netty入门(二十六)任务加入异步线程池源码剖析

1.handler中加入线程池和Context添加线程池
1.1 源码剖析目的
(1)在 Netty 中做耗时的,不可预料的操作,比如:数据库、网络请求、会严重影响 Netty 对 Socket 的处理速度。
(2)而解决方法就是将耗时任务添加到异步线程池中。但就添加线程池这步操作来讲,可以有2中方式,而且这2种方式实现的区别也蛮大的。
(3)处理耗时业务的第一种方式 -- handler 中加入线程池
(4)处理耗时业务的第二种方式 -- Context 中添加线程池
1.2 处理耗时业务的第一种方式--handler 种加入线程池
对前面的 Netty demo 源码进行修改,在 EchoServerHandler 的 channelRead 方法进行异步
@Sharable
public class EchoServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {// group 就是充当业务线程池,可以将任务提交到该线程池// 创建了 16 个线程static final EventExecutorGroup group = new DefaultEventExecutorGroup(16);@Overridepublic void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {System.out.println("EchoServerHandler 的线程是:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());/*ctx.channel().eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {Thread.sleep(5 * 1000);// 输出线程名System.out.println("EchoServerHandler execute 的线程是:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello,客户端~ 喵2", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));} catch (InterruptedException e) {System.out.println("发生异常 " + e.getMessage());e.printStackTrace();}}});*/// 将任务提交到 group 线程池group.submit(new Callable<Object>() {@Overridepublic Object call() throws Exception {// 接收客户端信息ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;byte[] bytes = new byte[buf.readableBytes()];buf.readBytes(bytes);String body = new String(bytes, Charset.forName("utf-8"));// 休眠10秒Thread.sleep(10 * 1000);System.out.println("group.submit 的 call 线程是" + Thread.currentThread().getName());ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello,客户端~ 2喵喵喵喵", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));return null;}});System.out.println("go on.....");}@Overridepublic void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {ctx.flush();}@Overridepublic void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {// Close the connection when an exception is raised.cause.printStackTrace();ctx.close();}
}说明:
在 channelRead 方法,模拟了一个耗时 10 秒的操作,这里,我们将这个任务提交到了一个自定义的业务线程池中,这样,就不会阻塞 Netty 的 IO 线程。
这样处理之后,整个程序的逻辑如图
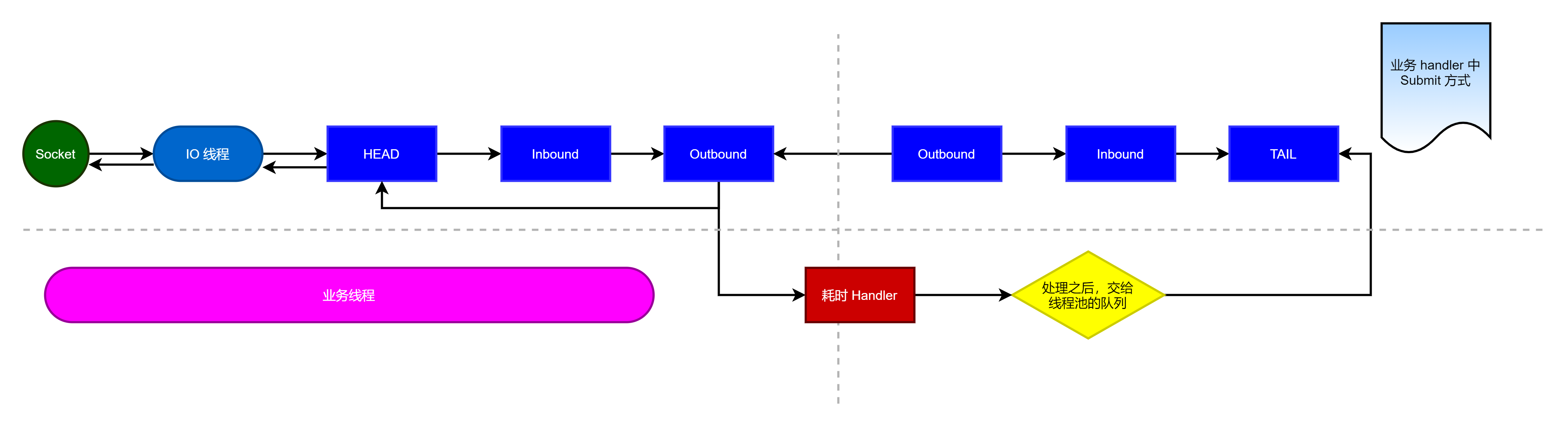
说明:
(1)解释上图,当 IO 线程轮询到一个 socket 事件,然后,IO 线程开始处理,当走到耗时 handler 的时候,将耗时任务交给业务线程池。
(2)当耗时任务执行完毕再执行 pipeline write 方法的时候,(代码中使用的是 context 的 write 方法,上图画的是执行 pipeline 方法,是一个意思)会将任务交给 IO 线程
write 方法的源码(在AbstractChannelHandlerContext 类)
private void write(Object msg, boolean flush, ChannelPromise promise) {AbstractChannelHandlerContext next = findContextOutbound();final Object m = pipeline.touch(msg, next);EventExecutor executor = next.executor();if (executor.inEventLoop()) {if (flush) {next.invokeWriteAndFlush(m, promise);} else {next.invokeWrite(m, promise);}} else {AbstractWriteTask task;if (flush) {task = WriteAndFlushTask.newInstance(next, m, promise);} else {task = WriteTask.newInstance(next, m, promise);}safeExecute(executor, task, promise, m);}}说明:
(1)当判定下个 outbound 的 executor 线程不是当前线程的时候,会将当前的工作封装成 task ,然后放入 mpsc 队列中,等待 IO 任务执行完毕后执行队列中的任务。
(2)这里可以Debug 来验证(提醒:Debug时,服务器端Debug ,客户端Run的方式),当我们使用了 group.submit(new Callable<Object>(){} 在handler 中加入线程池,就会进入到 safeExecute(executor, task, promise, m); 如果去掉这段代码,而使用普通方式来执行耗时的业务,那么就不会进入到 safeExecute(executor, task, promise, m); (说明:普通方式执行耗时代码,看我准备好的案例即可)
1.3 处理耗时业务的第一种方式--Context 中添加线程池
在添加 pipeline 中的 handler 时候,添加一个线程池
public final class EchoServer {static final boolean SSL = System.getProperty("ssl") != null;static final int PORT = Integer.parseInt(System.getProperty("port", "8007"));// 创建业务线程池// 创建2个子线程static final EventExecutorGroup group = new DefaultEventExecutorGroup(2);public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {// Configure SSL.final SslContext sslCtx;if (SSL) {SelfSignedCertificate ssc = new SelfSignedCertificate();sslCtx = SslContextBuilder.forServer(ssc.certificate(), ssc.privateKey()).build();} else {sslCtx = null;}// Configure the server.EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();try {ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class).option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 100).handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO)).childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {@Overridepublic void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {ChannelPipeline p = ch.pipeline();if (sslCtx != null) {p.addLast(sslCtx.newHandler(ch.alloc()));}p.addLast(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO));
// p.addLast(new EchoServerHandler());// 说明:如果在 addLast 添加 handler,前面有指定 EventExecutorGroup,那么该 handler 会优先加入到该线程池中p.addLast(group, new EchoServerHandler());}});// Start the server.ChannelFuture f = b.bind(PORT).sync();// Wait until the server socket is closed.f.channel().closeFuture().sync();} finally {// Shut down all event loops to terminate all threads.bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();}}
}@Sharable
public class EchoServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {// group 就是充当业务线程池,可以将任务提交到该线程池// 创建了 16 个线程static final EventExecutorGroup group = new DefaultEventExecutorGroup(16);@Overridepublic void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws InterruptedException {System.out.println("EchoServerHandler 的线程是:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());/*ctx.channel().eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {Thread.sleep(5 * 1000);// 输出线程名System.out.println("EchoServerHandler execute 的线程是:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello,客户端~ 喵2", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));} catch (InterruptedException e) {System.out.println("发生异常 " + e.getMessage());e.printStackTrace();}}});*/// 将任务提交到 group 线程池/*group.submit(new Callable<Object>() {@Overridepublic Object call() throws Exception {// 接收客户端信息ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;byte[] bytes = new byte[buf.readableBytes()];buf.readBytes(bytes);String body = new String(bytes, Charset.forName("utf-8"));// 休眠10秒Thread.sleep(10 * 1000);System.out.println("group.submit 的 call 线程是" + Thread.currentThread().getName());ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello,客户端~ 2喵喵喵喵", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));return null;}});*/// 普通方式// 接收客户端信息ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;byte[] bytes = new byte[buf.readableBytes()];buf.readBytes(bytes);String body = new String(bytes, Charset.forName("utf-8"));// 休眠10秒Thread.sleep(10 * 1000);System.out.println("普通调用方式的线程是" + Thread.currentThread().getName());ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello,客户端~ 2喵喵喵喵", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));System.out.println("go on.....");}@Overridepublic void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {ctx.flush();}@Overridepublic void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {// Close the connection when an exception is raised.cause.printStackTrace();ctx.close();}
}
说明:
(1)handler 中的代码就使用普通的方式来处理耗时业务。
(2)当我们在调用 addLast 方法添加线程池后,handler 将优先使用这个线程池,如果不添加,将使用 IO 线程。
(3)当走到 AbstractChannelHandlerContext 的 invokeChannelRead 方法的时候,executor.inEventLoop() 是不会通过的,因为当前线程是 IO 线程Context(也就是 Handler) 的 executor 是业务线程,所以会异步执行, debug 下源码。
static void invokeChannelRead(final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next, Object msg) {final Object m = next.pipeline.touch(ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(msg, "msg"), next);EventExecutor executor = next.executor();if (executor.inEventLoop()) {next.invokeChannelRead(m);} else {executor.execute(new Runnable() { //执行run@Overridepublic void run() {next.invokeChannelRead(m);}});}}(4)验证时,我们如果去掉 p.addLast(group,new EchoServerHandler() ); 改成 p.addLastnew EchoServerHandler() ); 你会发现代码不会进行异步执行。
(5)后面的整个流程就变成和第一个方式一样了
1.4 两种方式的比较
- 第一种方式在 handler 中添加异步,可能更加的自由,比如如果需要访问数据库,那我就异步,如果不需要,就不异步,异步会拖长接口响应时间。因为需要将任务放进 mpscTask 中。如果IO 时间很短,task 很多,可能一个循环下来,都没时间执行整个 task,导致响应时间达不到指标。
- 第二种方式是 Netty 标准方式(即加入到队列),但是,这么做会将整个 handler 都交给业务线程池。不论耗时不耗时,都加入到队列里,不够灵活。
- 各有优劣,从灵活性考虑,第一种较好。


