有效的括号长按键入验证外星语词典字符的最短距离用栈实现队列

有效的括号
来源:杭哥
20. 有效的括号 - 力扣(LeetCode)
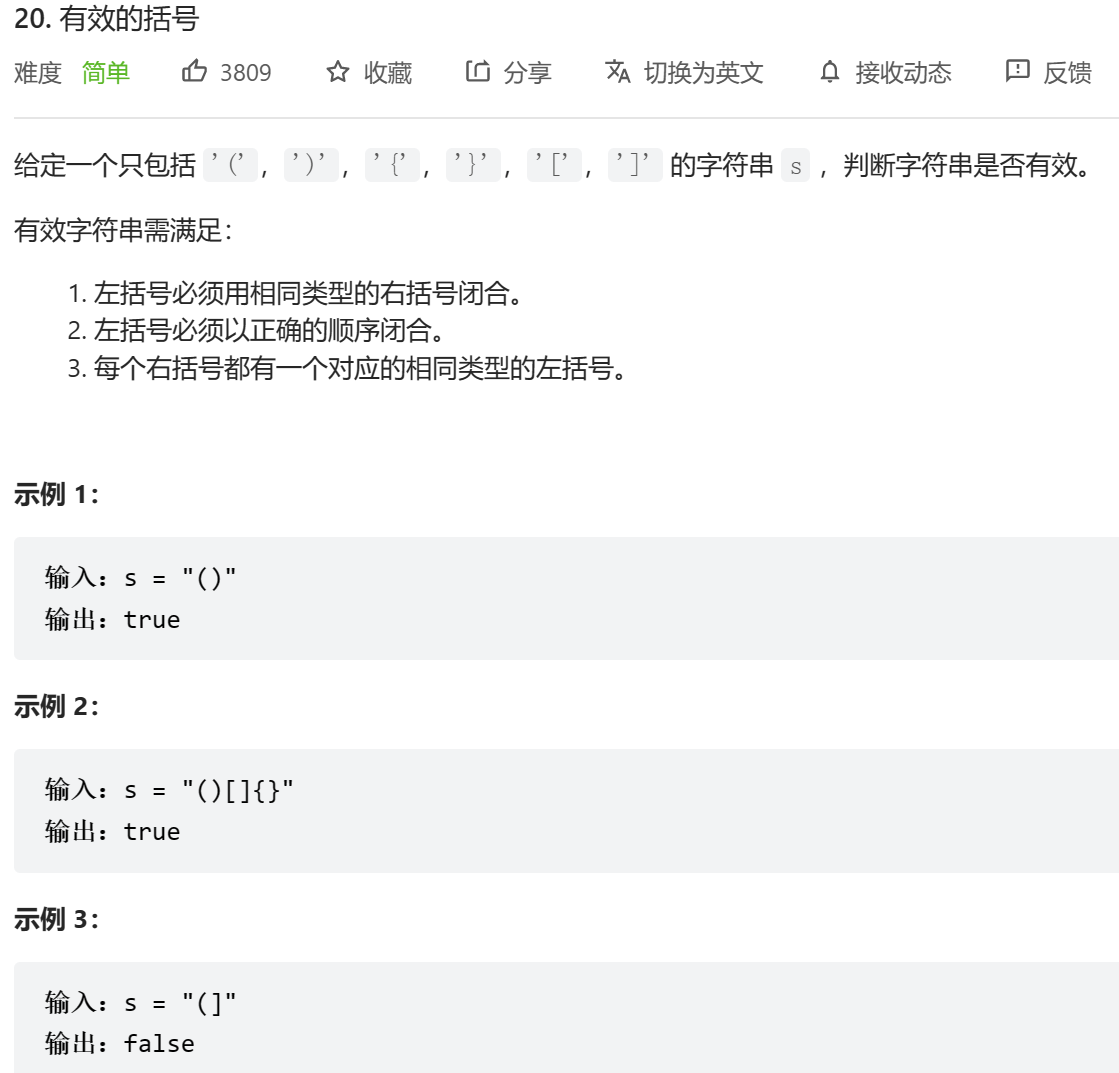
bool isValid(char * s)
{int sz=strlen(s);char stack[sz];int k=0;for (int i=0;i<sz;i++){if (s[i]=='(' || s[i]=='[' || s[i]=='{'){stack[k++]=s[i];}else{if (k==0){return false;}else if (s[i]=='}' && stack[k-1]!='{'){return false;}else if (s[i]==']' && stack[k-1]!='['){return false;}else if (s[i]==')' && stack[k-1]!='('){return false;}k--;}}if (k!=0){return false;}return true;
}我想说:
-
这时候就要用栈这种数据结构了,非常方便。
长按键入
来源:自己LeetCode刷题
925. 长按键入 - 力扣(LeetCode)
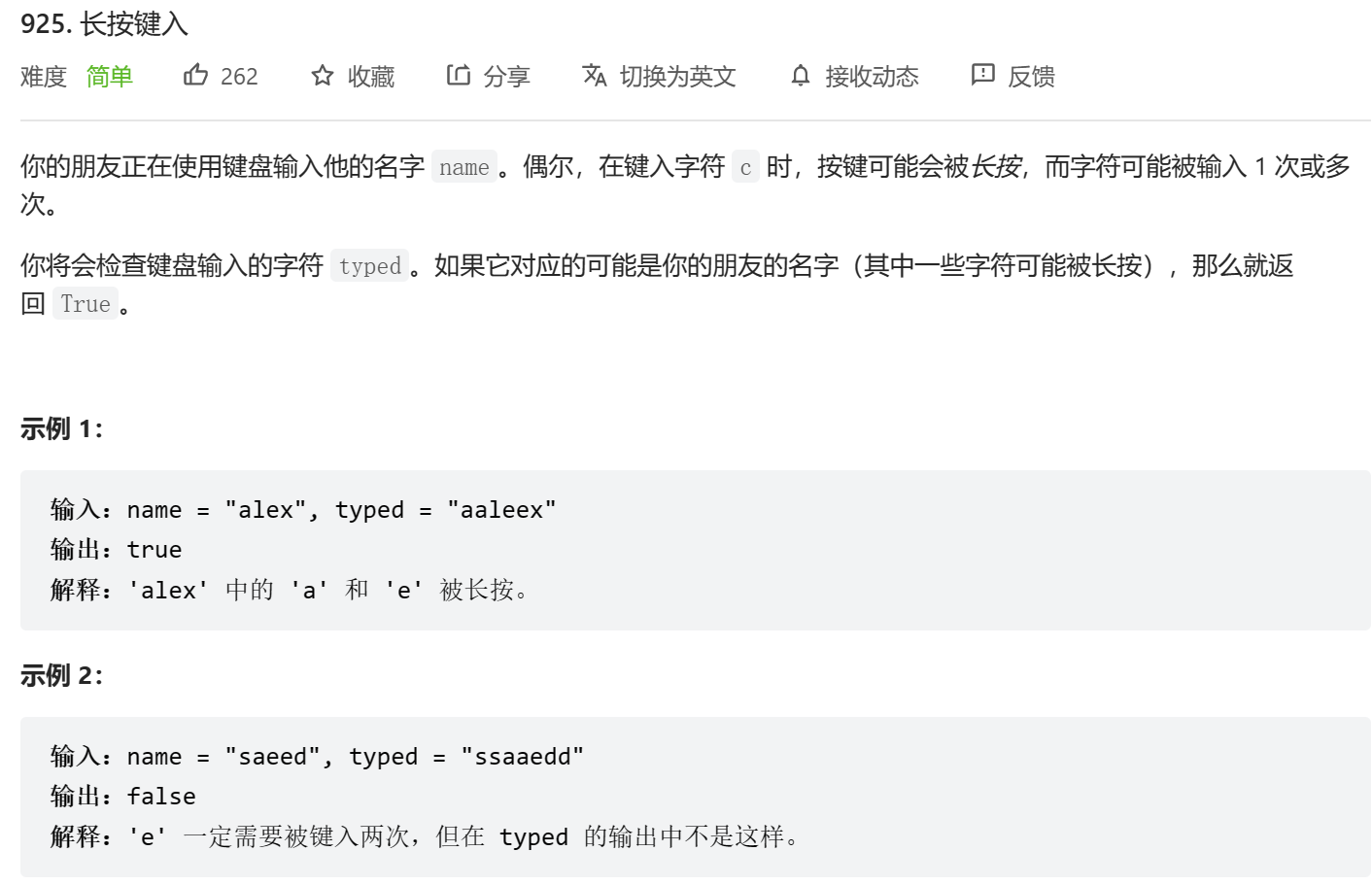
bool isLongPressedName(char * name, char * typed)
{int sz1=strlen(name);int sz2=strlen(typed);int i=0;int j=0;if (name[i]==typed[j]){i++;j++;}else{return false;}while(i<=sz1-1 && j<=sz2-1){if (name[i]==typed[j]){i++;j++;}else{if (typed[j]==typed[j-1]){j++;}else{return false;}}}if (i==sz1){if (j==sz2){return true;}char ch=name[sz1-1];while(j<sz2){if (typed[j]!=ch){return false;}j++;} }else{return false;}return true;
}我想说:
-
这道题目的话可以用双指针来做,逻辑关系想想清楚,然后代码能力稍微有一点的话就可以做出来
验证外星语词典
来源:自己LeetCode刷题
953. 验证外星语词典 - 力扣(LeetCode)
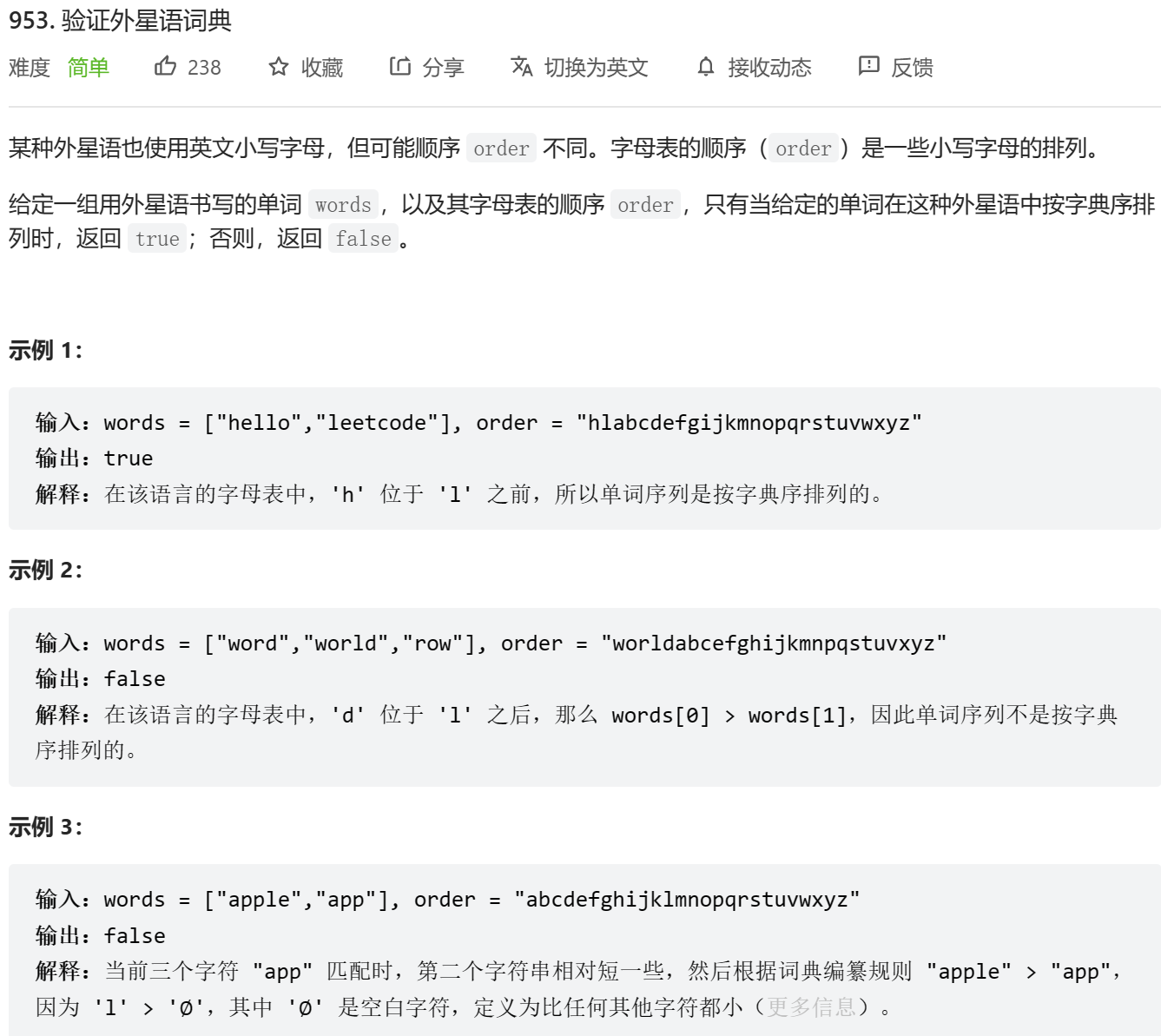
bool isAlienSorted(char words, int wordsSize, char * order)
{int alpha[26]={0};for (int i=0;i<26;i++){alpha[order[i]-'a']=i;}for (int i=0;i<wordsSize-1;i++){char* s1=words[i];char* s2=words[i+1];while (*s1!='\\0' && *s2!='\\0' && alpha[*s1-'a']==alpha[*s2-'a']){s1++;s2++;}if ((*s1=='\\0' && *s2!='\\0') || (*s1=='\\0' && *s2=='\\0')){continue;}else if (*s1!='\\0' && *s2=='\\0'){return false;}if (alpha[*s1-'a']<alpha[*s2-'a']){continue;}else if (alpha[*s1-'a']>alpha[*s2-'a']){return false;}}return true;
}我想说:
-
字符与整数之间可以灵活转化,因为字符其实本质上就是ACSII码,就是整型。
字符的最短距离
来源:自己LeetCode刷题
821. 字符的最短距离 - 力扣(LeetCode)
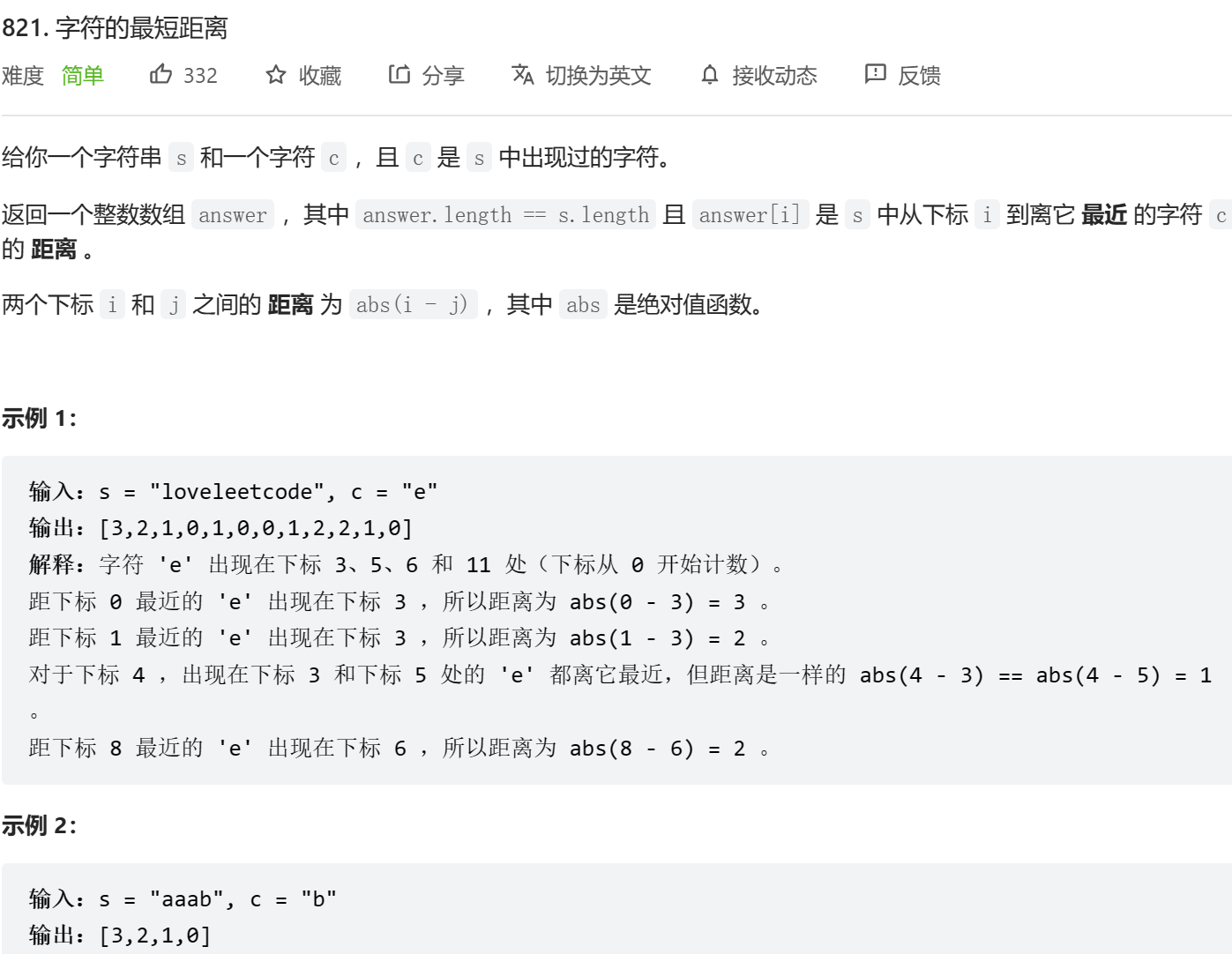
typedef struct point
{int a;int b;
}point;
int* shortestToChar(char * s, char c, int* returnSize)
{int sz=strlen(s);int* ans = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*sz);*returnSize=sz;for (int i=0;i<sz;i++){ans[i]=-1;}point queue[10000]={0};int hh=0;int tt=-1;for (int i=0;i<sz;i++){if (s[i]==c){tt++;queue[tt].a=i;queue[tt].b=0;ans[i]=0;}}while(hh<=tt){int aa=queue[hh].a;int bb=queue[hh].b;hh++;if (aa-1>=0 && ans[aa-1]==-1){ans[aa-1]=bb+1;tt++;queue[tt].a=aa-1;queue[tt].b=bb+1;}if (aa+1<sz && ans[aa+1]==-1){ans[aa+1]=bb+1;tt++;queue[tt].a=aa+1;queue[tt].b=bb+1;}}return ans;
}我想说:
-
首先得提一下语法问题,当用malloc在内存的堆区开辟一块连续空间的时候,其实我们都知道与数组没有什么区别,但是如果想把这块堆区空间的值,比如说全部初始化成-1,不能memset(arr , 0xff , sizeof(arr)),bty数组这样子干没有问题。这个与数组是有区别的,只能for循环一个一个去初始化。
-
这个方法用到了队列
#define MIN(a,b) ((a)<(b)?(a):(b))
int* shortestToChar(char * s, char c, int* returnSize)
{int sz=strlen(s);int* ans = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*sz);*returnSize=sz;int idx=(-1)*sz;for (int i=0;i<sz;i++){if (s[i]==c){idx=i;}ans[i]=i-idx;}idx=2*sz;for (int i=sz-1;i>=0;i--){if (s[i]==c){idx=i;}ans[i]=MIN(ans[i],idx-i);}return ans;
}我想说:
-
这种方法的话就比较新奇,先从左往右遍历,这时候我统计的是左端距离字符c最近是多少(只关注左端);然后我从右往左遍历,这时候我统计的是右端距离字符c最近是多少(只关注右端),注意:还要与之前的数值取小。
-
然后在遍历的时候一开始都是不知道字符c在哪里的,这时候就假定idx为-n 或者 2n
用栈实现队列
232. 用栈实现队列 - 力扣(LeetCode)
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{int top;int capacity;STDataType* p;
}ST;void STInit(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);pst->p = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType)*100);if (pst->p==NULL){perror("STInit::Malloc");return;}pst->top=0;pst->capacity=100;
}void STDestroy(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);free(pst->p);pst->p=NULL;pst->top=0;pst->capacity=0;
}void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x)
{assert(pst);if (pst->top==pst->capacity){STDataType* pp=(STDataType*)realloc(pst->p,sizeof(STDataType)*(pst->capacity)*2);if (pp==NULL){perror("STPush::Realloc");return;}pst->p=pp;pst->capacity*=2;}pst->p[pst->top]=x;pst->top++;
}void STPop(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);assert(pst->top>0);pst->top--;
}bool STEmpty(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);return pst->top==0;
}int STTop(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);assert(pst->top>0);return pst->p[pst->top-1];
} int STSize(ST* pst)
{assert(pst);return pst->top;
}///typedef struct
{ST pushst;ST popst;
} MyQueue;MyQueue* myQueueCreate()
{MyQueue* obj = (MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));if (obj==NULL){perror("malloc::fail");return NULL;}STInit(&obj->pushst);STInit(&obj->popst);return obj;
}void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x)
{assert(obj);STPush(&obj->pushst,x);
}int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj)
{assert(obj);if (STEmpty(&obj->popst)){int num=STSize(&obj->pushst);for (int i=0;i<num;i++){STDataType tmp=STTop(&obj->pushst);STPush(&obj->popst,tmp);STPop(&obj->pushst);}}int ans=STTop(&obj->popst);STPop(&obj->popst);return ans;
}bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj)
{assert(obj);return (&(obj->pushst))->top == 0 && (&(obj->popst))->top == 0;
}int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj)
{assert(obj);if (STEmpty(&obj->popst)){int num=STSize(&obj->pushst);for (int i=0;i<num;i++){STDataType tmp=STTop(&obj->pushst);STPush(&obj->popst,tmp);STPop(&obj->pushst);}}int ans=STTop(&obj->popst);return ans;
}void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj)
{assert(obj);STDestroy(&obj->pushst);STDestroy(&obj->popst);
}我想说:
-
这道题的话,它的方法非常的奇特,一个栈就是定向很明确的,专门用来放入数据,另外一个栈专门用来弹出数据,这个不像之前的用队列去模拟栈,哪个队列不为空,我就往哪个队列里面去插入数据。
-
然后这边的话出数据的栈它里面的数据都是从入数据的栈那边倒过来的,然后等到你这个栈出数据如果出空了,就再从另外一个栈那边把数据给倒过来。在这个问题当中,两个栈的功能是极其明确的,是固定的。


