73-Linux_线程安全

线程安全
一.什么是线程安全
线程安全即就是在多线程运行的时候,不论线程的调度顺序怎样,最终的结果都是一样的、正确的。那么就说这些线程是安全的。
要保证线程安全需要做到:
1) 对线程进行同步,保证同一时刻只有一个线程访问临界资源。(四个方法)
2) 在多线程中使用线程安全的函数(可重入函数),所谓线程安全的函数指的是:如果一个函数能被多个线程同时调用且不发生竟态条件,则我们程它是线程安全的。
二.strtok和strtok_r
1.strtok
strtok不是一个线程安全函数,它的内部使用了全局变量或者静态变量
代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<pthread.h>void *fun(void* arg)
{char buff[]={"a b c d e f g h"};char * s=strtok(buff," ");while(s!=NULL){printf("fun s=%s\\n",s);sleep(1);s=strtok(NULL," ");}
}int main()
{pthread_t id;pthread_create(&id,NULL,fun,NULL);char arr[]="1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8";char *s=strtok(arr," ");while(s!=NULL){printf("main s=%s\\n",s);sleep(1);s=strtok(NULL," ");}pthread_join(id,NULL);exit(0);}
运行结果截图:
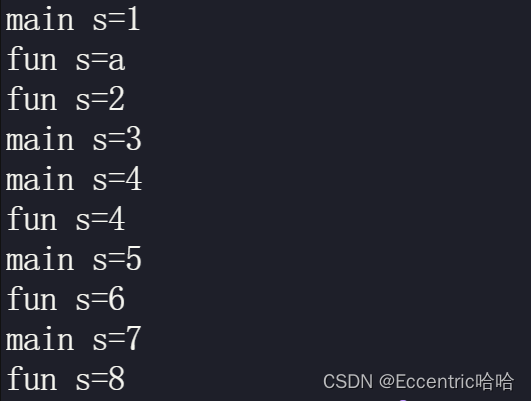
2.strtok_r
strtok是线程安全函数
代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<pthread.h>void *fun(void* arg)
{char buff[]={"a b c d e f g h"};char *ptr=NULL;char * s=strtok_r(buff," ",&ptr);while(s!=NULL){printf("fun s=%s\\n",s);sleep(1);s=strtok_r(NULL," ",&ptr);}
}int main()
{pthread_t id;pthread_create(&id,NULL,fun,NULL);char arr[]="1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8";char *ptr=NULL;char *s=strtok_r(arr," ",&ptr);while(s!=NULL){printf("main s=%s\\n",s);sleep(1);s=strtok_r(NULL," ",&ptr);}pthread_join(id,NULL);exit(0);
}
运行结果截图:
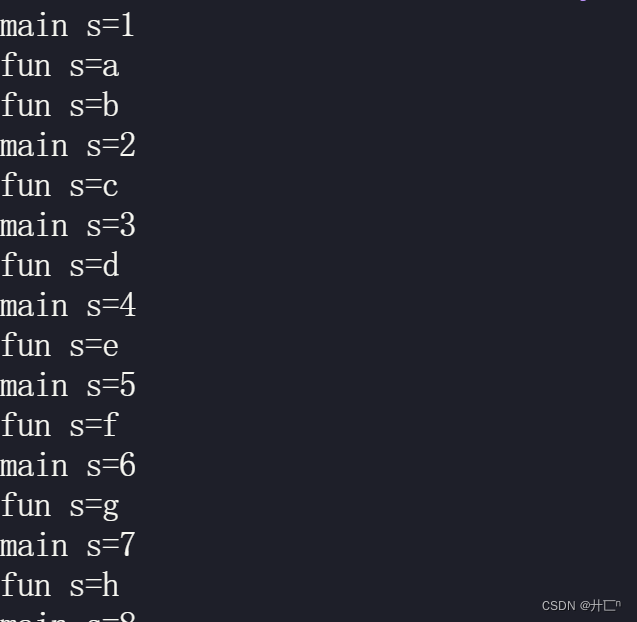
三.多线程中执行fork
1.多线程中某个线程调用 fork(),子进程会有和父进程相同数量的线程吗?
答:fork以后,不管父进程有多少条执行路径,子进程只有一条执行路径;这条执行路径就是fork所在的那条执行路径;
代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<pthread.h>void * fun(void*arg)
{for(int i=0;i<5;i++){printf("fun run pid=%d\\n",getpid());sleep(1);}
}
int main()
{pthread_t id;pthread_create(&id,NULL,fun,NULL);fork();for(int i=0;i<5;i++){printf("main run pid=%d\\n",getpid());sleep(1);}pthread_join(id,NULL);exit(0);
}
2.父进程被加锁的互斥锁 fork 后在子进程中是否已经加锁 ?
答:父进程有锁,子进程也被复制了锁;锁的状态取决于fork的那一刻父进程的锁的状态.也就是说锁的状态也会被复制进子进程 ;
代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>pthread_mutex_t mutex;
void * fun(void*arg)
{pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);printf("fun lock\\n");sleep(5);pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);printf("fun unlock\\n");
}void at_lock()
{pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
}
void at_unlock()
{pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}int main()
{pthread_t id;pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL);pthread_atfork(at_lock,at_unlock,at_unlock);pthread_create(&id,NULL,fun,NULL);sleep(1);pid_t pid=fork();if(pid==-1){exit(0);}if(pid==0){printf("子进程将要加锁\\n");pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);printf("子进程加锁成功\\n");pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);}else{wait(NULL);//阻塞printf("main over\\n");}exit(0);
}
