IGA_PLSM3D的理解1

文章目录
- 前言
- 一、IgaTop3D_FAST.m给的参数
- 二、Material properties 材料特性
-
- 对Geom_Mod3D的理解
- 对Pre_IGA3D的理解
-
- 输出1-----CtrPts:
- 输出2-----Ele:
- 输出3-----GauPts:
前言
只是为方便学习,不做其他用途
一、IgaTop3D_FAST.m给的参数
%老师给的初始参数:IgaTop3D_FAST(32,8,16,[1 1 1],[32 8 16], 1,0.3,1.2);
clear;
% clc;
L = 32;
W = 8;
H = 16;
Order = [1 1 1];
Num = [32 8 16];
BoundCon = 1;
Vmax = 0.3;
rmin = 1.2;
二、Material properties 材料特性
path = genpath(pwd); %系统自带函数 :PWD显示当前工作目录
addpath(path);
E0 = 1; Emin = 1e-3; nu = 0.3;
DH=E0*(1-nu)/(1+nu)/(1-2*nu)*...[1 nu/(1-nu) nu/(1-nu) 0 0 0;nu/(1-nu) 1 nu/(1-nu) 0 0 0; nu/(1-nu) nu/(1-nu) 1 0 0 0;0 0 0 (1-2*nu)/2/(1-nu) 0 0;0 0 0 0 (1-2*nu)/2/(1-nu) 0;0 0 0 0 0 (1-2*nu)/2/(1-nu)];
NURBS = Geom_Mod3D(L, W, H, Order, Num, BoundCon); close all
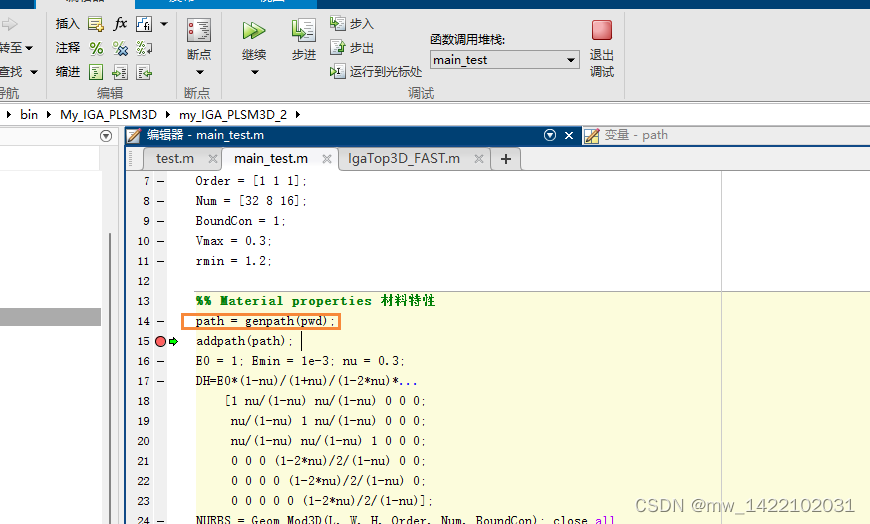
path =
D:\\Matlab\\bin\\My_IGA_PLSM3D\\my_IGA_PLSM3D_2;
D:\\Matlab\\bin\\My_IGA_PLSM3D\\my_IGA_PLSM3D_2\\Results;
D:\\Matlab\\bin\\My_IGA_PLSM3D\\my_IGA_PLSM3D_2\\nurbs1.3.13;
D:\\Matlab\\bin\\My_IGA_PLSM3D\\my_IGA_PLSM3D_2\\nurbs1.3.13\\inst;
D:\\Matlab\\bin\\My_IGA_PLSM3D\\my_IGA_PLSM3D_2\\nurbs-1.3.13\\src;
对Geom_Mod3D的理解
function NURBS = Geom_Mod3D(L, W, H, Order, Num, BoundCon)
switch BoundConcase {1, 2, 3}knots{1} = [0 0 1 1]; knots{2} = [0 0 1 1]; knots{3} = [0 0 1 1];ControlPts(:,:,1,1) = [0 L; 0 0; 0 0; 1 1]; % 下边界:[控制点的X坐标排序;控制点Y坐标排序;控制点Z坐标排序;加权参数坐标排序]ControlPts(:,:,2,1) = [0 L; W W; 0 0; 1 1]; % 上边界:。。。。。ControlPts(:,:,1,2) = [0 L; 0 0; H H; 1 1];ControlPts(:,:,2,2) = [0 L; W W; H H; 1 1];case 4knots{1} = [0 0 0.5 1 1]; knots{2} = [0 0 1 1];ControlPts(:,:,1) = [0 0 L; L 0 0; 0 0 0; 1 1 1];ControlPts(:,:,2) = [W W L; L W W; 0 0 0; 1 1 1];case 5W = W/2;knots{1} = [0 0 0 1 1 1]; knots{2} = [0 0 1 1];ControlPts(:,:,1) = [0 W W; W W 0; 0 0 0; 1 sqrt(2)/2 1]; % 内边界:[控制点1的x,y,z方向坐标;控制点2的xyz坐标,控制点3的xyz坐标]ControlPts(:,:,2) = [0 L L; L L 0; 0 0 0; 1 sqrt(2)/2 1]; % 外边界:。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。
end
coefs = zeros(size(ControlPts));
coefs(1,:,:,:) = ControlPts(1,:,:,:).*ControlPts(4,:,:,:);
coefs(2,:,:,:) = ControlPts(2,:,:,:).*ControlPts(4,:,:,:);
coefs(3,:,:,:) = ControlPts(3,:,:,:).*ControlPts(4,:,:,:);
coefs(4,:,:,:) = ControlPts(4,:,:,:);
NURBS = nrbmak(coefs, knots); % 构造NURBS数据结构
NURBS = nrbdegelev(NURBS,Order); % 升阶
nrbplot(NURBS,[Num(1)-1 Num(2)-1 Num(3)-1]); % ,'light','on') % 绘制设计域几何
iknot_u = linspace(0,1,Num(1)); iknot_v = linspace(0,1,Num(2)); iknot_w = linspace(0,1,Num(3));
NURBS = nrbkntins(NURBS,{setdiff(iknot_u,NURBS.knots{1}),setdiff(iknot_v,NURBS.knots{2}),setdiff(iknot_w,NURBS.knots{3})}); % 插入knots
end
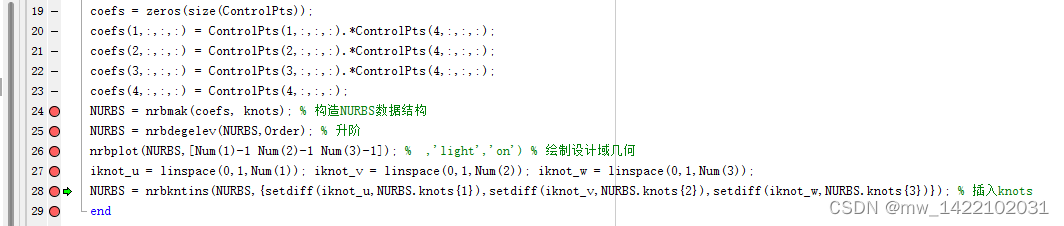
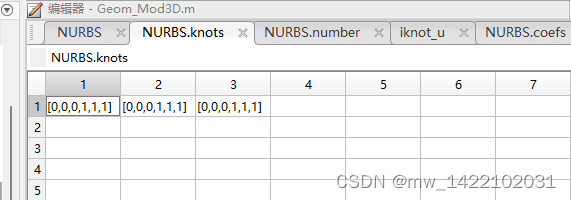
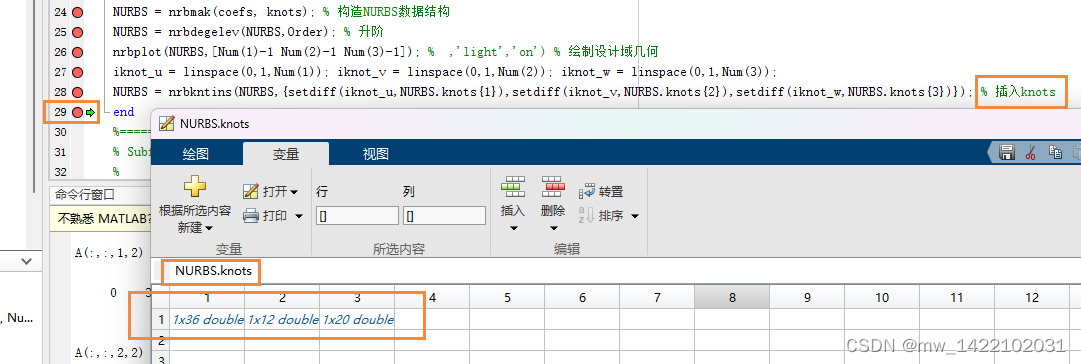
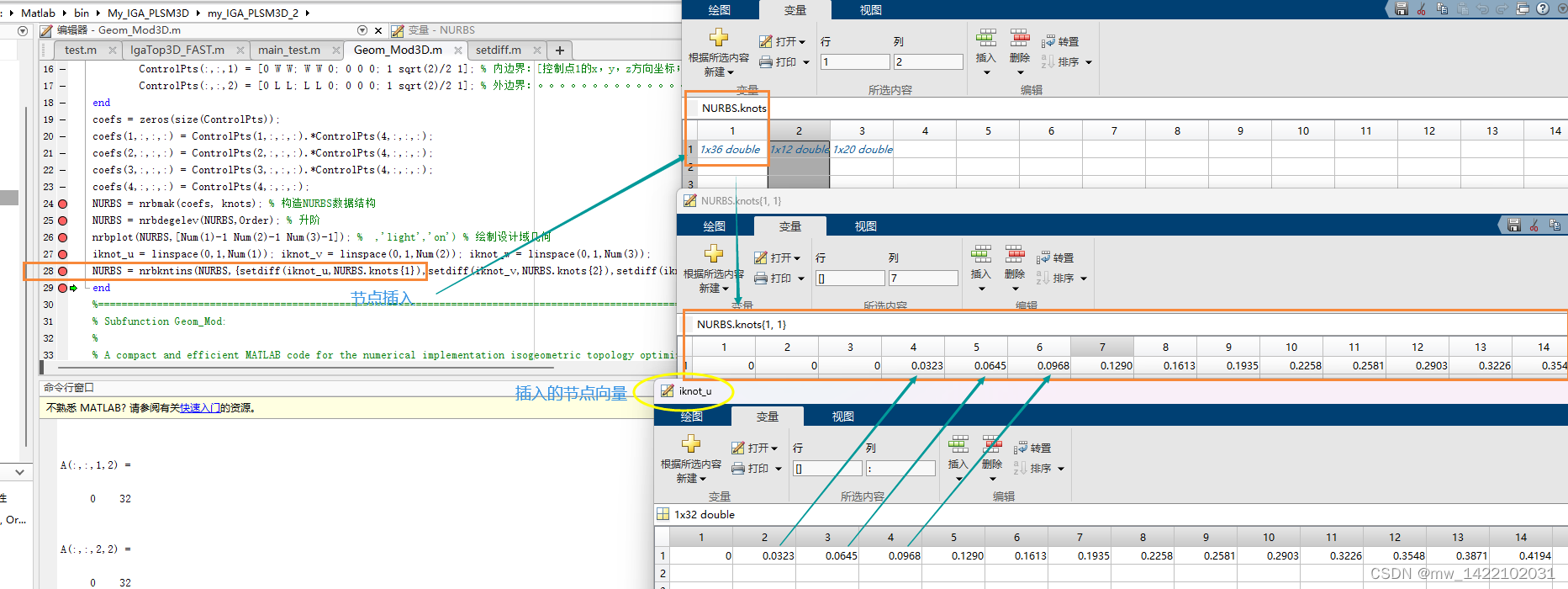
运行完Geom_Mod3D函数后得到一个NURBS体:
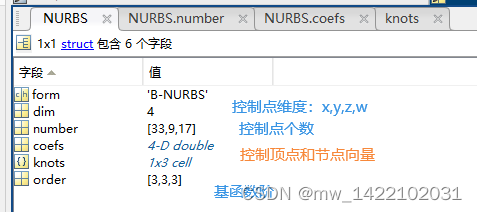
对Pre_IGA3D的理解
function [CtrPts, Ele, GauPts] = Pre_IGA3D(NURBS)
%% 注释
%{目标:生成NURBS实体
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Input:NURBS ---------- 初步生成的NURBS实体Output:CtrPts ---------- NURBS实体的控制点信息Ele ---------- NURBS实体的单元信息GauPts ---------- NURBS实体对应的参数空间中高斯点的信息
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------注:以IgaTop3D_FAST(32,8,16,[1 1 1],[6 4 3], 1,0.3,1.2);为例CtrPts结构体:CtrPts.Cordis ---------- 控制点坐标 4*140CtrPts.Num ---------- 控制点总数 140 CtrPts.NumU ---------- U方向控制点个数 7 CtrPts.NumV ---------- V方向控制点个数 5 CtrPts.Seque ---------- 三个方向控制点对应生成的序列 7*5*4 Ele结构体:CtrPts.NumU/V/W ---------- 分别表示三个方向的区间个数(单元个数)Ele.Num ---------- 单元总数Ele.KnotsU/V/W ---------- 分别表示三个方向去掉重节点的节点向量Ele.CtrPtsNum ---------- 单元上的控制点个数Ele.CtrPtsCon ---------- 单元信息---每个单元包含的全局节点编号GauPts结构体:GauPts.Weigh ---------- 一个单元(3D)上27个控制点在 标准区间[-1,1] 上的高斯权重GauPts.QuaPts ---------- 一个单元(3D)上27个控制点在 标准区间[-1,1] 上的高斯点GauPts.Num ---------- 单元个数*高斯点个数 30*27=810GauPts.Seque ---------- 将GauPts.Num排序---没有理解GauPts.CorU/V/W ---------- 标准高斯单元[-1,1]变换到单元对应的参数域对应生成的高斯点 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 孟伟, 大连理工大学- 1475207248@qq.com / mw21933005@mail.dlut.edu.cn
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
%}
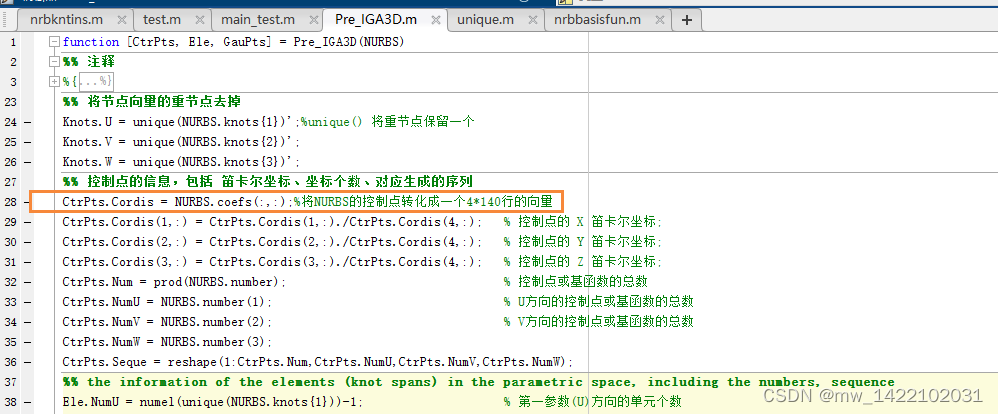
%% 将节点向量的重节点去掉
Knots.U = unique(NURBS.knots{1})';%unique() 将重节点保留一个
Knots.V = unique(NURBS.knots{2})';
Knots.W = unique(NURBS.knots{3})';
%% 控制点的信息,包括 笛卡尔坐标、坐标个数、对应生成的序列
CtrPts.Cordis = NURBS.coefs(:,:);%将NURBS的控制点转化成一个4*140行的向量
CtrPts.Cordis(1,:) = CtrPts.Cordis(1,:)./CtrPts.Cordis(4,:); % 控制点的 X 笛卡尔坐标;
CtrPts.Cordis(2,:) = CtrPts.Cordis(2,:)./CtrPts.Cordis(4,:); % 控制点的 Y 笛卡尔坐标;
CtrPts.Cordis(3,:) = CtrPts.Cordis(3,:)./CtrPts.Cordis(4,:); % 控制点的 Z 笛卡尔坐标;
CtrPts.Num = prod(NURBS.number); % 控制点或基函数的总数
CtrPts.NumU = NURBS.number(1); % U方向的控制点或基函数的总数
CtrPts.NumV = NURBS.number(2); % V方向的控制点或基函数的总数
CtrPts.NumW = NURBS.number(3);
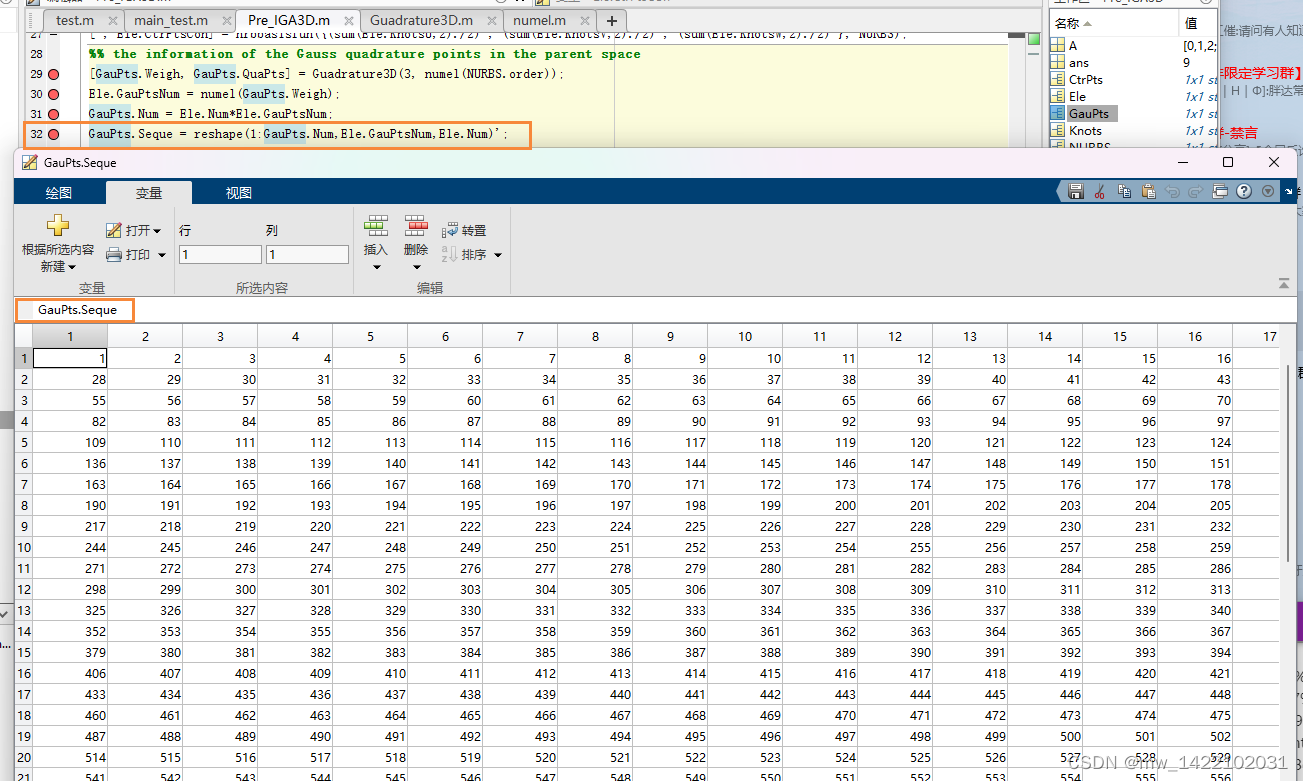
CtrPts.Seque = reshape(1:CtrPts.Num,CtrPts.NumU,CtrPts.NumV,CtrPts.NumW);
%% 参数空间中单元(节点区间)的信息,包括单元个数、单元对应生成的序列
Ele.NumU = numel(unique(NURBS.knots{1}))-1; % 第一参数(U)方向的单元个数
Ele.NumV = numel(unique(NURBS.knots{2}))-1; % 第二参数(V)方向的单元个数
Ele.NumW = numel(unique(NURBS.knots{3}))-1;
Ele.Num = Ele.NumU*Ele.NumV*Ele.NumW; % 单元总数
Ele.Seque = reshape(1:Ele.Num, Ele.NumU, Ele.NumV, Ele.NumW);
Ele.KnotsU = [Knots.U(1:end-1) Knots.U(2:end)]; % 元素在第一参数方向上的唯一节点---不太理解为什么这样分
Ele.KnotsV = [Knots.V(1:end-1) Knots.V(2:end)]; % 元素在第二参数方向上的唯一节点---不过会在划分单元信息的时候用到
Ele.KnotsW = [Knots.W(1:end-1) Knots.W(2:end)];
Ele.CtrPtsNum = prod(NURBS.order);
Ele.CtrPtsNumU = NURBS.order(1); Ele.CtrPtsNumV = NURBS.order(2); Ele.CtrPtsNumW = NURBS.order(3);
[~, Ele.CtrPtsCon] = nrbbasisfun({(sum(Ele.KnotsU,2)./2)', (sum(Ele.KnotsV,2)./2)', (sum(Ele.KnotsW,2)./2)'}, NURBS);
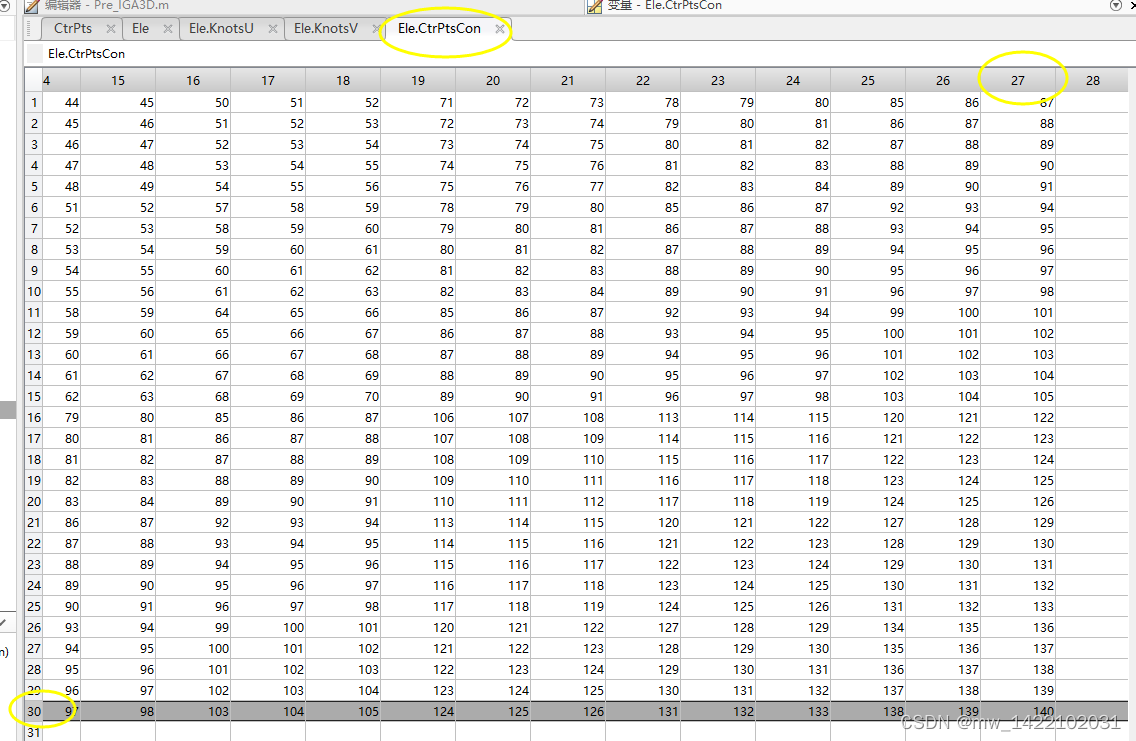
% Ele.CtrPtsCon: 单元信息---每个单元包含的全局节点编号
% [B, id] = nrbbasisfun (points, nrb) ----自己感觉 id表示控制点的全局编号 具体原理不理解
%% 参数空间中高斯正交点的信息
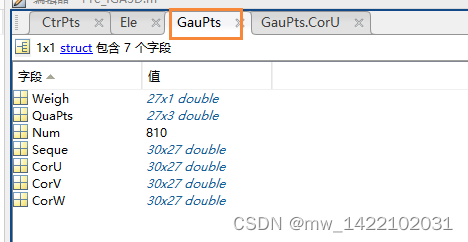
[GauPts.Weigh, GauPts.QuaPts] = Guadrature3D(3, numel(NURBS.order));
%[GauPts.Weigh, GauPts.QuaPts]: 一个单元(3D)上27个控制点的 标准区间[-1,1] 上的高斯权重和高斯点
Ele.GauPtsNum = numel(GauPts.Weigh); %高斯点个数 numel(A):表示A中矩阵元素总数 A的行数 * A的列数
GauPts.Num = Ele.Num*Ele.GauPtsNum;
GauPts.Seque = reshape(1:GauPts.Num,Ele.GauPtsNum,Ele.Num)';
GauPts.CorU = zeros(Ele.Num,Ele.GauPtsNum); % GauPts.CorU矩阵大小: 单元数*高斯点个数
GauPts.CorV = zeros(Ele.Num,Ele.GauPtsNum); % 第i行,表示 变换到单元对应的参数域 对应生成的高斯点
GauPts.CorW = zeros(Ele.Num,Ele.GauPtsNum);
for ide = 1:Ele.Num % ide:第ide个单元idw = ceil(ide/Ele.NumU/Ele.NumV);idv = ceil((ide - (idw-1)*Ele.NumU*Ele.NumV)/Ele.NumU);idu = ide - (idw-1)*Ele.NumU*Ele.NumV - (idv-1)*Ele.NumU;
% [idv, idu] = find(Ele.Seque == ide); % The two idices in two parametric directions for an elementEle_Knot_U = Ele.KnotsU(idu,:); % The knot span in the first parametric direction for an elementEle_Knot_V = Ele.KnotsV(idv,:); % The knot span in the second parametric direction for an elementEle_Knot_W = Ele.KnotsW(idw,:);for i = 1:Ele.GauPtsNumGauPts.CorU(ide,i) = ((Ele_Knot_U(2)-Ele_Knot_U(1)).*GauPts.QuaPts(i,1) + (Ele_Knot_U(2)+Ele_Knot_U(1)))/2;%单元上的高斯点GauPts.CorV(ide,i) = ((Ele_Knot_V(2)-Ele_Knot_V(1)).*GauPts.QuaPts(i,2) + (Ele_Knot_V(2)+Ele_Knot_V(1)))/2;GauPts.CorW(ide,i) = ((Ele_Knot_W(2)-Ele_Knot_W(1)).*GauPts.QuaPts(i,3) + (Ele_Knot_W(2)+Ele_Knot_W(1)))/2;end
end
end输出1-----CtrPts:
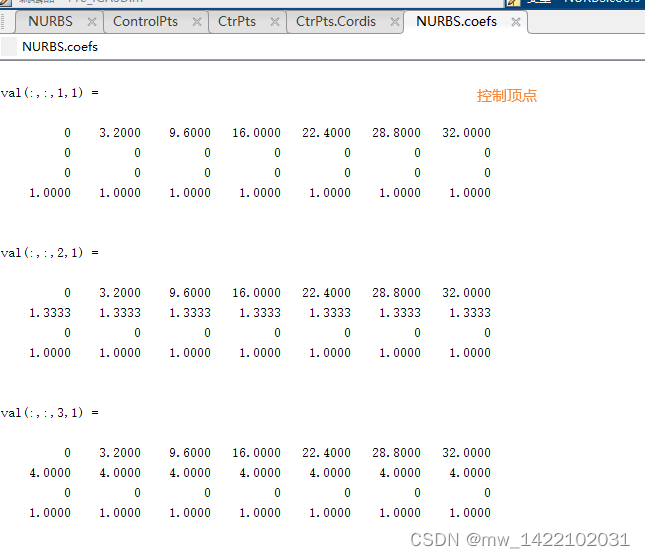
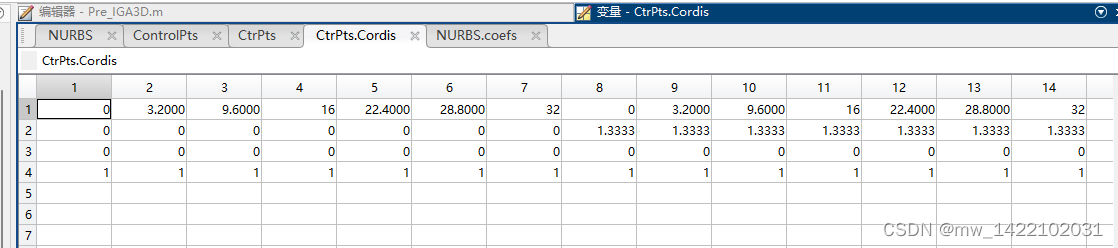
%% 将节点向量的重节点去掉
Knots.U = unique(NURBS.knots{1})';%unique() 将重节点保留一个
Knots.V = unique(NURBS.knots{2})';
Knots.W = unique(NURBS.knots{3})';
%% 控制点的信息,包括 笛卡尔坐标、坐标个数、对应生成的序列
CtrPts.Cordis = NURBS.coefs(:,:);%将NURBS的控制点转化成一个4*140行的向量
CtrPts.Cordis(1,:) = CtrPts.Cordis(1,:)./CtrPts.Cordis(4,:); % 控制点的 X 笛卡尔坐标;
CtrPts.Cordis(2,:) = CtrPts.Cordis(2,:)./CtrPts.Cordis(4,:); % 控制点的 Y 笛卡尔坐标;
CtrPts.Cordis(3,:) = CtrPts.Cordis(3,:)./CtrPts.Cordis(4,:); % 控制点的 Z 笛卡尔坐标;
CtrPts.Num = prod(NURBS.number); % 控制点或基函数的总数
CtrPts.NumU = NURBS.number(1); % U方向的控制点或基函数的总数
CtrPts.NumV = NURBS.number(2); % V方向的控制点或基函数的总数
CtrPts.NumW = NURBS.number(3);
CtrPts.Seque = reshape(1:CtrPts.Num,CtrPts.NumU,CtrPts.NumV,CtrPts.NumW);
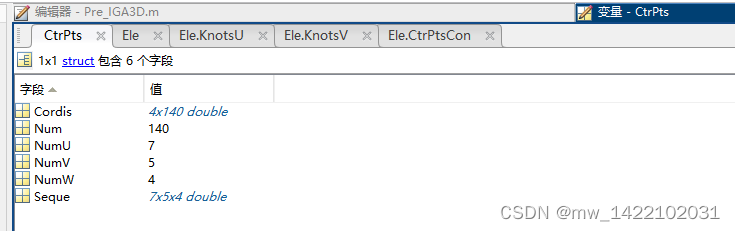
输出2-----Ele:
%% 参数空间中单元(节点区间)的信息,包括单元个数、单元对应生成的序列
Ele.NumU = numel(unique(NURBS.knots{1}))-1; % 第一参数(U)方向的单元个数
Ele.NumV = numel(unique(NURBS.knots{2}))-1; % 第二参数(V)方向的单元个数
Ele.NumW = numel(unique(NURBS.knots{3}))-1;
Ele.Num = Ele.NumU*Ele.NumV*Ele.NumW; % 单元总数
Ele.Seque = reshape(1:Ele.Num, Ele.NumU, Ele.NumV, Ele.NumW);
Ele.KnotsU = [Knots.U(1:end-1) Knots.U(2:end)]; % 元素在第一参数方向上的唯一节点---不太理解为什么这样分
Ele.KnotsV = [Knots.V(1:end-1) Knots.V(2:end)]; % 元素在第二参数方向上的唯一节点---不过会在划分单元信息的时候用到
Ele.KnotsW = [Knots.W(1:end-1) Knots.W(2:end)];
Ele.CtrPtsNum = prod(NURBS.order);
Ele.CtrPtsNumU = NURBS.order(1); Ele.CtrPtsNumV = NURBS.order(2); Ele.CtrPtsNumW = NURBS.order(3);
[~, Ele.CtrPtsCon] = nrbbasisfun({(sum(Ele.KnotsU,2)./2)', (sum(Ele.KnotsV,2)./2)', (sum(Ele.KnotsW,2)./2)'}, NURBS);
% Ele.CtrPtsCon: 单元信息---每个单元包含的全局节点编号
% [B, id] = nrbbasisfun (points, nrb) ----自己感觉 id表示控制点的全局编号 具体原理不理解
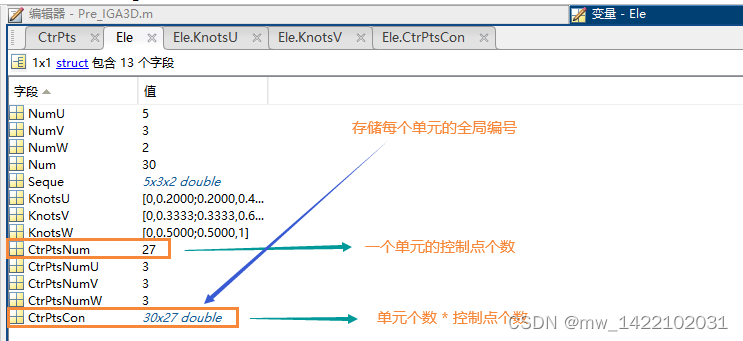
输出3-----GauPts:
%% 参数空间中高斯正交点的信息
[GauPts.Weigh, GauPts.QuaPts] = Guadrature3D(3, numel(NURBS.order));
%[GauPts.Weigh, GauPts.QuaPts]: 一个单元(3D)上27个控制点的 标准区间[-1,1] 上的高斯权重和高斯点
Ele.GauPtsNum = numel(GauPts.Weigh); %高斯点个数 numel(A):表示A中矩阵元素总数 A的行数 * A的列数
GauPts.Num = Ele.Num*Ele.GauPtsNum;
GauPts.Seque = reshape(1:GauPts.Num,Ele.GauPtsNum,Ele.Num)';
GauPts.CorU = zeros(Ele.Num,Ele.GauPtsNum); % GauPts.CorU矩阵大小: 单元数*高斯点个数
GauPts.CorV = zeros(Ele.Num,Ele.GauPtsNum); % 第i行,表示 变换到单元对应的参数域 对应生成的高斯点
GauPts.CorW = zeros(Ele.Num,Ele.GauPtsNum);
for ide = 1:Ele.Num % ide:第ide个单元idw = ceil(ide/Ele.NumU/Ele.NumV);idv = ceil((ide - (idw-1)*Ele.NumU*Ele.NumV)/Ele.NumU);idu = ide - (idw-1)*Ele.NumU*Ele.NumV - (idv-1)*Ele.NumU;
% [idv, idu] = find(Ele.Seque == ide); % The two idices in two parametric directions for an elementEle_Knot_U = Ele.KnotsU(idu,:); % The knot span in the first parametric direction for an elementEle_Knot_V = Ele.KnotsV(idv,:); % The knot span in the second parametric direction for an elementEle_Knot_W = Ele.KnotsW(idw,:);for i = 1:Ele.GauPtsNumGauPts.CorU(ide,i) = ((Ele_Knot_U(2)-Ele_Knot_U(1)).*GauPts.QuaPts(i,1) + (Ele_Knot_U(2)+Ele_Knot_U(1)))/2;%单元上的高斯点GauPts.CorV(ide,i) = ((Ele_Knot_V(2)-Ele_Knot_V(1)).*GauPts.QuaPts(i,2) + (Ele_Knot_V(2)+Ele_Knot_V(1)))/2;GauPts.CorW(ide,i) = ((Ele_Knot_W(2)-Ele_Knot_W(1)).*GauPts.QuaPts(i,3) + (Ele_Knot_W(2)+Ele_Knot_W(1)))/2;end
end