【数据结构】链表OJ(二)


Yan-英杰的博客
悟已往之不谏 知来者之可追
目录
一、反转链表
二、合并两个有序链表
三、链表分割
四、链表的回文结构
 一、反转链表
一、反转链表
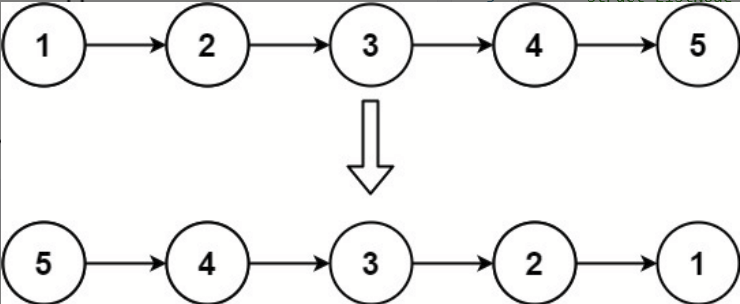
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[5,4,3,2,1]![]()
输入:head = [1,2]
输出:[2,1]示例 3:
输入:head = []
输出:[]提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围是
[0, 5000]-5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
方法一:
代码解析:
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){if(head == NULL){return NULL;}struct ListNode* n1,*n2,*n3;n1 = NULL;n2 = head;n3 = n2->next;while(n2){//翻转链表n2->next = n1;//迭代n1 = n2;n2 = n3;if(n3) n3 = n3->next;}return n1;
}画图解析:
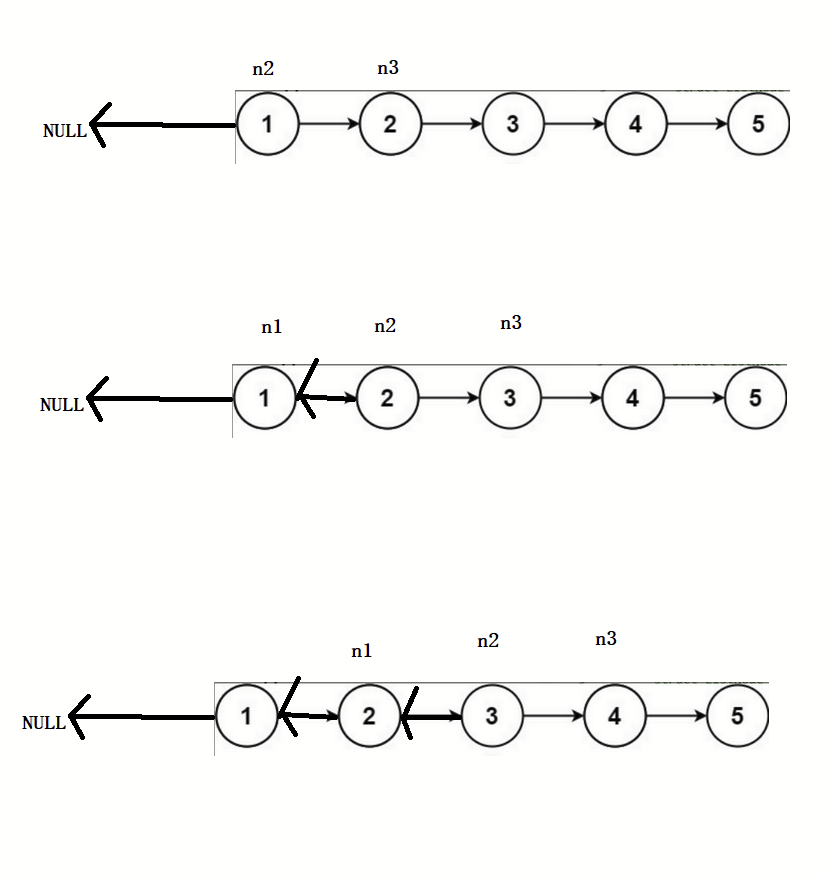
注:该题使用到了三指针
方法二:
代码解析:
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){struct ListNode* cur = head,*newhead = NULL;while(cur){struct ListNode* next = cur->next;//头插cur->next = newhead;newhead = cur;cur = next;}return newhead;
} 画图解析: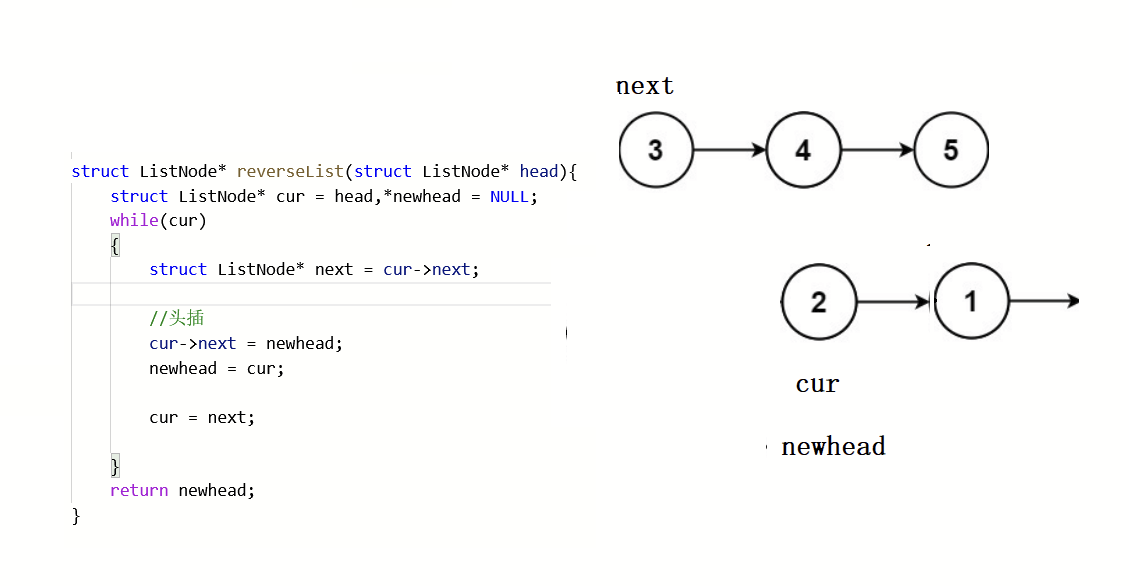
此方法采用头插方式
 二、合并两个有序链表
二、合并两个有序链表
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例 1:
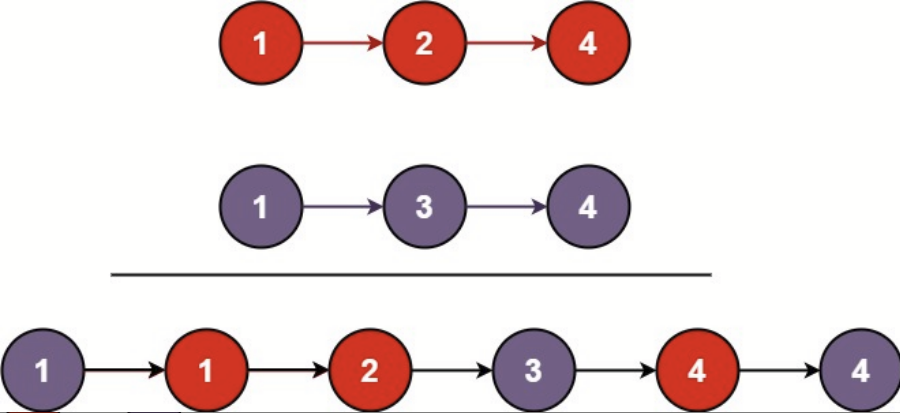
输入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]示例 2:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = []
输出:[]示例 3:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = [0]
输出:[0]提示:
两个链表的节点数目范围是 [0, 50]
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
l1 和 l2 均按 非递减顺序 排列
代码解析:
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2){if(list1 == NULL){return list2;}if(list2 == NULL){return list1;}struct ListNode* cur1 = list1,*cur2 = list2;struct ListNode* head = NULL,*tail = NULL;while(cur1 && cur2){if(cur1->val < cur2->val){if(head == NULL){head = tail = cur1;}else{tail->next = cur1;tail = tail->next;}cur1 = cur1->next;}else{if(head == NULL){head = tail = cur2;}else{tail->next = cur2;tail = tail->next;}cur2 = cur2->next;}}if(cur1){tail->next = cur1;}if(cur2){tail->next = cur2;}return head;
}画图解析:

 三、链表分割
三、链表分割
描述
现有一链表的头指针 ListNode* pHead,给一定值x,编写一段代码将所有小于x的结点排在其余结点之前,且不能改变原来的数据顺序,返回重新排列后的链表的头指针。
思路:
小于尾插到一个链表,大于等于尾插到另一个链表,再将两个链表链接起来
代码解析:
class Partition {
public:ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x) {// write code herestruct ListNode* gGurad,*gTail,*lGuard,*lTail;gGurad = gTail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));lGuard = lTail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));gTail->next = lTail->next = NULL;struct ListNode* cur = pHead;while(cur){if(cur->val < x){lTail->next = cur;lTail = lTail->next;}else{gTail->next = cur;gTail = gTail->next;}cur= cur->next;}lTail->next = gGurad->next;gTail->next =NULL;pHead = lGuard->next;free(gGurad);free(lGuard);return pHead;}
};画图解析:
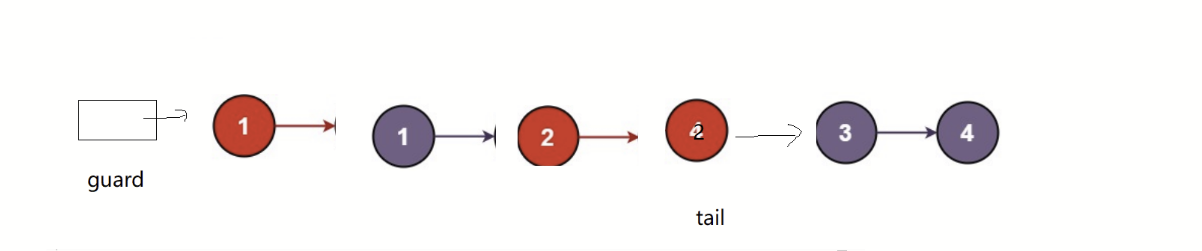
此题我们需要用到哨兵位的头节点
 四、链表的回文结构
四、链表的回文结构
描述
对于一个链表,请设计一个时间复杂度为O(n),额外空间复杂度为O(1)的算法,判断其是否为回文结构。
给定一个链表的头指针A,请返回一个bool值,代表其是否为回文结构。保证链表长度小于等于900。
测试样例:
1->2->2->1
返回:true代码解析:
//查找中间节点
struct ListNode* Mid(struct ListNode* Head) {struct ListNode* slow = Head;struct ListNode* fast = Head;while (fast && fast->next) {slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;}return slow;
}//链表逆置
struct ListNode* reverse(struct ListNode* Head)
{struct ListNode* cur = Head;struct ListNode* phead = NULL;while(cur){struct ListNode* next = cur->next;cur->next = phead;phead = cur;cur = next;}return phead;
}class PalindromeList {public:bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A) {struct ListNode* MidList = Mid(A);struct ListNode* ReList = reverse(MidList);struct ListNode* pphead = A;struct ListNode* ppheadR = ReList;while(pphead && ppheadR){if(pphead->val != ppheadR->val){return false;}else{pphead = pphead->next;ppheadR = ppheadR->next;}}return true;}
};
画图解析:

