MyBatis(十)MyBatis参数处理

准备工作:
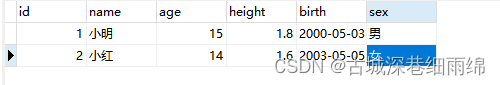
建表:t_student
表中现有数据:
一、单个简单类型参数
简单类型包括:
- byte short int long float double char
- Byte Short Integer Long Float Double Character
- String
- java.util.Date
- java.sql.Date
需求:根据name查、根据id查、根据birth查、根据sex查
第1步、创建接口、pojo类、工具类
1、pojo类:
package com.powernode.mybatis.pojo;import java.util.Date;/* 学生类* @author 老杜* @version 1.0* @since 1.0*/
public class Student {private Long id;private String name;private Integer age;private Double height;private Character sex;private Date birth;// constructor// setter and getter// toString
}2、StudentMapper
package com.powernode.mybatis.mapper;import com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Student;import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;/* @author wuw* @since 2023-04-10 13:46:17*/
public interface StudentMapper {/* 根据name查询* @param name* @return*/List<Student> selectByName(String name);/* 根据id查询* @param id* @return*/Student selectById(Long id);/* 根据birth查询* @param birth* @return*/List<Student> selectByBirth(Date birth);/* 根据sex查询* @param sex* @return*/List<Student> selectBySex(Character sex);}
3、工具类SqlSessionUtil
package com.powernode.mybatis.utils;import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;/* @author wuw* @since 2023-04-04 09:42:28*/
public class SqlSessionUtil {private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;/* 类加载时初始化sqlSessionFactory对象*/static {try {SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"));} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}private static ThreadLocal<SqlSession> local = new ThreadLocal<>();/* 每调用一次openSession()可获取一个新的会话,该会话支持自动提交。 @return 新的会话对象*/public static SqlSession openSession() {SqlSession sqlSession = local.get();if (sqlSession == null) {sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();local.set(sqlSession);}return sqlSession;}/* 关闭SqlSession对象* @param sqlSession*/public static void close(SqlSession sqlSession){if (sqlSession != null) {sqlSession.close();}local.remove();}
}
第2步、创建配置文件
1、mybatis-config
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configurationPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration><properties resource="jdbc.properties"/><typeAliases><package name="com.powernode.mybatis.pojo"/></typeAliases><environments default="dev"><environment id="dev"><transactionManager type="JDBC"/><dataSource type="POOLED"><property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/><property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/><property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/><property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/></dataSource></environment></environments><mappers><!--一定要注意这里的路径哦!!!--><mapper resource="StudentMapper.xml"/></mappers>
</configuration>2、StudentMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapperPUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN""http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"><mapper namespace="com.powernode.mybatis.mapper.StudentMapper"><select id="selectByName" resultType="Student">select * from t_student where name = #{name}</select><select id="selectById" resultType="Student">select * from t_student where id = #{id}</select><select id="selectByBirth" resultType="Student">select * from t_student where birth = #{birth}</select><select id="selectBySex" resultType="Student">select * from t_student where sex = #{sex}</select>
</mapper>3、logback.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><configuration debug="false"><!-- 控制台输出 --><appender name="STDOUT" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender"><encoder class="ch.qos.logback.classic.encoder.PatternLayoutEncoder"><!--格式化输出:%d表示日期,%thread表示线程名,%-5level:级别从左显示5个字符宽度%msg:日志消息,%n是换行符--><pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} [%thread] %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n</pattern></encoder></appender><!--mybatis log configure--><logger name="com.apache.ibatis" level="TRACE"/><logger name="java.sql.Connection" level="DEBUG"/><logger name="java.sql.Statement" level="DEBUG"/><logger name="java.sql.PreparedStatement" level="DEBUG"/><!-- 日志输出级别,logback日志级别包括五个:TRACE < DEBUG < INFO < WARN < ERROR --><root level="DEBUG"><appender-ref ref="STDOUT"/><appender-ref ref="FILE"/></root></configuration>4、jdbc.properties
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:1997/powernode
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=123456
第3步、创建测试类StudentMapperTest
package com.powernode.mybatis.test;import com.powernode.mybatis.mapper.StudentMapper;
import com.powernode.mybatis.pojo.Student;
import com.powernode.mybatis.utils.SqlSessionUtil;
import org.junit.Test;import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;public class StudentMapperTest {StudentMapper mapper = SqlSessionUtil.openSession().getMapper(StudentMapper.class);@Testpublic void testSelectByName(){List<Student> students = mapper.selectByName("张三");students.forEach(student -> System.out.println(student));}@Testpublic void testSelectById(){Student student = mapper.selectById(2L);System.out.println(student);}@Testpublic void testSelectByBirth(){try {Date birth = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd").parse("2022-08-16");List<Student> students = mapper.selectByBirth(birth);students.forEach(student -> System.out.println(student));} catch (ParseException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}@Testpublic void testSelectBySex(){List<Student> students = mapper.selectBySex('男');students.forEach(student -> System.out.println(student));}
}
第4步、运行测试
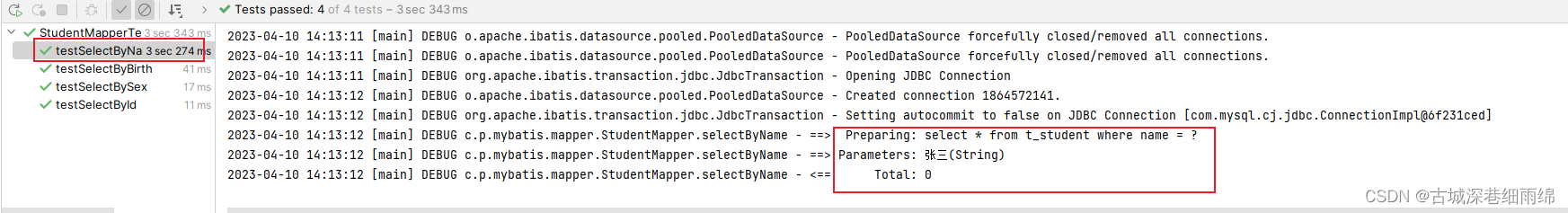
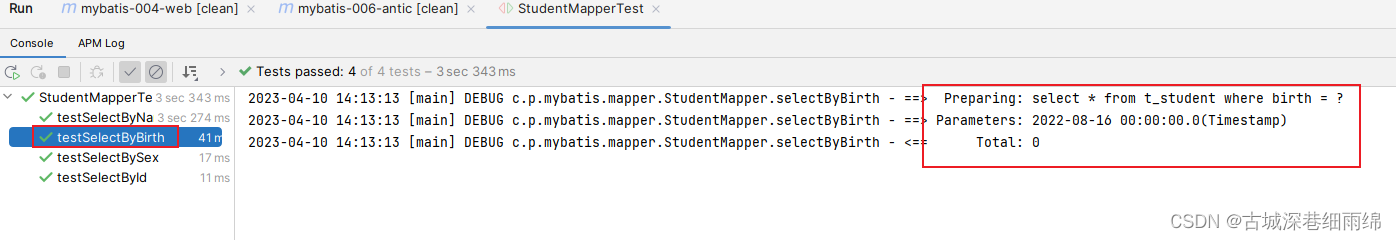
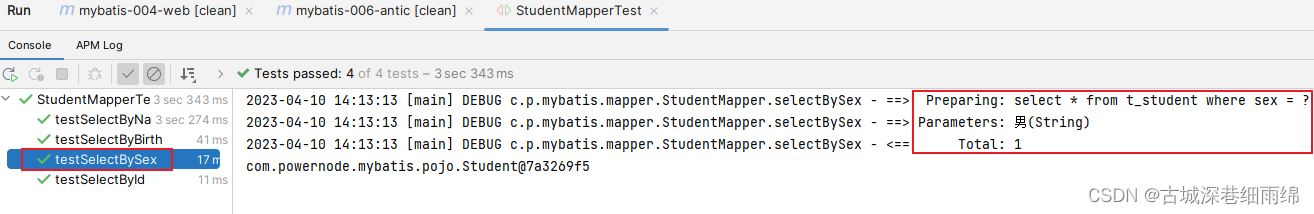
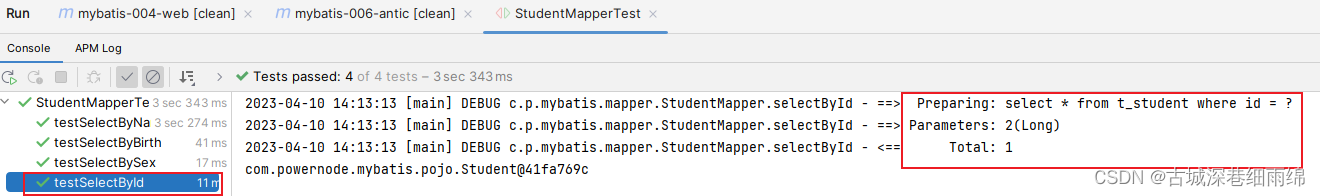
通过测试得知,简单类型对于mybatis来说都是可以自动类型识别的:
- 也就是说对于mybatis来说,它是可以自动推断出ps.setXxxx()方法的。ps.setString()还是ps.setInt()。它可以自动推断。
其实SQL映射文件中的配置比较完整的写法是:
<select id="selectByName" resultType="student" parameterType="java.lang.String">select * from t_student where name = #{name, javaType=String, jdbcType=VARCHAR}
</select>其中sql语句中的javaType,jdbcType,以及select标签中的parameterType属性,都是用来帮助mybatis进行类型确定的。不过这些配置多数是可以省略的。因为mybatis它有强大的自动类型推断机制。
- javaType:可以省略
- jdbcType:可以省略
- parameterType:可以省略
如果参数只有一个的话,#{} 里面的内容就随便写了。对于 ${} 来说,注意加单引号。
二·、Map参数
需求:根据name和age查询
1、StudentMapper接口:
/
* 根据name和age查询
* @param paramMap
* @return
*/
List<Student> selectByParamMap(Map<String,Object> paramMap);2、StudentMapper.xml:
<select id="selectByParamMap" resultType="student">select * from t_student where name = #{nameKey} and age = #{ageKey}
</select>3、运行测试:
@Test
public void testSelectByParamMap(){// 准备MapMap<String,Object> paramMap = new HashMap<>();paramMap.put("nameKey", "张三");paramMap.put("ageKey", 20);List<Student> students = mapper.selectByParamMap(paramMap);students.forEach(student -> System.out.println(student));
}4、结果:
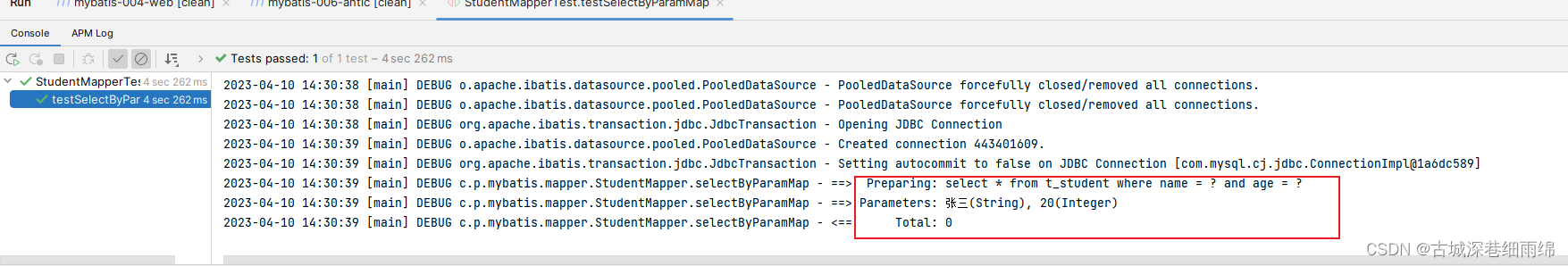
测试运行正常。
这种方式是手动封装Map集合,将每个条件以key和value的形式存放到集合中。然后在使用的时候通过#{map集合的key}来取值。
三、实体类参数
需求:插入一条Student数据
第1步、StudentMapper接口
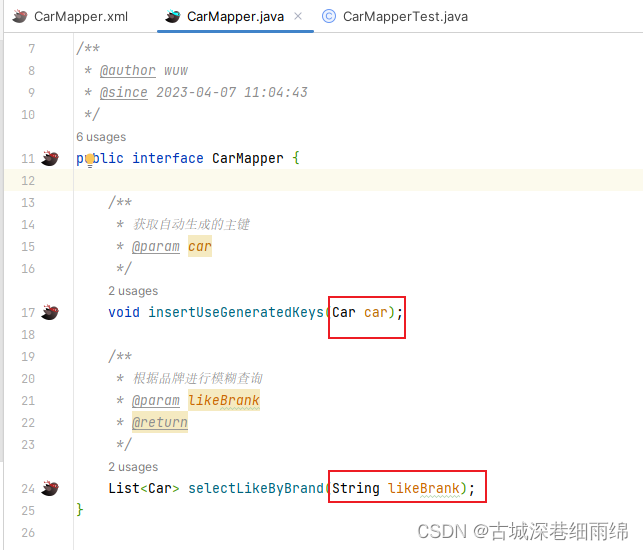
/* 保存学生数据* @param student* @return*/int insert(Student student);第2步、StudentMapper.xml
<insert id="insert">insert into t_student values(null,#{name},#{age},#{height},#{birth},#{sex})
</insert>第3步、运行测试类方法
@Test
public void testInsert(){Student student = new Student();student.setName("李四");student.setAge(30);student.setHeight(1.70);student.setSex('男');student.setBirth(new Date());int count = mapper.insert(student);SqlSessionUtil.openSession().commit();
}
运行正常,数据库中成功添加一条数据。
这里需要注意的是:#{} 里面写的是属性名字。这个属性名其本质上是:set/get方法名去掉set/get之后的名字。
四、多参数
需求:通过name和sex查询
第1步、StudentMapper接口
/* 根据name和sex查询* @param name* @param sex* @return*/List<Student> selectByNameAndSex(String name, Character sex);第2步、StudentMapper.xml
<select id="selectByNameAndSex" resultType="student">select * from t_student where name = #{name} and sex = #{sex}
</select>第3步、测试类
@Test
public void testSelectByNameAndSex(){List<Student> students = mapper.selectByNameAndSex("张三", '女');students.forEach(student -> System.out.println(student));
}第4步、运行
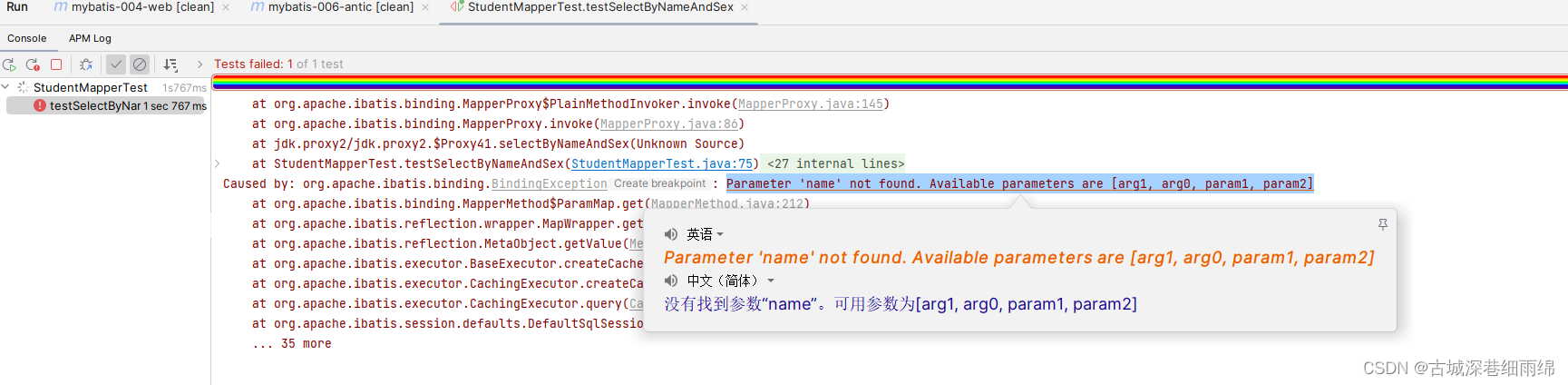
异常信息描述了:name参数找不到,可用的参数包括[arg1, arg0, param1, param2]
第5步、修改StudentMapper.xml配置文件:尝试使用[arg1, arg0, param1, param2]去参数
StudentMapper.xml文件:
<select id="selectByNameAndSex" resultType="student"><!--select * from t_student where name = #{name} and sex = #{sex}-->select * from t_student where name = #{arg0} and sex = #{arg1}
</select>第6步、再次运行
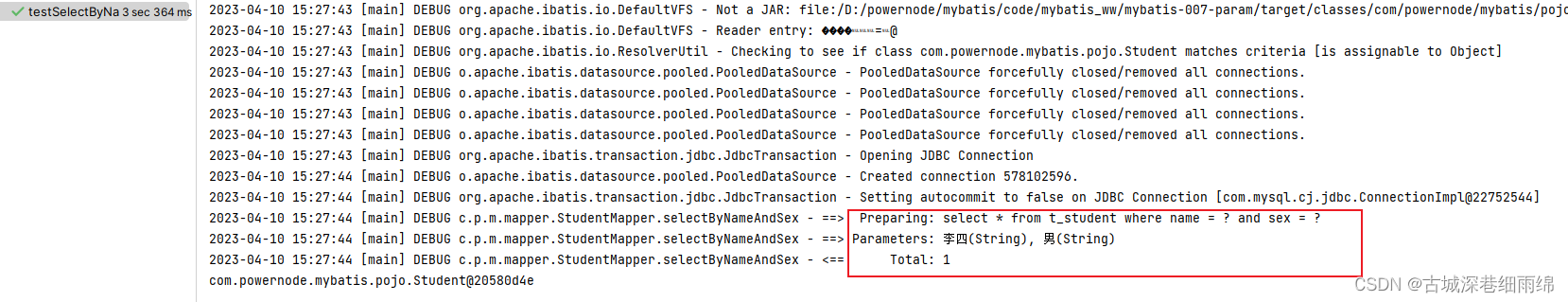
第7步、再次尝试修改StudentMapper.xml文件
<select id="selectByNameAndSex" resultType="student"><!--select * from t_student where name = #{name} and sex = #{sex}--><!--select * from t_student where name = #{arg0} and sex = #{arg1}--><!--select * from t_student where name = #{param1} and sex = #{param2}-->select * from t_student where name = #{arg0} and sex = #{param2}
</select>第8步、运行
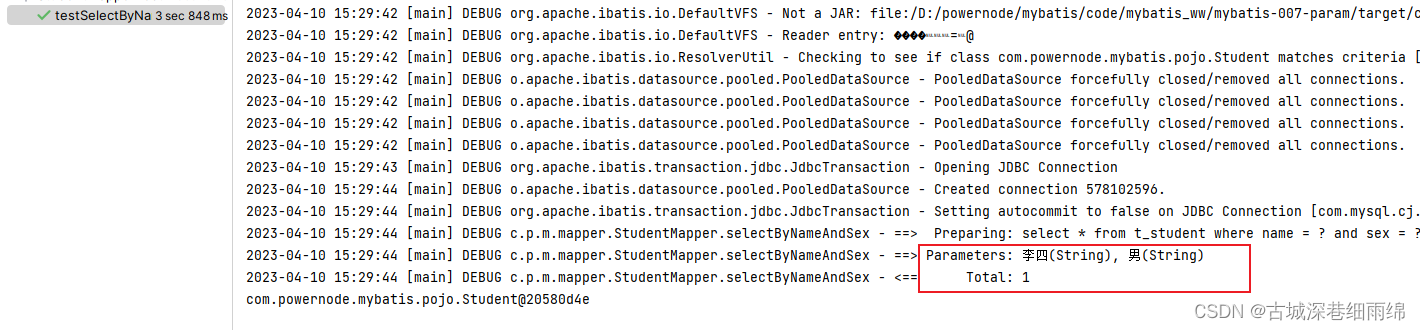
通过测试可以看到:
- arg0 是第一个参数
- param1是第一个参数
- arg1 是第二个参数
- param2是第二个参数
实现原理:实际上在mybatis底层会创建一个map集合,以arg0/param1为key,以方法上的参数为value,例如以下代码:
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("arg0", name);
map.put("arg1", sex);
map.put("param1", name);
map.put("param2", sex);// 所以可以这样取值:#{arg0} #{arg1} #{param1} #{param2}
// 其本质就是#{map集合的key}注意:使用mybatis3.4.2之前的版本时:要用#{0}和#{1}这种形式。
五、@Param注解(命名参数)
可以不用arg0 arg1 param1 param2吗?这个map集合的key我们自定义可以吗?当然可以。使用@Param注解即可。这样可以增强可读性。
需求:根据name和age查询
第1步、StudentMapper接口
/* 根据name和age查询* @param name* @param age* @return*/List<Student> selectByNameAndAge(@Param(value="name") String name, @Param("age") int age);第2步、StudentMapper.xml
<select id="selectByNameAndAge" resultType="student">select * from t_student where name = #{name} and age = #{age}
</select>第3步、测试类
@Testpublic void testSelectByNameAndAge(){List<Student> stus = mapper.selectByNameAndAge("张三", 20);stus.forEach(student -> System.out.println(student));}第4步、运行
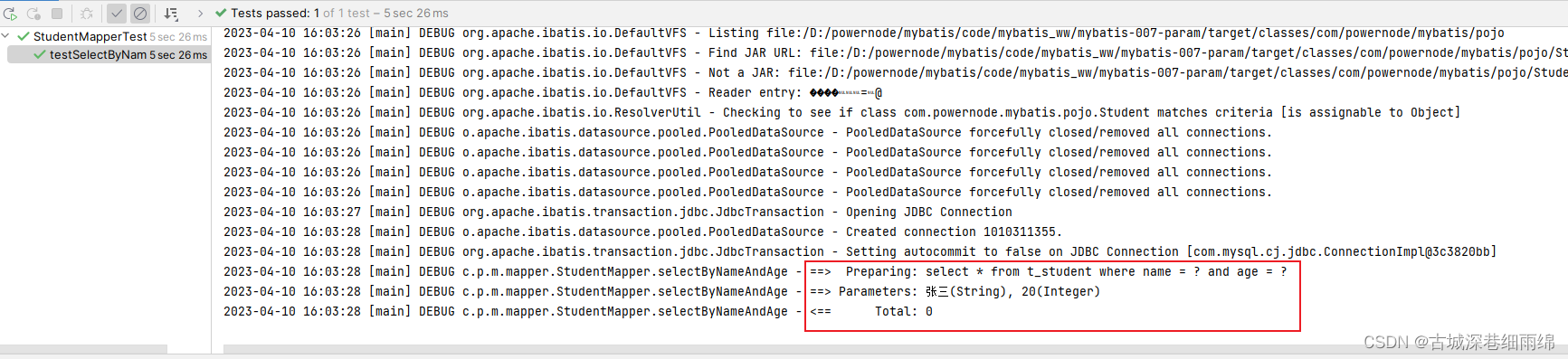
通过测试,一切正常。
核心:@Param("这里填写的其实就是map集合的key")