ResNet残差网络

ResNet
目的
Resnet网络是为了解决深度网络中的退化问题,即网络层数越深时,在数据集上表现的性能却越差。
原理
ResNet的单元结构如下:

类似动态规划的选择性继承,同时会在训练过程中逐渐增大(/缩小)该单元中权重层的参数,主要取决于是否是直接继承前面块更优。
实现
对于ResNet50及以上来说,采用的单元块是Bottleneck模块。
在实现Bottleneck模块前,需要先对ResNet中使用到的卷积核进行简化定义。
-
首先是卷积核kernel_sizef分别为1和3的定义:
def conv1x1(in_channel, out_channel, stride=1):return nn.Conv2d(in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False)def conv3x3(in_channel, out_channel, stride=1):return nn.Conv2d(in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False) -
接着定义Bottleneck单元模块:
这里有一个涉及到梯度是否能计算的问题,如果在bn3之后又进行了一次relu操作,然后再自加等,由于relu操作是限定为原地进行的,这就会导致在反向推导时无法计算出梯度,具体原因有待考究。
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):extension = 4# Bottleneck only decrease the [h,w] in conv1 when stride > 1,# so the [h,w] is to be [(h-1)/stride+1,(w-1)/stride+1].# the in_channel will be change to channel*extension.# channel is the temp variable.def __init__(self, in_channel, channel, stride, downsample=None):super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()self.conv1 = conv1x1(in_channel, channel, stride)self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(channel)self.conv2 = conv3x3(channel, channel)self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(channel)self.conv3 = conv1x1(channel, channel * self.extension)self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(channel * self.extension)self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)self.downsample = downsampleself.stride = stridedef forward(self, x):identity = xx = self.conv1(x)x = self.bn1(x)x = self.relu(x)x = self.conv2(x)x = self.bn2(x)x = self.relu(x)x = self.conv3(x)x = self.bn3(x)if self.downsample is not None:identity = self.downsample(identity)x += identityx = self.relu(x)return x -
最后是ResNet的主体,主体包含前向传播函数和构造集合体模块层函数:
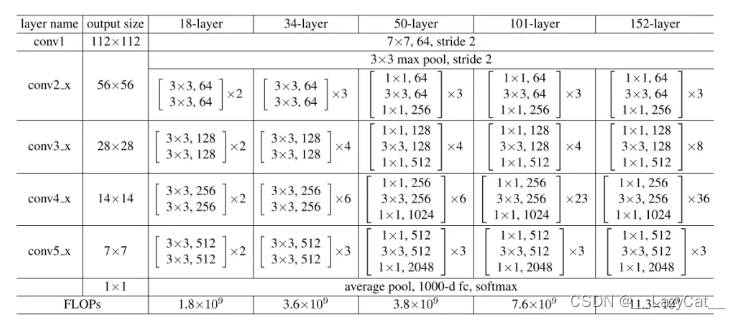
ResNet总共可看作6层结构。
-
第一层为大卷积核层,主要是以大卷积核进行卷积,同时将通道数上升到64。[h,w]=[h/2,w/2]。
-
第二至五层是残差模块,其中残差模块由多层Bottleneck组成。多层Bottleneck的第一层的in_channel为上一个模块的out_channel,中间的in_channel则为多层Bottleneck的上一层out_channel,每个Bottleneck的plane为其in_channel的1/2。
第二层的stride为1,但是有maxpool来使得图片尺寸缩小,其他层则通过stride=2使得图片尺寸缩小。
-
第六层则是全连接层,使用torch.flatten进行缩维度处理。
class ResNet(nn.Module):# size / 32 / 7def __init__(self, block, layers, num_class):super(ResNet, self).__init__()# the first layer changes the channel to 64,# and the [h,w] will be change to [(h-1)/stride+1,(w-1)/stride+1] after the first layer.self.in_channel = 64self.block = blockself.layers = layersself.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, self.in_channel, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False)self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.in_channel)self.relu = nn.ReLU()self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)# there are four block layers, each layers contains more than one block.self.stage1 = self.make_layer(self.block, 64, layers[0], stride=1)self.stage2 = self.make_layer(self.block, 128, layers[1], stride=2)self.stage3 = self.make_layer(self.block, 256, layers[2], stride=2)self.stage4 = self.make_layer(self.block, 512, layers[3], stride=2)# in the end, there will be a linear layer to classify all the classes.# self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(7)self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.extension, num_class)def make_layer(self, block, plane, block_num, stride=1):block_list = []downsample = None# if the in_channel isn't equal to the out_channel,# downsample will be needed to process the in_channel to same size as the out_channel# so that the in_channel can be added to the out_channel to achieve the resnet struct.if stride != 1 or self.in_channel != plane * block.extension:downsample = nn.Sequential(conv1x1(self.in_channel, plane * block.extension, stride),nn.BatchNorm2d(plane * block.extension))conv_block = block(self.in_channel, plane, stride, downsample=downsample)# the first block's in_channel is different to the another block_num-1 in_channel.block_list.append(conv_block)# modify the in_channel for the next stage layer.self.in_channel = plane * block.extensionfor _ in range(1, block_num):block_list.append(block(self.in_channel, plane, stride=1))return nn.Sequential(*block_list)def forward(self, x):x = self.conv1(x)x = self.bn1(x)x = self.relu(x)x = self.maxpool(x)x = self.stage1(x)x = self.stage2(x)x = self.stage3(x)x = self.stage4(x)# x = self.avgpool(x)x = torch.flatten(x, 1)x = self.fc(x)x = nn.Softmax(dim=1)(x)return x


