算法:什么是队列 用两个栈实现一个队列

题目
用两个栈实现一个队列。
队列、栈是一类,都是抽象模型
数组、链表是一类,都是具体实现
队列
逻辑结构,抽象模型,可以用任何语言来实现
- 先进先出
- add、delete、length
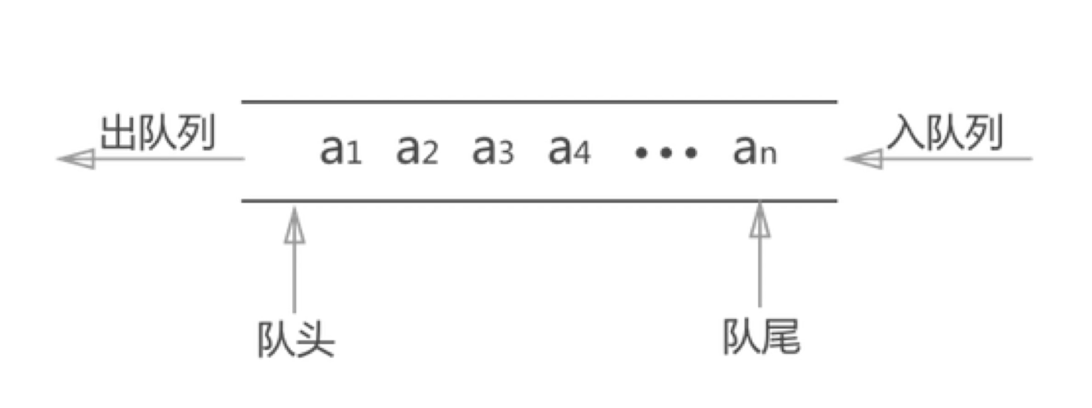
用数组来模拟
const queue = []
// 入队
queue.push(1)
queue.push(2)
queue.push(3)
...// 出队
queue.shift()
shift 性能不好,用数组实现队列肯定是不好的,我们先不管。后面用链表实现队列就不会有性能问题了。
简单的队列可以用数组、链表实现,复杂的队列服务需要单独设计,比如消息队列MQ
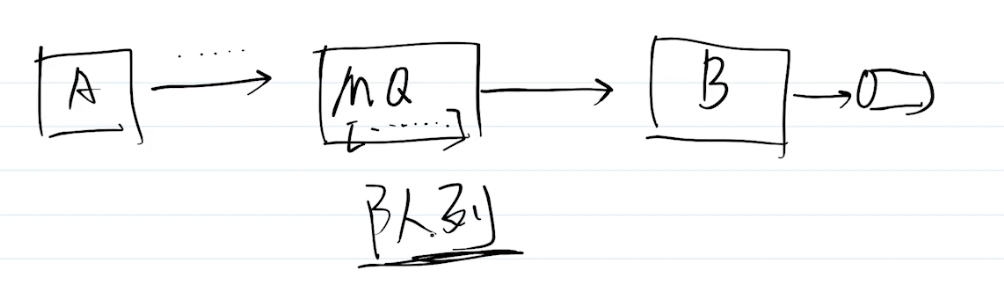
其实就是消息生产端把消息 A 发送到队列MQ中,消费者B来消费,比如存数据库或者数据分析等等。
思路
删除:
有两个 stack。
先让原始队列的数据入栈stack1,比如这时栈里是

队列A先进先出,那么我们需要把stack1中的C、B依次放入stack2中,然后让stack1中的A出栈,再把stack2重新入栈到stack1。
添加:
直接给stack1 push就行
代码
export class MyQueue {private stack1: number[] = []private stack2: number[] = []/* 入队* @param n n*/add(n: number) {this.stack1.push(n)}/* 出队*/delete(): number | null {let resconst stack1 = this.stack1const stack2 = this.stack2// 将 stack1 所有元素移动到 stack2 中while(stack1.length) {const n = stack1.pop()if (n != null) {stack2.push(n)}}// stack2 popres = stack2.pop()// 将 stack2 所有元素“还给”stack1while(stack2.length) {const n = stack2.pop()if (n != null) {stack1.push(n)}}return res || null}get length(): number {return this.stack1.length}
}
// 功能测试
const q = new MyQueue()
q.add(100)
q.add(200)
q.add(300)
console.info(q.length)
console.info(q.delete())
console.info(q.length)
console.info(q.delete())
console.info(q.length)
单元测试
import { MyQueue } from './two-stacks-one-queue'describe('两个栈,一个队列', () => {it('add and length', () => {const q = new MyQueue()expect(q.length).toBe(0)q.add(100)q.add(200)q.add(300)expect(q.length).toBe(3)})it('delete', () => {const q = new MyQueue()expect(q.delete()).toBeNull()q.add(100)q.add(200)q.add(300)expect(q.delete()).toBe(100)expect(q.length).toBe(2)expect(q.delete()).toBe(200)expect(q.length).toBe(1)})
})时间复杂度
add函数:O(1)
delete函数:O(n)


