第十四届蓝桥杯C++B组个人题解——无FJ

第十四届蓝桥杯C++B组个人题解——无FJ
本文章仅是个人题解,不能保证全对,但思路大抵就是那么个思路。今年的题感觉要比去年难了些,F想不到很好的判环方法,最后一题都不知道再说什么,图论苦手是这样的,不过其它倒是挺对我胃口。
但说实话线下在学校机房比,超级不适应啊!
(更新:编程题库 - C语言网 (dotcpp.com)这里有民间数据了,可以去测一测)
A、日期统计
问题描述
小蓝现在有一个长度为 100 的数组,数组中的每个元素的值都在 0 到 9 的范围之内。数组中的元素从左至右如下所示:
5 6 8 6 9 1 6 1 2 4 9 1 9 8 2 3 6 4 7 7 5 9 5 0 3 8 7 5 8 1 5 8 6 1 8 3 0 3 7 9 2 7 0 5 8 8 5 7 0 9 9 1 9 4 4 6 8 6 3 3 8 5 1 6 3 4 6 7 0 7 8 2 7 6 8 9 5 6 5 6 1 4 0 1 0 0 9 4 8 0 9 1 2 8 5 0 2 5 3 3
现在他想要从这个数组中寻找一些满足以下条件的子序列:
-
子序列的长度为 8;
-
这个子序列可以按照下标顺序组成一个 yyyymmdd 格式的日期,并且要求这个日期是 2023 年中的某一天的日期,例如 20230902,20231223。yyyy 表示年份,mm 表示月份,dd 表示天数,当月份或者天数的长度只有一位时需要一个前导零补充。
请你帮小蓝计算下按上述条件一共能找到多少个不同 的 2023 年的日期。对于相同的日期你只需要统计一次即可。
问题解析
答案:235
可以发现,到了第59个数字的时候,才第一次凑出2023的子序列,那么对于剩下的其它数字,可以用四个for循环来枚举mmdd,在判断dd(即天数)符不符合mm(月数),注意去重。
或者是可以直接枚举2023年的365天,即从20230101枚举到20231231为止,然后看能不能在字符串中找到这么个序列。
代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<map>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<iomanip>#define int long long
#define endl '\\n'
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<ll, ll> PII;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int f[100][100];
//"5686916124,9198236477,5950387581,5861830379,2705885709,919446863——38516346707827689565614010094809128502533";
void solve()
{map<int, int>mymap;mymap[1] = mymap[3] = mymap[5] = mymap[7] = mymap[8] = mymap[10] = mymap[12] = 31;mymap[4] = mymap[6] = mymap[9] = mymap[11] = 30;mymap[2] = 28;string s = "5686916124919823647759503875815861830379270588570991944686338516346707827689565614010094809128502533";string yy = "2023";int n = s.size(), idx = 0, cnt = 0;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){if (s[i] == yy[idx])idx++;if (idx == 4){idx = i + 1;break;}}for (int i = idx; i < n; i++){if (s[i] - '0' > 1)continue;for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++){if (s[i] - '0' == 1 && s[j] - '0' > 2)continue;for (int k = j + 1; k < n; k++){for (int l = k + 1; l < n; l++){int m = (s[i] - '0') * 10 + (s[j] - '0');int d = (s[k] - '0') * 10 + (s[l] - '0');if (d == 0)continue;if (mymap.count(m) && mymap[m] >= d && f[m][d] == 0){cout << m << "月" << d << "日" << endl;f[m][d] = 1;cnt++;}}}}}cout << cnt;
}signed main()
{ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);int t = 1;//cin>>t;while (t--){solve();}return 0;
}
B、01串的熵
问题描述

问题解析
答案:11027421
这题对我来说主要难点在于算log,说实话我之前真不知道有函数能直接算log,这题的log我是采用了浮点型二分的方法来算的。并且也测试了下S=100的情况发现是正确的。然后我们就枚举0的个数就好了,1的个数就是23333333-0的个数。
不过我这做法有两点要注意的:
- 没必要从0开始枚举0的个数,实际上debug几遍后就能发现大约在11000000左右的时候算出来的值就很接近题目的这个值了。
- 二分的精度要高,一开始我习惯性的设置精度为1e-6,结果咋都跑不出正确结果,后来折磨了半小时后才发现精度要开到1e-15左右才能出正确结果。哭死。
代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<map>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<iomanip>#define int long long
#define endl '\\n'
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<ll,ll> PII;
const int N=1e5+10;
int f[100][100];//算log2(a)的值(我不会用函数啥的算,也不知道有没有现成的函数,但我知道有现成的幂运算)
double check(double a)
{double l=-10,r=0;//精度开小了会寄掉,一开始我写的1e-6,咋都不出结果 while(abs(r-l)>=1e-15){double mid=(l+r)/2;if(pow(2,mid)>a)r=mid;else l=mid; }return l;
} //答案:11027421void solve()
{//double x=check(1.0/3),y=check(2.0/3);//测试后,答案等于1.3083,说明方法没问题 //cout<<fixed<<setprecision(5)<<-1.0/3*x+-2.0/3*y-2.0/3*y;//没必要从0开始枚举,算的太慢了 for(int i=11026000;i<=23333333/2;i++){if(i>=23333333-i)continue;double a=i/23333333.0,b=(23333333-i)/23333333.0;double x=check(a),y=check(b);double z=i*(-1.0*i/23333333.0*x)+(23333333-i)*(-1.0*(23333333-i)/23333333.0*y);if(abs(11625907.5798-z)<=1e-4){cout<<i<<endl;return;}}}signed main()
{ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);int t=1;//cin>>t;while(t--){solve();}return 0;
}
C、冶炼金属



问题解析
可以看出,V可能的最大值直接就是:a/b了,没有问题。
重点是最小值,既然要转换率V最小,那就是最后浪费的尽可能的多。用a/(b+1),即算出a个普通金属如果想冶炼出b+1个特殊金属,转化率是多少。再逆过来判断一下,如果a可以通过这个转化率冶炼出b+1个金属,则V++。直到正好冶炼出b个为止,这样最后浪费的数量就是最多的了。
最后,对于所有的炼金情况,它们的最大值我们取最小,它们的最小值我们取最大(实际就是区间合并的过程)
代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<map>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<iomanip>#define int long long
#define endl '\\n'
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<ll,ll> PII;
const int N=1e5+10;void solve()
{int n,a,b; cin>>n;int mx=10000000000,mn=-1;for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){cin>>a>>b;mx=min(mx,a/b);int c=a/(b+1);while(a/c>b)c++;mn=max(mn,c);} cout<<mn<<" "<<mx;
}signed main()
{ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);int t=1;//cin>>t;while(t--){solve();}return 0;
}
D、飞机降落



问题解析
一看数据,N<=10,直接枚举全部的排列次序,然后都模拟一遍,看能不能平稳落地就行。
代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<map>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<iomanip>#define int long long
#define endl '\\n'
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<ll, ll> PII;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;int T[N], D[N], L[N];
void solve()
{int n;cin >> n;vector<int>v(n);for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){cin >> T[i] >> D[i] >> L[i];v[i-1] = i;}do {//记录时间int time = 0;bool flag = true;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){if (time <= T[v[i]])time = T[v[i]] + L[v[i]];else if (time <= T[v[i]] + D[v[i]])time += L[v[i]];else{flag = false;break;}}if (flag){cout << "YES" << endl;return;}} while (next_permutation(v.begin(), v.end()));cout << "NO" << endl;
}signed main()
{ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);int t = 1;cin>>t;while (t--){solve();}return 0;
}
E、接龙数列
问题描述

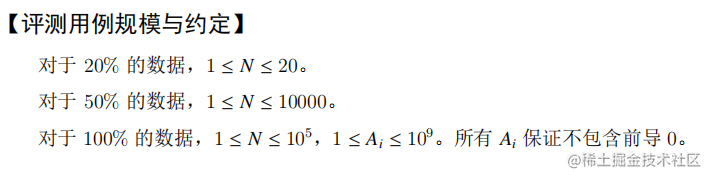
问题解析
经典的dp问题,送分了属于是。
让我们删除最少的数,使得剩下的序列是接龙序列,实际上就是让我们求最长接龙序列的长度len,答案就是:n-len
对于这种:求最长XXX子序列的问题,一般的状态设置就是:f[i]是以i结尾的xxx序列,长度为f[i]。
那么我们就设:f[i]是以数字i结尾的最长的接龙序列,i的取值是0到9(不含前导0嘛)
first是数字a的第一个数字,last是数字a的最后一个数字,则有状态转移方程:
f[last]=max(f[last,f[first]+1);
最后取所有的序列的最大长度即可。
代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<map>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<iomanip>#define int long long
#define endl '\\n'
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<ll,ll> PII;
const int N=1e5+10;
int f[10];
void solve()
{int n,mx=0;string s;cin>>n;for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){cin>>s;int a=s[0]-'0',b=s.back()-'0';//cout<<a<<" "<<b<<endl;f[b]=max(f[b],f[a]+1);}for(int i=0;i<=9;i++){mx=max(mx,f[i]);}cout<<n-mx;
}signed main()
{ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);int t=1;//cin>>t;while(t--){solve();}return 0;
}
G、子串简写
问题描述


问题解析
又是经典的题。
先用一个数组存下来从小到大所有c2字符的下标。
然后对s的每一个c1字符,在数组里找他俩下标相减大于等于k+1的即可。这一步我们可以用二分来优化掉。
代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<map>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<iomanip>#define int long long
#define endl '\\n'
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<ll,ll> PII;
const int N=1e5+10;void solve()
{int k;string s;char c1,c2;vector<int>v;cin>>k>>s>>c1>>c2;int n=s.size(),cnt=0;//注意,我这里写的下标是1for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){if(s[i-1]==c2)v.push_back(i);}int len=v.size();//这里变回0了for(int i=0;i<n;i++){if(s[i]==c1){//二分找数组中第一个坐标和i相减大于等于k的位置int l=0,r=len-1;while(l<r){int mid=(l+r)/2;//上面那俩这么做只是因为我不想写个k+1,只写个k(哈哈if(v[mid]>=i+k)r=mid;else l=mid+1;}//确保大于再算答案if(v[l]>=i+k){cnt+=len-l;}}}cout<<cnt;
}signed main()
{ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);int t=1;//cin>>t;while(t--){solve();}return 0;
}
H、整数删除
问题描述


问题解析
这一题我感觉我写复杂了,但是也暂时想不到更好的点子,一开始想的链表,但我讨厌指针这玩意,所以我换了个写法。
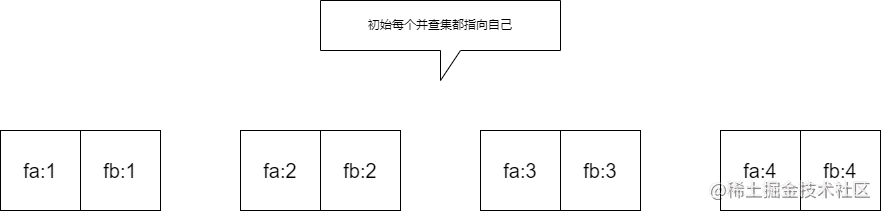
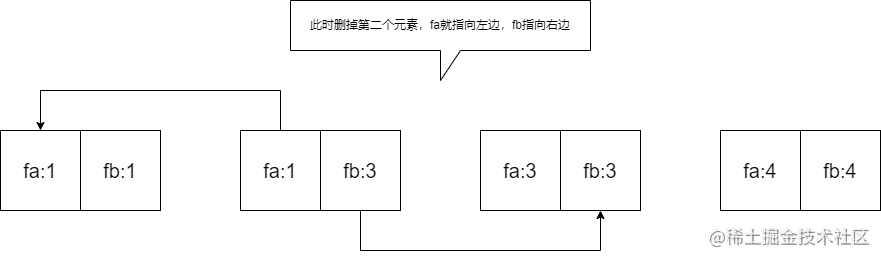
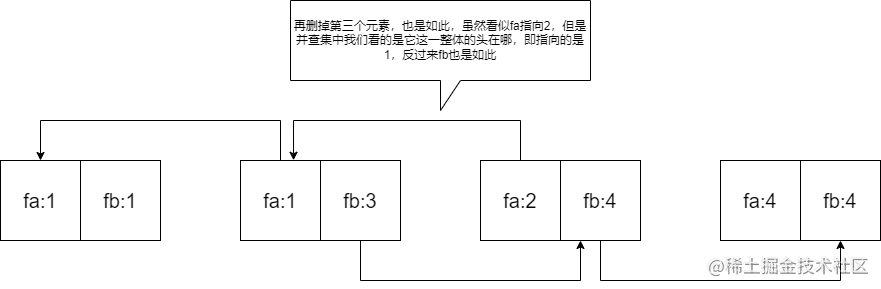
我用的是:线段树求数组最小值+双并查集。
用一个并查集fa来链接左边的数,另一个并查集fb来链接右边的数:(如图)
至于找数组最小值和修改数组的事情,就交给线段树就行了。
如果某个数被删除了,则在线段树中将对应位置修改成一个很大的值,不要让他影响我们的判断。
不会线段树的同学也可以看看我主页的文章,有教你如何掌握线段树(基础)。
(做法应该没啥问题,主要担心会不会写错代码+常数太大了导致tle。)
代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<map>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<iomanip>#define int long long
#define endl '\\n'
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<ll,ll> PII;
const int N=5e5+50;int f[4*N],a[N],st[N],fa[N],fb[N]; void build_tree(int k,int l,int r)
{if(l==r){f[k]=a[l];return;}int mid=(l+r)/2;build_tree(k+k,l,mid);build_tree(k+k+1,mid+1,r);f[k]=min(f[k+k],f[k+k+1]);
}PII query(int k,int l,int r)
{if(l==r){return {f[k],l};}int mid=(l+r)/2;PII ans={0,0};if(f[k+k]<=f[k+k+1])ans=query(k+k,l,mid);else ans=query(k+k+1,mid+1,r);return ans;
}void revise(int k,int l,int r,int x,int y)
{if(l==r){f[k]+=y;return;}int mid=(l+r)/2;if(x<=mid)revise(k+k,l,mid,x,y);else revise(k+k+1,mid+1,r,x,y);f[k]=min(f[k+k],f[k+k+1]);
}int finda(int x)
{if(fa[x]!=x)fa[x]=finda(fa[x]);return fa[x];
}int findb(int x)
{if(fb[x]!=x)fb[x]=findb(fb[x]);return fb[x];
}void solve()
{int n,k;cin>>n>>k;for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){cin>>a[i];}build_tree(1,1,n);for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){fa[i]=i;fb[i]=i;}while(k--){//查找的结果以pair的形式返回,first是最小值,second是它在数组的下标PII ans=query(1,1,n);//找当前元素挨着的左边元素l,和右边元素rint l=finda(ans.second-1),r=findb(ans.second+1);//改变指向fa[ans.second]=l;fb[ans.second]=r;//修改原最小值,让它不要影响我们之后的操作revise(1,1,n,ans.second,1e18);//在线段树中修改原最小值两边的元素revise(1,1,n,l,ans.first);revise(1,1,n,r,ans.first);//在数组中也要修改a[l]+= ans.first;a[r]+= ans.first;}//输出for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){//如果fa的指向没变,说明这个元素没被删if(fa[i]==i)cout<<a[i]<<" ";}
}signed main()
{ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);int t=1;//cin>>t;while(t--){solve();}return 0;
}
I、景区导游
问题描述


问题解析
首先,根据题目的解释来看,如果路线是:2->6->5->1,那就相当于求出sum=dis(2,6)+dis(6,5)+dis(5,1)。dis(x,y)表示点x到点y的时间。
至于跳过某点,比如跳过6点,那么就是:sum-dis(2,6)-dis(6,5)+dis(2,5).
这样对于每次跳过某点,我们并不用重新计算花费时间,只要把修改跟跳过的点有关的三条路径长度求出来,再在sum的基础上修改即可。
那么此时问题就变成了,如何快速的求从x点到y点的距离。
注意题目说的,这个景区的路线呈现树的样子。也就是说,这是让我们求在树中任意两点的距离:(样例如图)
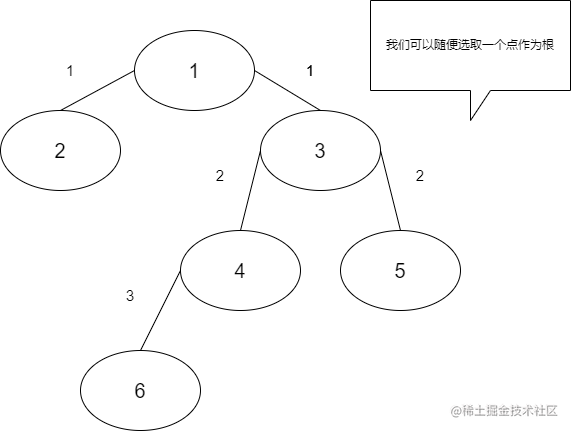
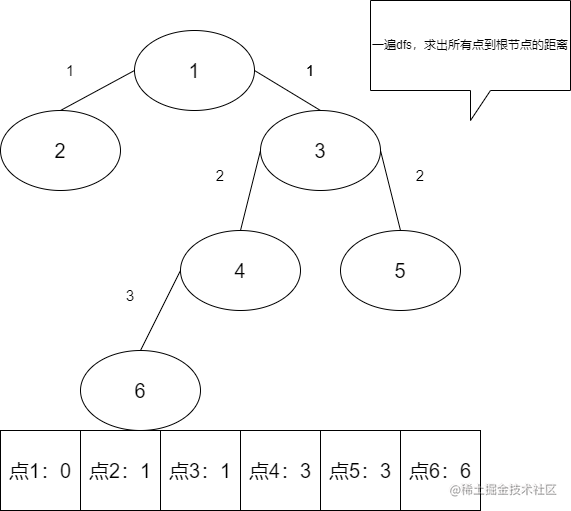
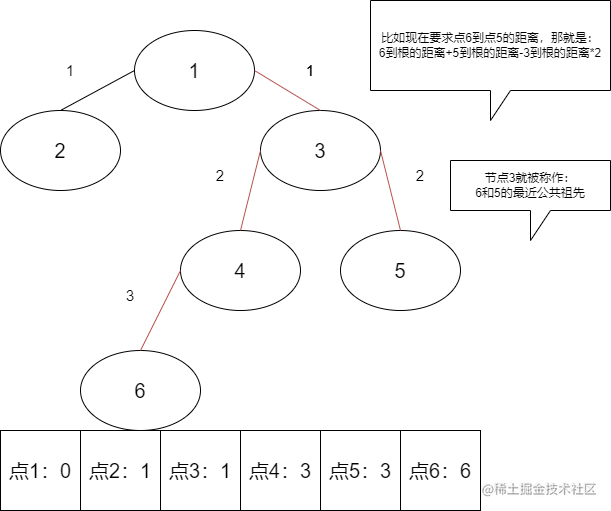
由此可知,只要知道了两个点的最近公共祖先,就可以很快的求出在树中任意两点的距离。
现在,要解决的就是快速求出两个点的最近公共祖先了。
关于这个,我这里用的是倍增法求lca,具体的这里就不展开了,感兴趣的同学可以去自行学习一下。
代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<map>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<iomanip>#define int long long
#define endl '\\n'
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<ll, ll> PII;
const int N = 1e5 + 50;int deep[N], fa[N][31], a[N], dis[N];
vector<int>tree[N];
unordered_map<int, unordered_map<int, int>>mymap;// dfs,用来为 lca 算法做准备。接受两个参数:dfs 起始节点和它的父亲节点。
void dfs(int root, int fno) {// 初始化:第 2^0 = 1 个祖先就是它的父亲节点,dep 也比父亲节点多 1。dis[root] = dis[fno] + mymap[root][fno];fa[root][0] = fno;deep[root] = deep[fa[root][0]] + 1;// 初始化:其他的祖先节点:第 2^i 的祖先节点是第 2^(i-1) 的祖先节点的第// 2^(i-1) 的祖先节点。for (int i = 1; i < 31; ++i) {fa[root][i] = fa[fa[root][i - 1]][i - 1];}// 遍历子节点来进行 dfs。int sz = tree[root].size();for (int i = 0; i < sz; ++i) {if (tree[root][i] == fno) continue;dfs(tree[root][i], root);}
}// lca。用倍增算法算取 x 和 y 的 lca 节点。
int lca(int x, int y) {// 令 y 比 x 深。if (deep[x] > deep[y]) swap(x, y);// 令 y 和 x 在一个深度。int tmp = deep[y] - deep[x], ans = 0;for (int j = 0; tmp; ++j, tmp >>= 1)if (tmp & 1) y = fa[y][j];// 如果这个时候 y = x,那么 x,y 就都是它们自己的祖先。if (y == x) return x;// 不然的话,找到第一个不是它们祖先的两个点。for (int j = 30; j >= 0 && y != x; --j) {if (fa[x][j] != fa[y][j]) {x = fa[x][j];y = fa[y][j];}}// 返回结果。return fa[x][0];
}//求两个点之间的距离
int get_dis(int x, int y)
{int z = lca(x, y);return dis[x] + dis[y] - dis[z] * 2;
}/*
6 4
1 2 1
1 3 1
3 4 2
3 5 2
4 6 3
2 6 5 1
*/void solve()
{int n, x, y, m, k, w;cin >> n >> k;for (int i = 1; i < n; i++){cin >> x >> y >> w;tree[x].push_back(y);tree[y].push_back(x);mymap[x][y] = w;mymap[y][x] = w;}dfs(1, 0);int sum = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++){cin >> a[i];if (i > 1){sum += get_dis(a[i], a[i - 1]);}}for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++){int res = 0;if (i == 1){res = sum - get_dis(a[i], a[i + 1]);}else if (i == k){res = sum - get_dis(a[i], a[i - 1]);}else{res = sum - get_dis(a[i - 1], a[i]) - get_dis(a[i + 1], a[i]) + get_dis(a[i - 1], a[i + 1]);}cout << res << " ";}
}signed main()
{ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);int t = 1;//cin>>t;while (t--){solve();}return 0;
}


