算法训练营 - 广度优先BFS

目录
从层序遍历开始
N 叉树的层序遍历
经典BFS最短路模板
经典C++ queue
数组模拟队列
打印路径
示例1.bfs查找所有连接方块
C++queue版
数组模拟队列
示例2.从多个位置同时开始BFS
示例3.抽象最短路类(作图关键)
示例4.跨过障碍的最短路
从层序遍历开始
广度优先搜索(Breadth First Search,BFS),又称为宽度优先搜索,是最常见的图搜索方法之一。广度优先搜索是从某个顶点(源点)出发,一次性访问所有未被访问的邻接点,再依次从这些访问过邻接点出发,…,似水中涟漪,似声音传播,一层层地传播开来。
广度优先遍历是按照广度优先搜索的方式对图进行遍历。
广度优先搜索模型
Bfs()
{
1. 建立起始步骤,队列初始化
2. 遍历队列中的每一种可能,whlie(队列不为空)
{
通过队头元素带出下一步的所有可能,并且依次入队
{
判断当前情况是否达成目标:按照目标要求处理逻辑
}
继续遍历队列中的剩余情况
}
}
(看不懂没有关系,直接看题就完事儿了)
N 叉树的层序遍历
力扣
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:int val;vector<Node*> children;Node() {}Node(int _val) {val = _val;}Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) {val = _val;children = _children;}
};
*/class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(Node* root) {vector<int> v;vector<vector<int>> vec;queue<Node*> q;if(!root) return vec;q.push(root);//将开始bfs位置入队while(!q.empty()){int n=q.size();//需要遍历这一层的元素个数for(int i=0;i<n;i++)//记录该层元素并将其所连接的点入队{Node* temp=q.front();q.pop();if(!temp) continue;v.push_back(temp->val);//将这个点所连接的点入队vector<Node*> son=temp->children;for(int j=0;j<son.size();j++)q.push(son[j]); }vec.push_back(v);v.clear();}return vec;}
};经典BFS最短路模板
经典C++ queue
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;const int N = 110;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
int n, m;
int g[N][N], d[N][N];int bfs()
{queue< pair<int, int> > q;q.push({0, 0});memset(d, -1, sizeof(d));d[0][0] = 0;int dx[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};while (q.size())//队列不为空{PII t = q.front();//取队头元素q.pop();//出队for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++){int x = t.first + dx[i], y = t.second + dy[i];if (x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < m && g[x][y] == 0 && d[x][y] == -1){d[x][y] = d[t.first][t.second] + 1;//当前点到起点的距离q.push({x, y});//将新坐标入队}}}return d[n - 1][m -1];
}int main()
{cin >> n >> m;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)cin >> g[i][j];cout << bfs() << endl;return 0;
}数组模拟队列
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
int n, m;
int g[N][N];//存放地图
int d[N][N];//存 每一个点到起点的距离
PII q[N * N];//手写队列
int bfs()
{int hh = 0, tt = 0;q[0] = {0, 0};memset(d, - 1, sizeof d);//距离初始化为- 1表示没有走过d[0][0] = 0;//表示起点走过了int dx[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};//x 方向的向量和 y 方向的向量组成的上、右、下、左while(hh <= tt)//队列不空{PII t = q[hh ++ ];//取队头元素for(int i = 0; i < 4; i ++ )//枚举4个方向{int x = t.first + dx[i], y = t.second + dy[i];//x表示沿着此方向走会走到哪个点if(x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < m && g[x][y] == 0 && d[x][y] == -1)//在边界内 并且是空地可以走 且之前没有走过{d[x][y] = d[t.first][t.second] + 1;//到起点的距离q[ ++ tt ] = {x, y};//新坐标入队}}}return d[n - 1][m - 1]; //输出右下角点距起点的距离即可
}
int main()
{cin >> n >> m;for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )for(int j = 0; j < m; j ++ )cin >> g[i][j];cout << bfs() << endl;return 0;
}打印路径
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
PII q[N*N],Prev[N][N];
int g[N][N], d[N][N];
int n, m;
int bfs()
{int hh = 0, tt = 0;q[0] = {0, 0};memset(d, -1, sizeof d);int dx[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};d[0][0] = 0;while(hh <= tt){PII t = q[hh ++ ];for(int i = 0; i < 4; i ++ ){int x = dx[i] + t.first, y = t.second + dy[i];if(x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < m && g[x][y] == 0 && d[x][y] == -1){d[x][y] = d[t.first][t.second] + 1;Prev[x][y] = t;q[++ tt] = {x, y};}}}int x = n - 1, y = m - 1;while(x || y)//有一个不d等于0{cout << x << ' ' << y << endl;PII t = Prev[x][y];x = t.first, y = t.second;}return d[n - 1][m - 1];
}
int main()
{cin >> n >> m;for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )for(int j = 0; j < m;j ++)cin >> g[i][j];cout << bfs() << endl;return 0;
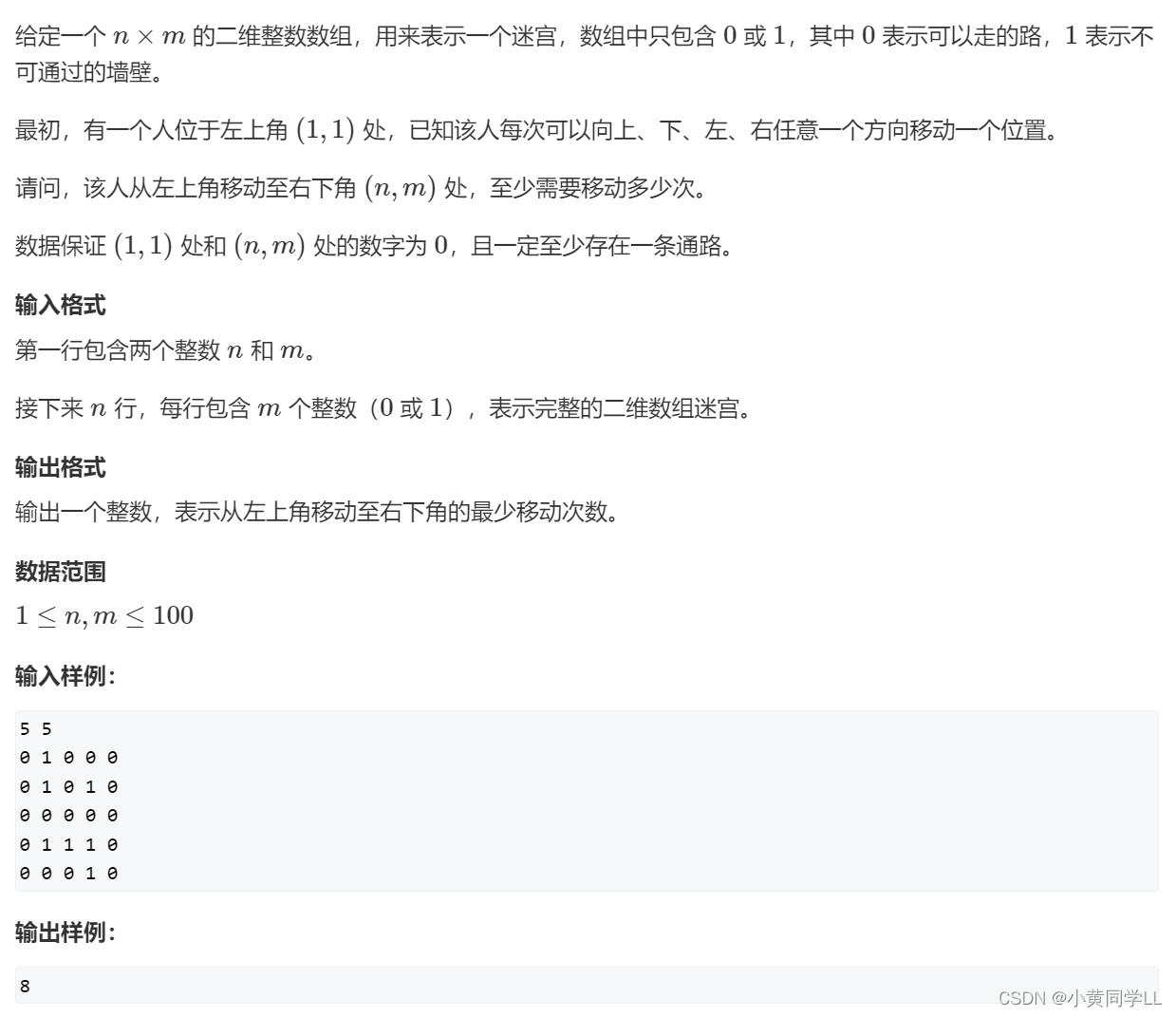
}输入
5 5
0 1 0 0 0
0 1 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 1 1 1 0
0 0 0 1 0输出
4 4
3 4
2 4
2 3
2 2
2 1
2 0
1 0
8示例1.bfs查找所有连接方块
力扣
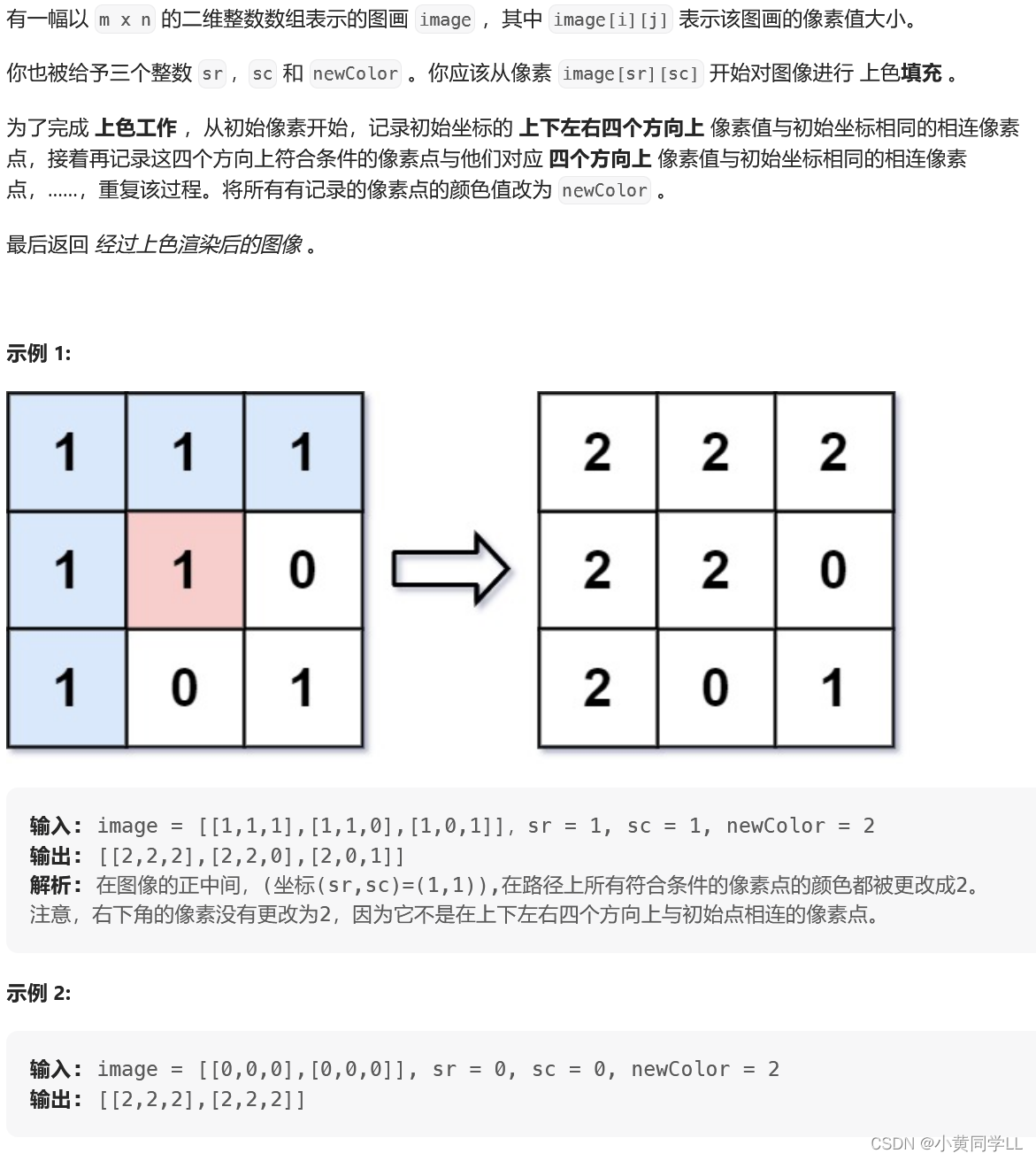
思路:
非常简单,就是把图块的四个方向都搜索一遍,对于每个相邻的同色图块修改成新色即可
C++queue版
class Solution {
public:const int dx[4]={1,-1,0,0},dy[4]={0,0,1,-1};vector<vector<int>> floodFill(vector<vector<int>>& image, int sr, int sc, int color) {int old=image[sr][sc];if(old==color) return image;int n=image.size(),m=image[0].size();queue<pair<int,int>> q;q.push({sr,sc});image[sr][sc]=color;while(!q.empty()){pair<int,int> t=q.front();q.pop();for(int i=0;i<4;i++){int x=t.first+dx[i],y=t.second+dy[i];if(x>=0&&x<n&&y>=0&&y<m&&image[x][y]==old){q.push({x,y});image[x][y]=color;}}}return image;}
};数组模拟队列
class Solution {
public:const int dx[4] = {1, 0, 0, -1},dy[4] = {0, 1, -1, 0};vector<vector<int>> floodFill(vector<vector<int>>& image, int sr, int sc, int color) {int old = image[sr][sc];if (old == color) return image;int n = image.size(), m = image[0].size();int hh=0,tt=0;pair<int,int> q[n*m];q[0]={sr,sc};image[sr][sc] = color;while (hh<=tt) {pair<int,int> t=q[hh++];for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {int x = t.first+dx[i], y = t.second+dy[i];if (x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < m && image[x][y] == old) {q[++tt]={x,y};image[x][y] = color;}}}return image;}
};示例2.从多个位置同时开始BFS
力扣
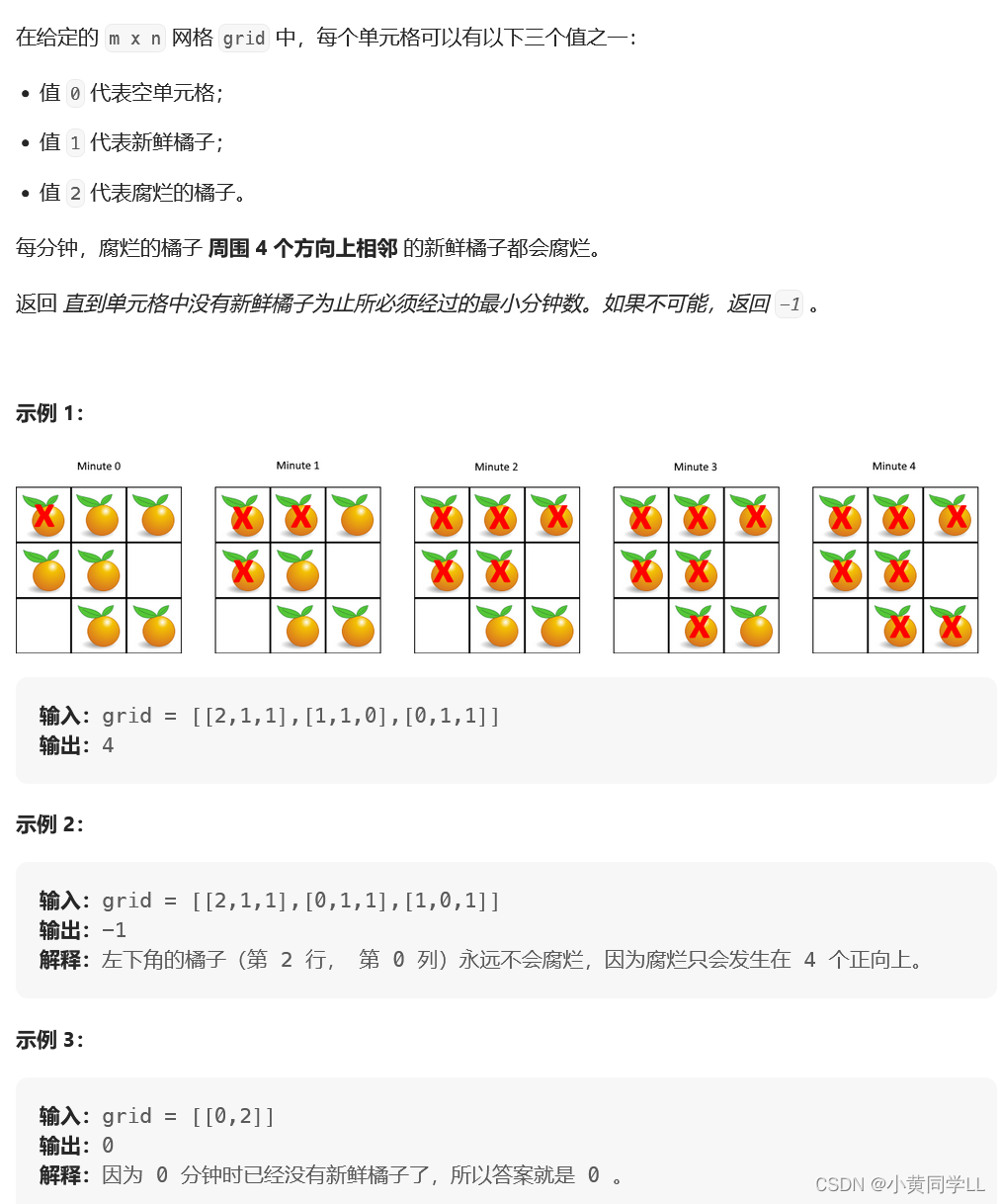
本题可以先找到所有的腐烂橘子,入队,用第一批带出新一批腐烂的橘子
每以匹橘子都会在一分钟之内腐烂,所以此题可以转化为求BFS执行的大循环的次数
这里的step的更新需要有一个标记,只有新的腐烂的橘子加入,step才能自加
最后BFS执行完之后,说明所有可以被腐烂的都完成了,再去遍历grid,如何还有
值为1的,说明没有办法完全腐烂,返回-1,如果没有,则返回step
class Solution {
public:int dx[4]={1,-1,0,0},dy[4]={0,0,1,-1};int orangesRotting(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {int n=grid.size(),m=grid[0].size();queue<pair<int,int>> q;int cnt=0;int step=0;for(int i=0;i<n;i++)for(int j=0;j<m;j++)if(grid[i][j]==2) q.push({i,j});else if(grid[i][j]==1) cnt++;while(!q.empty()){int tot=q.size();bool flag=false;while(tot--)//多个位置同时开始{pair<int,int> t=q.front();q.pop();for(int i=0;i<4;i++){int x=t.first+dx[i],y=t.second+dy[i];if(x>=0&&x<n&&y>=0&&y<m&&grid[x][y]==1){q.push({x,y});grid[x][y]=2;cnt--;flag=true;}}}if(flag) ++step;}return cnt?-1:step; }
};示例3.抽象最短路类(作图关键)
力扣

思路:
- 通过BFS, 首先用beginWord带出转换一个字母之后所有可能的结果
- 每一步都要把队列中上一步添加的所有单词转换一遍,最短的转换肯定在这些单词当中, 所有这些词的转换只能算一次转换,因为都是上一步转换出来的,这里对于每个单词的每个位置都可以用26个字母进行转换,所以一个单词一次转换的可能有:单词的长度 * 26
- 把转换成功的新词入队,进行下一步的转换
- 最后整个转换的长度就和BFS执行的次数相同
class Solution {
public:int ladderLength(string beginWord, string endWord, vector<string>& wordList) {//hash表的查询效率最高,将单词存入哈希表unordered_set<string> wordDict(wordList.begin(), wordList.end());//标记单词是否已经访问过,访问过的不再访问unordered_set<string> visited;visited.insert(beginWord);//初始化队列queue<string> q;q.push(beginWord);int res = 1;while (!q.empty()) {int nextSize = q.size();while (nextSize--){string curWord = q.front();q.pop();if (curWord == endWord)return res ;//尝试转换当前单词的每一个位置for (int i = 0; i < curWord.size(); i++) {string newWord = curWord;//每一个位置用26个字母分别替换for (char ch = 'a'; ch <= 'z'; ch++) {newWord[i] = ch;//在字典里且没有用过if (wordDict.count(newWord) && !visited.count(newWord)){visited.insert(newWord);//标记用过q.push(newWord);} }}}res++;}//转换不成功,返回0return 0;}
};示例4.跨过障碍的最短路
力扣

障碍指不可到达的路径,这种障碍一般用数组或者hash表存储,用if判断此路不通;
思路:
深度优先不适合解此题,递归深度太大,会导致栈溢出
本题的密码为4位密码,每位密码可以通过拨动一次进行改变,注意这里的数的回环以及拨动的方向
拨动方向:向前,向后
回环:如果当前是9,0时,向前,向后拨动需要变成最小最大,而不是简单的自加自减
class Solution {
public:int openLock(vector<string>& deadends, string target) {// 哈希表的查找更快unordered_set<string> deadendsSet(deadends.begin(), deadends.end());//如果"0000"在死亡字符串中,则永远到达不了if (deadendsSet.find("0000") != deadendsSet.end())return -1;//初始化队列queue<string> que;que.push("0000");//加标记,已经搜索过的字符串不需要再次搜索unordered_set<string> book;book.insert("0000");int step = 0;while (!que.empty()) {int n = que.size();//从上一步转换之后的字符串都需要进行验证和转换//并且只算做一次转换,类似于层序遍历,转换的步数和层相同//同一层的元素都是经过一步转换得到的while(n--) {string curStr = que.front();que.pop();if (curStr == target) return step;//四位密码锁,每个位置每次都可以转一次for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {string newStr1 = curStr, newStr2 = curStr;//当前位置可以向前或者向后拨一位newStr1[j] = newStr1[j] == '9' ? '0' : newStr1[j] + 1;newStr2[j] = newStr2[j] == '0' ? '9' : newStr2[j] - 1;//如果不会死锁且没有尝试过,则入队if (deadendsSet.find(newStr1) == deadendsSet.end()&& book.find(newStr1) == book.end()) {que.push(newStr1);book.insert(newStr1);}if (deadendsSet.find(newStr2) == deadendsSet.end()&& book.find(newStr2) == book.end()) {que.push(newStr2);book.insert(newStr2);}}}step++;}return -1;}
};



