the registration has been completed at this point.// i.e. It's safe to attempt bind() or connect() now because the channel has been registered.// 2) If we attempted registration from the other thread, the registration request has been successfully// added to the event loop's task queue for later execution.// i.e. It's safe to attempt bind() or connect() now:// because bind() or connect() will be executed *after* the scheduled registration task is executed// because register(), bind(), and connect() are all bound to the same thread.return regFuture;
}
(9)bind方法中——initAndRegister方法中Channel创建逻辑
在initAndRegister调用了channelFactory.newChannel();之后,实际是调用了ReflectiveChannelFactory中,newChannel方法,通过反射创建Channel:
// io.netty.channel.ReflectiveChannelFactory#newChannel
@Override
public T newChannel() {try {return clazz.getConstructor().newInstance();} catch (Throwable t) {throw new ChannelException("Unable to create Channel from class " + clazz, t);}
}
NioServerSocketChannel的构造方法,做了许多NioServerSocketChannel的初始化工作:
private static ServerSocketChannel newSocket(SelectorProvider provider) {try {/* Use the {@link SelectorProvider} to open {@link SocketChannel} and so remove condition in* {@link SelectorProvider#provider()} which is called by each ServerSocketChannel.open() otherwise. See <a href="https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2308">#2308</a>.*/return provider.openServerSocketChannel();} catch (IOException e) {throw new ChannelException("Failed to open a server socket.", e);}
}/* Create a new instance*/
public NioServerSocketChannel() {this(newSocket(DEFAULT_SELECTOR_PROVIDER));
}
(1) 通过 NIO 的 SelectorProvider 的 openServerSocketChannel 方法得到JDK 的 channel。目的是让 Netty 包装 JDK 的 channel。
(2) 创建了一个唯一的 ChannelId,创建了一个 NioMessageUnsafe,用于操作消息,创建了个 DefaultChannelPipeline 管道,是个双向链表结构,用于过滤所有的进出的消息。
(3) 创建了一个 NioServerSocketChannelConfig 对象,用于对外展示一些配置。
(10)bind方法中——initAndRegister方法中init方法
init方法是在ServerBootstrap中实现的一个方法:
// io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap#init
@Override
void init(Channel channel) throws Exception {// 获取Options配置的属性final Map<ChannelOption<?>, Object> options = options0();synchronized (options) {// 线程不安全,LinkedHashMap,所以需要同步setChannelOptions(channel, options, logger);}final Map<AttributeKey<?>, Object> attrs = attrs0();synchronized (attrs) { // 处理attr属性for (Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object> e: attrs.entrySet()) {@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")AttributeKey<Object> key = (AttributeKey<Object>) e.getKey();channel.attr(key).set(e.getValue());}}// 处理pipelineChannelPipeline p = channel.pipeline();final EventLoopGroup currentChildGroup = childGroup;final ChannelHandler currentChildHandler = childHandler;final Entry<ChannelOption<?>, Object>[] currentChildOptions;final Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object>[] currentChildAttrs;synchronized (childOptions) {currentChildOptions = childOptions.entrySet().toArray(newOptionArray(childOptions.size()));}synchronized (childAttrs) {currentChildAttrs = childAttrs.entrySet().toArray(newAttrArray(childAttrs.size()));}p.addLast(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() {@Overridepublic void initChannel(final Channel ch) throws Exception {final ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();ChannelHandler handler = config.handler();if (handler != null) {pipeline.addLast(handler);}ch.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {pipeline.addLast(new ServerBootstrapAcceptor(ch, currentChildGroup, currentChildHandler, currentChildOptions, currentChildAttrs));}});}});
}
(11)Pipeline的addLast方法
Pipeline的addLast方法是核心。
// io.netty.channel.DefaultChannelPipeline#addLast(io.netty.util.concurrent.EventExecutorGroup, java.lang.String, io.netty.channel.ChannelHandler)
@Override
public final ChannelPipeline addLast(EventExecutorGroup group, String name, ChannelHandler handler) {final AbstractChannelHandlerContext newCtx;synchronized (this) {// 检查handler是否符合标准checkMultiplicity(handler);// 创建一个AbstractChannelHandlerContext 对象,该对象是ChannelHandler和ChannelPipeline之间的关联,每当有ChannelHandler添加到Pipeline中时,都会创建COntext。Context的主要功能是管理他所关联的Handler和同一个Pipeline中其他Handler之间的交互。newCtx = newContext(group, filterName(name, handler), handler);// 将newContext保存addLast0(newCtx);// If the registered is false it means that the channel was not registered on an eventloop yet.// In this case we add the context to the pipeline and add a task that will call// ChannelHandler.handlerAdded(...) once the channel is registered.if (!registered) {newCtx.setAddPending();callHandlerCallbackLater(newCtx, true);return this;}EventExecutor executor = newCtx.executor();if (!executor.inEventLoop()) {newCtx.setAddPending();executor.execute(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {callHandlerAdded0(newCtx);}});return this;}}callHandlerAdded0(newCtx);return this;
}
// io.netty.channel.DefaultChannelPipeline#addLast0
private void addLast0(AbstractChannelHandlerContext newCtx) {AbstractChannelHandlerContext prev = tail.prev;newCtx.prev = prev;newCtx.next = tail;prev.next = newCtx;tail.prev = newCtx;
}
我们可以看到,addLast方法并不是将Handler放到了最后,而是将我们自定义的Handler放到了tail的前一个,这样tail永远会在最后面,做一些系统的固定工作。
(13)bind方法中——dobind0方法
// io.netty.bootstrap.AbstractBootstrap#doBind0
private static void doBind0(final ChannelFuture regFuture, final Channel channel,final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {// This method is invoked before channelRegistered() is triggered. Give user handlers a chance to set up// the pipeline in its channelRegistered() implementation.channel.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {if (regFuture.isSuccess()) {// 调用channel的bind方法,因为此刻channel已经初始化完成了channel.bind(localAddress, promise).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE_ON_FAILURE);} else {promise.setFailure(regFuture.cause());}}});
}
channel.bind方法我们一步一步追溯:
// io.netty.channel.AbstractChannel#bind(java.net.SocketAddress, io.netty.channel.ChannelPromise)
@Override
public ChannelFuture bind(SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) {return pipeline.bind(localAddress, promise);
}
// io.netty.channel.DefaultChannelPipeline#bind(java.net.SocketAddress, io.netty.channel.ChannelPromise)
@Override
public final ChannelFuture bind(SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) {return tail.bind(localAddress, promise);
}
// io.netty.channel.AbstractChannelHandlerContext#bind(java.net.SocketAddress, io.netty.channel.ChannelPromise)
@Override
public ChannelFuture bind(final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {if (localAddress == null) {throw new NullPointerException("localAddress");}if (isNotValidPromise(promise, false)) {// cancelledreturn promise;}final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next = findContextOutbound();EventExecutor executor = next.executor();if (executor.inEventLoop()) {// 执行next.invokeBind(localAddress, promise);} else {safeExecute(executor, new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {next.invokeBind(localAddress, promise);}}, promise, null);}return promise;
}
// io.netty.channel.AbstractChannelHandlerContext#invokeBind
private void invokeBind(SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) {if (invokeHandler()) {try {// 执行((ChannelOutboundHandler) handler()).bind(this, localAddress, promise);} catch (Throwable t) {notifyOutboundHandlerException(t, promise);}} else {bind(localAddress, promise);}
}
// io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler#bind
@Override
public void bind(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {if (logger.isEnabled(internalLevel)) {logger.log(internalLevel, format(ctx, "BIND", localAddress));}ctx.bind(localAddress, promise);
}
//
@Override
public ChannelFuture bind(final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {if (localAddress == null) {throw new NullPointerException("localAddress");}if (isNotValidPromise(promise, false)) {// cancelledreturn promise;}final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next = findContextOutbound();EventExecutor executor = next.executor();if (executor.inEventLoop()) {// 执行next.invokeBind(localAddress, promise);} else {safeExecute(executor, new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {next.invokeBind(localAddress, promise);}}, promise, null);}return promise;
}
// io.netty.channel.AbstractChannelHandlerContext#invokeBind
private void invokeBind(SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) {if (invokeHandler()) {try {// 执行((ChannelOutboundHandler) handler()).bind(this, localAddress, promise);} catch (Throwable t) {notifyOutboundHandlerException(t, promise);}} else {bind(localAddress, promise);}
}
// io.netty.channel.DefaultChannelPipeline.HeadContext#bind
@Override
public void bind(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise)throws Exception {// unsafe.bindunsafe.bind(localAddress, promise);
}
// io.netty.channel.AbstractChannel.AbstractUnsafe#bind
@Override
public final void bind(final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {assertEventLoop();if (!promise.setUncancellable() || !ensureOpen(promise)) {return;}// See: https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/576if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(config().getOption(ChannelOption.SO_BROADCAST)) &&localAddress instanceof InetSocketAddress &&!((InetSocketAddress) localAddress).getAddress().isAnyLocalAddress() &&!PlatformDependent.isWindows() && !PlatformDependent.maybeSuperUser()) {// Warn a user about the fact that a non-root user can't receive a// broadcast packet on *nix if the socket is bound on non-wildcard address.logger.warn("A non-root user can't receive a broadcast packet if the socket " +"is not bound to a wildcard address; binding to a non-wildcard " +"address (" + localAddress + ") anyway as requested.");}boolean wasActive = isActive();try {// 关键方法doBind(localAddress);} catch (Throwable t) {safeSetFailure(promise, t);closeIfClosed();return;}if (!wasActive && isActive()) {invokeLater(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {pipeline.fireChannelActive();}});}safeSetSuccess(promise);
}
debug追了一大顿,终于来到了我们关键了!这里就是执行了NIO的channel的bind方法了:
// io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel#doBind
@Override
protected void doBind(SocketAddress localAddress) throws Exception {if (PlatformDependent.javaVersion() >= 7) {// 版本大于jdk7javaChannel().bind(localAddress, config.getBacklog());} else {// 版本小于jdk7javaChannel().socket().bind(localAddress, config.getBacklog());}
}
3、启动完毕的事件循环
bind方法执行完毕之后,此时debug一直下去的话,会最终进入到NioEventLoop的run方法中,这是一个死循环:
// io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop#run
@Override
protected void run() {for (;;) {try {switch (selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTasks())) {case SelectStrategy.CONTINUE:continue;case SelectStrategy.SELECT:select(wakenUp.getAndSet(false));// 'wakenUp.compareAndSet(false, true)' is always evaluated// before calling 'selector.wakeup()' to reduce the wake-up// overhead. (Selector.wakeup() is an expensive operation.)//// However, there is a race condition in this approach.// The race condition is triggered when 'wakenUp' is set to// true too early.//// 'wakenUp' is set to true too early if:// 1) Selector is waken up between 'wakenUp.set(false)' and// 'selector.select(...)'. (BAD)// 2) Selector is waken up between 'selector.select(...)' and// 'if (wakenUp.get()) { ... }'. (OK)//// In the first case, 'wakenUp' is set to true and the// following 'selector.select(...)' will wake up immediately.// Until 'wakenUp' is set to false again in the next round,// 'wakenUp.compareAndSet(false, true)' will fail, and therefore// any attempt to wake up the Selector will fail, too, causing// the following 'selector.select(...)' call to block// unnecessarily.//// To fix this problem, we wake up the selector again if wakenUp// is true immediately after selector.select(...).// It is inefficient in that it wakes up the selector for both// the first case (BAD - wake-up required) and the second case// (OK - no wake-up required).if (wakenUp.get()) {selector.wakeup();}// fall throughdefault:}cancelledKeys = 0;needsToSelectAgain = false;final int ioRatio = this.ioRatio;if (ioRatio == 100) {try {processSelectedKeys();} finally {// Ensure we always run tasks.runAllTasks();}} else {final long ioStartTime = System.nanoTime();try {processSelectedKeys();} finally {// Ensure we always run tasks.final long ioTime = System.nanoTime() - ioStartTime;runAllTasks(ioTime * (100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio);}}} catch (Throwable t) {handleLoopException(t);}// Always handle shutdown even if the loop processing threw an exception.try {if (isShuttingDown()) {closeAll();if (confirmShutdown()) {return;}}} catch (Throwable t) {handleLoopException(t);}}
}
此时,就开始接收事件,Netty算是正式启动了。
BoosGroup已经创建完毕并且启动完成,开始下面的Accept接收客户端请求的过程了。