【基础算法】栈和队列

系列综述:
💞目的:本系列是个人整理为了秋招算法的,整理期间苛求每个知识点,平衡理解简易度与深入程度。
🥰来源:材料主要源于代码随想录进行的,每个算法代码参考leetcode高赞回答和其他平台热门博客,其中也可能含有一些的个人思考。
🤭结语:如果有帮到你的地方,就点个赞和关注一下呗,谢谢🎈🎄🌷!!!
🌈【C++】秋招&实习面经汇总篇
文章目录
😊点此到文末惊喜↩︎
理论基础
基础知识
- 基本使用
queue<type> q; stack<type> s; // 共同函数 type x; sq.empty();// 返回堆栈是否为空的真假值 sq.push(x);// 向堆栈中压入元素x sq.pop();// 弹出堆栈顶元素 s.top();// 返回栈顶元素 q.front();// 返回堆顶元素 - 归纳法写程序
// 健壮性检查:判断函数参数是否符合基本要求
if(形参不符合) return false;
// 初始化:初始化工作变量,即符合要求的第一次循环条件
type var = nullptr/0;// 变量声明一定要初始化
// 循环条件一般是对于容器的遍历
while(!结束条件){doing();// 对结果序列操作的函数// 工作变量的迭代
}
// 收尾:对于递推末尾条件的处理
相关算法题目
232. 用栈实现队列
- 232. 用栈实现队列

class MyQueue { public:MyQueue() {}void push(int x) {s1.push(x);}int pop() {if(s2.empty()){while(!s1.empty()){s2.push(s1.top());s1.pop();}}int result = s2.top();s2.pop();return result;}int peek() {int res = this->pop(); // 直接使用已有的pop函数s2.push(res); // 因为pop函数弹出了元素res,所以再添加回去return res;}bool empty() {if(s1.empty() && s2.empty())return true;return false;}private:stack<int> s1;stack<int> s2; };
用队列实现栈
- 225. 用队列实现栈

class MyStack { public:queue<int> que;/ Initialize your data structure here. */MyStack() {}/ Push element x onto stack. */void push(int x) {que.push(x);}/ Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */int pop() {// 初始化int size = que.size();size--;// 循环while (size--) { // 将队列头部的元素(除了最后一个元素外) 重新添加到队列尾部que.push(que.front());que.pop();}// 收尾int result = que.front(); // 此时弹出的元素顺序就是栈的顺序了que.pop();return result;}/ Get the top element. */int top() {return que.back();}/ Returns whether the stack is empty. */bool empty() {return que.empty();} };
有效的括号
- 20. 有效的括号
- 将相反的东西统一
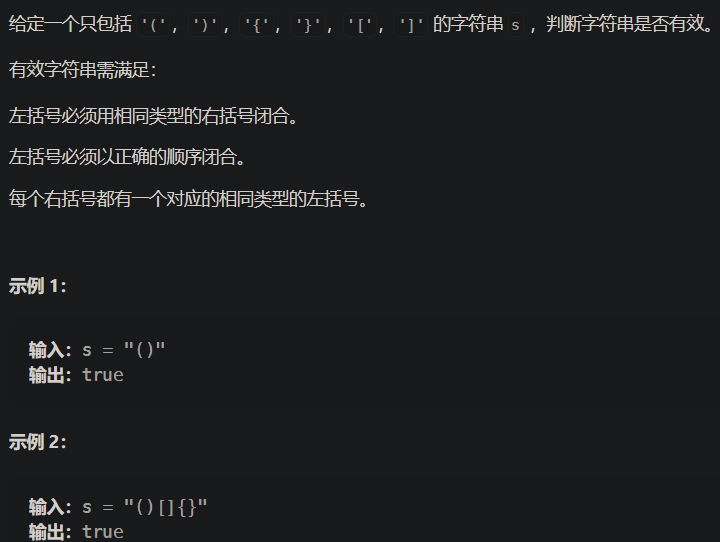
- 将相反的东西统一
bool isValid(string s) {// 健壮性检查if (s.size() % 2 != 0) return false; // 如果s的长度为奇数,一定不符合要求// 初始化stack<char> st;// 循环迭代for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {// 将相反的东西统一if (s[i] == '(') st.push(')');else if (s[i] == '{') st.push('}');else if (s[i] == '[') st.push(']');// 开始匹配:不同或者为空则false,相同则弹出else if (st.empty() || st.top() != s[i]) return false;else st.pop(); }return st.empty();}找出与子字符串匹配的主字符串中的字串个数
- 20. 有效的括号
- 定义同时必须要初始化
- 容器反转:
reverse (container.begin(), container.end()); - 栈中元素的遍历,先缓存st.top(),再st.pop()。
string removeDuplicates(string S) {stack<char> st;for (char s : S) {if (st.empty() || s != st.top()) {st.push(s);} else {st.pop();}}string result = "";// 定义同时必须初始化// 遍历栈中元素while (!st.empty()) { result += st.top();st.pop();}// 容器反转reverse (result.begin(), result.end());return result; }
150. 逆波兰表达式求值
-
150. 逆波兰表达式求值
- string类型转换成int类型:
atoi(str.c_str())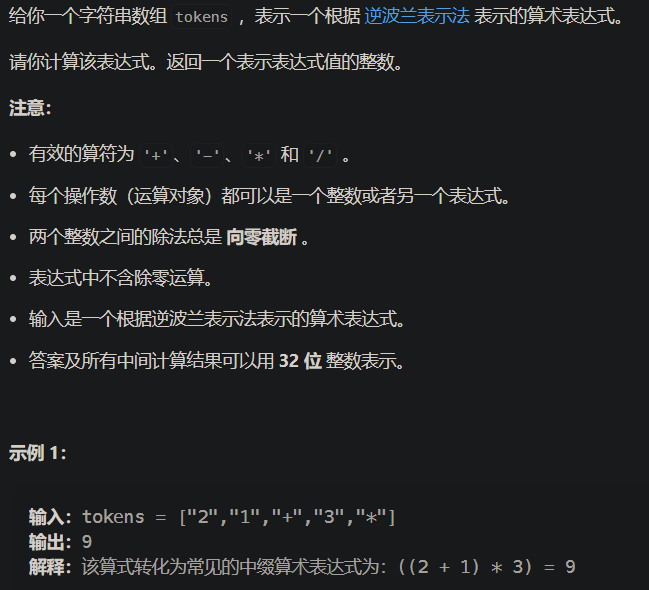
int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens) {stack<int> st;int n = 0;for(const auto &i : tokens){char c = i[0];if(c >='0' && c <= '9' || i.size() > 1){n = atoi(i.c_str());st.push(n);}else if(c == '+'){int a = st.top();st.pop();int b = st.top();st.pop();st.push(a+b);}else if(c == '-'){int a = st.top();st.pop();int b = st.top();st.pop();st.push(b-a);}else if(c == '*'){int a = st.top();st.pop();int b = st.top();st.pop();st.push(a*b);}else if(c == '/'){int a = st.top();st.pop();int b = st.top();st.pop();st.push(b/a);cout << a << " "<< b;}}return st.top(); } - string类型转换成int类型:
239. 滑动窗口最大值
- 239. 滑动窗口最大值
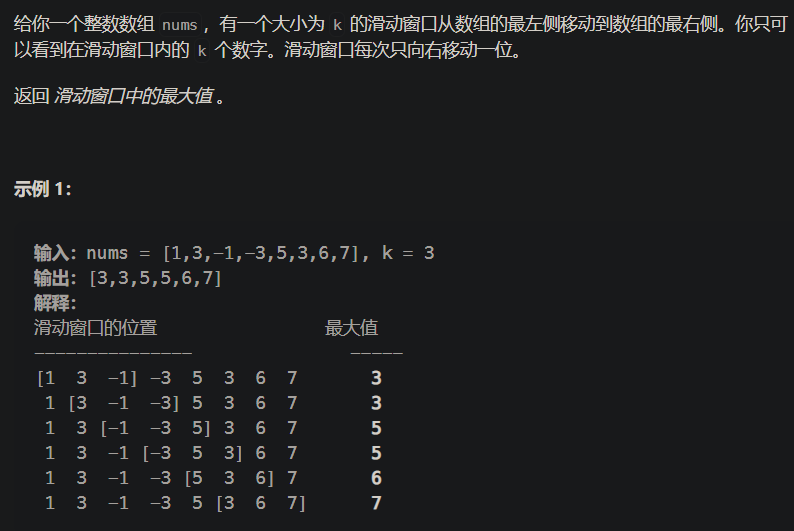
vector<int> maxSlidingWindow(vector<int>& nums, int k) {deque<int>q; //双端队列vector<int>res;for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){while(q.size() && i - k + 1 > q.front()) q.pop_front(); //判断队头是否在滑动窗口范围内while(q.size() && nums[i] >= nums[q.back()]) q.pop_back();//维护单调递减队列q.push_back(i); //将当前元素插入队尾if(i >= k - 1) res.push_back(nums[q.front()]); //滑动窗口的元素达到了k个,才可以将其加入答案数组中}return res; }
347. 前 K 个高频元素
- 347. 前 K 个高频元素
- 优先队列的使用
vector<int> topKFrequent(vector<int>& nums, int k) {//1.map记录元素出现的次数unordered_map<int,int>map;//两个int分别是元素和出现的次数for(auto& c:nums){map[c]++;}//2.利用优先队列,将出现次数排序//自定义优先队列的比较方式,小顶堆struct myComparison{bool operator()(pair<int,int>&p1,pair<int,int>&p2){return p1.second>p2.second;//小顶堆是大于号}};//创建优先队列priority_queue<pair<int,int>,vector<pair<int,int>>,myComparison> q;//遍历map中的元素//1.管他是啥,先入队列,队列会自己排序将他放在合适的位置//2.若队列元素个数超过k,则将栈顶元素出栈(栈顶元素一定是最小的那个)for(auto& a:map){q.push(a);if(q.size()>k){q.pop(); }}//将结果导出vector<int>res;while(!q.empty()){res.emplace_back(q.top().first);q.pop();}return res;}
少年,我观你骨骼清奇,颖悟绝伦,必成人中龙凤。 不如点赞·收藏·关注一波

🚩点此跳转到首行↩︎
参考博客
- leetcode二分查找
- 代码随想录
- 二分查找算法详解
- 待定引用
- 待定引用
- 待定引用
- 待定引用
- 待定引用


