十月每日打卡

文章目录
- 每日打卡
-
- 10.1 [重新格式化电话号码 lc1694]([1694. 重新格式化电话号码 - 力扣(LeetCode)](https://leetcode.cn/problems/reformat-phone-number/))
- 10.2 [在LR字符串中交换相邻字符 lc 777]([777. 在LR字符串中交换相邻字符 - 力扣(LeetCode)](https://leetcode.cn/problems/swap-adjacent-in-lr-string/))
- 10.2 [每日温度 lc739]([739. 每日温度 - 力扣(LeetCode)](https://leetcode.cn/problems/daily-temperatures/))
- 10.3 [检查二进制字符串字段 lc1784]([1784. 检查二进制字符串字段 - 力扣(LeetCode)](https://leetcode.cn/problems/check-if-binary-string-has-at-most-one-segment-of-ones/))
- 10.3 [柱状图中的最大矩形 lc 84]([84. 柱状图中最大的矩形 - 力扣(LeetCode)](https://leetcode.cn/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/))
- 10.3 [最大矩形 lc85]([85. 最大矩形 - 力扣(LeetCode)](https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximal-rectangle/))
- 10.4 [使括号有效的最少添加 lc 921]([921. 使括号有效的最少添加 - 力扣(LeetCode)](https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-add-to-make-parentheses-valid/))
- 10.4 [最短无序连续子数组 lc 581] ([581. 最短无序连续子数组 - 力扣(LeetCode)](https://leetcode.cn/problems/shortest-unsorted-continuous-subarray/))
- 10.5 [子域名访问计数 lc 811]([811. 子域名访问计数 - 力扣(LeetCode)](https://leetcode.cn/problems/subdomain-visit-count/))
- [10.5 盛最多水的容器 lc 11]([11. 盛最多水的容器 - 力扣(LeetCode)](https://leetcode.cn/problems/container-with-most-water/))
- [10.5 删掉链表的倒数第n个节点 lc 19]([19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点 - 力扣(LeetCode)](https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/))
- [10.6 三等分 lc 927]([927. 三等分 - 力扣(LeetCode)](https://leetcode.cn/problems/three-equal-parts/))
- [10.6 下一个排列 lc 31]([31. 下一个排列 - 力扣(LeetCode)](https://leetcode.cn/problems/next-permutation/))
- [10.7 最大升序子序列和 lc1800]([1800. 最大升序子数组和 - 力扣(LeetCode)](https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-ascending-subarray-sum/))
- [10.7 寻找重复数 lc 287]([287. 寻找重复数 - 力扣(LeetCode)](https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-the-duplicate-number/))
- [10.7 找到数组中消失的数字 lc 448]([448. 找到所有数组中消失的数字 - 力扣(LeetCode)](https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-all-numbers-disappeared-in-an-array/))
- [10.8 优势洗牌 lc 870]([870. 优势洗牌 - 力扣(LeetCode)](https://leetcode.cn/problems/advantage-shuffle/))
- 10.8 三数之和 lc 15
- [10.10 数组中第k个元素]([215. 数组中的第K个最大元素 - 力扣(LeetCode)](https://leetcode.cn/problems/kth-largest-element-in-an-array/submissions/))
-
- 1. 快速排序
- 2. 建堆
- 10.10 使序列递增的最小交换次数 lc 801
- 10.11 仅执行一次字符串交换能否使两个字符串相等 lc 1790
- 10.12 链表组件 lc 817
- 10.12 接雨水 lc 42
- 10.13 合并K个升序链表 lc 23
- 10.13 [找到字符串中所有字母异位词](https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-all-anagrams-in-a-string/) lc 438
- 10.13 最多能完成排序的块 lc 769
- 10.14 不同的子序列II lc940
- 10.14 不同的子序列 I lc 115
- 10.14 路径总和 I lc 112
- 10.14 路径总和II lc 113
- 10.14 路径总和III lc 437
- 10.14 二叉树的序列化与反序列化 lc 297
-
- BFS
- DFS
- 10.15 目标和 lc494
-
- 1.简单dfs
- 2. dfs+记忆化搜索
- 3. 01背包
- 10.15 分割等和子集 lc 416
- 10.15 用栈操作构建数组 lc 1441
- 10.16 可能的二分法 lc 886
- 10.17 完全平方数
- 10.17 零钱兑换 lc 322
- 10.17 水果成篮 lc 904
- 10.18 最大为 N 的数字组合 lc 902
- 10.18 环形链表 lc 141
- 10.18 环形链表|| lc 142
- 10.18 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点 lc 19
- 10.19 无法吃午餐肉的同学 lc 1700
- 10.19 括号的生成 lc 22
- 10.19 组合总和 lc 39
- 10.19 组合总数 II lc 40
- 10.19 电话号码的字母组合 lc 17
- 10.20 缺失的第一个正数 lc 41
- 10.20 寻找重复数 lc 287
- 10.20 找到所有数组中消失的数字 lc 448
- 10.20 第K个语法符号lc 779
- 10.21 股票价格跨度 lc 901
- 10.22 根据身高重建队列 lc 406
- 10.22 规划兼职工作lc 1235
- 10.24 除自身以外的乘积 lc 238
- 10.24 和为k的子数组 lc 560
- 10.24 分割数组 lc 915
- 10.25 最短的桥 934
- 10.26 任务调度器 lc 621
- 10.26 和至少为k的最短子数组 lc 862
- 10.28 戳气球 lc 312
- 10.28 子数组的最小值之和 lc 907
- 10.30 LRU缓存 lc 146
- 10.30 字母大小写全排列 lc 784
- 10.30 最小栈 lc 155
- 10.31 滑动窗口的最大值 lc 239
- 10.31 神奇字符串 lc481
- 10.31 课程表 lc 207
- 10.31 神奇字符串 lc481
- 10.31 课程表 lc 207
每日打卡
10.1 [重新格式化电话号码 lc1694](1694. 重新格式化电话号码 - 力扣(LeetCode))

模拟题:特殊情况就是在最后划分完全部三个之后,还剩四个需要变成aa-bb
class Solution {
public:string reformatNumber(string number) {string ans;queue<char> q;for(char ch: number){if(ch != ' ' && ch != '-')q.push(ch);}int cnt = 0;while(q.size()){if(cnt == 0 && q.size() == 4){ans += q.front();q.pop();ans += q.front();q.pop();ans += '-';ans += q.front();q.pop();ans += q.front();q.pop();}if(!q.size())break;if(cnt == 3){ans += '-';cnt = 0;}else{ans += q.front();q.pop();cnt++;}}return ans;}
};
10.2 [在LR字符串中交换相邻字符 lc 777](777. 在LR字符串中交换相邻字符 - 力扣(LeetCode))

题目的意思是L可以越过X向左移动,R可以越过X向右移动。但R和L的相对位置不变。
-
!也就是去掉X后start和end字符串的L和R位置相同!
-
R只能右移,L只能左移,所以如果R左边的X多了是不可以的,因为R不能左移过去;同理,L右边的X多了也不可。
class Solution {
public:bool canTransform(string start, string end) {int n = start.size();int i = 0, j = 0;while(1){//越过所有的Xwhile(i < n && start[i] == 'X')i++;while(j < n && end[j] == 'X')j++;//判断现在的i和j情况//如果两个都走到底了那可以if(i == n && j == n)return true;//有一个走到底了另一个没有或者二者对应的不相同那不行if(i == n || j == n || start[i] != end[j])return false;//两者的位置不同也不行L可以左移所以start的可以在end后面if(start[i] == 'L' && i < j)return false;//R可以右移所以start的可以在end前面if(start[i] =='R' && i > j)return false;i++;j++;}return true;}
};
10.2 [每日温度 lc739](739. 每日温度 - 力扣(LeetCode))
单调栈

单调栈模板题。
就是说维持这个栈单调递减,违反单调性的时候就是需要调整并记录。
如果出现比栈顶大的元素,说明下一个更高温度已经出现,可以将其pop出来了。
如果比栈顶元素小,那么就放在栈里,等待更新最大元素
最终留在栈里的就是没有右边最大元素了,按照初始化的0即可
class Solution {
public:vector<int> dailyTemperatures(vector<int>& temp) {int n = temp.size();vector<int> ans(n, 0);stack<int> stk;for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){while(!stk.empty() && temp[stk.top()] < temp[i]){ans[stk.top()] = i - stk.top();stk.pop();}stk.push(i);}return ans;}
};
10.3 [检查二进制字符串字段 lc1784](1784. 检查二进制字符串字段 - 力扣(LeetCode))

题目含义很难理解,看了评论区之后:连续若干个"1"组成的字段是由一个或者多个连续‘1’组成的,如果这样的字段不超过1个,就返回true,多于1个就返回false。
1000 true 110001 false 统计即可
class Solution {
public:bool checkOnesSegment(string s) {int cnt = 0;int n = s.size();int len = 0;for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){while(i < n && s[i] == '1'){len++;i++;}if(len >= 1)cnt++;if(i < n && s[i] == '0')len = 0;}return cnt <= 1;}
};
10.3 [柱状图中的最大矩形 lc 84](84. 柱状图中最大的矩形 - 力扣(LeetCode))
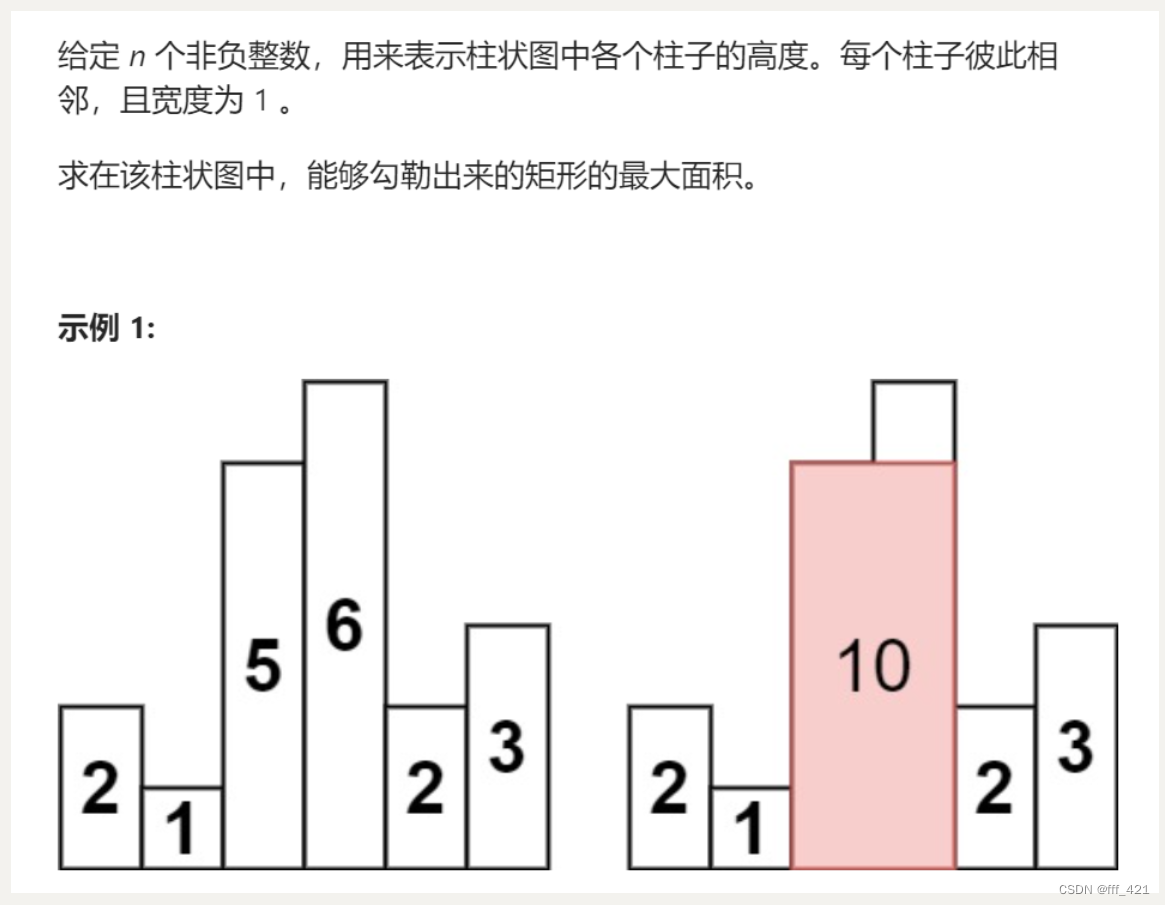
我们之前做过一个类似的,盛最多水的容器,那个是构造的矩形是两个边界中最小即可,也即是双指针就行。这个不一样的是你需要使用整个容器内的最矮的作为高。所以我们想遍历每个柱子,以其作为高h,然后去寻找最宽的边,也即是向两边分别找高于h的柱子,找到第一个低于h的就停止。
这个也是单调栈,对于单调递增的栈来说:栈里的前一个元素就是左边第一个小于该元素的值,右边第一个小于我们可以在比较中得到。当发现小于栈顶元素时就可以得到右边第一个了,否则就加入栈中即可。
class Solution {
public:int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {int n = heights.size() + 2;//向两边加一个哨兵heights.insert(heights.begin(), 0);heights.push_back(0);int ans = 0;stack<int> s;for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){while(!s.empty() && heights[i] < heights[s.top()]){int j = s.top();s.pop();ans = max(ans, heights[j] * (i - s.top() - 1));}s.push(i);}return ans;}
};
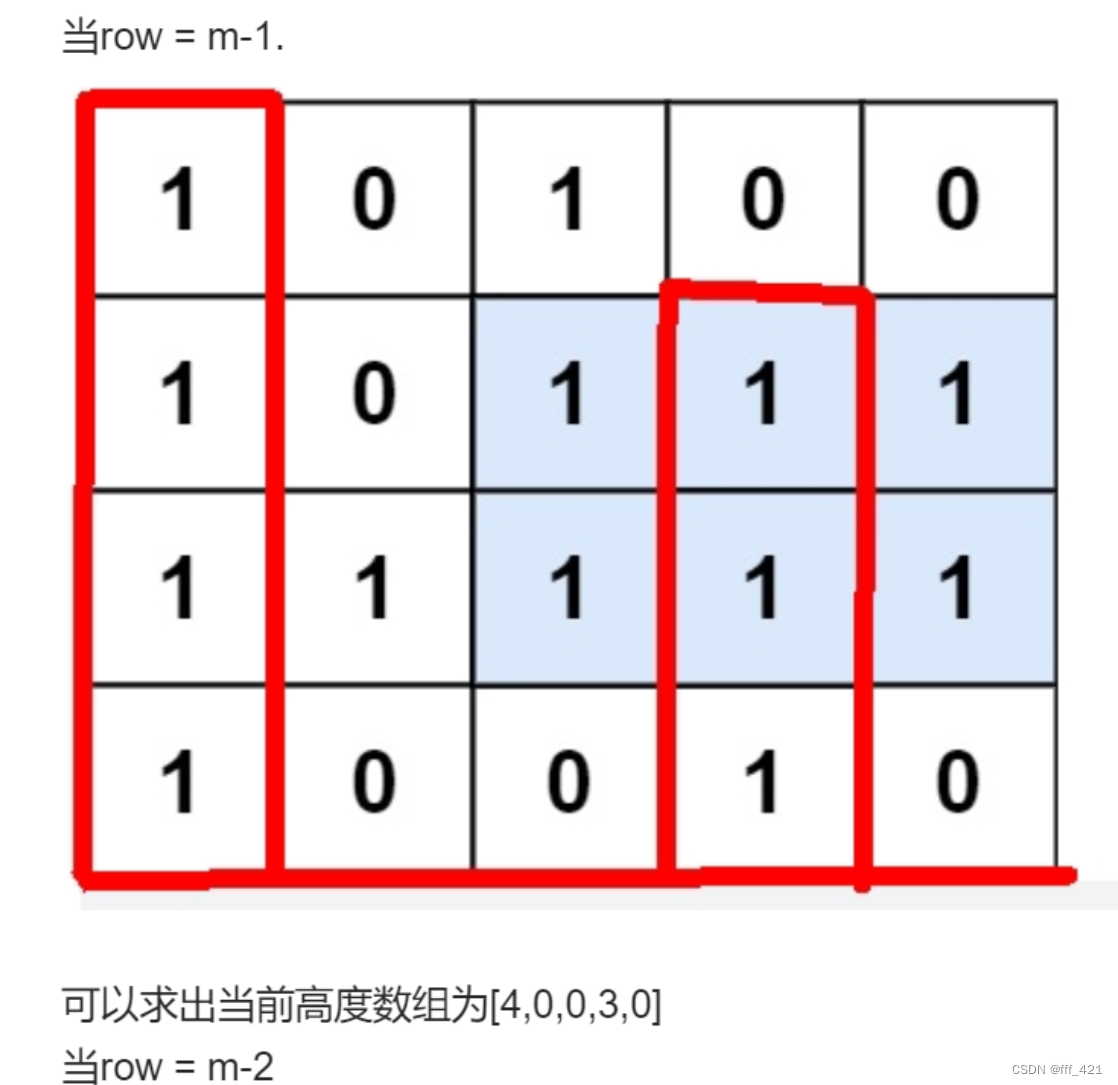
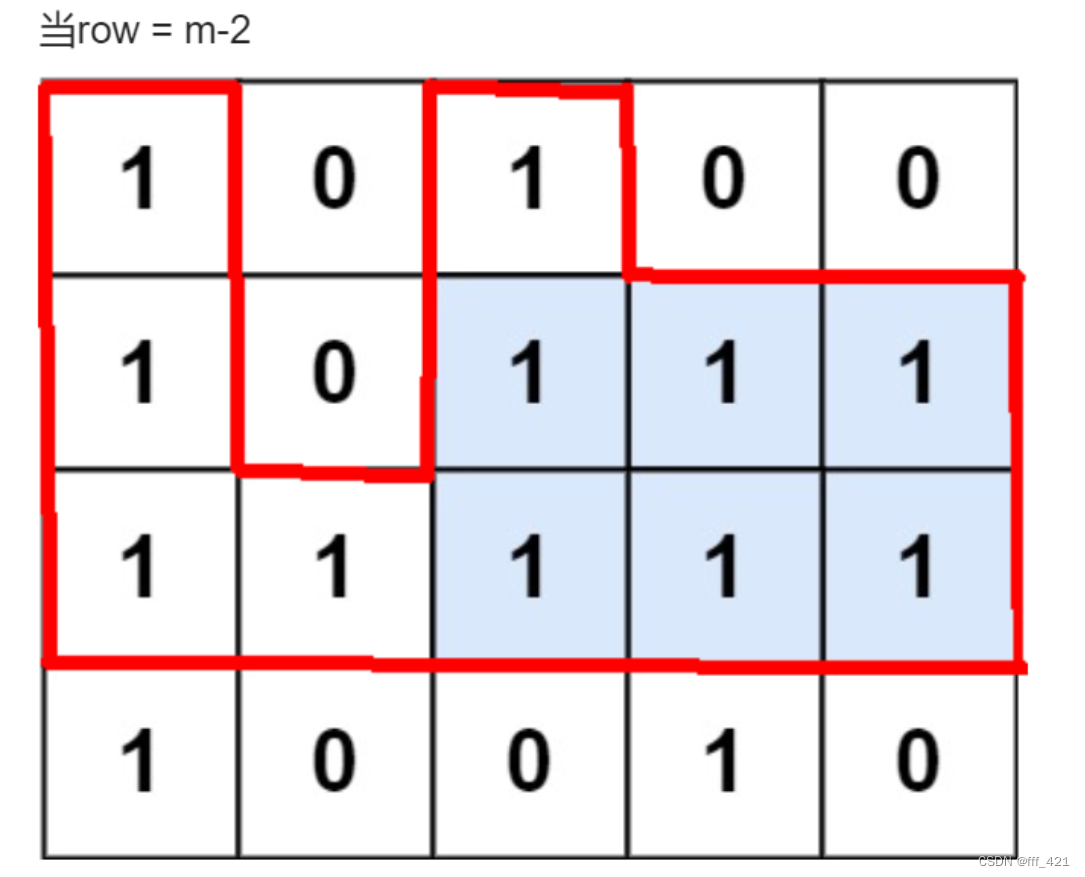
10.3 [最大矩形 lc85](85. 最大矩形 - 力扣(LeetCode))
就是上面lc84的二维版本
最形象的图就是这个
只用第一行高度是 1 0 1 0 0
12行高度是 2 0 2 1 1
13行高度是 3 1 3 2 2
这几行分别调用lc84即可取最大即可!
class Solution {
public:int maximalRectangle(vector<vector<char>>& matrix) {int row = matrix.size(), col = matrix[0].size();if(row == 0 || col == 0)return 0;int ans = 0;vector<int> height(col, 0);for(int i = 0; i < row; i++){for(int j = 0; j < col; j++){if(matrix[i][j] == '1')height[j] = height[j] + 1;elseheight[j] = 0;}for(int x: height)cout << x << " ";cout << endl;ans = max(ans, largestRectangleArea(height));}return ans;}int largestRectangleArea(vector<int> heights) {int n = heights.size() + 2;heights.insert(heights.begin(), 0);heights.push_back(0);int ans = 0;stack<int> s;for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){while(!s.empty() && heights[i] < heights[s.top()]){int j = s.top();s.pop();ans = max(ans, heights[j] * (i - s.top() - 1));}s.push(i);}return ans;}
};
10.4 [使括号有效的最少添加 lc 921](921. 使括号有效的最少添加 - 力扣(LeetCode))
这个就是有效的括号,但是由于是任意位置插入左括号和右括号都行,只需要数量对应上即可。左括号+1,右括号先抵消再计数即可
class Solution {
public:int minAddToMakeValid(string s) {int l = 0, cnt = 0;for(char ch: s){if(ch == '(')l++;else if(l > 0 && ch == ')')l--;else if(l == 0 && ch == ')')cnt++;}return cnt + l;}
};
10.4 [最短无序连续子数组 lc 581] (581. 最短无序连续子数组 - 力扣(LeetCode))
这个看起来很简单,本来想着从两边向中间扩展出现无序就停止来着,但是其中的等号很麻烦。这个题一点都不简单。
两个边界l, r。l是最左边需要开始排序的数,应该从右边开始遍历。如果不需要排序的话,那么从右边开始应该每一个数nums[j]都小于等于右边遍历过的min。反之若nums[j] > min的话,就需要记录下来需要排序的值l。
同理,r是最右边需要开始排序的数,应该从左边开始遍历。如果不需要排序的话,那么从左边开始应该每一个数nums[i]都大于等于左边遍历过前i - 1个数的max。反之若nums[j] < max的话,就需要记录下来需要排序的值r。
class Solution {
public:int findUnsortedSubarray(vector<int>& nums) {int n = nums.size();int ma = INT_MIN, mi = INT_MAX;int l = 0, r = 0;for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){if(nums[i] < ma)r = i;elsema = max(ma, nums[i]);}for(int j = n - 1; j >= 0; j--){if(nums[j] > mi)l = j;elsemi = min(mi, nums[j]);} if(l == r)return 0;elsereturn r - l + 1;}
};
10.5 [子域名访问计数 lc 811](811. 子域名访问计数 - 力扣(LeetCode))
简单模拟:使用hashmap的key存储域名,value存储个数,处理字符串计数即可。
class Solution {
public:vector<string> subdomainVisits(vector<string>& cpdomains) {unordered_map<string, int> hashMap;vector<string> ans;for(string s: cpdomains){int i = 0;while(i < s.size() && s[i] != ' ')i++;int cnt = atoi(s.substr(0, i).c_str());string s1 = s.substr(++i); //google.mail.comif(hashMap.find(s1) != hashMap.end())hashMap[s1] += cnt;elsehashMap[s1] = cnt;while(i < s.size() && s[i] != '.')i++;string s2 = s.substr(++i); //mail.comif(hashMap.find(s2) != hashMap.end())hashMap[s2] += cnt;elsehashMap[s2] = cnt;while(i < s.size() && s[i] != '.')i++;if(i < s.size() && s[i] == '.'){string s3 = s.substr(++i); //comif(hashMap.find(s3) != hashMap.end())hashMap[s3] += cnt;elsehashMap[s3] = cnt;}}for(auto x: hashMap){string s = to_string(x.second) + " " + x.first;ans.push_back(s);}return ans;}
};
[10.5 盛最多水的容器 lc 11](11. 盛最多水的容器 - 力扣(LeetCode))
这个就很简单啦,双指针遍历一下
class Solution {
public:int maxArea(vector<int>& height) {int n = height.size();int i = 0, j = n - 1;int ans = 0;while(i < j){int s = min(height[i], height[j]) * (j - i);ans = max(ans, s);if(height[i] < height[j])i++;elsej--;}return ans;}
};
[10.5 删掉链表的倒数第n个节点 lc 19](19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点 - 力扣(LeetCode))
也很简单啦,就是快慢指针先找到倒数第n个节点,然后删除即可。
注意一些边界条件,比如删除头节点、删除只有一个元素的链表等
/* Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {ListNode* p = head;if(head->next == nullptr)return nullptr;for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)p = p->next;ListNode* q = head;if(p == nullptr)return head->next; //删掉头节点while(p->next != nullptr){p = p->next;q = q->next;}ListNode* nx = q->next;q->next = nx->next; return head;}
};
[10.6 三等分 lc 927](927. 三等分 - 力扣(LeetCode))
三个指针判断三部分是否相等,二进制是否相等首先看1的个数,其次看第一个1后的排列是否相等。`
class Solution {
public:vector<int> threeEqualParts(vector<int>& arr) {vector<int> ans = {-1, -1};int n = arr.size();int cnt = 0;//求出所有1的数量for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)cnt += arr[i];if(cnt == 0)return {0, n - 1};//三者平分 能分继续 不能分就不行if(cnt % 3) return ans;cnt = cnt / 3;int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0, s = 0;//根据1的数量将三个指针定位到各自第一个1的位置while(i < n && s < 1) { s += arr[i++];}s = 0;while(j < n && s < cnt + 1) { s += arr[j++];}s = 0;while(k < n && s < 2 * cnt + 1) { s += arr[k++];}//开始判断第一个1后面的是否完全相同while(k < n && arr[i] == arr[j] && arr[j] == arr[k]){i++; j++; k++;}if(k < n)return ans;elsereturn {i - 1, j};}
};
[10.6 下一个排列 lc 31](31. 下一个排列 - 力扣(LeetCode))
这个题挺巧妙的,需要仔细分析排列。我们以2 6 3 5 4 1为例,可以从右边开始分析。就是如果是降序比如5 4 1这样的,就是已经是最大的了,不会再有下一个排列了。所以我们第一步需要从右边找第一个升序的,找到了 3 5。为了是下一个排列因此我们需要使这个排列尽可能地小,所以我们从后面5 4 1中选一个第一个比3大地和他交换,得到一个比3大一点的新开头,2 6 4 5 3 1。接下来需要将后面的变成最小的,因为是逆序,所以直接反转即可。
class Solution {
public:void nextPermutation(vector<int>& nums) {int n = nums.size();int i = n - 1;//找到第一个升序的 3 5 while(i > 0 && nums[i] <= nums[i - 1]) i--;//如果不存在升序说明全部倒序,直接全部逆序即可if(i <= 0) {reverse(nums.begin(), nums.end()); return;}int j = i - 1; // j是3 等着待交换的那个//向右边倒序序列中找比nums[j]大一点的值 i - 1就是那个4while(i < n && nums[i] > nums[j]) i++;cout << nums[j] << " " << nums[i - 1] << endl;//swap(nums[j], nums[i - 1]); 将二者交换int t = nums[j];nums[j] = nums[i - 1];nums[i - 1] = t;//最后将后面的倒序逆转变小一点的排列reverse(nums.begin() + j + 1, nums.end());}
};
单调栈版本 等价于lc 556
class Solution {
public://nums是有n数字分割来的,所以是倒序的int nextGreaterElement(vector<int> nums) {stack<int> stk;int x = -1, y = -1;for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){if(stk.size() && nums[i] < nums[stk.top()]){x = i;while(stk.size() && nums[i] < nums[stk.top()]){y = stk.top();stk.pop();}swap(nums[x], nums[y]);reverse(nums.begin(), nums.begin() + x);break;}stk.push(i); }if(x == -1) return -1;long long ans = 0, k = 1;for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){ans += nums[i] * k;k = k * 10;}cout << ans << endl;if(ans > INT_MAX) return -1;else return ans;}
};
[10.7 最大升序子序列和 lc1800](1800. 最大升序子数组和 - 力扣(LeetCode))
class Solution {
public:int maxAscendingSum(vector<int>& nums) {int ans = nums[0], s = nums[0];for(int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i++){if(nums[i - 1] < nums[i])s += nums[i];elses = nums[i];ans = max(ans, s);}return ans;}
};
[10.7 寻找重复数 lc 287](287. 寻找重复数 - 力扣(LeetCode))
快慢指针,将1,3,4,2,2看成链表,判断链表是否有环以及找到链表的入口。
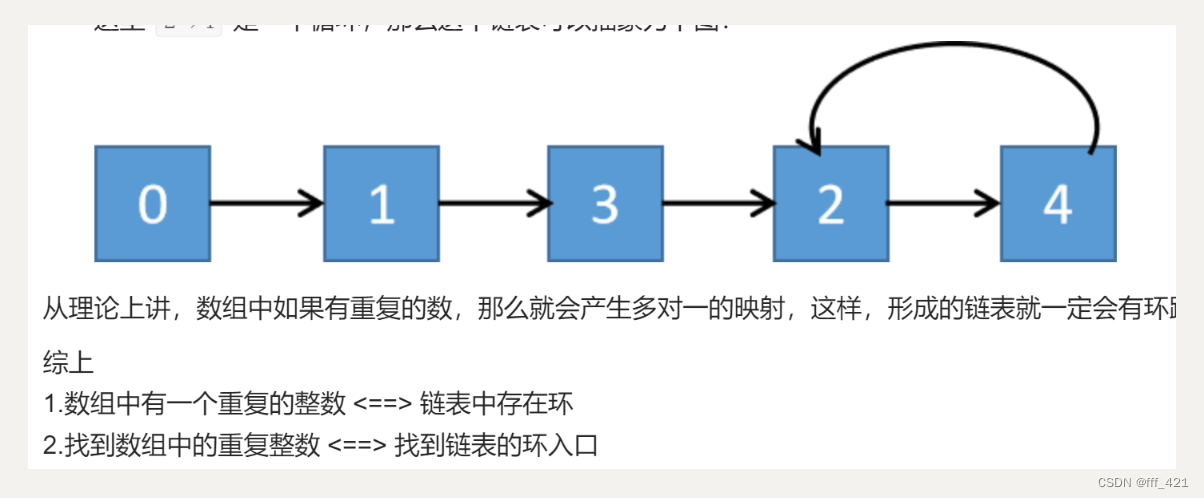
class Solution {
public:int findDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) {//将数组看成链表,找到环的入口int slow = 0, fast = 0;while(1){slow = nums[slow];fast = nums[nums[fast]];if(slow == fast)break;}fast = 0;while(slow != fast){slow = nums[slow];fast = nums[fast];}return slow;}
};
[10.7 找到数组中消失的数字 lc 448](448. 找到所有数组中消失的数字 - 力扣(LeetCode))
这个题也是将数组中的值和下标映射起来,比如[4,3,2,7,8,2,3,1],nums[0] = 4,则将4对应的nums[4] = 8换成-8代表有4了,重复的已经成为负数的就不变,最后值为正的下标就是消失的数字。
class Solution {
public:vector<int> findDisappearedNumbers(vector<int>& nums) {vector<int> ans;for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){nums[abs(nums[i]) - 1] = - abs(nums[abs(nums[i]) - 1]);}for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){if(nums[i] > 0)ans.push_back(i + 1);}return ans;}
};
[10.8 优势洗牌 lc 870](870. 优势洗牌 - 力扣(LeetCode))
贪心之田忌赛马:在nums1中找大于nums2[i]的最小值,如果没有则返回nums1中的最小值。直接找会导致超时,二分查找第一个。
class Solution {
public:vector<int> advantageCount(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {int n = nums1.size();vector<int> ans(n, 0);bool st[n];int idx = 0;memset(st, false, sizeof st);sort(nums1.begin(), nums1.end());for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){int l = 0, r = n;while(l < r){int mid = l + r >> 1;if(nums1[mid] > nums2[i])r = mid;elsel = mid + 1;}while(l < n && (st[l] || nums1[l] == nums2[i]))l++;if(l < n){ans[i] = nums1[l];st[l] = true;}else{while(st[idx]) idx++;ans[i] = nums1[idx];st[idx++] = true;}}return ans; }
};
10.8 三数之和 lc 15
排序的两数之和的变形 lc 167:如果一个数组已经排序了求两数之和那么可以使用双指针,一个从0开始,一个从n - 1开始,如果和大于sum那么j–,小于sum那么i++;
这道题:他说顺序不重要,我们可以按照i < j < k的顺序返回
还要去除重复就是如果i j k在遇到和上一个一样的时候要跳过。
两个优化:
- 如果nums[i]和离他最近的两个(最小的)都 大于0了,那么全部不可能
- 如果nums[i]和离他最远的两个(最大的)都小于0了,那么当前x不可能
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> threeSum(vector<int>& nums) {vector<vector<int>> ans;sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());int n = nums.size();for(int i = 0; i < n - 2; i++){if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1])continue;//优化1:if(nums[i] + nums[i + 1] + nums[i + 2] > 0) break;//优化2:if(nums[i] + nums[n - 2] + nums[n - 1] < 0) continue;int j = i + 1, k = n - 1;while(j < k){ int s = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k];if(!s) {ans.push_back({nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]});while(j < k && nums[j] == nums[j + 1]) j++;while(j < k && nums[k] == nums[k - 1]) k--;j++; k--;}else if(s > 0) k--;else j++; }}return ans;}
};
[10.10 数组中第k个元素](215. 数组中的第K个最大元素 - 力扣(LeetCode))
1. 快速排序
快速排序每次都可以使nums[r]== x,然后左侧都小于等于x,右侧都大于等于x。因此只要某次确定值的下标是k就可以返回第k个最大的元素了。
class Solution {
public:int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k) {return quicksort(nums, k, 0, nums.size() - 1);}int quicksort(vector<int>& nums, int k, int left, int right){if(right < left)return INT_MAX;int x = nums[(left + right) >> 1];int l = left - 1, r = right + 1;while(l < r){do l++; while(nums[l] > x);do r--; while(nums[r] < x);if(l < r){int t = nums[l]; nums[l] = nums[r]; nums[r] = t;}}int p;if(nums[l] == x)p = l;if(nums[r] == x)p = r;if(p == k - 1)return nums[p];else if(p > k - 1)return quicksort(nums, k, left, r);elsereturn quicksort(nums, k, r + 1, right);}
};
2. 建堆
维护一个k长度的大顶堆,堆顶元素就是第k大,当堆顶元素不再是第k大的时候,就调整堆。
最小堆 - 数组中的第K个最大元素 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution {
public:int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k) {int n = nums.size();make_heap(nums, k);for(int i = k; i < n; i++){if(nums[i] < nums[0])continue;else{nums[0] = nums[i];shift_down(nums, k, 0);}}return nums[0];}void shift_down(vector<int>& nums, int k, int i){int j = 2 * i + 1;while(j < k){if(j + 1 < k && nums[j] > nums[j + 1]) j++;if(nums[i] > nums[j]){swap(nums[i], nums[j]);i = j;j = 2 * i + 1;}elsebreak;}}void make_heap(vector<int>& nums, int k){for(int i = k / 2; i >= 0; i--)shift_down(nums, k, i);}
};
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;class Solution {
public:int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k) {int n = nums.size();//构建具有k个元素(nums[0..k-1])的最小堆, 时间复杂度O(nlogk)make_heap(nums, k);//从数组nums的第k+1个元素(nums[k])开始,依次替换堆顶,然后调整为最小堆for (int i = k; i < n; i++) {if (nums[i] < nums[0]) //扫描到的元素nums[i]比堆顶元素小,丢弃continue;nums[0] = nums[i]; //替换堆顶元素sift_down(nums, 0, k); //堆顶元素下沉}return nums[0]; //堆顶元素即为第k大数}//将编号为i的结点下沉。时间复杂度:O(logk)void sift_down(vector<int> &nums, int i, int k) {int j = i * 2 + 1; //计算结点i的左孩子编号while (j < k) { //结点i有左孩子//结点i有右孩子,且右孩子的值小于左孩子if (j + 1 < k && nums[j + 1] < nums[j])j++;if (nums[i] > nums[j]) { //双亲的值大,应该下沉到孩子结点的位置swap(nums[i], nums[j]); //将孩子交换到双亲位置i = j;j = i * 2 + 1;} else break;}}//创建最小堆:O(nlogk)void make_heap(vector<int> &nums, int k) {//从最后一个非叶子结点开始进行调整(下沉)for (int i = k / 2; i >= 0; i--) //k最大可以取到n(数组长度)sift_down(nums, i, k); //时间复杂度O(logk)}
};int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{vector<int> nums = {3, 2, 1, 5, 6, 4};int k = 2;// vector<int> nums = {3, 2, 3, 1, 2, 4, 5, 5, 6};// int k = 4;Solution obj;int res = obj.findKthLargest(nums, k);cout << res << endl;return 0;
}
10.10 使序列递增的最小交换次数 lc 801
状态机dp:dp[i] [0]表示第i位不发生交换使得前i位递增的最小交换次数,1同理。
有两种情况可以交换:
- 两组都满足前后大于,这种就是要不i和i-1都不交换,要么都交换。
- 交叉满足前后大小关系,这种要不i- 1交换要不i交换。
class Solution {
public:int minSwap(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {int n = nums1.size();int dp[n][2];memset(dp, 0x3f, sizeof dp);dp[0][0] = 0;dp[0][1] = 1;for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){if(nums1[i] > nums1[i - 1] && nums2[i] > nums2[i - 1]){dp[i][0] = dp[i - 1][0]; //要么不交换dp[i][1] = dp[i - 1][1] + 1; //要么两个都交换}if(nums1[i] > nums2[i - 1] && nums2[i] > nums1[i - 1]){dp[i][0] = min(dp[i][0], dp[i - 1][1]); //前一个发生交换dp[i][1] = min(dp[i][1], dp[i - 1][0] + 1); //后面这个发生交换}}return min(dp[n - 1][0], dp[n - 1][1]);}
};
10.11 仅执行一次字符串交换能否使两个字符串相等 lc 1790
记录下两个不同的下标,超过两个不同返回false,最后看不同的两个下标交换后是否相同。
class Solution {
public:bool areAlmostEqual(string s1, string s2) {int n = s1.size();int cnt = 0;int a[2];for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){if(s1[i] != s2[i]){if(cnt == 2){cnt++;break;}a[cnt++] = i;}}if(cnt == 1 || cnt > 2)return false;if(cnt == 0)return true;if(s1[a[0]] == s2[a[1]] && s1[a[1]] == s2[a[0]])return true;return false;}
};
10.12 链表组件 lc 817
模拟即可
/* Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:
// 被骗了,是求所有组件的个数而不是求组件的最大长度无语无语int numComponents(ListNode* head, vector<int>& nums) {int n = nums.size(), ans = 0;unordered_set<int> hashset;for(int x: nums)hashset.insert(x);ListNode* p = head;int cnt = 0;while(p != nullptr){if(hashset.find(p->val) != hashset.end())cnt++;else{if(cnt)ans++;cnt = 0;}p = p->next;}if(cnt)ans++;return ans;}
};
10.12 接雨水 lc 42
接雨水的关键就是单调栈
不同于柱状图的最大矩形(向两边找低于栈顶的递增),接雨水需要向两边找高于栈顶的,这样才能接住雨水,因此是递减栈。
以栈顶元素作为雨水高度t = height[stk.top()],当右边高于栈顶时,就是找到了右边高于的,然后去找左边高于的,也即是下一个栈顶。还有要是有和栈顶相同的也要pop出去,而且高度要减去。下一个栈顶就是左边高于栈顶的了height[stk.top()]。比较这两边高的选小的作为高,减去t,乘上宽度即可。
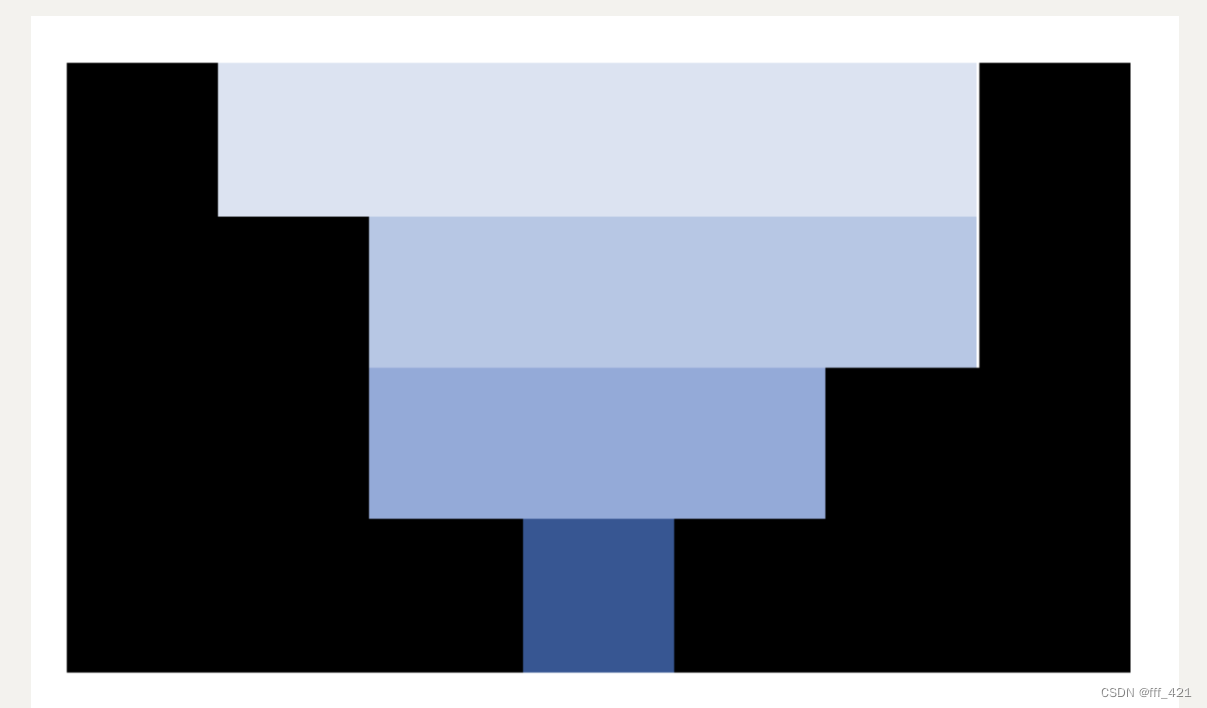

class Solution {
public:int trap(vector<int>& height) {int n = height.size();int ans = 0;stack<int> stk;for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){while(!stk.empty() && height[i] > height[stk.top()]){int t = stk.top();stk.pop();while(!stk.empty() && height[stk.top()] == height[t])stk.pop();if(!stk.empty())ans += ( min(height[stk.top()], height[i]) - height[t] ) * (i - stk.top() - 1);}stk.push(i);}return ans;}
};
10.13 合并K个升序链表 lc 23
两两归并,最后变成两个合并。
/* Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2){ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1);ListNode* p = dummy;if(l1 == nullptr && l2 == nullptr)return nullptr;while(l1 != nullptr && l2 != nullptr){if(l1->val < l2->val){p->next = l1;l1 = l1->next;}else{p->next = l2;l2 = l2->next;}p = p->next;}while(l1 != nullptr){p->next = l1;l1 = l1->next;p = p->next;}while(l2 != nullptr){p->next = l2;l2 = l2->next;p = p->next;}return dummy->next;}ListNode* binaryMerge(vector<ListNode*>& lists, int low, int high){if(low > high)return nullptr;if(low == high)return lists[low];if(high - low == 1)return mergeTwoLists(lists[low], lists[high]);int mid = (low + high) >> 1;return mergeTwoLists(binaryMerge(lists, low, mid), binaryMerge(lists, mid + 1, high));}ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {return binaryMerge(lists, 0, lists.size() - 1);}
};
10.13 找到字符串中所有字母异位词 lc 438

滑动窗口
class Solution {
public:vector<int> findAnagrams(string s, string p) {vector<int> ans;int sn = s.size();int pn = p.size();if(pn > sn) return {};int cnts[26];int cntp[26];memset(cnts, 0, sizeof cnts);memset(cntp, 0, sizeof cntp);for(int i = 0; i < pn; i++)cntp[p[i] - 'a']++;int i = 0, j = 0;for(; j < pn; j++)cnts[s[j] - 'a']++;while(j < sn){bool f = true;for(int k = 0; k < 26; k++){if(cnts[k] != cntp[k])f = false;}if(f)ans.push_back(i);cnts[s[i++] - 'a']--;if(j < sn)cnts[s[j++] - 'a']++; }bool f = true;for(int k = 0; k < 26; k++){if(cnts[k] != cntp[k])f = false;}if(f)ans.push_back(i);return ans;}
};
10.13 最多能完成排序的块 lc 769
规律:区间数的最大值小于等于下标就可以分块
或者统计下标的和等于区块的和也可以分块。
总之就是区块内的元素需要和下标一致。
class Solution {
public:int maxChunksToSorted(vector<int>& arr) {//区间的最大值小于等于索引则可以划分区间int n = arr.size();int ans = 0, ma = 0;for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){if(arr[i] > ma)ma = arr[i];if(ma <= i){ans++;ma = 0;}}return ans;}
};
10.14 不同的子序列II lc940
题目翻译一下是从s的子序列中选出t的个数
还是不太懂捏(别急,11月的我来再学一遍)
这回彻底明白了
我们对于每个s[i]有在之前情况上再进行选和不选两种情况,首先不选的情况就是上一次s[i - 1]的那些字符串,选就是在s[i - 1]那些字符串上加上a后缀,然后再加上一个以s[i]为单独子序列的字符串。
但是可以造成重复,比如“aba” 前面是 a, b, ab, 我们在选第三个a的时候,把a当作单独子序列时会与不选a时的之前的a重复。
因此我们以是否以s[i]为后缀区分,dp[i] [j]表示使用前i个字符以j为后缀的字符串数量,分两步:
-
不选s[i]:dp[i] [j] = dp[i - 1] [j] //a, b, ab
-
选s[i],重新计算以s[i]为后缀的字符串数量,这时我们不考虑之前的以s[i]为后缀的,我们仅仅考虑以当前s[i]为后缀,这样就不会导致重复//不考虑a, b, ab中的a
dp[i] [s[i] - ‘a’] = 1 + (求和, j从1到26)dp[i - 1] [j]
class Solution {
public:const int mod = 1e9 + 7;int distinctSubseqII(string s) {int sn = s.size(), ans = 0;int dp[sn][26];memset(dp, 0, sizeof dp);dp[0][s[0] - 'a'] = 1;for(int i = 1; i < sn; i++){for(int j = 0; j < 26; j++)dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j]; //不选s[i],这些以j结尾的字符串数量和s[i - 1]时一样//下面这段可以换成//dp[i][s[i] - 'a'] = accumulate(dp[i], dp[i] + 26, 1L) % mod;dp[i][s[i] - 'a'] = 1; //以s[i]单独为一个字符串for(int j = 0; j < 26; j++)dp[i][s[i] - 'a'] = ((long long)dp[i][s[i] - 'a'] + dp[i - 1][j]) % mod; //选上s[i], 就是改一下以s[i]结尾的字符串数量}for(int i = 0; i < 26; i++)ans = ((long long)ans + dp[sn - 1][i]) % mod;return ans;}
};
10.14 不同的子序列 I lc 115
class Solution {
public:const int mod = 1e9 + 7;int numDistinct(string s, string t) {int sn = s.size(), tn = t.size();int dp[sn + 1][tn + 1];//dp[i][j]表示st中使用前i个去匹配t中的前j个用的个数memset(dp, 0, sizeof dp);for(int i = 0; i <= sn; i++)dp[i][0] = 1;for(int i = 1; i <= sn; i++){for(int j = 1; j <= tn; j++){//匹配上了:我们可以选择用不用s[i]去匹配,不用是s[i]是后面可能还有,我们先不用s[i]if(s[i - 1] == t[j - 1])dp[i][j] = (dp[i - 1][j - 1] + dp[i - 1][j]) % mod;elsedp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];}}return dp[sn][tn];}
};
10.14 路径总和 I lc 112
我一开始写的是,先不管下面这个空树是否为空。看[1, 2] 1 这个例子,就是这棵树只有1 ,2 一侧两个节点。在我的判断中走到1这个节点就可以判断true了。但是题目要求的是到叶子节点,所以判断条件要加上节点的左右节点都为空。
//wrong
class Solution {
public:bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {if(root == nullptr && targetsum == 0)return true;if(root == nullptr)return false;return hasPathSum(root->left, targetSum - root->val) || hasPathSum(root->right, targetSum - root->val);}
};
//right
class Solution {
public:bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {if(root == nullptr)return false;if(targetSum == root->val && root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr)return true;return hasPathSum(root->left, targetSum - root->val) || hasPathSum(root->right, targetSum - root->val);}
};
10.14 路径总和II lc 113
在1的基础上要记录下满足要求的路径和
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> ans;vector<int> tmp;vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {if(root == nullptr)return {};helper(root, targetSum);return ans;}void helper(TreeNode* root, int targetSum){if(root == nullptr)return;if(targetSum == root->val && !root->left && !root->right){tmp.push_back(root->val);ans.push_back(tmp);tmp.pop_back();return ;}tmp.push_back(root->val);helper(root->left, targetSum - root->val);helper(root->right, targetSum - root->val);tmp.pop_back();}
};
10.14 路径总和III lc 437
路径不需要从父节点开始,也不需要在叶子节点结束,但方向要向下。
两个dfs,第一个dfs遍历每个节点,第二dfs去计算和是否满足。
class Solution {
public:long long ans = 0;int ts;int pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {if(root == nullptr)return 0;ts = targetSum;dfs1(root);return ans;}void dfs1(TreeNode* root){if(root == nullptr)return;dfs2(root, 0);dfs1(root->left);dfs1(root->right);}void dfs2(TreeNode* root, long long curSum){if(root == nullptr)return;curSum += root->val;if(curSum == ts)ans++;dfs2(root->left, curSum);dfs2(root->right, curSum);}
};
树上的前缀和:哇塞!最完整的路径是从根节点到叶子节点,这题相当于在这些路径上找区间和=targetsum的,那不就是前缀和吗!
curSum - preSum = targetSum即可。
class Solution {
public:unordered_map<long long, int> preSum;int targetSum;int ans = 0;int pathSum(TreeNode* root, int ts) {if(root == nullptr)return 0;targetSum = ts;preSum[0] = 1;dfs(root, 0);return ans;}void dfs(TreeNode* root, long long curSum){if(root == nullptr)return;curSum += root->val;if(preSum.find(curSum - targetSum) != preSum.end()){ans += preSum[curSum - targetSum];}preSum[curSum]++;dfs(root->left, curSum);dfs(root->right, curSum);preSum[curSum]--;}
};
10.14 二叉树的序列化与反序列化 lc 297
这道题主要是区分每个节点的值和null处理、负值处理的问题,其他就是递归即可
BFS
class Codec {
public:const int nll = 2000;// Encodes a tree to a single string.string serialize(TreeNode* root) {if(root == nullptr)return "";string data;queue<TreeNode*> q;q.push(root);while(q.size()){TreeNode* tmp = q.front();q.pop();if(tmp == nullptr){data += "_#";continue;}adata += "_" + to_string(tmp->val);q.push(tmp->left);q.push(tmp->right);}cout << data << endl;return data;}// Decodes your encoded data to tree.TreeNode* deserialize(string data) {if(data.size() == 0)return nullptr;vector<int> v;int i = 0;while(i < data.size()){int j = i + 1;while(j < data.size() && data[j] != '_')j++;string s = data.substr(i + 1, j - i - 1);cout << s << endl;if(s == "#")v.push_back(nll);elsev.push_back(atoi(s.c_str()));i = j;}i = 0;TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(v[i++]);queue<TreeNode*> q;q.push(root);while(q.size()){TreeNode* tmp = q.front();q.pop();if(v[i] == nll)tmp->left = nullptr;else{tmp->left = new TreeNode(v[i]);q.push(tmp->left);}i++;if(v[i] == nll)tmp->right = nullptr;else{tmp->right = new TreeNode(v[i]);q.push(tmp->right);}i++;}return root;}
};
DFS
class Codec {
public:const int nll = 2000;vector<int> v;int i = 1;// Encodes a tree to a single string.string serialize(TreeNode* root) {if(root == nullptr)return "_#";return "_" + to_string(root->val) + serialize(root->left) + serialize(root->right);}void helper(string data){int i = 0;while(i < data.size()){int j = i + 1;while(j < data.size() && data[j] != '_')j++;string s = data.substr(i + 1, j - i - 1);cout << s << endl;if(s == "#")v.push_back(nll);elsev.push_back(atoi(s.c_str()));i = j;}}TreeNode* build(TreeNode* root){if(v[i] == nll){root->left = nullptr;i++;}else{root->left = new TreeNode(v[i]);i++;build(root->left);}if(v[i] == nll){root->right = nullptr;i++;}else{root->right = new TreeNode(v[i]);i++;build(root->right);}return root;}// Decodes your encoded data to tree.TreeNode* deserialize(string data) {if(data == "_#")return nullptr;helper(data);TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(v[0]);return build(root);}
};
10.15 目标和 lc494
1.简单dfs
class Solution {
public:int n;//int ans = 0;int findTargetSumWays(vector<int>& nums, int target) {n = nums.size();return dfs(nums, target, 0, 0);}int dfs(vector<int>& nums, int target, int curSum, int i){if(i == n && curSum == target)return 1;if(i == n)return 0;int n1 = dfs(nums, target, curSum + nums[i], i + 1);int n2 = dfs(nums, target, curSum - nums[i], i + 1);return n1 + n2;}
};
2. dfs+记忆化搜索
memo记录的是key = (i, cursum), value=要求的个数
class Solution {
public:int n;//int ans = 0;unordered_map<string, int> memo;int findTargetSumWays(vector<int>& nums, int target) {n = nums.size();return dfs(nums, target, 0, 0);}int dfs(vector<int>& nums, int target, int curSum, int i){string key = to_string(i) + "_" + to_string(curSum);if(memo.count(key))return memo[key];if(i == n && curSum == target){memo[key]++;return memo[key];}if(i == n){memo[key] = 0;return memo[key];}int n1 = dfs(nums, target, curSum + nums[i], i + 1);int n2 = dfs(nums, target, curSum - nums[i], i + 1);memo[key] = n1 + n2;return n1 + n2;}
};
3. 01背包
在记忆化的基础上变成01背包
class Solution {
public:int findTargetSumWays(vector<int>& nums, int target) {int n = nums.size();int sum = 0;for(int x: nums)sum += x;if(target > sum || target < -sum) return 0;vector<vector<int>> dp(n + 1, vector<int>(2 * sum + 1, 0));dp[0][0 + sum] = 1;for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){for(int cur = -sum; cur <= sum; cur++){if(cur - nums[i - 1] >= -sum)dp[i][cur + sum] = dp[i - 1][cur - nums[i - 1] + sum];if(cur + nums[i - 1] <= sum)dp[i][cur + sum] += dp[i - 1][cur + nums[i - 1] + sum];}}return dp[n][target + sum];}
};
10.15 分割等和子集 lc 416
划分两个子集使得x = y,也即是找到一个子集使得x=sum/2。也就是从这些数字中选一些数使得和为sum/2。
01背包问题
class Solution {
public:int n;bool canPartition(vector<int>& nums) {n = nums.size();int sum = 0;for(int x: nums)sum += x;if(sum % 2) return false;else return findTargetSumWays(nums, sum / 2);}int findTargetSumWays(vector<int>& nums, int target){vector<vector<bool>> dp(n + 1, vector<bool>(target + 1, false));for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++)dp[i][0] = true;for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){for(int cur = 0; cur <= target; cur++){dp[i][cur] = dp[i - 1][cur];if(nums[i - 1] <= cur)dp[i][cur] = dp[i][cur] || dp[i - 1][cur - nums[i - 1]];}}return dp[n][target];}
};

10.15 用栈操作构建数组 lc 1441
根据操作结果反向推出操作
class Solution {
public:vector<string> buildArray(vector<int>& target, int n) {int tn = target.size();vector<string> ans;int i = 1, j = 0;while(j < tn){//if(i == target[j]){ans.push_back("Push");i++;j++;}while(i <= n && j < tn && i < target[j]){ans.push_back("Push");ans.push_back("Pop");i++;}}return ans;}
};
10.16 可能的二分法 lc 886
染色法判定二分图
const int N = 20020;
const int M = 2010;class Solution {
private:int h[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;int color[M];
public:void add(int a, int b){e[idx] = b; ne[idx] = h[a]; h[a] = idx++;}bool dfs(int i, int c){color[i] = c;for(int j = h[i]; j != -1; j = ne[j]){int t = e[j];if(color[t] == c) return false;if(!color[t]){if(!dfs(t, 3 - c))return false;}}return true;}bool possibleBipartition(int n, vector<vector<int>>& dislikes) {memset(h, -1, sizeof h);for(int i = 0; i < dislikes.size(); i++){int a = dislikes[i][0], b = dislikes[i][1];add(a, b);add(b, a);}for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){if(!color[i]){if(!dfs(i, 1))return false;}cout << color[i] << endl;}return true;}
};
10.17 完全平方数
还是01背包问题,就是从平方和中选选到和为target的最小数量
class Solution {
public:const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;int numSquares(int n) {vector<int> sq;for(int i = 0; i * i <= n; i++)sq.push_back(i * i);int dp[n + 1];memset(dp, INF, sizeof dp);dp[1] = 1;dp[0] = 0; for(int i = 0; i < sq.size(); i++){for(int j = 0; j <= n; j++){if(sq[i] <= j)dp[j] = min(dp[j], dp[j - sq[i]] + 1);}}return dp[n];}
};
10.17 零钱兑换 lc 322
完全背包问题:物品可以无限使用,要求背包装满,要求使用的数量最少。
在满足:amount=v1x1+v2x2+v3x3+…+vnxn 的条件下,求: target=min{x1+x2+x3+…xn}可以dfs将所有的组合拿出来,然后取硬币数最小。
dp[i]表示硬币和为i时的最小硬币数,然后看取不取前i个硬币,取最小即可。
class Solution {
public:const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;int coinChange(vector<int>& coins, int amount) {int n = coins.size();int dp[amount + 1];memset(dp, INF, sizeof dp);dp[0] = 0;for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){for(int j = 0; j <= amount; j++){if(coins[i] <= j){dp[j] = min(dp[j], dp[j - coins[i]] + 1);}}}if(dp[amount] == INF)return -1;elsereturn dp[amount];}
};
10.17 水果成篮 lc 904
滑动窗口应用 类似于lc992 //最多两个不同元素的最长连续子数组
理解题意:fruit[i] = 1表示种类1, 2表示种类2,0表示种类0,不是表示种类个数
class Solution {
public:int totalFruit(vector<int>& nums) {//最多两个不同元素的最长连续子数组unordered_map<int, int> hashmap;int ans = 0;int l = 0, r = 0;while(r < nums.size()){hashmap[nums[r++]]++;while(hashmap.size() > 2){hashmap[nums[l]]--;if(!hashmap[nums[l]]) hashmap.erase(nums[l]);l++;}ans = max(ans, r - l);}return ans;}
};
class Solution {
public:int totalFruit(vector<int>& fruits) {int n = fruits.size();int i = 0, j = 0, tot = 0, ans = 0;vector<int> cnt(n + 10, 0);for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){if((++cnt[fruits[j]]) == 1)tot++;while(tot > 2){if(--cnt[fruits[i++]] == 0)tot--;}ans = max(ans, j - i + 1);}return ans;}
};
10.18 最大为 N 的数字组合 lc 902
数位dp
class Solution {
public:vector<int> d;int m;string sn;vector<int> dp;int atMostNGivenDigitSet(vector<string>& digits, int n) {for(int i = 0; i < digits.size(); i++)d.push_back(atoi(digits[i].c_str()));sn = to_string(n);m = sn.size();for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)dp.push_back(-1);return dfs(n, 0, true, false);}int dfs(int n, int i, bool isLimit, bool isNum){if(i == m)return isNum;int ans = 0;if(!isLimit && isNum && dp[i] >= 0) return dp[i];if(!isNum)ans += dfs(n, i + 1, false, false);int up = isLimit? sn[i] - '0': 9;for(int j = 0; j < d.size(); j++){if(d[j] > up)break;ans += dfs(n, i + 1, isLimit && d[j] == up, true);}if(!isLimit && isNum)dp[i] = ans;return ans;}
};
10.18 环形链表 lc 141
快慢指针
/* Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {if(head == nullptr)return false;if(head->next == nullptr)return false;ListNode* fast = head;ListNode* slow = head;while(fast != nullptr){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next;if(fast != nullptr)fast = fast->next;if(slow == fast)return true;}return false;}
};
10.18 环形链表|| lc 142
/* Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {ListNode* fast = head, *slow = head;if(head == nullptr) return nullptr;if(head->next == nullptr) return nullptr;while(fast != nullptr){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next;if(fast != nullptr)fast = fast->next;if(fast == slow){fast = head;while(fast != slow){fast = fast->next;slow = slow->next;}return fast;}}return nullptr;}
};
10.18 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点 lc 19
还是快慢指针找到倒数第n个节点然后再删除~下次再练习
class Solution {
public:ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {ListNode* p = head;if(head->next == nullptr)return nullptr;for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)p = p->next;ListNode* q = head;if(p == nullptr)return head->next; //删掉头节点while(p->next != nullptr){p = p->next;q = q->next;}ListNode* nx = q->next;q->next = nx->next; return head;}
};
10.19 无法吃午餐肉的同学 lc 1700
模拟
class Solution {
public:int countStudents(vector<int>& students, vector<int>& sandwiches) {int n = students.size();int s0 = 0, s1 = 0;for(int x: students){if(x) s1++;else s0++;}for(int x: sandwiches){if(x == 1 && s1 > 0) s1--;else if(x == 0 && s0 > 0) s0--;else break;}return s0 + s1;}
};
10.19 括号的生成 lc 22
回溯
class Solution {
public:
//主要是保证右括号不能在左括号之前生成vector<string> ans;string tmp;vector<string> generateParenthesis(int n) {dfs(n, n, tmp);return ans;}void dfs(int left, int right, string tmp){if(left == 0 && right == 0){ans.push_back(tmp);tmp = "";return;}if(left > 0)dfs(left - 1, right, tmp +'(');if(right > left)dfs(left, right - 1, tmp +')');}
};
10.19 组合总和 lc 39
回溯
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> ans;vector<int> tmp;vector<vector<int>> combinationSum(vector<int>& candidates, int target) {sort(candidates.begin(), candidates.end());dfs(candidates, target, 0, 0);return ans;}void dfs(vector<int>& candidates, int target, int curSum, int i){if(curSum == target){ans.push_back(tmp);return;}if(curSum > target){return;}for(int j = i; j < candidates.size(); j++){tmp.push_back(candidates[j]);dfs(candidates, target, curSum + candidates[j], j);tmp.pop_back();}}
};
10.19 组合总数 II lc 40
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> ans;vector<int> tmp;vector<vector<int>> combinationSum2(vector<int>& candidates, int target) {sort(candidates.begin(), candidates.end());dfs(candidates, target, 0, 0);return ans;}void dfs(vector<int>& candidates, int target, int cur, int last){if(cur == target){ans.push_back(tmp);return;}if(cur > target){return;}for(int i = last; i < candidates.size(); i++){if(i > last && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1])continue;tmp.push_back(candidates[i]);dfs(candidates, target, cur + candidates[i], i + 1);tmp.pop_back();}}
};
10.19 电话号码的字母组合 lc 17
回溯
class Solution {
public:unordered_map<char, string> map;vector<string> ans;int n;string tmp;vector<string> letterCombinations(string digits) {n = digits.size();if(n == 0) return {};map['2'] = "abc";map['3'] = "def";map['4'] = "ghi";map['5'] = "jkl";map['6'] = "mno";map['7'] = "pqrs";map['8'] = "tuv";map['9'] = "wxyz";dfs(digits, 0, tmp);return ans;}void dfs(string digits, int i, string tmp){if(tmp.size() == n){ans.push_back(tmp);tmp = "";return;}int s = digits[i];for(int j = 0; j < map[s].size(); j++){char ch = map[s][j];dfs(digits, i + 1, tmp + ch);} }
};
10.20 缺失的第一个正数 lc 41
最大的缺失的正数也不会超过nums.size()。还是和下标相关
把每个数放在下标应该在的数上,然后从0开始判断如果和下标不一样的第一个数就是缺失的第一个正数。
class Solution {
public:int firstMissingPositive(vector<int>& nums) {int n = nums.size();for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){while(nums[i] > 0 && nums[i] < n && nums[i] != nums[nums[i] - 1])swap(nums[i], nums[nums[i] - 1]);}for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){if(nums[i] != i + 1)return i + 1;}return n + 1;}
};
10.20 寻找重复数 lc 287
把数组看成链表,找到环的入口
class Solution {
public:int findDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) {//将数组看成链表,找到环的入口int slow = 0, fast = 0;while(1){slow = nums[slow];fast = nums[nums[fast]];if(slow == fast)break;}fast = 0;while(slow != fast){slow = nums[slow];fast = nums[fast];}return slow;}
};
10.20 找到所有数组中消失的数字 lc 448
就是把出现的数字和下标关联起来,将出现的数字的下标存储的数变成负数,最后是正数的就是缺失的。
class Solution {
public:vector<int> findDisappearedNumbers(vector<int>& nums) {vector<int> ans;for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){nums[abs(nums[i]) - 1] = - abs(nums[abs(nums[i]) - 1]);}for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++){if(nums[i] > 0)ans.push_back(i + 1);}return ans;}
};
10.20 第K个语法符号lc 779
class Solution {
public:int kthGrammar(int n, int k) {if(n == 1)return 0;return !(k % 2)^kthGrammar(n - 1, (k + 1) / 2);}
};
10.21 股票价格跨度 lc 901
单调栈:单调递减栈,当出现新价格大于栈顶价格时,就需要pop找出栈里面所有小于的,保持单调递减
class StockSpanner {
public:stack<int> stk;vector<int> v;int idx = 0;StockSpanner() {idx++;v.push_back(INT_MAX);stk.push(0);}int next(int price) {v.push_back(price);while(stk.size() && v[stk.top()] <= price) {stk.pop();}int i = stk.top();stk.push(idx);return idx++ - i;}
};10.22 根据身高重建队列 lc 406
按照身高从大到小排序,如果身高相同先排k小的。然后一个个插入,如果现有元素数量大于k的要求了,说明前面高个的太多了,需要把当前元素往前排。如果小于k的要求则直接插入即可,后面会随着插入而满足条件的。
struct peo
{int h, k;
};
bool cmp(const peo& p1, const peo& p2)
{if(p1.h != p2.h)return p1.h > p2.h;else return p1.k < p2.k;
}
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> reconstructQueue(vector<vector<int>>& people) {int n = people.size();peo P[n];for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){P[i].h = people[i][0];P[i].k = people[i][1];}sort(P, P + n, cmp);vector<vector<int>> ans;for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){if(ans.size() <= P[i].k)ans.push_back({P[i].h, P[i].k});elseans.insert(ans.begin() + P[i].k, {P[i].h, P[i].k});return ans;}
};
10.22 规划兼职工作lc 1235
按照endtime排序,然后dp[i]表示使用前i个元素的获得的最大报酬。
struct job {int s, e, p;
};
bool cmp(const job& j1, const job& j2) {return j1.e < j2.e;
}
class Solution {
public:int jobScheduling(vector<int>& startTime, vector<int>& endTime, vector<int>& profit) {int n = startTime.size();job jobs[n];for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {jobs[i].s = startTime[i];jobs[i].e = endTime[i];jobs[i].p = profit[i];}sort(jobs, jobs + n, cmp);int dp[n];dp[0] = jobs[0].p;for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) {dp[i] = max(dp[i - 1], jobs[i].p);for(int j = i - 1; j >= 0; j--) {if(jobs[j].e <= jobs[i].s) {dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[j] + jobs[i].p);break;}}}return dp[n - 1];}
};
10.24 除自身以外的乘积 lc 238
剑指offer中的一道题,前缀统计nums[i]左侧的,后缀统计nums[i]右侧的,一共O(n)
class Solution {
public:vector<int> productExceptSelf(vector<int>& nums) {int n = nums.size();vector<int> ans(n, 1);int pre = 1, suf = 1;for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {ans[i] *= pre;pre *= nums[i];}for(int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {ans[i] *= suf;suf *= nums[i];}return ans;}
};
10.24 和为k的子数组 lc 560
前缀和+哈希表
class Solution {
public:int subarraySum(vector<int>& nums, int k) {unordered_map<int, int> hmap;hmap[0] = 1;int sum = 0, ans = 0;for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {sum += nums[i];if(hmap.count(sum - k)) {ans += hmap[sum - k];}hmap[sum]++;}return ans;}
};
10.24 分割数组 lc 915
只要左边的max <= 右边的min即可, O(n)的
右边的min可以先统计以下,最后加上一个INT_MAX哨兵
class Solution {
public:int partitionDisjoint(vector<int>& nums) {int mi = INT_MAX, ma = 0;vector<int> minNums(nums.size(), INT_MAX);for(int i = nums.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {mi = min(mi, nums[i]);minNums[i] = mi;}minNums.push_back(INT_MAX);for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {ma = max(ma, nums[i]);if(ma <= minNums[i + 1]) {return i + 1;}}return 0;}
};
10.25 最短的桥 934
10.26 任务调度器 lc 621
class Solution {
public:int leastInterval(vector<char>& tasks, int n) {int cnt[26];int max_cnt = 0, max_cnt_same = 0;memset(cnt, 0, sizeof cnt);for(int i = 0; i < tasks.size(); i++) {cnt[tasks[i] - 'A']++;}for(int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {max_cnt = max(max_cnt, cnt[i]);}for(int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {if(max_cnt == cnt[i]) {max_cnt_same++;}}int ans = (n + 1) * (max_cnt - 1) + max_cnt_same;//而当任务数超过该值时,我们可以在将其横向添加每个n+1 块的后面,同时不会引入额外的冻结时间return max(ans, tasks.size()); }
};
10.26 和至少为k的最短子数组 lc 862
暴力解法(超时):按照len遍历+滑动窗口,O(n2)O(n ^2)O(n2)的复杂度(注意:所有sum小于k不一定代表里面没有大于等于k的子数组,因为有负数的存在)。
class Solution {
public:int shortestSubarray(vector<int>& nums, int k) {int n = nums.size();for(int len = 1; len <= n; len++) {int s = accumulate(nums.begin(), nums.begin() + len, 0);if(s >= k) return len;for(int l = 1; l + len - 1 < n; l++) {int r = l + len - 1;s = s + nums[r] - nums[l - 1];if(s >= k) return len;}}return -1;}
};
10.28 戳气球 lc 312
很难的区间dp
class Solution {
public:int maxCoins(vector<int>& nums) {int n = nums.size();nums.push_back(1);nums.insert(nums.begin(), 1);int dp[n + 2][n + 2];memset(dp, 0, sizeof dp);//全都戳破的上一个状态是只剩一个没被戳破//dp[l][r]不包含l, r中k表示最后戳破的气球,最后就剩下 l, k, r了for(int len = 3; len <= n + 2; len++) {for(int l = 0; l + len - 1 <= n + 1; l++) {int r = l + len - 1;for(int k = l + 1; k <= r - 1; k++) {dp[l][r] = max(dp[l][r], dp[l][k] + dp[k][r] + nums[l] * nums[k] * nums[r]);}}}return dp[0][n + 1];}
};
10.28 子数组的最小值之和 lc 907
单调栈的应用题:计算每个值作为子数组最小值的次数,就需要分别向左向右找第一个小于arr[i]的值,假设最远子数组为(l, r),依据乘法原理子数组的个数就是(i - l) * (r - i)
还有很重要的一点就是:可能有重复的!
比如[1, 2, 3, 2, 3, 1]两个2计算的最远子数组都是(0, 5),那么就会在[1, 4]这个区间内重复计算两个2的子数组个数
我们需要向左找第一个小于的,向右找第一个小于等于的,那么这样左边的2最远子数组就是(0, 3),右边的就是(0, 5),这样就不会重复计算了!
class Solution {
public:const int mod = 1e9 + 7;int sumSubarrayMins(vector<int>& arr) {int n = arr.size();//加俩哨兵arr.push_back(0);arr.insert(arr.begin(), 0);int ans = 0;stack<int> stk;stack<int> stk1;int left[n + 2];int right[n + 2];stk.push(0);for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {while(!stk.empty() && arr[stk.top()] >= arr[i]) {stk.pop();}left[i] = i - stk.top();//cout << i << " " << left[i] << endl;stk.push(i);}stk1.push(n + 1);for(int i = n; i > 0; i--) {while(!stk1.empty() && arr[stk1.top()] > arr[i]) {stk1.pop();}right[i] = stk1.top() - i;stk1.push(i);}for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {ans = (ans + (long long)left[i] * right[i] * arr[i]) % mod;}return ans;}
};
10.30 LRU缓存 lc 146
哈希表+ 双向链表:最关键的就是加上一个头节点和尾节点,剩下的就仔细写仔细调试就可以了。
struct Node
{int key;int value;Node* next;Node* pre;Node(int k, int v){key = k;value = v;next = nullptr;pre = nullptr;}
};
class LRUCache {
public:Node* head;Node* nail;int cnt = 0;int cap;unordered_map<int, Node*> hashmap;LRUCache(int capacity) {cap = capacity;head = new Node(-1, -1);nail = new Node(-1, -1);head->next = nail;head->pre = nail;nail->next = head;nail->pre = head;}int get(int key) {if(hashmap.find(key) == hashmap.end())return -1;Node* tmp = hashmap[key];remove(tmp);addFromHead(tmp);return tmp->value;}void remove(Node* t){hashmap.erase(t->key);Node* pt = t->pre;Node* nt = t->next;pt->next = nt;nt->pre = pt;cnt--;}void addFromHead(Node* t){hashmap[t->key] = t;Node* nt = head->next;t->next = nt;t->pre = head;head->next = t;nt->pre = t;cnt++;}void put(int key, int value) {if(get(key) != -1){head->next->value = value;return;}if(cnt < cap){Node* tmp = new Node(key, value);addFromHead(tmp);}else{Node* tmp = new Node(key, value);Node* nt = nail->pre;remove(nt);addFromHead(tmp);}}
};
10.30 字母大小写全排列 lc 784
回溯
class Solution {
public:vector<string> ans;string tmp;vector<string> letterCasePermutation(string s) {dfs(s, 0);return ans;}void dfs(string s, int i){if(i == s.size()){ans.push_back(tmp);return;}if(s[i] >= '0' && s[i] <= '9'){tmp += s[i];dfs(s, i + 1);tmp.pop_back();}else if(s[i] >= 'a' && s[i] <= 'z'){tmp += s[i];dfs(s, i + 1);tmp.pop_back();tmp += (s[i] - 32);dfs(s, i + 1);tmp.pop_back();}else{tmp += s[i];dfs(s, i + 1);tmp.pop_back();tmp += (s[i] + 32);dfs(s, i + 1);tmp.pop_back();}}
};
10.30 最小栈 lc 155
两个栈辅助的
class MinStack {
public:stack<int> stk;stack<int> minstack;MinStack() {}void push(int val) {stk.push(val);if(minstack.empty() || val <= minstack.top())minstack.push(val);}void pop() {int x = stk.top();cout << x << endl;stk.pop();if(minstack.size() && x == minstack.top())minstack.pop();}int top() {return stk.top();}int getMin() {cout << minstack.top() << endl;return minstack.top();}
};
链表解决的:头插法,每个节点中记录栈顶当前值和当前值作为栈顶时的最小值。
struct node
{int val;int min;node* next;node(int x, int y){val = x;min = y;next = nullptr;}
};
class MinStack {
public:node* head;MinStack() {head = nullptr;}void push(int val) {if(head == nullptr)head = new node(val, val);else{int m = val <= head->min? val: head->min;node* tmp = new node(val, m);tmp->next = head;head = tmp; }}void pop() {head = head->next;}int top() {return head->val;}int getMin() {return head->min;}
};
10.31 滑动窗口的最大值 lc 239
模拟滑动窗口不行因为如果排出最大值要重新遍历找最大值,会超时
因此,选择双向队列维护一个单调递减的队列,当删掉的值==左边最大值时,将其删掉.当加入的值大于队尾的值时,删掉队尾维持递减队列.
class Solution {
public:vector<int> maxSlidingWindow(vector<int>& nums, int k) {vector<int> ans;int n = nums.size();deque<int> q;int l = 0, r = k - 1;for(int i = l; i <= r; i++){while(q.size() && nums[i] > q.back())q.pop_back();if(!q.size() || nums[i] <= q.back())q.push_back(nums[i]);}ans.push_back(q.front());while(r + 1 < n){if(q.size() && nums[l] == q.front())q.pop_front();while(q.size() && nums[r + 1] > q.back())q.pop_back();q.push_back(nums[r + 1]);ans.push_back(q.front());l++;r++;}return ans;}
};
class Solution {
public:vector<int> maxSlidingWindow(vector<int>& nums, int k) {deque<int> q;vector<int> ans;for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {if(!q.empty() && i >= k && nums[i - k] == q.front()) {q.pop_front();}while(!q.empty() && nums[i] > q.back()) {q.pop_back();}q.push_back(nums[i]);if(i >= k - 1) {ans.push_back(q.front());}}return ans;}
};
10.31 神奇字符串 lc481
模拟题目即可,小技巧 1^3 = 2 2^3 = 1
class Solution {
public:int magicalString(int n) {int x1 = 3, x2 = 3; //x1是总的字符串数量,x2是生成到哪一个vector<int> s(4, 0);s[1] = 1; s[2] = 2; s[3] = 2;int cnt = 1, f = 1;;while(x1 < n){int t = 0;if(s[x2] == 1){s.push_back(f);cnt += (f == 1);x1++;}else{s.push_back(f);s.push_back(f);x1 += 2;cnt += (f == 1) * 2;}f = f ^ 3;x2++;} if(x1 > n && s[x1] == 1) cnt--;return cnt;}
};
10.31 课程表 lc 207
气死我了,一个拓扑排序写了这么久…
const int N = 5010;
int h[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;
void add(int a, int b) {e[idx] = b;ne[idx] = h[a];h[a] = idx++;
}
class Solution {
public:bool canFinish(int numCourses, vector<vector<int>>& prerequisites) {idx = 0;int inorder[numCourses];queue<int> q;memset(h, -1, sizeof h);memset(inorder, 0, sizeof inorder);for(int i = 0; i < prerequisites.size(); i++) {add(prerequisites[i][1], prerequisites[i][0]);inorder[prerequisites[i][0]]++;}for(int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {if(inorder[i] == 0) {q.push(i);inorder[i] = -1;}}int cnt = 0;while(!q.empty()) {int t = q.front();q.pop();cnt++;for(int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {int b = e[i];inorder[b]--;if(!inorder[b]) {q.push(b);}}}return cnt == numCourses;}
};
ans.push_back(q.front());
while(r + 1 < n)
{
if(q.size() && nums[l] == q.front())
q.pop_front();
while(q.size() && nums[r + 1] > q.back())q.pop_back();q.push_back(nums[r + 1]);ans.push_back(q.front());l++;r++;}return ans;
}
};
```C++
class Solution {
public:vector<int> maxSlidingWindow(vector<int>& nums, int k) {deque<int> q;vector<int> ans;for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {if(!q.empty() && i >= k && nums[i - k] == q.front()) {q.pop_front();}while(!q.empty() && nums[i] > q.back()) {q.pop_back();}q.push_back(nums[i]);if(i >= k - 1) {ans.push_back(q.front());}}return ans;}
};
10.31 神奇字符串 lc481
模拟题目即可,小技巧 1^3 = 2 2^3 = 1
class Solution {
public:int magicalString(int n) {int x1 = 3, x2 = 3; //x1是总的字符串数量,x2是生成到哪一个vector<int> s(4, 0);s[1] = 1; s[2] = 2; s[3] = 2;int cnt = 1, f = 1;;while(x1 < n){int t = 0;if(s[x2] == 1){s.push_back(f);cnt += (f == 1);x1++;}else{s.push_back(f);s.push_back(f);x1 += 2;cnt += (f == 1) * 2;}f = f ^ 3;x2++;} if(x1 > n && s[x1] == 1) cnt--;return cnt;}
};
10.31 课程表 lc 207
气死我了,一个拓扑排序写了这么久…
const int N = 5010;
int h[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;
void add(int a, int b) {e[idx] = b;ne[idx] = h[a];h[a] = idx++;
}
class Solution {
public:bool canFinish(int numCourses, vector<vector<int>>& prerequisites) {idx = 0;int inorder[numCourses];queue<int> q;memset(h, -1, sizeof h);memset(inorder, 0, sizeof inorder);for(int i = 0; i < prerequisites.size(); i++) {add(prerequisites[i][1], prerequisites[i][0]);inorder[prerequisites[i][0]]++;}for(int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {if(inorder[i] == 0) {q.push(i);inorder[i] = -1;}}int cnt = 0;while(!q.empty()) {int t = q.front();q.pop();cnt++;for(int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {int b = e[i];inorder[b]--;if(!inorder[b]) {q.push(b);}}}return cnt == numCourses;}
};


