STL——list、stack与queue


📖作者介绍:22级树莓人(计算机专业),热爱编程<目前在c++阶段>——目标Windows,MySQL,Qt,数据结构与算法,Linux,多线程,会持续分享学习成果和小项目的
📖作者主页:热爱编程的小K
📖专栏链接:c++🎉欢迎各位→点赞👏 + 收藏💞 + 留言🔔
💬总结:希望你看完之后,能对你有所帮助,不足请指正!共同学习交流 🐾

文章目录
-
- 一、list
-
- 1、简介
- 2、操作基本数据类型
- 3、操作自定义类型
- 4、sort函数的五花八门
- 5、删除操作
- 二、stack
-
- 1、stack概念
- 2、简单应用—进制转换
- 3、练习—leetcode20.有效的括号
- 三、queue
-
- 1、queue
-
- A、概念
- B、操作
- 2、deque
-
- A、概念
- B、操作
- 3、priority_queue
-
- A、概念
- B、操作基本数据类型
- C、操作自定义类型
一、list
1、简介
list 容器,又称双向链表容器,即该容器的底层是以双向链表的形式实现的。这意味着,list 容器中的元素可以分散存储在内存空间里,而不是必须存储在一整块连续的内存空间中。
2、操作基本数据类型
初始化可以直接赋值,也可以不赋值
void testOne()
{list<int> nums = { 1,2,3,4 };list<string> str;str.push_back("king");str.push_back("link");for (auto v : str) {cout << v << " ";}cout << endl;//删除方式遍历while (!str.empty()) {cout << str.front() << endl;str.pop_front();}
}
3、操作自定义类型
记得重载输出运算符,或者提供打印接口
class MM
{
public:MM(string name=" ",int age=0):name(name),age(age){}friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out,const MM& object){out << object.age << "\\t" << object.name << endl;return out;}string getName() const{ return name; }int getAge() const{ return age; }
protected:string name;int age;
};
void testTwo()
{list<MM> mm;mm.push_back(MM("king", 18));mm.push_back(MM("貂蝉", 28));mm.push_back(MM("妲己", 19));for (auto v : mm) {cout << v;}cout << endl;}
4、sort函数的五花八门
sort函数默认的是从小到大排序(less<>()),也可以greater<>()方式进行排序,sort的参数是一个排序准则(后面可以用仿函数,会方便很多),这里我们自己写函数排序准则
bool cmpAge(const MM& one, const MM& two) {return one.getAge() < two.getAge();
}
bool cmpName(const MM& one, const MM& two ) {return one.getName() < two.getName();
}
void testthree() {list<int> nums = { 2,3,8,65,43,0,4 };nums.sort();for (auto v : nums) {cout << v << " ";}cout << endl;nums.sort(less<int>()); //等价于默认for (auto v : nums) {cout << v << " ";}cout << endl;nums.sort(greater<int>()); //重大到小for (auto v : nums) {cout << v << " ";}cout << endl;nums.reverse(); //反转for (auto v : nums) {cout << v << " ";}cout << endl;list<MM> info;info.push_back(MM("貂蝉", 18));info.push_back(MM("狂铁", 19));info.push_back(MM("妲己", 34));cout << "按年龄排序" << endl;info.sort(cmpAge);for (auto v : info) {cout << v;}cout << endl;cout << "按姓名排" << endl;info.sort(cmpName);for (auto v : info) {cout << v;}cout << endl;
}
5、删除操作
当使用一个容器的insert或者erase函数通过迭代器插入或删除元素"可能"会导致迭代器失效,因此我们为了避免危险,应该获取insert或者erase返回的迭代器,以便用重新获取的新的有效的迭代器进行正确的操作
bool find_name(const MM& three, string name) {return three.getName() == name;
}
void Test()
{list<MM> info;info.push_back(MM("貂蝉", 18));info.push_back(MM("狂铁", 19));info.push_back(MM("妲己", 34));auto iter = find_if(info.begin(), info.end(), bind(find_name, placeholders::_1, "妲己"));info.erase(iter);for (auto v : info) {cout << v;}cout << endl;//迭代器删除for (auto i = info.begin(); i != info.end();){if (i->getName() == "狂铁") {i = info.erase(i);}else {i++;}}for (auto v : info) {cout << v;}
}
二、stack
1、stack概念
stack是一种容器适配器,专门设计用于在LIFO上下文(后进先出)中操作,在LIFO上下文中,仅从容器的一端插入和提取元素。
stack作为容器适配器实现,它们是使用特定容器类的封装对象作为其基础容器的类,提供了一组特定的成员函数来访问其元素。元素从特定容器的尾部被推入*/弹出,这被称为堆栈的*顶部。
容器应支持以下操作:
- empty
- size
- back
- push_back
- pop_back
标准容器类vector,deque 和list满足这些要求。默认情况下,使用标准容器 deque来作为底层容器。
2、简单应用—进制转换
将123转换为二进制
void test1() {int nums = 123;stack<int> mm;while (nums) {mm.push(nums % 2);nums /= 2;}while (!mm.empty()) {cout << mm.top();mm.pop();}
}
3、练习—leetcode20.有效的括号
给定一个只包括 ‘(’,’)’,’{’,’}’,’[’,’]’ 的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
- 左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
- 左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
- 每个右括号都有一个对应的相同类型的左括号。
示例 1:
输入:s = “()”
输出:true
示例 2:
输入:s = “()[]{}”
输出:true
示例 3:
输入:s = “(]”
输出:false
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 104
s 仅由括号 ‘()[]{}’ 组成
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-parentheses
题解放在代码中啦
class Solution {
public:bool isValid(string s) {stack<char> result;for (auto v : s) {if (v == '(' || v == '[' || v == '{') {result.push(v);}else {//列举反例的情况if (!result.empty()) //v='}'{char out = result.top();if (v == '}' && out != '{') {return false;}if (v == ']' && out != '[') {return false;}if (v == ')' && out != '(') {return false;}//括号匹配,出栈result.pop();}//进来的不是左括号,且栈也是空的(进来的是右括号)else {return false;}}}//最后判断栈中还有没有单个元素return result.empty();}
};
三、queue
1、queue
A、概念
FIFO队列
queue是一种容器适配器,专门设计用于在FIFO上下文中(先进先出)进行操作,在FIFO上下文中,将元素插入到容器的一端,并从另一端提取元素。
queue被实现为容器适配器,它们是使用特定容器类的封装对象作为其基础容器的类,提供了一组特定的成员函数来访问其元素。元素被推入特定容器的*“后部”,并从其“前部”弹出*。
基础容器可以是标准容器类模板之一,也可以是其他一些专门设计的容器类。此基础容器应至少支持以下操作:
- empty
- size
- front
- back
- push_back
- pop_front
标准容器类 deque和list满足这些要求。默认情况下,如果未为特定容器指定容器类队列,类实例化,默认用标准容器 deque
B、操作
//入栈
void push(Type data);
void pop();//获取栈顶元素
Type front()
int size();
bool empty();
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
void testOne()
{queue<int> mm;mm.push(9);mm.push(8);mm.push(7);while (!mm.empty()){cout << mm.front() << " ";mm.pop();}cout << endl;
}
int main()
{testOne();return 0;
}
2、deque
A、概念
deque是“double-ended queue”的缩写,和vector一样都是STL的容器,deque是双端队列,而vector是单端的。
deque在接口上和vector非常相似,在许多操作的地方可以直接替换。
- deque 容器也擅长在序列尾部添加或删除元素(时间复杂度为
O(1)),而不擅长在序列中间添加或删除元素。 - deque 容器也可以根据需要修改自身的容量和大小。
和 vector 不同的是,deque 还擅长在序列头部添加或删除元素,所耗费的时间复杂度也为常数阶O(1)。并且更重要的一点是,deque 容器中存储元素并不能保证所有元素都存储到连续的内存空间中。
B、操作
class MM
{
public:MM(string name=" ",int age=0):name(name),age(age){}void print() const { cout << name << "\\t" << age << endl; }string getName() { return name; }int getAge() { return age; }
protected:string name;int age;
};
void testTwo()
{deque<MM> info;info.push_back(MM("貂蝉", 19));info.push_back(MM("妲己", 20));info.push_back(MM("狂铁", 20));while (!info.empty()) {info.front().print();info.pop_front();}
}
3、priority_queue
A、概念
priority_que(优先级队列)是一种容器适配器,经过专门设计,以使其按照某些*严格的弱排序(strict weak ordering)*标准,其第一个元素始终是其中包含的最大元素。
严格是说在判断的时候会用"<",而不是"<=",弱排序是因为,一旦"<“成立便认为存在”<“关系,返回ture,而忽略了”=“关系和”>"区别,把它们归结为false。
此上下文类似于堆,可以在任何时候插入元素,并且只能检索最大堆元素(优先级队列顶部的元素)。
优先级队列被实现为容器适配器,它们是使用特定容器类的封装对象作为其基础容器的类,提供了一组特定的成员函数来访问其元素。元素被弹出从特定容器的*“后退”,称为优先级队列的顶部*。
基础容器可以是任何标准容器类模板或某些其他专门设计的容器类。该容器应可通过随机访问迭代器访问并支持以下操作:
empty()size()front()push_back()pop_back()
标准容器类 vector和 deque满足这些要求。默认情况下,如果未为特定容器指定容器类
priority_queue 类实例化,默认使用vector作为底层容器。
需要支持随机访问迭代器,以始终在内部保持堆结构。容器适配器通过自动调用算法函数(make_heap, push_heap,pop_heap )维持堆结构。
B、操作基本数据类型
void testthree()
{cout << "偷懒版本" << "\\t";priority_queue<int> q1;//默认less排,出队重大到小q1.push(1);q1.push(99);q1.push(0);while (!q1.empty()){cout << q1.top() << " ";q1.pop();}cout << endl;cout << "完整版本 less" << "\\t";priority_queue<int, vector<int>, less<int>> king;king.push(1);king.push(2);king.push(88);king.push(0);while (!king.empty()){cout << king.top() << " ";king.pop();}cout << endl;cout << "完整版本 greater" << "\\t";priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> kin;kin.push(1);kin.push(2);kin.push(88);kin.push(0);while (!kin.empty()){cout << kin.top() << " ";kin.pop();}cout << endl;
}
C、操作自定义类型
第一种是写运算符重载,不常用,第二种是自己写仿函数描述函数准则
class MM
{
public:MM(string name=" ",int age=0):name(name),age(age){}void print() const { cout << name << "\\t" << age << endl; }bool operator<(const MM& object) const{return this->age < object.age;}string getName()const { return name; }int getAge()const { return age; }
protected:string name;int age;
};
struct cmpAgeless
{bool operator()(const MM& one, const MM& two) {return one.getAge() > two.getAge();}
};
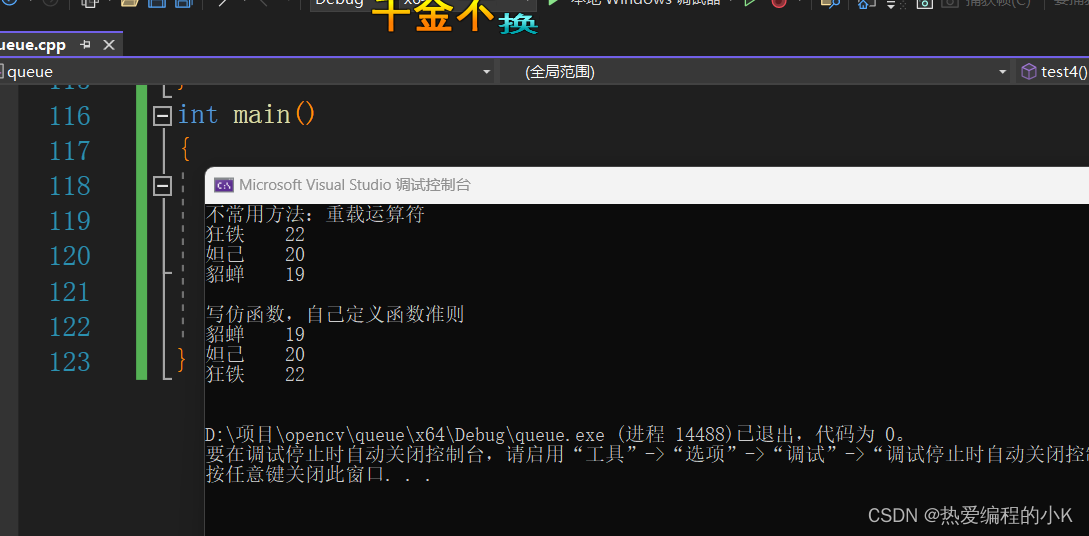
void test4()
{cout << "不常用方法:重载运算符" << endl;priority_queue<MM, vector<MM>, less<MM>> mm;mm.push(MM("貂蝉", 19));mm.push(MM("妲己", 20));mm.push(MM("狂铁", 22));while (!mm.empty()){mm.top().print();mm.pop();}cout << endl;cout << "写仿函数,自己定义函数准则" << endl;priority_queue<MM, vector<MM>, cmpAgeless> mm1;mm1.push(MM("貂蝉", 19));mm1.push(MM("妲己", 20));mm1.push(MM("狂铁", 22));while (!mm1.empty()){mm1.top().print();mm1.pop();}cout << endl;
}


