C++ 实现 matlab 的 zp2tf 函数

文章目录
1. matlab 的 zp2tf 函数的作用
作用是将极点形式的 H(s) 函数的分母展开
2. matlab 的 zp2tf 函数的使用方法
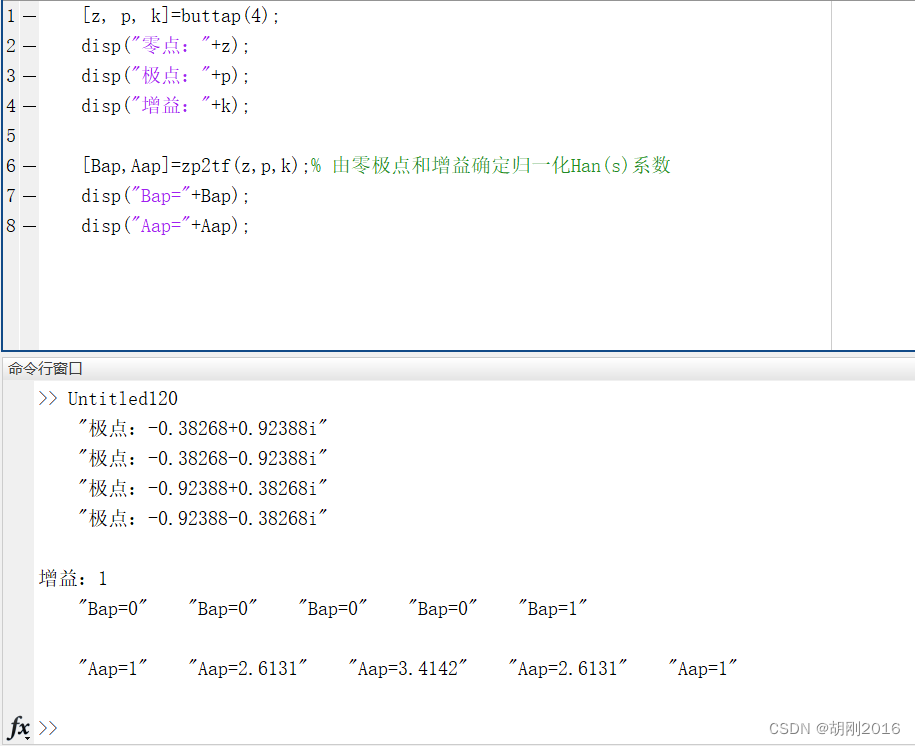
[z, p, k]=buttap(4);
disp("零点:"+z);
disp("极点:"+p);
disp("增益:"+k);[Bap,Aap]=zp2tf(z,p,k);% 由零极点和增益确定归一化Han(s)系数
disp("Bap="+Bap);
disp("Aap="+Aap);
3. C++实现
3.1 complex.h 文件
#pragma once
#include <iostream>typedef struct Complex
{double real;// 实数double img;// 虚数Complex(){real = 0.0;img = 0.0;}Complex(double r, double i){real = r;img = i;}
}Complex;/*复数乘法*/
int complex_mul(Complex* input_1, Complex* input_2, Complex* output)
{if (input_1 == NULL || input_2 == NULL || output == NULL){std::cout << "complex_mul error!" << std::endl;return -1;}output->real = input_1->real * input_2->real - input_1->img * input_2->img;output->img = input_1->real * input_2->img + input_1->img * input_2->real;return 0;
}
3.2 zp2tf.h 文件
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
#include <vector>
#include "complex.h"#define pi ((double)3.141592653589793)using namespace std;pair<Complex*, int> pair_mul(pair<Complex*, int> p1, pair<Complex*, int> p2)
{pair<Complex*, int> result;Complex* new_coeff = (Complex*)malloc(sizeof(Complex));int ret = complex_mul(p1.first, p2.first, new_coeff);if (ret == -1){cout << "pair_mul error!" << endl;return result;}int new_pow = p1.second + p2.second;result.first = new_coeff;result.second = new_pow;return result;
}vector<pair<Complex*, int>> element_mul(vector<pair<Complex*, int>> element1, vector<pair<Complex*, int>> element2)
{ vector<pair<Complex*, int>> result;if (element1.size() <= 0 || element2.size() <= 0){cout << "element_mul error!" << endl;return result;}for (int i = 0; i < element1.size(); i++){pair<Complex*, int> p1 = element1[i];pair<Complex*, int> p;for (int j = 0; j < element2.size(); j++){pair<Complex*, int> p2 = element2[j];p = pair_mul(p1, p2);if (result.size() == 0){result.push_back(p);}else{bool merge_flg = false;for (int k = 0; k < result.size(); k++){// 如果指数一样,就合并if (result[k].second == p.second){result[k].first->real += p.first->real;result[k].first->img += p.first->img;free(p.first);p.first = NULL;p.second = 0;merge_flg = true;break;}}if (!merge_flg){result.push_back(p);}}}}return result;
}vector<pair<Complex*, int>> zp2tf(vector<Complex*> poles)
{vector<pair<Complex*, int>> tf; // pair 的 first代表极点形式H(s)的分母展开后的每一项的系数,second 代表每一项的指数if (poles.size() <= 0){return tf;}// 先构造 n 个 (s-极点)vector<vector<pair<Complex*, int>>> elements(poles.size());for (int i = 0; i < poles.size(); i++){vector<pair<Complex*, int>> element;pair<Complex*, int> e1;Complex* c1 = (Complex*)malloc(sizeof(Complex));c1->real = -1.0 * poles[i]->real;c1->img = -1.0 * poles[i]->img;e1 = make_pair(c1, 0);// -1.0 * 极点element.push_back(e1);pair<Complex*, int> e2;Complex* c2 = (Complex*)malloc(sizeof(Complex));c2->real = 1.0;c2->img = 0.0;e2 = make_pair(c2, 1);// selement.push_back(e2);elements[i] = element;}if (elements.size() == 1){return elements[0];}// 再将 n 个 (s-极点) 乘起来vector<pair<Complex*, int>> element = elements[0];for (int i = 1; i < poles.size(); i++){vector<pair<Complex*, int>> result = element_mul(element, elements[i]);if (result.size() <= 0){return tf;}element = result;}return element;
}
4. 测试结果
4.1 测试文件
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <vector>
#include "buttap.h"
#include "zp2tf.h"
using namespace std;#define pi ((double)3.141592653589793)int main()
{vector<Complex*> poles = buttap(4);for (int i = 0; i < poles.size(); i++){printf("%.15lf, %.15lf\\n", poles[i]->real, poles[i]->img);}vector<pair<Complex*, int>> tf = zp2tf(poles);return 0;
}
4.2 测试结果
3阶模拟低通巴特沃斯滤波器

8阶模拟低通巴特沃斯滤波器

结果与 matlab 均一致,大家可以自行验证
