6.【动手学深度学习v2】 矩阵计算

6. 矩阵计算【动手学深度学习v2】
李沐
B站:https://space.bilibili.com/1567748478/channel/seriesdetail?sid=358497
课程主页:https://courses.d2l.ai/zh-v2/
教材:https://zh-v2.d2l.ai/
课件:https://courses.d2l.ai/zh-v2/assets/pdfs/part-0_6.pdf
参考:https://zh-v2.d2l.ai/chapter_preliminaries/calculus.html#subsec-calculus-grad
1. 标量
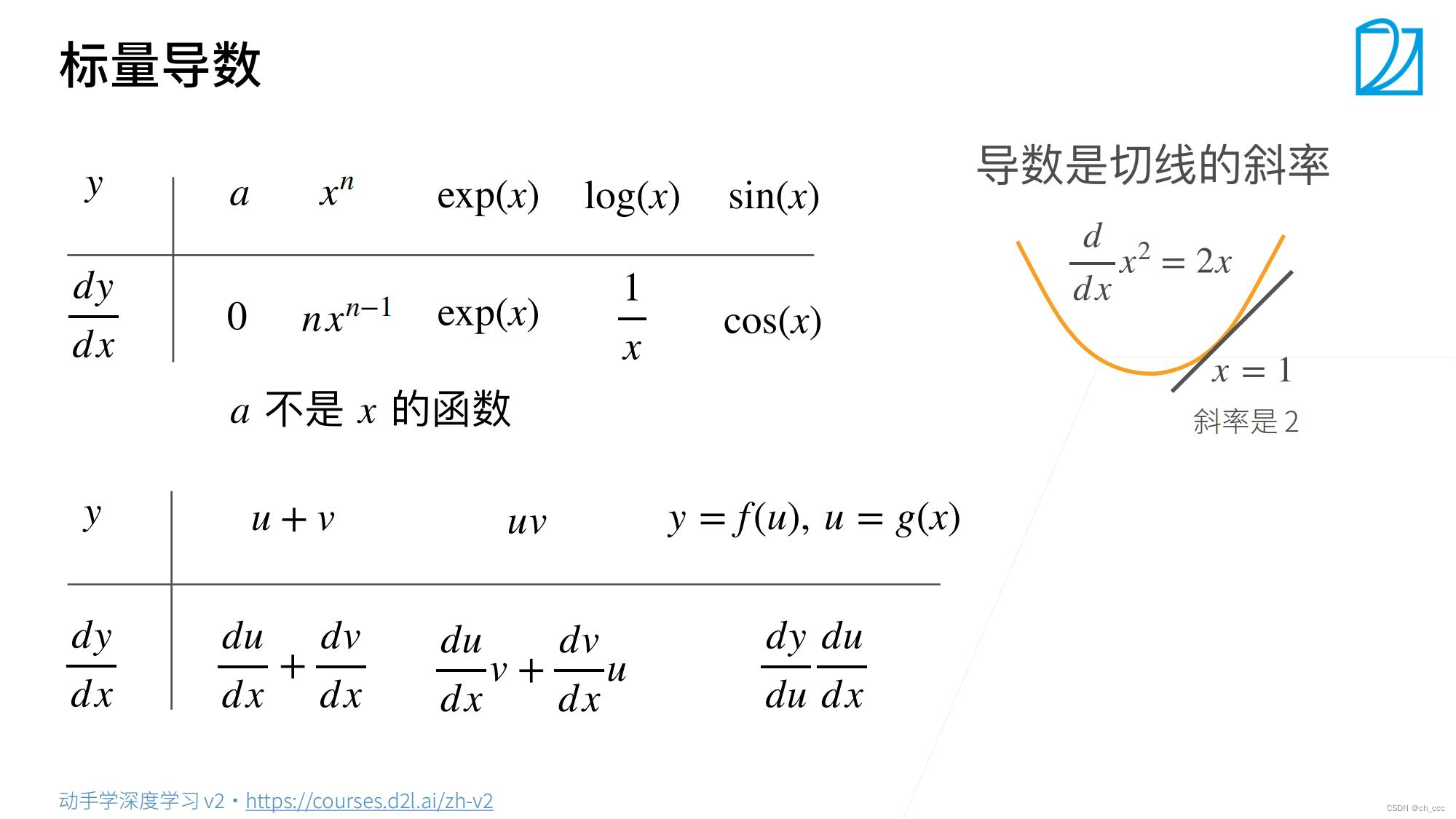
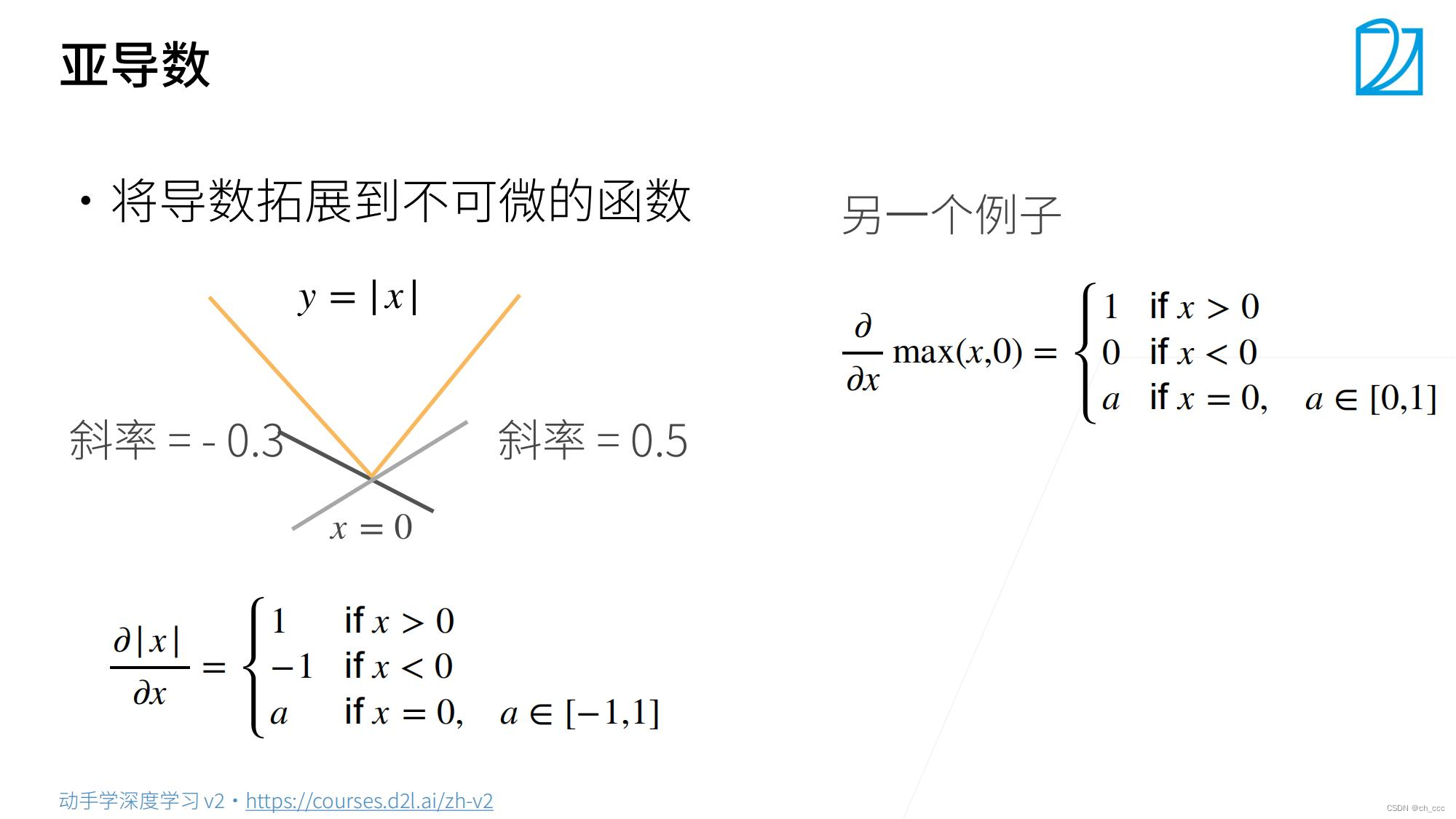
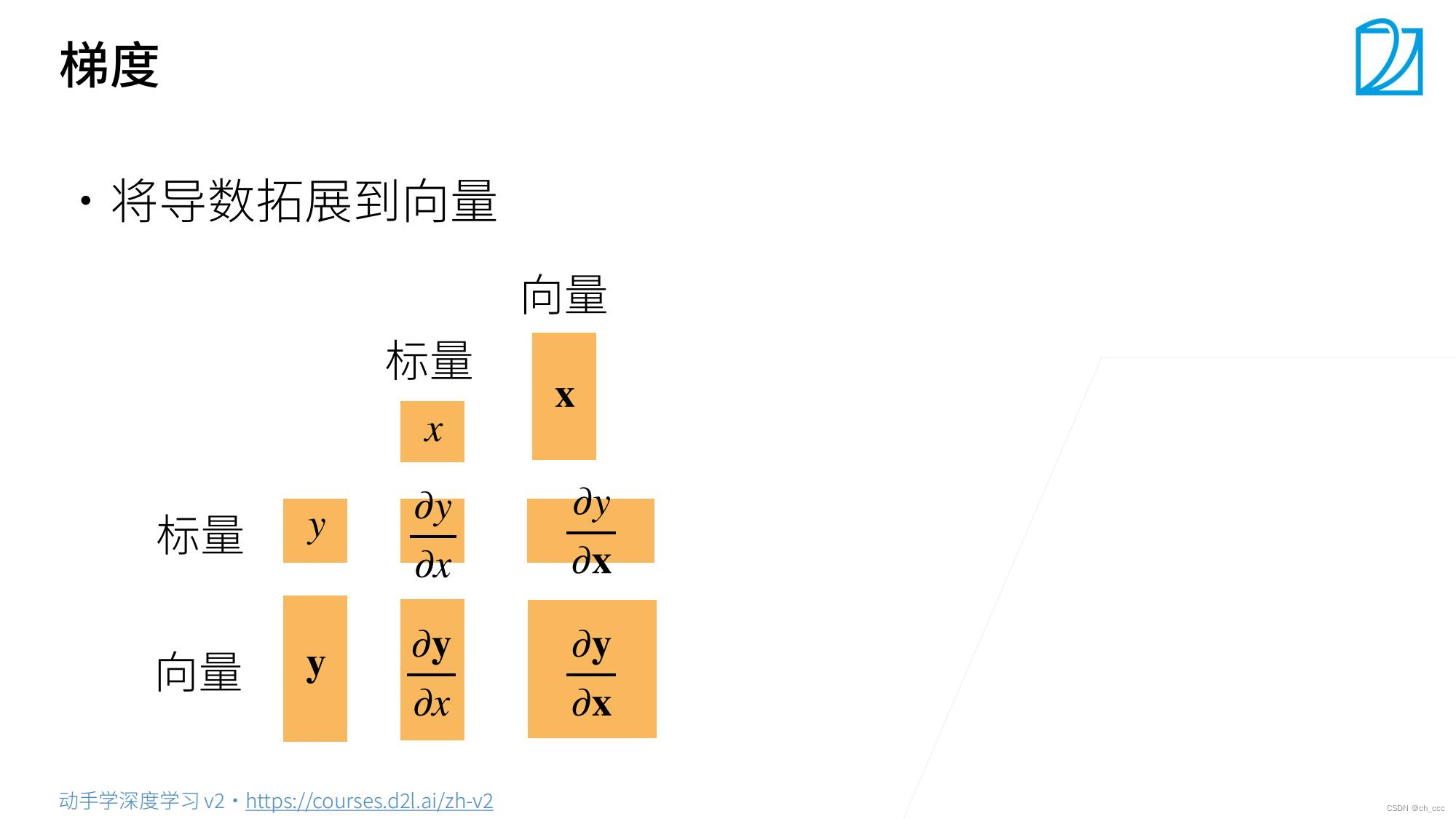
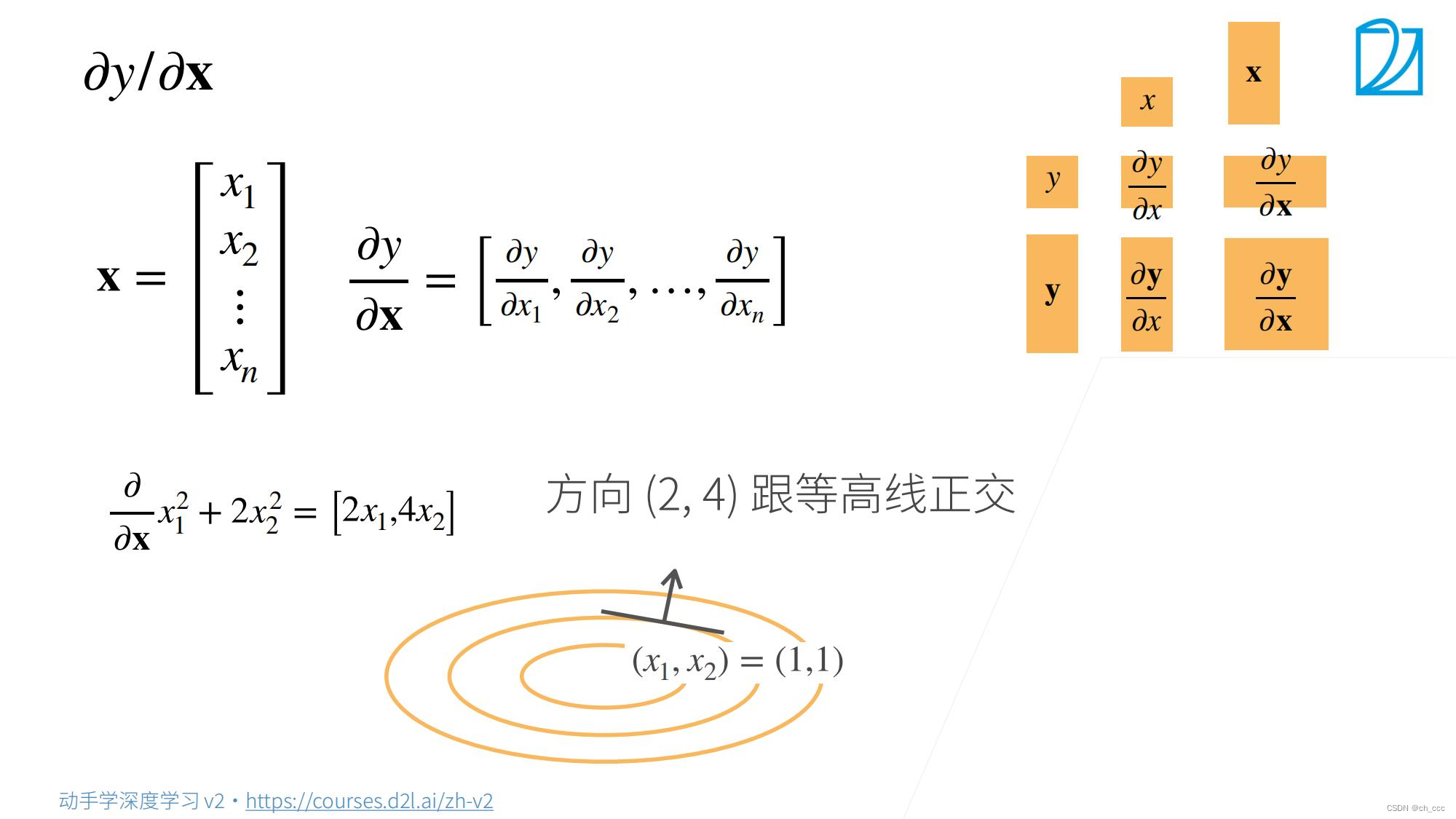
2.标量对向量求导
XXX是一个列向量,偏导数之后得到行向量。
标量/向量,要从列向量变为行向量 。(torch中更没有行列向量区别)
3. 向量对标量求导
列向量还是行向量——>不变
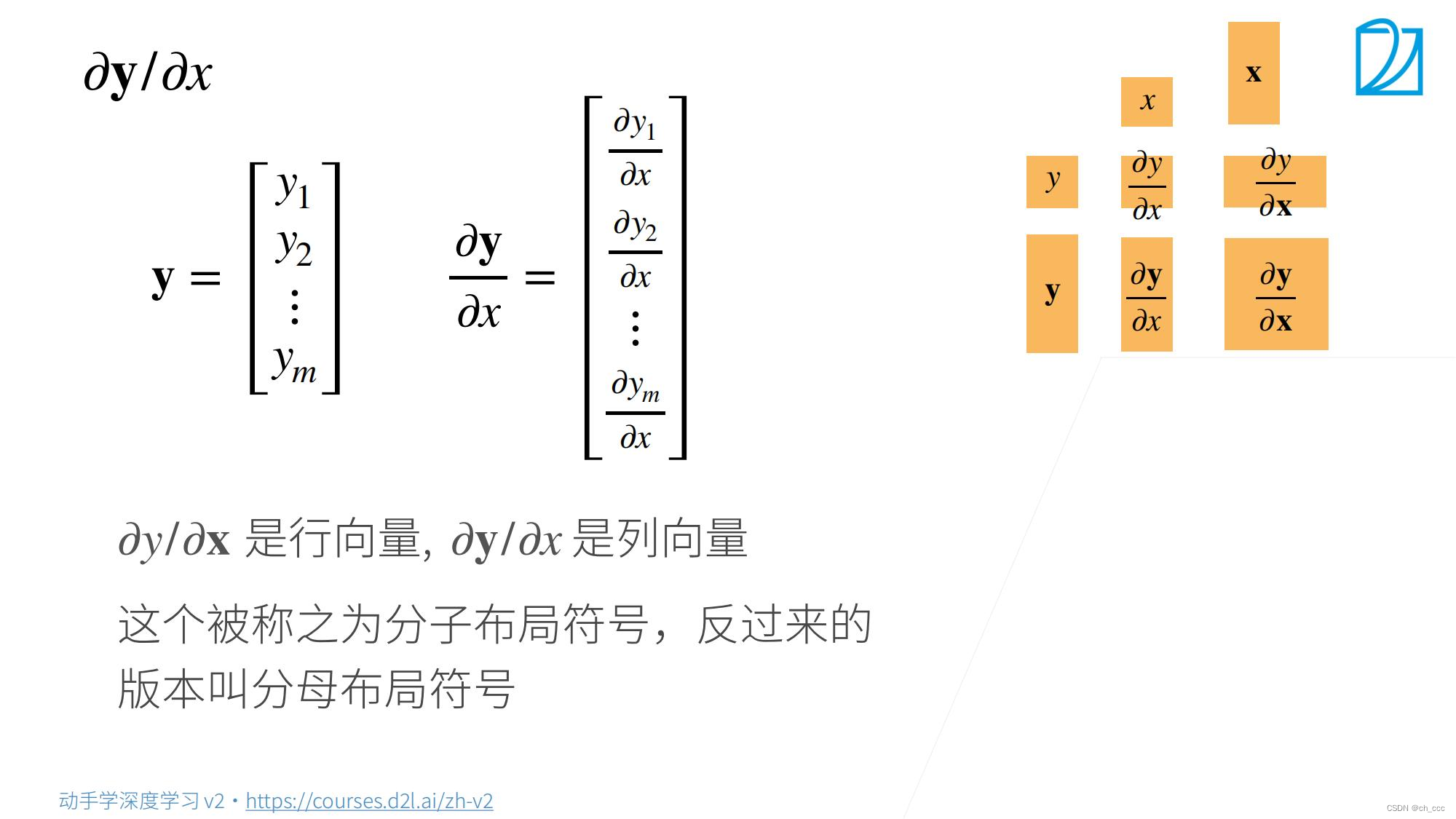
4. 向量对向量求导
综合2、3步骤;
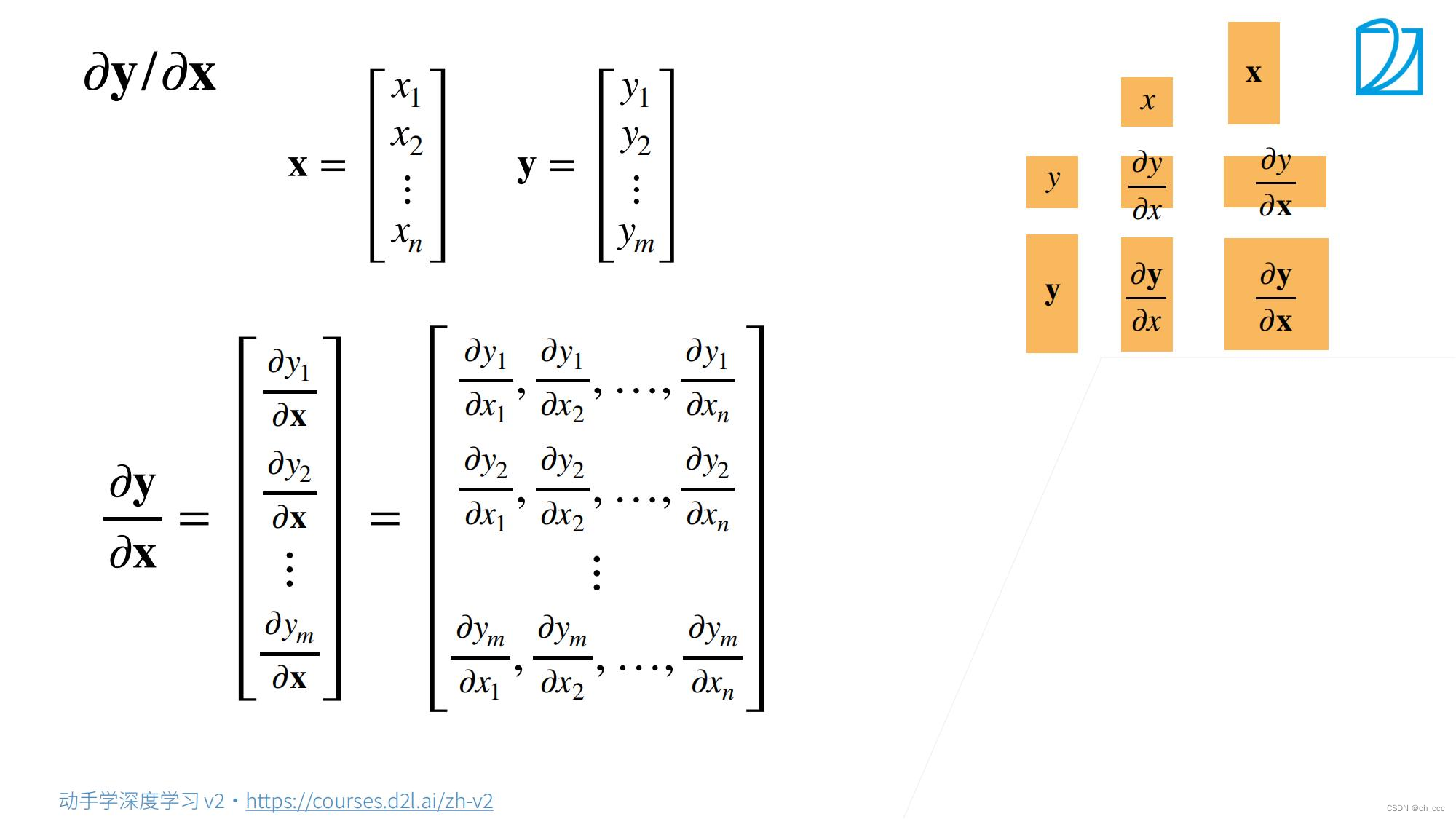
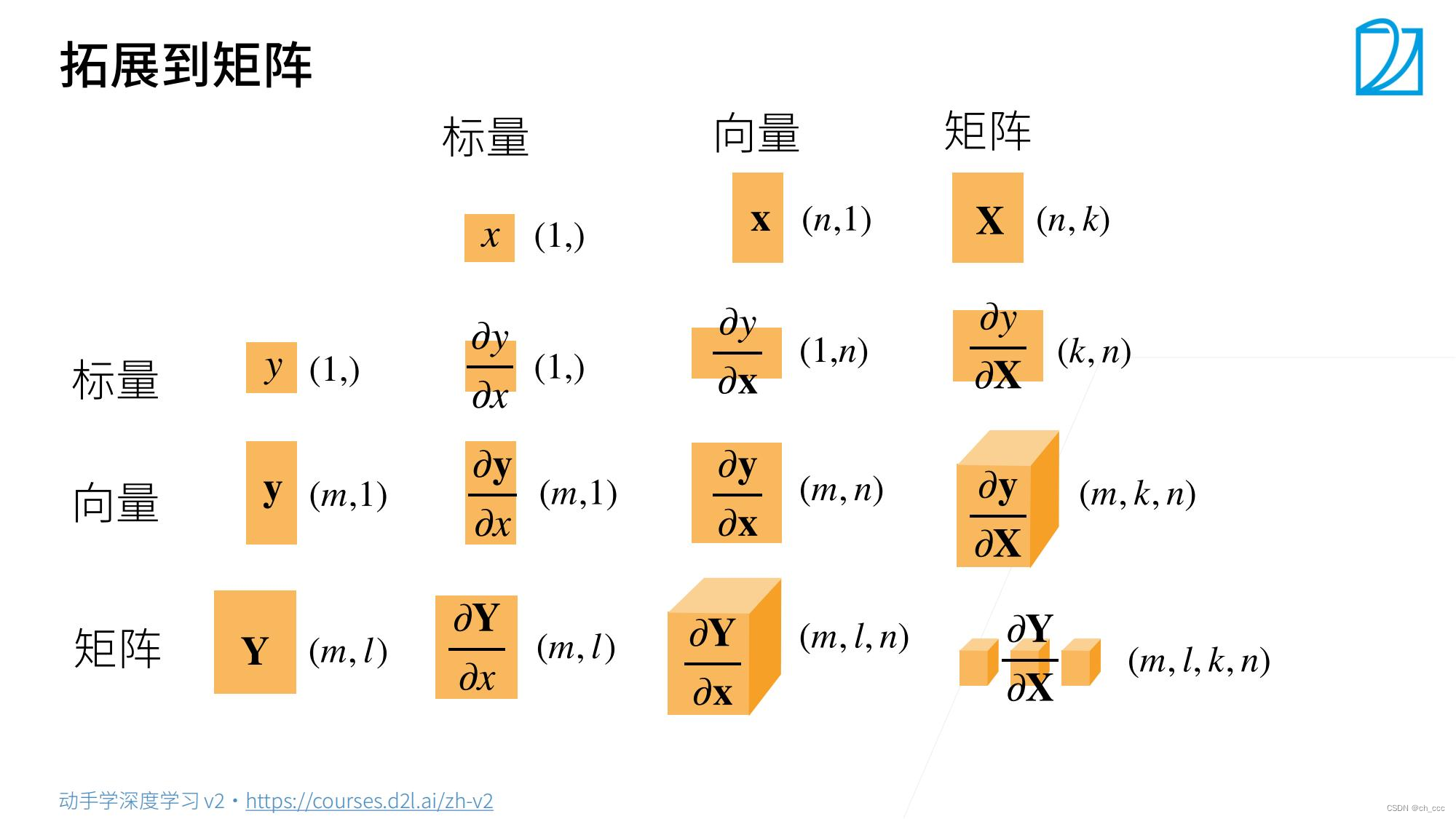
5. 梯度和导数
6. 正向和反向计算
计算中忽略了参数bbb。
x2=w1∗x1+by=w2∗x2+bL=Y−yx_2 = w_1*x_1+b \\\\ y = w_2*x_2+b \\\\ L = Y-y x2=w1∗x1+by=w2∗x2+bL=Y−y
∂L∂x1=∂L∂y∂y∂x2∂x2∂x1∂L∂w1=∂L∂y∂y∂x2∂x2∂w1∂L∂w2=∂L∂y∂y∂w2\\frac{\\partial L}{\\partial x_1} = \\frac{\\partial L}{\\partial y} \\frac{\\partial y}{\\partial x_2} \\frac{\\partial x_2}{\\partial x_1} \\\\ \\frac{\\partial L}{\\partial w_1} = \\frac{\\partial L}{\\partial y} \\frac{\\partial y}{\\partial x_2} \\frac{\\partial x_2}{\\partial w_1} \\\\ \\frac{\\partial L}{\\partial w_2} = \\frac{\\partial L}{\\partial y} \\frac{\\partial y}{\\partial w_2} ∂x1∂L=∂y∂L∂x2∂y∂x1∂x2∂w1∂L=∂y∂L∂x2∂y∂w1∂x2∂w2∂L=∂y∂L∂w2∂y
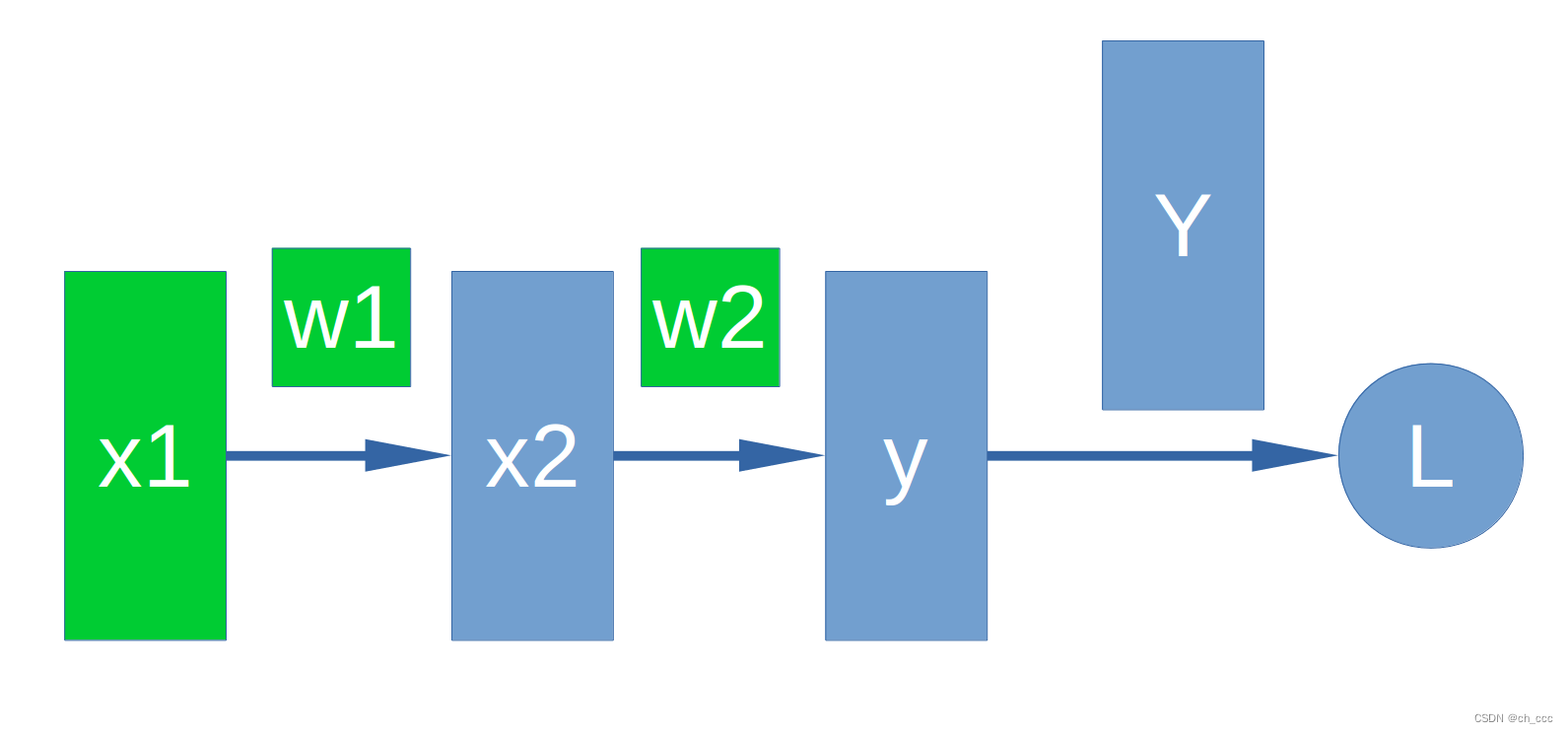
# 实例2
# 正向计算
x1 = torch.from_numpy( 2*np.ones((2, 2), dtype=np.float32) )
x1.requires_grad_(True) #设置该tensor可被记录操作用于梯度计算
w1 = torch.from_numpy( 5*np.ones((2, 2), dtype=np.float32) )
w1.requires_grad_(True)
print("x1 =", x1,",x1 shape:",x1.shape)
print("w1 =", w1)x2 = x1 * w1
w2 = torch.from_numpy( 6*np.ones((2,2), dtype=np.float32) )
w2.requires_grad_(True)
print("x2 =", x2)
print("w2 =", w2)y = x2 * w2
Y = torch.from_numpy( 10*np.ones((2,2), dtype=np.float32) )
print("y =", y)
print("Y =", Y)L = Y - y# 反向计算
L.backward(torch.ones(2,2,dtype=torch.float32))
print("x1 grad:",x1.grad)
print("w1 grad:",w1.grad)
print("w2 grad:",w2.grad)# x1 = tensor([[2., 2.],
# [2., 2.]], requires_grad=True) ,x1 shape: torch.Size([2, 2])
# w1 = tensor([[5., 5.],
# [5., 5.]], requires_grad=True)
# x2 = tensor([[10., 10.],
# [10., 10.]], grad_fn=<MulBackward0>)
# w2 = tensor([[6., 6.],
# [6., 6.]], requires_grad=True)
# y = tensor([[60., 60.],
# [60., 60.]], grad_fn=<MulBackward0>)
# Y = tensor([[10., 10.],
# [10., 10.]])
# x1 grad: tensor([[-30., -30.],
# [-30., -30.]])
# w1 grad: tensor([[-12., -12.],
# [-12., -12.]])
# w2 grad: tensor([[-10., -10.],
# [-10., -10.]])


