Java基础(十八):java比较器、系统相关类、数学相关类
j.jpg)
Java基础系列文章
Java基础(一):语言概述
Java基础(二):原码、反码、补码及进制之间的运算
Java基础(三):数据类型与进制
Java基础(四):逻辑运算符和位运算符
Java基础(五):流程控制语句
Java基础(六):数组
Java基础(七):面向对象编程
Java基础(八):封装、继承、多态性
Java基础(九):Object 类的使用
Java基础(十):关键字static、代码块、关键字final
Java基础(十一):抽象类、接口、内部类
Java基础(十二):枚举类
Java基础(十三):注解(Annotation)
Java基础(十四):包装类
Java基础(十五):异常处理
Java基础(十六):String的常用API
Java基础(十七):日期时间API
Java基础(十八):java比较器、系统相关类、数学相关类
目录
- 一、Java比较器
-
- 1、自然排序:java.lang.Comparable
- 2、定制排序:java.util.Comparator
- 二、系统相关类
-
- 1、java.lang.System类
- 2、java.lang.Runtime类
- 三、数学相关的类
-
- 1、java.lang.Math
- 2、java.math.BigInteger
- 3、java.math.BigDecimal
- 4、java.util.Random(用于产生随机数)
一、Java比较器
1、自然排序:java.lang.Comparable
- Comparable接口强行对实现它的每个类的对象进行整体排序。这种排序被称为类的自然排序
- 实现
Comparable的类必须实现compareTo(Object obj)方法- 两个对象即通过 compareTo(Object obj) 方法的返回值来比较大小
- 如果当前对象this大于形参对象obj,则返回正整数
- 如果当前对象this小于形参对象obj,则返回负整数
- 如果当前对象this等于形参对象obj,则返回零
package java.lang;public interface Comparable{int compareTo(Object obj);
}
- 实现Comparable接口的对象列表(和数组)可以通过
Collections.sort或Arrays.sort进行自动排序 - Comparable 的典型实现:(
默认都是从小到大排列的)- String:按照字符串中字符的Unicode值进行比较
- Character:按照字符的Unicode值来进行比较
- 数值类型对应的包装类以及BigInteger、BigDecimal:按照它们对应的数值大小进行比较
- Boolean:true 对应的包装类实例大于 false 对应的包装类实例
- Date、Time等:后面的日期时间比前面的日期时间大
举例1:
@Test
public void test1() {String[] arr = new String[]{"Tom", "Jerry", "Tony", "Rose", "Jack", "Lucy"};Arrays.sort(arr);// 排序后,遍历for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {System.out.println(arr[i]);}
}
输出结果:
Jack
Jerry
Lucy
Rose
Tom
Tony
举例2:
public class Product implements Comparable { // 商品类private String name;// 商品名称private double price;// 价格public Product(String name, double price) {this.name = name;this.price = price;}public Product() {}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public double getPrice() {return price;}public void setPrice(double price) {this.price = price;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Product{" +"name='" + name + '\\'' +", price=" + price +'}';}// 比较的标准:先比较价格(从大到小),价格相同,进行名字的比较 (从小到大)@Overridepublic int compareTo(Object o) {if (o == this) {return 0;}if (o instanceof Product) {Product p = (Product) o;int value = Double.compare(this.price, p.price);if (value != 0) {return -value;}return this.name.compareTo(p.name);}// 手动抛出一个异常类的对象throw new RuntimeException("类型不匹配");}
}
- 排序
@Test
public void test2() {Product[] arr = new Product[5];arr[0] = new Product("HuaweiMate50pro", 6299);arr[1] = new Product("Xiaomi13pro", 4999);arr[2] = new Product("VivoX90pro", 5999);arr[3] = new Product("Iphone14ProMax", 9999);arr[4] = new Product("HonorMagic4", 6299);Arrays.sort(arr);// 排序后,遍历for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {System.out.println(arr[i]);}
}
- 对象比较大小
@Test
public void test3() {Product p1 = new Product("HuaweiMate50pro", 6299);Product p2 = new Product("VivoX90pro", 5999);int compare = p1.compareTo(p2);if (compare > 0) {System.out.println("p1大");} else if (compare < 0) {System.out.println("p2大");} else {System.out.println("p1和p2一样大");}
}
2、定制排序:java.util.Comparator
- 思考?
- 当元素的类型没有实现java.lang.Comparable接口而又不方便修改代码(例如:一些第三方的类,你只有.class文件,没有源文件)
- 如果一个类,实现了Comparable接口,也指定了两个对象的比较大小的规则,但是此时此刻我不想按照它预定义的方法比较大小,但是我又不能随意修改,因为会影响其他地方的使用,怎么办?
- JDK在设计类库之初,也考虑到这种情况,所以又增加了一个java.util.Comparator接口。强行对多个对象进行整体排序的比较
- 重写compare(Object o1,Object o2)方法,比较o1和o2的大小:如果方法返回正整数,则表示o1大于o2;如果返回0,表示相等;返回负整数,表示o1小于o2
- 可以将 Comparator 传递给 sort 方法(如 Collections.sort 或 Arrays.sort),从而允许在排序顺序上实现精确控制
package java.util;public interface Comparator{int compare(Object o1,Object o2);
}
举例1:
@Test
public void test1(){String[] arr = new String[]{"Tom","Jerry","Tony","Rose","Jack","Lucy"};Arrays.sort(arr,new Comparator(){@Overridepublic int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {if(o1 instanceof String && o2 instanceof String){String s1 =(String) o1;String s2 =(String) o2;return -s1.compareTo(s2);}throw new RuntimeException("类型不匹配");}});//排序后,遍历for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {System.out.println(arr[i]);}
}
举例2:
public class Product{ // 商品类private String name;// 商品名称private double price;// 价格public Product(String name, double price) {this.name = name;this.price = price;}public Product() {}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public double getPrice() {return price;}public void setPrice(double price) {this.price = price;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Product{" +"name='" + name + '\\'' +", price=" + price +'}';}
}
@Test
public void test2(){Product[] arr = new Product[5];arr[0] = new Product("HuaweiMate50pro",6299);arr[1] = new Product("Xiaomi13pro",4999);arr[2] = new Product("VivoX90pro",5999);arr[3] = new Product("Iphone14ProMax",9999);arr[4] = new Product("HonorMagic4",6299);//创建一个实现了Comparator接口的实现类的对象Comparator comparator = new Comparator(){//如果判断两个对象o1,o2的大小,其标准就是此方法的方法体要编写的逻辑。//比如:按照name从低到高排序@Overridepublic int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {if(o1 instanceof Product && o2 instanceof Product){Product p1 = (Product) o1;Product p2 = (Product) o2;return p1.getName().compareTo(p2.getName());}throw new RuntimeException("类型不匹配");}};Arrays.sort(arr,comparator1);//排序后,遍历for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {System.out.println(arr[i]);}
}
二、系统相关类
1、java.lang.System类
- System类代表系统,系统级的很多属性和控制方法都放置在该类的内部。该类位于
java.lang包 - 由于该类的构造器是
private的,所以无法创建该类的对象 - 其内部的成员变量和成员方法都是
static的,所以也可以很方便的进行调用 - 成员方法
native long currentTimeMillis():- 该方法的作用是返回当前的计算机时间
- 时间的表达格式为当前计算机时间和GMT时间(格林威治时间)1970年1月1号0时0分0秒所差的毫秒数
void exit(int status):- 该方法的作用是退出程序
- 其中status的值为0代表正常退出,非零代表异常退出
- 使用该方法可以在图形界面编程中实现程序的退出功能等
void gc():- 该方法的作用是请求系统进行垃圾回收
- 至于系统是否立刻回收,则取决于系统中垃圾回收算法的实现以及系统执行时的情况
String getProperty(String key):- 该方法的作用是获得系统中属性名为key的属性对应的值
- 系统中常见的属性名以及属性的作用如下表所示
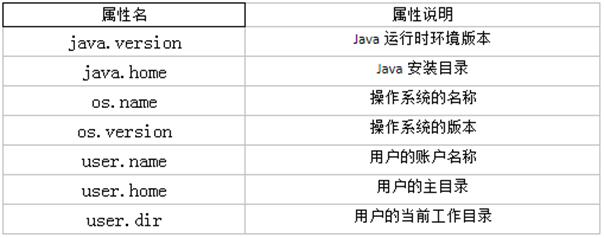
举例:
@Test
public void test1() {String javaVersion = System.getProperty("java.version");System.out.println("java的version:" + javaVersion);String javaHome = System.getProperty("java.home");System.out.println("java的home:" + javaHome);String osName = System.getProperty("os.name");System.out.println("os的name:" + osName);String osVersion = System.getProperty("os.version");System.out.println("os的version:" + osVersion);String userName = System.getProperty("user.name");System.out.println("user的name:" + userName);String userHome = System.getProperty("user.home");System.out.println("user的home:" + userHome);String userDir = System.getProperty("user.dir");System.out.println("user的dir:" + userDir);
}
输出结果:
java的version:1.8.0_345
java的home:/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/zulu-8.jdk/Contents/Home/jre
os的name:Mac OS X
os的version:12.5
user的name:xuchang
user的home:/Users/xuchang
user的dir:/Users/xuchang/Documents/javaCode/study/java基础/JavaSECode/chapter11_api_teacher
2、java.lang.Runtime类
- 每个 Java 应用程序都有一个
Runtime类实例,使应用程序能够与其运行的环境相连接 public static Runtime getRuntime():- 返回与当前 Java 应用程序相关的运行时对象
- 应用程序不能创建自己的 Runtime 类实例
public long totalMemory():- 返回 Java 虚拟机中初始化时的内存总量
- 此方法返回的值可能随时间的推移而变化,这取决于主机环境
- 默认为物理电脑内存的1/64
public long maxMemory():- 返回 Java 虚拟机中最大程度能使用的内存总量
- 默认为物理电脑内存的1/4
public long freeMemory():- 回 Java 虚拟机中的空闲内存量
- 调用 gc 方法可能导致 freeMemory 返回值的增加
举例:
@Test
public void test2() {Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();long initialMemory = runtime.totalMemory(); //获取虚拟机初始化时堆内存总量long maxMemory = runtime.maxMemory(); //获取虚拟机最大堆内存总量String str = "";//模拟占用内存for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {str += i;}long freeMemory = runtime.freeMemory(); //获取空闲堆内存总量System.out.println("总内存:" + initialMemory / 1024 / 1024 * 64 + "MB");System.out.println("总内存:" + maxMemory / 1024 / 1024 * 4 + "MB");System.out.println("空闲内存:" + freeMemory / 1024 / 1024 + "MB") ;System.out.println("已用内存:" + (initialMemory-freeMemory) / 1024 / 1024 + "MB");
}
输出结果:
总内存:16640MB
总内存:16384MB
空闲内存:139MB
已用内存:120MB
三、数学相关的类
1、java.lang.Math
java.lang.Math类包含用于执行基本数学运算的方法- 如初等指数、对数、平方根和三角函数
- 类似这样的工具类,其所有方法均为静态方法,并且不会创建对象,调用起来非常简单
public static double abs(double a):返回 double 值的绝对值
double d1 = Math.abs(-5); //d1的值为5
double d2 = Math.abs(5); //d2的值为5
public static double ceil(double a):返回大于等于参数的最小的整数- ceil:天花板
double d1 = Math.ceil(3.3); //d1的值为 4.0
double d2 = Math.ceil(-3.3); //d2的值为 -3.0
double d3 = Math.ceil(5.1); //d3的值为 6.0
public static double floor(double a):返回小于等于参数最大的整数- floor:地板
double d1 = Math.ceil(3.3); //d1的值为 4.0
double d2 = Math.ceil(-3.3); //d2的值为 -3.0
double d3 = Math.ceil(5.1); //d3的值为 6.0
public static long round(double a):返回最接近参数的 long。(相当于四舍五入方法)
long d1 = Math.round(5.5); //d1的值为6
long d2 = Math.round(5.4); //d2的值为5
long d3 = Math.round(-3.3); //d3的值为-3
long d4 = Math.round(-3.8); //d4的值为-4
public static double random():返回[0,1)的double随机值
double rand = Math.random(); // 0.49063812186909517
2、java.math.BigInteger
- Integer类作为int的包装类,能存储的最大整型值为2^31-1,Long类也是有限的,最大为2^63-1
- 如果要表示再大的整数,不管是基本数据类型还是他们的包装类都无能为力,更不用说进行运算了
- java.math包的BigInteger可以表示
不可变的任意精度的整数- BigInteger 提供所有 Java 的基本整数操作符的对应物,并提供 java.lang.Math 的所有相关方法
- BigInteger 还提供以下运算:模算术、GCD 计算、质数测试、素数生成、位操作以及一些其他操作
构造器
- BigInteger(String val):根据字符串构建BigInteger对象
方法
- public BigInteger
abs():返回此 BigInteger 的绝对值的 BigInteger - BigInteger
add(BigInteger val) :返回其值为 (this+val) 的 BigInteger - BigInteger
subtract(BigInteger val) :返回其值为 (this-val) 的 BigInteger - BigInteger
multiply(BigInteger val) :返回其值为 (this*val) 的 BigInteger - BigInteger
divide(BigInteger val) :返回其值为 (this/val) 的 BigInteger。整数相除只保留整数部分 - BigInteger
remainder(BigInteger val) :返回其值为 (this%val) 的 BigInteger
@Test
public void test3(){BigInteger b1 = new BigInteger("12345678912345678912345678");BigInteger b2 = new BigInteger("78923456789123456789123456789");System.out.println("和:" + b1.add(b2)); // 78935802468035802468035802467System.out.println("减:" + b1.subtract(b2));// -78911111110211111110211111111System.out.println("乘:" + b1.multiply(b2));// 974363656170906866147450004116994361840451151863907942System.out.println("除:" + b2.divide(b1));// 6392System.out.println("余:" + b2.remainder(b1));// 9877181409877181409883013
}
3、java.math.BigDecimal
- 一般的Float类和Double类可以用来做科学计算或工程计算
- 但在商业计算中,要求数字精度比较高,故用到java.math.BigDecimal类
- BigDecimal类支持不可变的、任意精度的有符号十进制定点数
构造器
- public BigDecimal(double val)
- public BigDecimal(String val) --> 推荐
常用方法
- public BigDecimal
add(BigDecimal augend) - public BigDecimal
subtract(BigDecimal subtrahend) - public BigDecimal
multiply(BigDecimal multiplicand) - public BigDecimal
divide(BigDecimal divisor, int scale, int roundingMode)- divisor是除数
- scale指明保留几位小数
- roundingMode指明舍入模式
- ROUND_UP :向上加1、ROUND_DOWN :直接舍去、ROUND_HALF_UP:四舍五入
@Test
public void test4(){BigDecimal bd = new BigDecimal("12435.351");BigDecimal bd2 = new BigDecimal("11");System.out.println(bd); // 12435.351System.out.println(bd.divide(bd2, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP)); // 1130.486System.out.println(bd.divide(bd2, 15, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP)); // 1130.486454545454545
}
4、java.util.Random(用于产生随机数)
boolean nextBoolean():返回下一个伪随机数,它是取自此随机数生成器序列的均匀分布的 boolean 值void nextBytes(byte[] bytes):生成随机字节并将其置于用户提供的 byte 数组中double nextDouble():返回下一个伪随机数,它是取自此随机数生成器序列的、在 0.0 和 1.0 之间均匀分布的 double 值float nextFloat():返回下一个伪随机数,它是取自此随机数生成器序列的、在 0.0 和 1.0 之间均匀分布的 float 值int nextInt():返回下一个伪随机数,它是此随机数生成器的序列中均匀分布的 int 值int nextInt(int n):返回一个伪随机数,它是取自此随机数生成器序列的、在 0(包括)和指定值(不包括)之间均匀分布的 int 值long nextLong():返回下一个伪随机数,它是取自此随机数生成器序列的均匀分布的 long 值
@Test
public void test5(){Random random = new Random();int i = random.nextInt();System.out.println(i); // -235025063int j = random.nextInt(10); //随机获取[0,10)范围的整数System.out.println(j); // 7
}


