Spring注解开发之组件注册(一)

Spring注解开发
Spring注解开发之组件注册下半篇
IOC,中文名为控制反转,是将Java的bean对象存储在容器中,当需要使用时,通过名字获取该对象。而不是通过new关键字去创建。
1.@Configuration & @Bean给容器中注册组件
第一种:
beans.xml:

启动类:
通过beans.xml获取bean
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");Person person = (People) applicationContext.getBean("person");System.out.println(bean);
第二种:
通过注解来注册组件(@Bean(”person“)可以设定id名)

启动类:
通过配置类 注解
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);application.getBean(Person.class)System.out.println(bean);
2.@ComponentScan 自动扫描组件
XML中配置
// 包扫描,只要标注了@Controller、@Service、@Reposity、@Component <context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu"></context:component-scan>
通过注解开发
只需要配置包扫描 @ComponentScan(value = “com.atguigu”)
// 指定扫描规则
// excludeFilters = Filter[] 指定扫描的时候按照什么规则排除那些组件
// includeFilters = Filter[] 指定扫描的时候只需要包含那些组件
// useDefaultFilters = false 关闭全部扫描 默认为true
@ComponentScan(value = "com.atguigu",excludeFilters = {@Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {Controller.class}),@Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {UserService.class}),@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM,classes = {MyTypeFilter.class})},useDefaultFilters = false )// 可以多配置几个
@ComponentScans(value = {@ComponentScan(value = "com.atguigu",excludeFilters = {@Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {Controller.class})},useDefaultFilters = false)}
)
//FilterType.ANNOTATION 按照注释//FilterType.ASSINGABLE_TYPE 按照给定的类型,实现类和子类//FilterType.ASPECTJ 使用ASPECTJ表达式//FilterType.REGEX 使用正则指定//FilterType.CUSTOM 使用自定义规则
自定义TypeFilter指定过滤规则

import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotationMetadata;
import org.springframework.core.type.ClassMetadata;
import org.springframework.core.type.classreading.MetadataReader;
import org.springframework.core.type.classreading.MetadataReaderFactory;
import org.springframework.core.type.filter.TypeFilter;import java.io.IOException;public class MyTypeFilter implements TypeFilter {/* metadataReader:读取到的当前正在扫描的类的信息* metadataReaderFactory:可以获取到其他任何类信息的*/public boolean match(MetadataReader metadataReader, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory)throws IOException {// TODO Auto-generated method stub//获取当前类注解的信息AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata = metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata();//获取当前正在扫描的类的类信息ClassMetadata classMetadata = metadataReader.getClassMetadata();//获取当前类资源(类的路径)Resource resource = metadataReader.getResource();String className = classMetadata.getClassName();System.out.println("--->"+className);if(className.contains("ll")){ // 扫描到了return true; }return false;}
}3.@Scope 设置组件作用域
在IOC容器里面默认bean都是单实例的
Scope用来声明容器中的对象所应该处的限定场景或者说该对象的存活时间,即容器在对象进入其相应的scope之前生成并装配这些对象,在该对象不再处于这些scope的限定之后,容器通常会销毁这些对象。
@Scope注解有四种作用域,即
-
SINGLETON:单例模式,默认模式,不写的时候默认是SINGLETON
ioc容器启动的时候就已经创建了person实例,在Spring的IOC容器从创建到退出都只会存在一个实例,所有对该对象的引用将共享这个实例。以后每次获取都是直接从容器中取(map.get())
-
PROTOTYPE:原型模式 多实例 ioc启动时并不会去创建person实例,而是每次获取的时候才会调用方法创建对象
-
REQUEST:同一次请求则只创建一次实例
-
SESSION:同一个session只创建一次实例
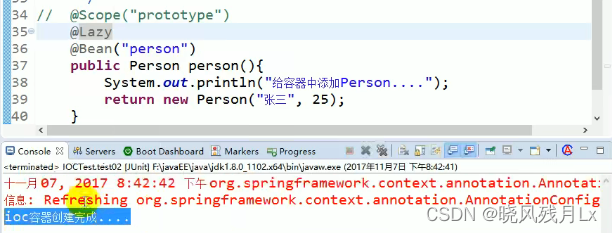
懒加载 :
单实例bean,默认在容器启动的时候创建对象
懒加载,容器启动的时候先不创建对象。第一次获取Bean创建对象并初始化
4.@Conditional 按照条件注册bean
@Conditional 按照一定的条件进行判断,满足条件给容器中注册bean
@Conditional源码@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Conditional {// 传入一个Condition数组Class<? extends Condition>[] value();}
Condition接口源码:@FunctionalInterface
public interface Condition {/* ConditionContext:判断条件能使用的上下文环境* AnnotatedTypeMetadata:注释信息*/boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata);}
业务场景
如果是linux系统则注册linus,如果是windows系统则注册bill Gates
// 编写windows条件,需要实现接口Condition,重写matches方法
public class WindowsCondition implements Condition {@Overridepublic boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {// 判断是否是Windows系统// 1. 获取到IOC使用的beanFactoryConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();// 2. 获取类加载器ClassLoader classLoader = context.getClassLoader();// 3. 获取运行环境Environment environment = context.getEnvironment();// 4. 获取到bean定义的注册类BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = context.getRegistry();// 容器中是否包含person,判断容器中的bean注册情况,也可以给容器中注册beanboolean person = registry.containsBeanDefinition("person");// 运行环境是否是WindowsString property = environment.getProperty("os.name");assert property != null;return property.contains("Windows");}
}// 编写linux系统
public class LinuxCondition implements Condition {@Overridepublic boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {Environment environment = context.getEnvironment();String property = environment.getProperty("os.name");assert property != null;return property.contains("linux");}
}// 编写配置类
@Configuration // 告诉Spring这是一个配置类
@ComponentScan(value = "com.lv")
public class MainConfig3 {@Bean("bill")@Conditional({WindowsCondition.class})public Person person() {return new Person("bill gates", 62);}@Bean("linus")@Conditional({LinuxCondition.class})public Person person2() {return new Person("linus", 48);}
}// 测试
@Test
public void test3() {AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig3.class);Map<String, Person> beansOfType = applicationContext.getBeansOfType(Person.class);System.out.println(beansOfType);
}Spring注解开发之组件注册下半篇


