循环队列、双端队列 C和C++

队列
目录
概念
实现方式
顺序队列
循环队列
队列的数组实现
用循环链表实现队列
STL 之 queue 实现队列
STL 之 dequeue 实现双端队列
概念
队列是一种特殊的线性表,它只允许在表的前端(称为队头,front)进行删除操作——出队,而在表的后端(称为队尾,rear)进行插入操作——入队,是一种操作受限的线性表。
最先进入队列的元素最先被删除,是“先进先出”的线性表。
实现方式
- 数组
- 链表
- C++ 中可以使用 STL 中的 queue 实现
- 其中 STL 中还包括双端队列 dequeue
顺序队列
必须静态分配或者动态申请空间,并设置两个指针管理,一个是队头指针 front(指向队头元素),另一个是队尾指针 rear(指向下一个入队元素的存储位置)。
队空的判断条件是:front==rear,队满的条件为:rear==MAXQSIZE。
循环队列
为了使队列空间可以重复使用,可以对循环队列进行改进,无论是插入或者删除,一旦 rear 指针或者 front 指针超出了所分配的队列空间,就让它指向这篇连续空间的起始位置,自己从 MAXQSIZE 增 1 变为 1,可以用取余运算实现: (rear+1)%MAXQSIZE、 (front+1)%MAXQSIZE.
其中队空的判断条件为:front==rear,队满的条件为:(rear+1)%MAXQSIZE==front。
队列的数组实现
定义一个结构体实现队列:
struct node {int* data;int front;int rear;
};初始化队列:(将队头和队尾指针都赋为 1),数组长度为 MAXQSIZE,开辟一块空间为 MAXQSIZE-1 的数组:
//为队列开辟空间并初始化(也可以在结构体中定义int data[MAXQSIZE])
void InitQueue(struct node& Q) {Q.rear = 1;Q.front = 1;Q.data = (int*)malloc(MAXQSIZE+1 * sizeof(int));
}入队:
//入队
int EnQueue(struct node &Q,int y) {if (Q.rear != MAXQSIZE) {Q.data[Q.rear] = y;Q.rear++;return 1;}return 0;
}出队:
//出队
int DeQueue(struct node& Q, int &y) {if (Q.rear != Q.front){y = Q.data[Q.front];Q.front++;return 1;}return 0;
}总代码为:
//数组实现队列
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define MAXQSIZE 100
int queue[MAXQSIZE];
struct node {int* data;int front;int rear;
};
//为队列开辟空间并初始化(也可以在结构体中定义int data[MAXQSIZE])
void InitQueue(struct node& Q) {Q.rear = 1;Q.front = 1;Q.data = (int*)malloc(MAXQSIZE+1 * sizeof(int));
}
//入队
int EnQueue(struct node &Q,int y) {if (Q.rear != MAXQSIZE) {Q.data[Q.rear] = y;Q.rear++;return 1;}return 0;
}
//出队
int DeQueue(struct node& Q, int &y) {if (Q.rear != Q.front){y = Q.data[Q.front];Q.front++;return 1;}return 0;
}
int main() {int n;int x, y;struct node Q;InitQueue(Q);//以1开头为插入(插入操作输入两个数),以0开头为删除printf("输入操作个数:(以1开头为插入(插入操作输入两个数),以0开头为删除)\\n");scanf("%d", &n);while (n--) {printf("输入操作:");scanf("%d", &x);if (x == 1){scanf("%d", &y);if (EnQueue(Q, y))printf("入队成功\\n");elseprintf("入队失败\\n");}else if (x == 0){if (DeQueue(Q, y) == 0)printf("出队失败\\n");elseprintf("出队的元素为:%d\\n",y);}else{printf("输入正确的操作\\n");n++;}}return 0;
}用循环链表实现队列
不用循环时将初始化时的 Q->next=Q 删去。
以带头结点的循环链表表示队列,并且只设一个指针指向队尾结点,不设头指针。
定义一个结构体:
struct node {int data;struct node* next;
};入队:
//入队
void EnQueue(struct node* Q, int y) {struct node* p;p = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));p->data = y;p->next = Q->next;Q->next = p;Q = p;
}出队:
//出队
int DeQueue(struct node* Q, int& y) {if (Q->next == Q)return 0;struct node* p;p = Q->next;y = p->data;Q->next = p->next;free(p);return 1;
}总代码:
//以带头结点的循环链表表示队列,
//并且只设一个指针指向队尾结点,不设头指针。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct node {int data;struct node* next;
};
//循环队列的初始化
void InitQueue(struct node* Q) {Q->next = Q;//初始化循环队列
}
//入队
void EnQueue(struct node* Q, int y) {struct node* p;p = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));p->data = y;p->next = Q->next;Q->next = p;Q = p;
}
//出队
int DeQueue(struct node* Q, int& y) {if (Q->next == Q)return 0;struct node* p;p = Q->next;y = p->data;Q->next = p->next;free(p);return 1;
}
int main() {struct node* Q;Q = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));InitQueue(Q);printf("输入操作个数:(以1开头为插入(插入操作输入两个数),以0开头为删除)\\n");int x, y, n;scanf("%d", &n);while(n--){printf("输入操作:");scanf("%d", &x);if(x==1){scanf("%d", &y);EnQueue(Q, y);printf("入队成功\\n");}else if(x==0){if (DeQueue(Q, y) == 1)printf("%d\\n", y);elseprintf("出队失败\\n");}}return 0;
}STL 之 queue 实现队列
要加上头文件:#include<queue>
对应的函数: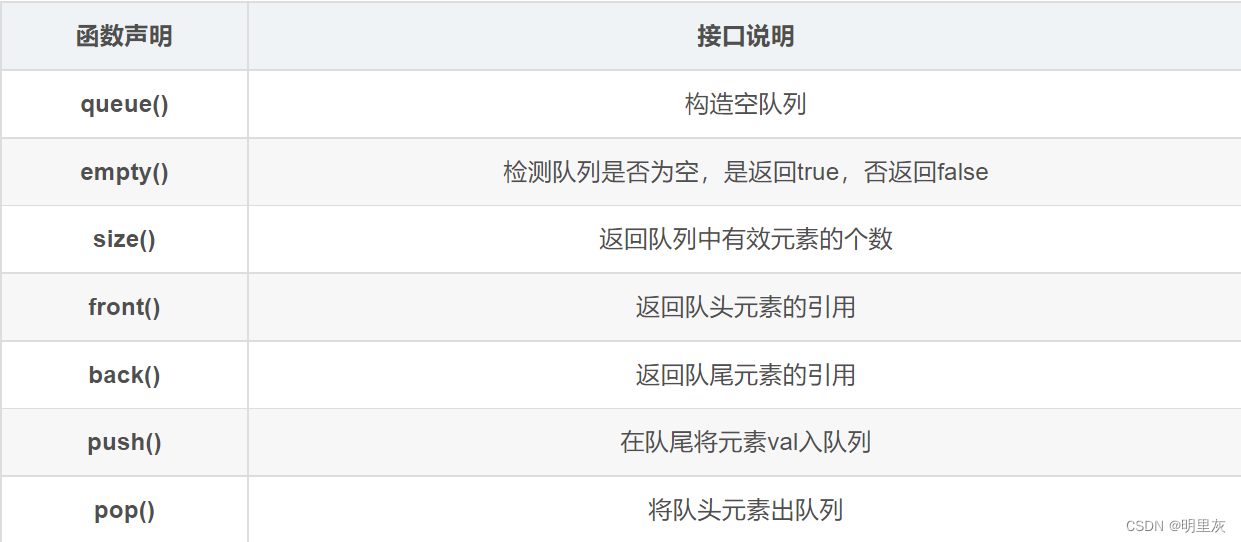
构造空队列:
queue<int>q;总代码:
//用queue函数实现队列
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int main() {queue<int>q;int n;int x, y;printf("输入操作个数:");scanf("%d", &n);printf("以1开头为插入(插入操作输入两个数),以0开头为删除\\n");while (n--) {scanf("%d", &x);if (x == 1) {scanf("%d", &y);q.push(y);}else if(x==0){if (!q.empty()) {//判断队列不为空printf("%d\\n", q.front());q.pop();}elseprintf("出队失败\\n");}else{printf("输入正确的操作\\n");n++;}printf("队列中元素个数为:%d\\n", q.size());}return 0;
}STL 之 dequeue 实现双端队列
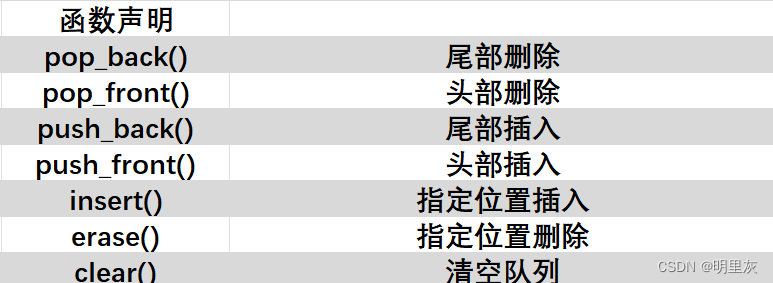
//用dequeue实现双端队列
#include<iostream>
#include<deque>
using namespace std;
struct node {int *data;
}Q;
int main() {deque<int>q(10);deque<int>::iterator idex;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {q[i] = i;}for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {printf("%d ", q[i]);}printf("\\n");//在头尾加入新元素printf("加入新元素后:\\n");q.push_back(100);//加入队尾q.push_front(10);//加入队头printf("输出deque的数据:\\n");for (idex = q.begin(); idex != q.end(); idex++) {printf("%d ", *idex);}printf("\\n");//查找int x = 5;idex = find(q.begin(), q.end(), x);if (idex != q.end())printf("找到%d元素\\n",x);elseprintf("队列中没有%d元素\\n",x);//在头尾删除数据q.pop_back();//删除队尾q.pop_front();//删除队头printf("输出deque的数据:\\n");for (idex = q.begin(); idex != q.end(); idex++) {printf("%d ", *idex);}return 0;
}