Linux驱动——高级I/O操作(四)

目录
几种I/O模型总结
异步通知
几种I/O模型总结

阻塞 IO:在资源不可用时,进程阻塞,阻塞发生在驱动中,资源可用后进程被唤醒,在阻塞期间不占用CPU,是最常用的一种方式。
非阻塞 I/O: 调用立即返回,即便是在资源不可用的情况下,通过返回值来确定 IO操作是否成功,如果不成功,程序将在之后继续尝试。对于大多数时间内资源都不可用的设备 (如鼠标、键盘),这种尝试将会白白消耗 CPU 大量的时间,如果将尝试的间隔时间增加,又可能会产生不能及时处理设备的数据。
I/O 多路复用:可以同时监听多个设备的状态,如果被监听的所有设备都没有关心的事件产生,那么系统调用被阻塞。当被监听的任何一个设备有对应关心的事件发生,将会唤醒系统调用,系统调用将再次遍历所监听的设备,获取其事件信息,然后系统调用返回。之后可以对设备发起非阻塞的读或写操作。
异步 IO: 调用者只是发起 I/O 操作的请求,然后立即返回,程序可以去做别的事情具体的IO操作在驱动中完成,驱动中可能会被阻塞,也可能不会被阻塞。当驱动的IO操作完成后,调用者将会得到通知,通常是内核向调用者发送信号,或者自动调用调用者注册的回调函数,通知操作是由内核完成的,而不是驱动本身。
异步通知
异步通知类似于前面讲解的异步 I/O,只是当设备资源可用时它是向应用层发信号而不能直接调用应用层注册的回调函数,并且发信号的操作也是驱动程序自身来完成的在前面讲解的 I/O 模型中,应用程序都是主动获取设备的资源信息,即便是异步 I/O 也要先发起一个 I/O 操作请求。而异步通知则是当设备资源可获得时,由驱动主动通知应用程序,再由应用程序发起访问。这种机制和中断非常相似,以至于我们可以完全借用中断的思想来理解这一过程(信号其实相当于应用层的中断)。下面是异步通知的应用程序实现步骤。
(1)注册信号处理函数,这相当于注册中断处理函数
(2)打开设备文件,设置文件属主。目的是使驱动根据打开文件的 file 结构,找到对应的进程,从而向该进程发送信号。
(3)设置设备资源可用时驱动向进程发送的信号,这一过程并不是必需的,但正如我们下面看到的,如果要使用 sigaction 的高级特性,该步骤是必不可少的。
(4)设置文件的 FASYNC 标志,使能异步通知机制,这相当于打开中断使能位典型的应用程序如下
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <poll.h>
#include <signal.h>#include "vser.h"int fd;void sigio_handler(int signum, siginfo_t *siginfo, void *act)
{int ret;char buf[32];if (signum == SIGIO) {if (siginfo->si_band & POLLIN) {printf("FIFO is not empty\\n");if ((ret = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf))) != -1) {buf[ret] = '\\0';puts(buf);}}if (siginfo->si_band & POLLOUT)printf("FIFO is not full\\n");}
}int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{int ret;int flag;struct sigaction act, oldact;sigemptyset(&act.sa_mask);sigaddset(&act.sa_mask, SIGIO);act.sa_flags = SA_SIGINFO;act.sa_sigaction = sigio_handler;if (sigaction(SIGIO, &act, &oldact) == -1)goto fail;fd = open("/dev/vser0", O_RDWR | O_NONBLOCK);if (fd == -1) goto fail;if (fcntl(fd, F_SETOWN, getpid()) == -1)goto fail;if (fcntl(fd, F_SETSIG, SIGIO) == -1)goto fail;if ((flag = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL)) == -1)goto fail;if (fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, flag | FASYNC) == -1)goto fail;while (1)sleep(1);fail:perror("fasync test");exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
代码第 41 行至第46行对应步骤(1),即注册信号处理函数。sigaction 比 signal 更高级,主要是信号阻塞和提供信号信息两方面。使用 sigaction 注册的信号处理函数的参数有三个,而第二个参数就是关于信号的一些信息,我们随后会用到里面的内容。另外,代码第 41 行和第 42行阻塞了 SIGIO自己,防止信号处理函数的嵌套调用。
代码第 48 行至第 53 行对应步(2),即设置文件属主。驱动在发信号时,处于一个所谓的任意进程上下文,即不知道当前运行的进程,要给一个特定的进程发信号,则需要一些额外的信息,可以通过 fcntl 将所属的进程信息保存在 file 结构中,从而驱动可以根据 file 结构来找到对应的进程。
代码第 54行和第55 行对应步(3),设置了当设备资源可用时,向进程发送 SIGIO信号,虽然这是默认发送的信号,但是为了使用信号的更多信息(主要是发送信号的原因,或者说是具体资源的情况),需要显式地进行这一步操作。
代码第 56行和第 59 行对应步骤(4),首先获取了文件的标志,然后再添加 FASYNC标志,这就打开了异步通知的机制。
之后主函数一直休眠,等待驱动发来的信号。当进程收到驱动发来的信号后,注册的信号处理函数 sigio_handler 自动被调用,函数的第一个参数是信号值,第二个参数是信号的附带信息,比如ID 号、发送的时间等。这里关心的是 si_band 成员,它将记录资源是可读还是可写,从而进行相应的操作。
在编写对应的驱动代码之前,我们先来看一下内核中关于异步通知方面的处理。/*fs/fcntl.c*/
/ linux/fs/fcntl.c Copyright (C) 1991, 1992 Linus Torvalds*/#include <linux/syscalls.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/mm.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/file.h>
#include <linux/fdtable.h>
#include <linux/capability.h>
#include <linux/dnotify.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/pipe_fs_i.h>
#include <linux/security.h>
#include <linux/ptrace.h>
#include <linux/signal.h>
#include <linux/rcupdate.h>
#include <linux/pid_namespace.h>
#include <linux/user_namespace.h>#include <asm/poll.h>
#include <asm/siginfo.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>#define SETFL_MASK (O_APPEND | O_NONBLOCK | O_NDELAY | O_DIRECT | O_NOATIME)static int setfl(int fd, struct file * filp, unsigned long arg)
{struct inode * inode = file_inode(filp);int error = 0;/ O_APPEND cannot be cleared if the file is marked as append-only* and the file is open for write.*/if (((arg ^ filp->f_flags) & O_APPEND) && IS_APPEND(inode))return -EPERM;/* O_NOATIME can only be set by the owner or superuser */if ((arg & O_NOATIME) && !(filp->f_flags & O_NOATIME))if (!inode_owner_or_capable(inode))return -EPERM;/* required for strict SunOS emulation */if (O_NONBLOCK != O_NDELAY)if (arg & O_NDELAY)arg |= O_NONBLOCK;if (arg & O_DIRECT) {if (!filp->f_mapping || !filp->f_mapping->a_ops ||!filp->f_mapping->a_ops->direct_IO)return -EINVAL;}if (filp->f_op->check_flags)error = filp->f_op->check_flags(arg);if (error)return error;/ ->fasync() is responsible for setting the FASYNC bit.*/if (((arg ^ filp->f_flags) & FASYNC) && filp->f_op->fasync) {error = filp->f_op->fasync(fd, filp, (arg & FASYNC) != 0);if (error < 0)goto out;if (error > 0)error = 0;}spin_lock(&filp->f_lock);filp->f_flags = (arg & SETFL_MASK) | (filp->f_flags & ~SETFL_MASK);spin_unlock(&filp->f_lock);out:return error;
}static void f_modown(struct file *filp, struct pid *pid, enum pid_type type,int force)
{write_lock_irq(&filp->f_owner.lock);if (force || !filp->f_owner.pid) {put_pid(filp->f_owner.pid);filp->f_owner.pid = get_pid(pid);filp->f_owner.pid_type = type;if (pid) {const struct cred *cred = current_cred();filp->f_owner.uid = cred->uid;filp->f_owner.euid = cred->euid;}}write_unlock_irq(&filp->f_owner.lock);
}int __f_setown(struct file *filp, struct pid *pid, enum pid_type type,int force)
{int err;err = security_file_set_fowner(filp);if (err)return err;f_modown(filp, pid, type, force);return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(__f_setown);int f_setown(struct file *filp, unsigned long arg, int force)
{enum pid_type type;struct pid *pid;int who = arg;int result;type = PIDTYPE_PID;if (who < 0) {type = PIDTYPE_PGID;who = -who;}rcu_read_lock();pid = find_vpid(who);result = __f_setown(filp, pid, type, force);rcu_read_unlock();return result;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(f_setown);void f_delown(struct file *filp)
{f_modown(filp, NULL, PIDTYPE_PID, 1);
}pid_t f_getown(struct file *filp)
{pid_t pid;read_lock(&filp->f_owner.lock);pid = pid_vnr(filp->f_owner.pid);if (filp->f_owner.pid_type == PIDTYPE_PGID)pid = -pid;read_unlock(&filp->f_owner.lock);return pid;
}static int f_setown_ex(struct file *filp, unsigned long arg)
{struct f_owner_ex __user *owner_p = (void __user *)arg;struct f_owner_ex owner;struct pid *pid;int type;int ret;ret = copy_from_user(&owner, owner_p, sizeof(owner));if (ret)return -EFAULT;switch (owner.type) {case F_OWNER_TID:type = PIDTYPE_MAX;break;case F_OWNER_PID:type = PIDTYPE_PID;break;case F_OWNER_PGRP:type = PIDTYPE_PGID;break;default:return -EINVAL;}rcu_read_lock();pid = find_vpid(owner.pid);if (owner.pid && !pid)ret = -ESRCH;elseret = __f_setown(filp, pid, type, 1);rcu_read_unlock();return ret;
}static int f_getown_ex(struct file *filp, unsigned long arg)
{struct f_owner_ex __user *owner_p = (void __user *)arg;struct f_owner_ex owner;int ret = 0;read_lock(&filp->f_owner.lock);owner.pid = pid_vnr(filp->f_owner.pid);switch (filp->f_owner.pid_type) {case PIDTYPE_MAX:owner.type = F_OWNER_TID;break;case PIDTYPE_PID:owner.type = F_OWNER_PID;break;case PIDTYPE_PGID:owner.type = F_OWNER_PGRP;break;default:WARN_ON(1);ret = -EINVAL;break;}read_unlock(&filp->f_owner.lock);if (!ret) {ret = copy_to_user(owner_p, &owner, sizeof(owner));if (ret)ret = -EFAULT;}return ret;
}#ifdef CONFIG_CHECKPOINT_RESTORE
static int f_getowner_uids(struct file *filp, unsigned long arg)
{struct user_namespace *user_ns = current_user_ns();uid_t __user *dst = (void __user *)arg;uid_t src[2];int err;read_lock(&filp->f_owner.lock);src[0] = from_kuid(user_ns, filp->f_owner.uid);src[1] = from_kuid(user_ns, filp->f_owner.euid);read_unlock(&filp->f_owner.lock);err = put_user(src[0], &dst[0]);err |= put_user(src[1], &dst[1]);return err;
}
#else
static int f_getowner_uids(struct file *filp, unsigned long arg)
{return -EINVAL;
}
#endifstatic long do_fcntl(int fd, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg,struct file *filp)
{long err = -EINVAL;switch (cmd) {case F_DUPFD:err = f_dupfd(arg, filp, 0);break;case F_DUPFD_CLOEXEC:err = f_dupfd(arg, filp, O_CLOEXEC);break;case F_GETFD:err = get_close_on_exec(fd) ? FD_CLOEXEC : 0;break;case F_SETFD:err = 0;set_close_on_exec(fd, arg & FD_CLOEXEC);break;case F_GETFL:err = filp->f_flags;break;case F_SETFL:err = setfl(fd, filp, arg);break;case F_GETLK:err = fcntl_getlk(filp, (struct flock __user *) arg);break;case F_SETLK:case F_SETLKW:err = fcntl_setlk(fd, filp, cmd, (struct flock __user *) arg);break;case F_GETOWN:/ XXX If f_owner is a process group, the* negative return value will get converted* into an error. Oops. If we keep the* current syscall conventions, the only way* to fix this will be in libc.*/err = f_getown(filp);force_successful_syscall_return();break;case F_SETOWN:err = f_setown(filp, arg, 1);break;case F_GETOWN_EX:err = f_getown_ex(filp, arg);break;case F_SETOWN_EX:err = f_setown_ex(filp, arg);break;case F_GETOWNER_UIDS:err = f_getowner_uids(filp, arg);break;case F_GETSIG:err = filp->f_owner.signum;break;case F_SETSIG:/* arg == 0 restores default behaviour. */if (!valid_signal(arg)) {break;}err = 0;filp->f_owner.signum = arg;break;case F_GETLEASE:err = fcntl_getlease(filp);break;case F_SETLEASE:err = fcntl_setlease(fd, filp, arg);break;case F_NOTIFY:err = fcntl_dirnotify(fd, filp, arg);break;case F_SETPIPE_SZ:case F_GETPIPE_SZ:err = pipe_fcntl(filp, cmd, arg);break;default:break;}return err;
}static int check_fcntl_cmd(unsigned cmd)
{switch (cmd) {case F_DUPFD:case F_DUPFD_CLOEXEC:case F_GETFD:case F_SETFD:case F_GETFL:return 1;}return 0;
}SYSCALL_DEFINE3(fcntl, unsigned int, fd, unsigned int, cmd, unsigned long, arg)
{ struct fd f = fdget_raw(fd);long err = -EBADF;if (!f.file)goto out;if (unlikely(f.file->f_mode & FMODE_PATH)) {if (!check_fcntl_cmd(cmd))goto out1;}err = security_file_fcntl(f.file, cmd, arg);if (!err)err = do_fcntl(fd, cmd, arg, f.file);out1:fdput(f);
out:return err;
}#if BITS_PER_LONG == 32
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(fcntl64, unsigned int, fd, unsigned int, cmd,unsigned long, arg)
{ struct fd f = fdget_raw(fd);long err = -EBADF;if (!f.file)goto out;if (unlikely(f.file->f_mode & FMODE_PATH)) {if (!check_fcntl_cmd(cmd))goto out1;}err = security_file_fcntl(f.file, cmd, arg);if (err)goto out1;switch (cmd) {case F_GETLK64:err = fcntl_getlk64(f.file, (struct flock64 __user *) arg);break;case F_SETLK64:case F_SETLKW64:err = fcntl_setlk64(fd, f.file, cmd,(struct flock64 __user *) arg);break;default:err = do_fcntl(fd, cmd, arg, f.file);break;}
out1:fdput(f);
out:return err;
}
#endif/* Table to convert sigio signal codes into poll band bitmaps */static const long band_table[NSIGPOLL] = {POLLIN | POLLRDNORM, /* POLL_IN */POLLOUT | POLLWRNORM | POLLWRBAND, /* POLL_OUT */POLLIN | POLLRDNORM | POLLMSG, /* POLL_MSG */POLLERR, /* POLL_ERR */POLLPRI | POLLRDBAND, /* POLL_PRI */POLLHUP | POLLERR /* POLL_HUP */
};static inline int sigio_perm(struct task_struct *p,struct fown_struct *fown, int sig)
{const struct cred *cred;int ret;rcu_read_lock();cred = __task_cred(p);ret = ((uid_eq(fown->euid, GLOBAL_ROOT_UID) ||uid_eq(fown->euid, cred->suid) || uid_eq(fown->euid, cred->uid) ||uid_eq(fown->uid, cred->suid) || uid_eq(fown->uid, cred->uid)) &&!security_file_send_sigiotask(p, fown, sig));rcu_read_unlock();return ret;
}static void send_sigio_to_task(struct task_struct *p,struct fown_struct *fown,int fd, int reason, int group)
{/ F_SETSIG can change ->signum lockless in parallel, make* sure we read it once and use the same value throughout.*/int signum = ACCESS_ONCE(fown->signum);if (!sigio_perm(p, fown, signum))return;switch (signum) {siginfo_t si;default:/* Queue a rt signal with the appropriate fd as itsvalue. We use SI_SIGIO as the source, not SI_KERNEL, since kernel signals always get delivered even if we can't queue. Failure toqueue in this case _should_ be reported; we fallback to SIGIO in that case. --sct */si.si_signo = signum;si.si_errno = 0;si.si_code = reason;/* Make sure we are called with one of the POLL_*reasons, otherwise we could leak kernel stack intouserspace. */BUG_ON((reason & __SI_MASK) != __SI_POLL);if (reason - POLL_IN >= NSIGPOLL)si.si_band = ~0L;elsesi.si_band = band_table[reason - POLL_IN];si.si_fd = fd;if (!do_send_sig_info(signum, &si, p, group))break;/* fall-through: fall back on the old plain SIGIO signal */case 0:do_send_sig_info(SIGIO, SEND_SIG_PRIV, p, group);}
}void send_sigio(struct fown_struct *fown, int fd, int band)
{struct task_struct *p;enum pid_type type;struct pid *pid;int group = 1;read_lock(&fown->lock);type = fown->pid_type;if (type == PIDTYPE_MAX) {group = 0;type = PIDTYPE_PID;}pid = fown->pid;if (!pid)goto out_unlock_fown;read_lock(&tasklist_lock);do_each_pid_task(pid, type, p) {send_sigio_to_task(p, fown, fd, band, group);} while_each_pid_task(pid, type, p);read_unlock(&tasklist_lock);out_unlock_fown:read_unlock(&fown->lock);
}static void send_sigurg_to_task(struct task_struct *p,struct fown_struct *fown, int group)
{if (sigio_perm(p, fown, SIGURG))do_send_sig_info(SIGURG, SEND_SIG_PRIV, p, group);
}int send_sigurg(struct fown_struct *fown)
{struct task_struct *p;enum pid_type type;struct pid *pid;int group = 1;int ret = 0;read_lock(&fown->lock);type = fown->pid_type;if (type == PIDTYPE_MAX) {group = 0;type = PIDTYPE_PID;}pid = fown->pid;if (!pid)goto out_unlock_fown;ret = 1;read_lock(&tasklist_lock);do_each_pid_task(pid, type, p) {send_sigurg_to_task(p, fown, group);} while_each_pid_task(pid, type, p);read_unlock(&tasklist_lock);out_unlock_fown:read_unlock(&fown->lock);return ret;
}static DEFINE_SPINLOCK(fasync_lock);
static struct kmem_cache *fasync_cache __read_mostly;static void fasync_free_rcu(struct rcu_head *head)
{kmem_cache_free(fasync_cache,container_of(head, struct fasync_struct, fa_rcu));
}/ Remove a fasync entry. If successfully removed, return* positive and clear the FASYNC flag. If no entry exists,* do nothing and return 0. NOTE! It is very important that the FASYNC flag always* match the state "is the filp on a fasync list"./
int fasync_remove_entry(struct file *filp, struct fasync_struct fapp)
{struct fasync_struct *fa, fp;int result = 0;spin_lock(&filp->f_lock);spin_lock(&fasync_lock);for (fp = fapp; (fa = *fp) != NULL; fp = &fa->fa_next) {if (fa->fa_file != filp)continue;spin_lock_irq(&fa->fa_lock);fa->fa_file = NULL;spin_unlock_irq(&fa->fa_lock);*fp = fa->fa_next;call_rcu(&fa->fa_rcu, fasync_free_rcu);filp->f_flags &= ~FASYNC;result = 1;break;}spin_unlock(&fasync_lock);spin_unlock(&filp->f_lock);return result;
}struct fasync_struct *fasync_alloc(void)
{return kmem_cache_alloc(fasync_cache, GFP_KERNEL);
}/ NOTE! This can be used only for unused fasync entries:* entries that actually got inserted on the fasync list* need to be released by rcu - see fasync_remove_entry.*/
void fasync_free(struct fasync_struct *new)
{kmem_cache_free(fasync_cache, new);
}/ Insert a new entry into the fasync list. Return the pointer to the* old one if we didn't use the new one. NOTE! It is very important that the FASYNC flag always* match the state "is the filp on a fasync list".*/
struct fasync_struct *fasync_insert_entry(int fd, struct file *filp, struct fasync_struct fapp, struct fasync_struct *new)
{struct fasync_struct *fa, fp;spin_lock(&filp->f_lock);spin_lock(&fasync_lock);for (fp = fapp; (fa = *fp) != NULL; fp = &fa->fa_next) {if (fa->fa_file != filp)continue;spin_lock_irq(&fa->fa_lock);fa->fa_fd = fd;spin_unlock_irq(&fa->fa_lock);goto out;}spin_lock_init(&new->fa_lock);new->magic = FASYNC_MAGIC;new->fa_file = filp;new->fa_fd = fd;new->fa_next = *fapp;rcu_assign_pointer(*fapp, new);filp->f_flags |= FASYNC;out:spin_unlock(&fasync_lock);spin_unlock(&filp->f_lock);return fa;
}/ Add a fasync entry. Return negative on error, positive if* added, and zero if did nothing but change an existing one.*/
static int fasync_add_entry(int fd, struct file *filp, struct fasync_struct fapp)
{struct fasync_struct *new;new = fasync_alloc();if (!new)return -ENOMEM;/ fasync_insert_entry() returns the old (update) entry if* it existed. So free the (unused) new entry and return 0 to let the* caller know that we didn't add any new fasync entries.*/if (fasync_insert_entry(fd, filp, fapp, new)) {fasync_free(new);return 0;}return 1;
}/ fasync_helper() is used by almost all character device drivers* to set up the fasync queue, and for regular files by the file* lease code. It returns negative on error, 0 if it did no changes* and positive if it added/deleted the entry.*/
int fasync_helper(int fd, struct file * filp, int on, struct fasync_struct fapp)
{if (!on)return fasync_remove_entry(filp, fapp);return fasync_add_entry(fd, filp, fapp);
}EXPORT_SYMBOL(fasync_helper);/ rcu_read_lock() is held*/
static void kill_fasync_rcu(struct fasync_struct *fa, int sig, int band)
{while (fa) {struct fown_struct *fown;unsigned long flags;if (fa->magic != FASYNC_MAGIC) {printk(KERN_ERR "kill_fasync: bad magic number in ""fasync_struct!\\n");return;}spin_lock_irqsave(&fa->fa_lock, flags);if (fa->fa_file) {fown = &fa->fa_file->f_owner;/* Don't send SIGURG to processes which have not set aqueued signum: SIGURG has its own default signallingmechanism. */if (!(sig == SIGURG && fown->signum == 0))send_sigio(fown, fa->fa_fd, band);}spin_unlock_irqrestore(&fa->fa_lock, flags);fa = rcu_dereference(fa->fa_next);}
}void kill_fasync(struct fasync_struct fp, int sig, int band)
{/* First a quick test without locking: usually* the list is empty.*/if (*fp) {rcu_read_lock();kill_fasync_rcu(rcu_dereference(*fp), sig, band);rcu_read_unlock();}
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(kill_fasync);static int __init fcntl_init(void)
{/ Please add new bits here to ensure allocation uniqueness.* Exceptions: O_NONBLOCK is a two bit define on parisc; O_NDELAY* is defined as O_NONBLOCK on some platforms and not on others.*/BUILD_BUG_ON(20 - 1 /* for O_RDONLY being 0 */ != HWEIGHT32(O_RDONLY | O_WRONLY | O_RDWR |O_CREAT | O_EXCL | O_NOCTTY |O_TRUNC | O_APPEND | /* O_NONBLOCK | */__O_SYNC | O_DSYNC | FASYNC |O_DIRECT | O_LARGEFILE | O_DIRECTORY |O_NOFOLLOW | O_NOATIME | O_CLOEXEC |__FMODE_EXEC | O_PATH | __O_TMPFILE));fasync_cache = kmem_cache_create("fasync_cache",sizeof(struct fasync_struct), 0, SLAB_PANIC, NULL);return 0;
}module_init(fcntl_init)
代码第348行是 fcntl 系统调用对应的代码,它调用了 do_fcntl来完成具体的操作,代码第272行断如果是F_SETFL 则调用setfl 函数,setfl会调用驱动代码中的fasync接口函数(代码第68行),并传递FASYNC标志是否被设置。驱动中的 fasync 接口函数会调用fasync_helper函数(代码第680行)fasync_helper 函数根据FASYNC标志是否设置来决定在链表中添加一个struct fasync_struct节点还是删除一个节点,而这个结构中最主要的成员就是 fa_file,它是一个打开文件的结构,还包含了进程信息(前面设置的文件为主)。当资源可用时,驱动调用 kill_fasync 函数发送信号,该函数会遍历 struct fasync_struct链表,从而找到所有要接收信号的进程,并调用 send_sigio 依次发送信号(代码第692行至第714行)。
了修了异步通知在内核中的实现后,就不难理解驱动代码了。驱动代码要完成以下几个操作。
(1)构造struct fasync_struct链表的头。
(2)实现fasync接口函数,调用fasync_helper 函数来构造 struct fasync_struct 节点,并加入到链表。
(3)在资源可用时,调用kill_fasync 发送信号,并设置资源的可用类型是可读还是可写。
(4)文件最后一次关团时,即在release 接口中,需要显式调用驱动实现的fasync接口函数,将节点从链表中删除,这样进程就不会再收到信号。
实现了众多口的虚拟率口驱动的完整代码如下。
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/kfifo.h>#include <linux/ioctl.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>#include <linux/wait.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
#include <linux/aio.h>#include "vser.h"#define VSER_MAJOR 256
#define VSER_MINOR 0
#define VSER_DEV_CNT 1
#define VSER_DEV_NAME "vser"struct vser_dev {unsigned int baud;struct option opt;struct cdev cdev;wait_queue_head_t rwqh;wait_queue_head_t wwqh;struct fasync_struct *fapp;
};DEFINE_KFIFO(vsfifo, char, 32);
static struct vser_dev vsdev;static int vser_fasync(int fd, struct file *filp, int on);static int vser_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{return 0;
}static int vser_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{vser_fasync(-1, filp, 0);return 0;
}static ssize_t vser_read(struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *pos)
{int ret;unsigned int copied = 0;if (kfifo_is_empty(&vsfifo)) {if (filp->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK)return -EAGAIN;if (wait_event_interruptible_exclusive(vsdev.rwqh, !kfifo_is_empty(&vsfifo)))return -ERESTARTSYS;}ret = kfifo_to_user(&vsfifo, buf, count, &copied);if (!kfifo_is_full(&vsfifo)) {wake_up_interruptible(&vsdev.wwqh);kill_fasync(&vsdev.fapp, SIGIO, POLL_OUT);}return ret == 0 ? copied : ret;
}static ssize_t vser_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *pos)
{int ret;unsigned int copied = 0;if (kfifo_is_full(&vsfifo)) {if (filp->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK)return -EAGAIN;if (wait_event_interruptible_exclusive(vsdev.wwqh, !kfifo_is_full(&vsfifo)))return -ERESTARTSYS;}ret = kfifo_from_user(&vsfifo, buf, count, &copied);if (!kfifo_is_empty(&vsfifo)) {wake_up_interruptible(&vsdev.rwqh);kill_fasync(&vsdev.fapp, SIGIO, POLL_IN);}return ret == 0 ? copied : ret;
}static long vser_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
{if (_IOC_TYPE(cmd) != VS_MAGIC)return -ENOTTY;switch (cmd) {case VS_SET_BAUD:vsdev.baud = arg;break;case VS_GET_BAUD:arg = vsdev.baud;break;case VS_SET_FFMT:if (copy_from_user(&vsdev.opt, (struct option __user *)arg, sizeof(struct option)))return -EFAULT;break;case VS_GET_FFMT:if (copy_to_user((struct option __user *)arg, &vsdev.opt, sizeof(struct option)))return -EFAULT;break;default:return -ENOTTY;}return 0;
}static unsigned int vser_poll(struct file *filp, struct poll_table_struct *p)
{int mask = 0;poll_wait(filp, &vsdev.rwqh, p);poll_wait(filp, &vsdev.wwqh, p);if (!kfifo_is_empty(&vsfifo))mask |= POLLIN | POLLRDNORM;if (!kfifo_is_full(&vsfifo))mask |= POLLOUT | POLLWRNORM;return mask;
}static ssize_t vser_aio_read(struct kiocb *iocb, const struct iovec *iov, unsigned long nr_segs, loff_t pos)
{size_t read = 0;unsigned long i;ssize_t ret;for (i = 0; i < nr_segs; i++) {ret = vser_read(iocb->ki_filp, iov[i].iov_base, iov[i].iov_len, &pos);if (ret < 0)break;read += ret;}return read ? read : -EFAULT;
}static ssize_t vser_aio_write(struct kiocb *iocb, const struct iovec *iov, unsigned long nr_segs, loff_t pos)
{size_t written = 0;unsigned long i;ssize_t ret;for (i = 0; i < nr_segs; i++) {ret = vser_write(iocb->ki_filp, iov[i].iov_base, iov[i].iov_len, &pos);if (ret < 0)break;written += ret;}return written ? written : -EFAULT;
}static int vser_fasync(int fd, struct file *filp, int on)
{return fasync_helper(fd, filp, on, &vsdev.fapp);
}static struct file_operations vser_ops = {.owner = THIS_MODULE,.open = vser_open,.release = vser_release,.read = vser_read,.write = vser_write,.unlocked_ioctl = vser_ioctl,.poll = vser_poll,.aio_read = vser_aio_read,.aio_write = vser_aio_write,.fasync = vser_fasync,
};static int __init vser_init(void)
{int ret;dev_t dev;dev = MKDEV(VSER_MAJOR, VSER_MINOR);ret = register_chrdev_region(dev, VSER_DEV_CNT, VSER_DEV_NAME);if (ret)goto reg_err;cdev_init(&vsdev.cdev, &vser_ops);vsdev.cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE;vsdev.baud = 115200;vsdev.opt.datab = 8;vsdev.opt.parity = 0;vsdev.opt.stopb = 1;ret = cdev_add(&vsdev.cdev, dev, VSER_DEV_CNT);if (ret)goto add_err;init_waitqueue_head(&vsdev.rwqh);init_waitqueue_head(&vsdev.wwqh);return 0;add_err:unregister_chrdev_region(dev, VSER_DEV_CNT);
reg_err:return ret;
}static void __exit vser_exit(void)
{dev_t dev;dev = MKDEV(VSER_MAJOR, VSER_MINOR);cdev_del(&vsdev.cdev);unregister_chrdev_region(dev, VSER_DEV_CNT);
}module_init(vser_init);
module_exit(vser_exit);MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("name <mail>");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("A simple character device driver");
MODULE_ALIAS("virtual-serial");
代码第 30 行定义了链表的指针,实现了步骤 (1); 代码第 170行至第 173 行和代码第185行,实现了步骤 (2);代码第 66 行和第 90行发送信号,实现了步骤(3),注意此时资源状态为 POLLIN 和 POLLOUT,在信号发送函数中会转换成 POLLIN 和POLLOUT:代码第45 行完成了步骤 (4)。编译和测试的命令如下。
这个程序在我的5.4.0编译不过去只能在3.14成功,我就浅浅的捉妖一下
先是io文件找不到,我查过后发现在x86的ubuntu下叫<linux/uio.h>
现在就认识iovec了然后aio的read和write不认识
没死成还是报错
Linux内核4.1在file_operations的read_iter和write_iter_潜行金枪鱼的博客-CSDN博客
终于被我找到了
那就换就好了
Asynchronous block loop I/O [LWN.net]
先放弃先放弃。改写对于我的难度有点大。

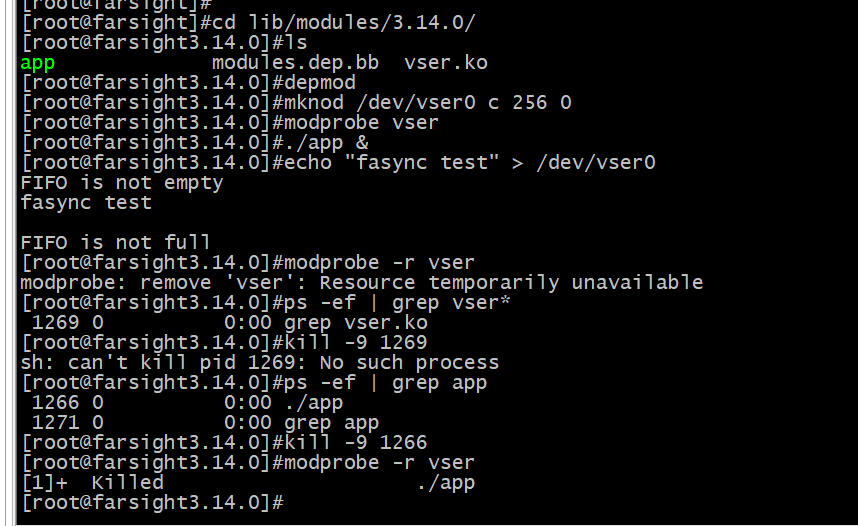
往意,在编译应用程序时,需要在命令行中加入-D_GNU_SOURCE 来定义_GNU_SOURCE,因为F_SETSIG 不是 POSIX标准。

