【云原生|Docker】14-Dokcer Harbor高可用部署

【云原生Docker】14-Dokcer Harbor高可用部署
文章目录
- 【云原生Docker】14-Dokcer Harbor高可用部署
-
- 前言
- Harbor高可用方案
-
- 单主复制
- 双主复制
- 多Harbor共享后端存储
- Harbor高可用部署
-
- 方案说明
- 环境说明
- 部署步骤
- 安装nfs
- 安装redis和PostgreSQL
- 安装harbor
- 配置nginx
- 访问测试
- 总结
前言
在上一篇【云原生|Docker】12-Docker Harbor企业级镜像管理中,我们简要说明了单机版本harbor的配置以及部署方式。然而这种单机部署显然无法满足在生产中需求,必须要保证应用的高可用性。
目前Harbor有两种主流的方案来解决这个问题:
- 双主复制
- 多harbor实例共享后端存储
Harbor高可用方案
单主复制
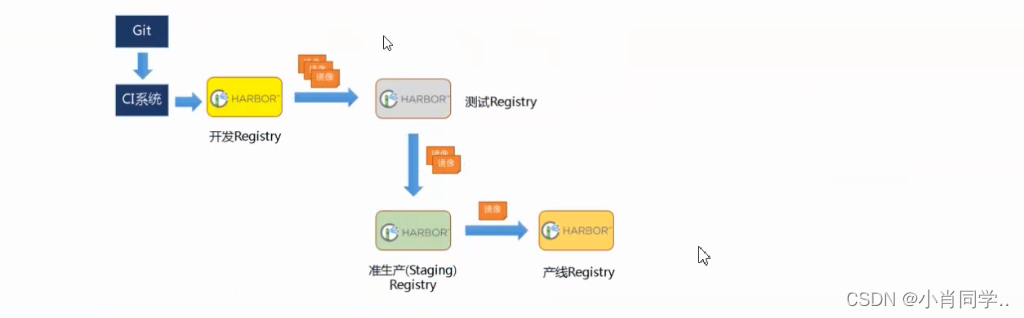
- harbor官方默认提供主从复制的方案来解决镜像同步问题,通过复制的方式,我们可以实时将测试环境harbor仓库的镜像同步到生产环境harbor,类似于如下流程:
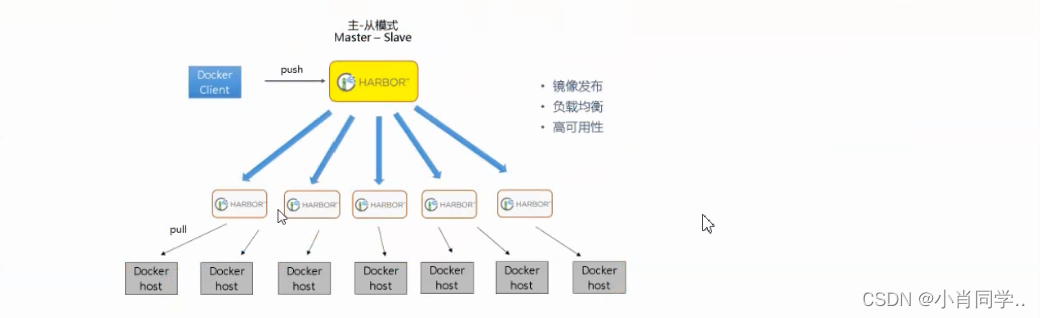
- 在实际生产运维的中,往往需要把镜像发布到几十或上百台集群节点上。这时,单个Registry已经无法满足大量节点的下载需求,因此要配置多个Registry实例做负载均衡。手工维护多个Registry实例上的镜像,将是十分繁琐的事情。Harbor可以支持一主多从的镜像发布模式,可以解决大规模镜像发布的难题,只要往一台Registry上发布,镜像就像“仙女散花”般地同步到多个Registry中,高效可靠。
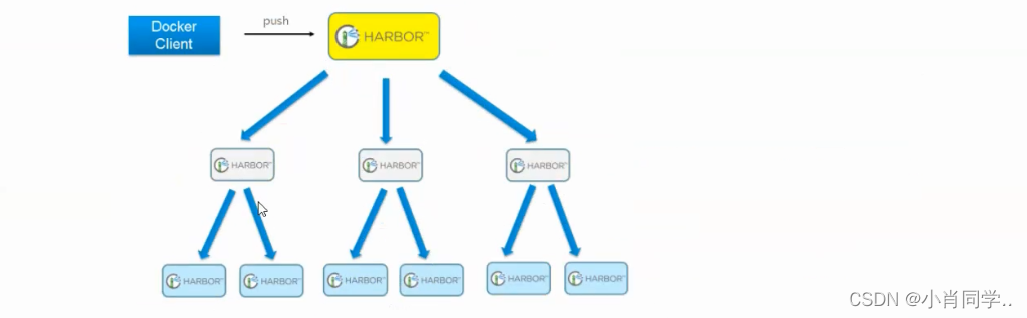
单点同步实际上还是所有的docker主机都在向同一个Harbor发送上传或者下载的请求,然而单靠主从同步,仍然解决不了harbor主节点的单点问题。
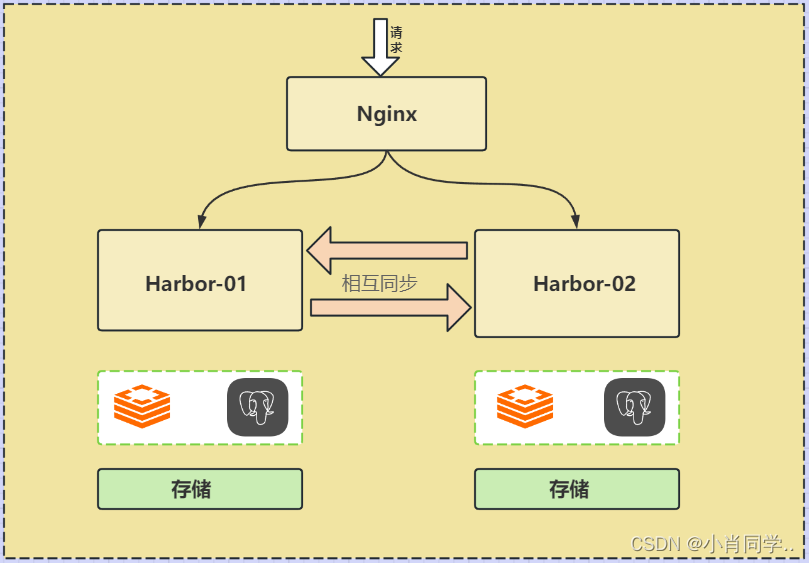
双主复制
所谓的双主复制其实就是复用主从同步实现两个harbor节点之间的双向同步,来保证数据的一致性,然后在两台harbor前端顶一个负载均衡器将进来的请求分流到不同的实例中去,只要有一个实例中有了新的镜像,就是自动的同步复制到另外的的实例中去,这样实现了负载均衡,也避免了单点故障,在一定程度上实现了Harbor的高可用性:
这个方案有一个问题:有可能两个Harbor实例中的数据不一致。假设如果一个实例A挂掉了,这个时候有新的镜像进来,那么新的镜像就会在另外一个实例B中,后面即使恢复了挂掉的A实例,Harbor实例B也不会自动去同步镜像,这样只能手动的先关掉Harbor实例B的复制策略,然后再开启复制策略,才能让实例B数据同步,让两个实例的数据一致。
多Harbor共享后端存储
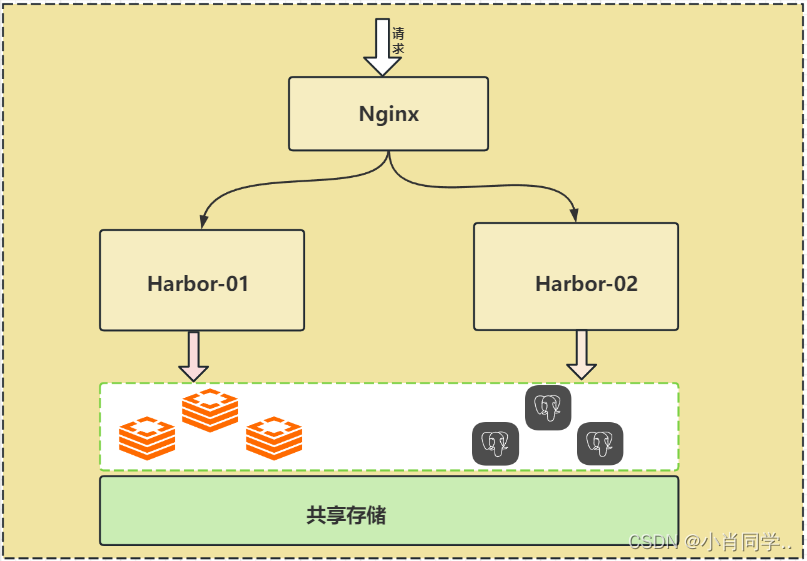
- 共享后端存储算是一种比较标准的方案,就是多个Harbor实例共享同一个后端存储,任何一个实例持久化到存储的镜像,都可被其他实例中读取。通过前置LB进来的请求,可以分流到不同的实例中去处理,这样就实现了负载均衡,也避免了单点故障。
- 这个方案在实际生产环境中部署需要考虑三个问题:
- 共享存储的选取,Harbor的后端存储目前支持AWS S3、Openstack Swift, Ceph等;
- Session在不同的实例上共享,这个现在其实已经不是问题了,在最新的harbor中,默认session会存放在redis中,我们只需要将redis独立出来即可。可以通过redis sentinel或者redis cluster等方式来保证redis的可用性。在我们的实验环境里,仍然使用单台redis
- Harbor多实例数据库问题,这个也只需要将harbor中的数据库拆出来独立部署即可。让多实例共用一个外部数据库,数据库的高可用也可以通过数据库的高可用方案保证。
Harbor高可用部署
方案说明
- 生产运维中以共享后端存储为标准方案,本章以该方案为例;
- 在我们的实验环境里,共享存储就直接使用nfs;
- 可以通过redis sentinel或者redis cluster等方式来保证redis的可用性。在我们的实验环境里,仍然使用单台redis。
- 数据库的高可用也可以通过数据库的高可用方案保证,在我们使用环境中还是使用单台PostgreSQL 。
环境说明
| 地址(ip) | 角色(role) |
|---|---|
| 192.168.194.128 | Harbor-01 |
| 192.168.194.130 | Harbor-02 |
| 192.168.194.131 | nginx |
| 192.168.194.132 | nfs,PostgreSQL,Redis |
部署步骤
安装nfs
Step1: 安装nfs服务端
[root@nfs ~]#yum install nfs-utils rpcbind
Step2: 配置nfs服务端
[root@nfs ~]# mkdir /data
[root@nfs ~]# vim /etc/exports
[root@nfs ~]#
[root@nfs ~]#
[root@nfs ~]# chmod 777 -R /data/
[root@nfs ~]# cat /etc/exports
/data *(rw,no_root_squash)
[root@nfs ~]#
[root@nfs ~]# systemctl restart nfs
[root@nfs ~]#
Step3: harbor01和harbor02上挂载nfs的共享目录
- 安装nfs客户端
harbor01:
[root@harbor01 ~]# yum -y install nfs-utilsharbor02:
[root@harbor01 ~]# yum -y install nfs-utils
- 检查共享目录
harbor01:
[root@harbor01 ~]# showmount -e 192.168.194.134
Export list for 192.168.194.134:
/data *
[root@harbor01 ~]#harbor02:
[root@harbor02 ~]# showmount -e 192.168.194.134
Export list for 192.168.194.134:
/data *
[root@harbor02 ~]#
- 挂载共享目录
harbor01:
[root@harbor01 ~]# mount -t nfs 192.168.194.134:/data /data
[root@harbor01 ~]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
devtmpfs 899M 0 899M 0% /dev
tmpfs 910M 0 910M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 910M 9.8M 900M 2% /run
tmpfs 910M 0 910M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/mapper/centos-root 39G 6.6G 32G 18% /
/dev/sda1 1014M 183M 832M 18% /boot
/dev/mapper/centos-home 19G 33M 19G 1% /home
tmpfs 182M 0 182M 0% /run/user/0
192.168.194.134:/data 39G 2.7G 36G 7% /data
[root@harbor01 ~]#harbor02:
[root@harbor02 ~]# mount -t nfs 192.168.194.134:/data /data
[root@harbor02 ~]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
devtmpfs 898M 0 898M 0% /dev
tmpfs 910M 0 910M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 910M 10M 900M 2% /run
tmpfs 910M 0 910M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/mapper/centos-root 39G 6.1G 33G 16% /
/dev/sda1 1014M 227M 788M 23% /boot
/dev/mapper/centos-home 19G 33M 19G 1% /home
tmpfs 182M 0 182M 0% /run/user/0
192.168.194.134:/data 39G 2.7G 36G 7% /data
[root@harbor02 ~]#
- 添加开机自动挂载
[root@harbor01 ~]# cat /etc/fstab
# /etc/fstab
/dev/mapper/centos-root / xfs defaults 0 0
UUID=9659ae54-578c-4666-b3c5-39b18f221a71 /boot xfs defaults 0 0
/dev/mapper/centos-home /home xfs defaults 0 0
/dev/mapper/centos-swap swap swap defaults 0 0
192.168.194.134:/data /data nfs defaults 0 0
[root@harbor01 ~]#
安装redis和PostgreSQL
- 使用docker-compose的方式安装
[root@nfs compose-test]# cat docker-compose.yml
version: '3'
services:redis:image: redis:latestcontainer_name: my-rediscommand: redis-server --requirepass 123456ports:- 6379:6379restart: alwayspostgres:image: postgres:latestcontainer_name: my-postgresrestart: alwaysenvironment:POSTGRES_PASSWORD: 123456ports:- 5432:5432
[root@nfs compose-test]#
- 启动docker-compose
[root@nfs compose-test]# docker-compose up -d
[root@nfs compose-test]#
[root@nfs compose-test]# docker ps -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
dba904cb520d redis:latest "docker-entrypoint.s…" 12 seconds ago Up 10 seconds 0.0.0.0:6379->6379/tcp, :::6379->6379/tcp my-redis
96742ff92ed8 postgres:latest "docker-entrypoint.s…" 12 seconds ago Up 10 seconds 0.0.0.0:5432->5432/tcp, :::5432->5432/tcp my-postgres
[root@nfs compose-test]#
安装harbor
- 官方配置文档:https://goharbor.io/docs/2.8.0/install-config/configure-yml-file/
- harbor01
[root@harbor02 harbor]# cat harbor.yml
# Configuration file of Harbor# The IP address or hostname to access admin UI and registry service.
# DO NOT use localhost or 127.0.0.1, because Harbor needs to be accessed by external clients.
hostname: 192.168.194.128# http related config
http:# port for http, default is 80. If https enabled, this port will redirect to https portport: 80# https related config
#https:# https port for harbor, default is 443
# port: 443# The path of cert and key files for nginx
# certificate: /your/certificate/path
# private_key: /your/private/key/path# Uncomment external_url if you want to enable external proxy
# And when it enabled the hostname will no longer used
# external_url: https://reg.mydomain.com:8433# The initial password of Harbor admin
# It only works in first time to install harbor
# Remember Change the admin password from UI after launching Harbor.
harbor_admin_password: Harbor12345# Harbor DB configuration
#database:# The password for the root user of Harbor DB. Change this before any production use.
# password: root123# The maximum number of connections in the idle connection pool. If it <=0, no idle connections are retained.
# max_idle_conns: 50# The maximum number of open connections to the database. If it <= 0, then there is no limit on the number of open connections.# Note: the default number of connections is 100 for postgres.
# max_open_conns: 100# The default data volume
data_volume: /data# Harbor Storage settings by default is using /data dir on local filesystem
# Uncomment storage_service setting If you want to using external storage
# storage_service:
# # ca_bundle is the path to the custom root ca certificate, which will be injected into the truststore
# # of registry's and chart repository's containers. This is usually needed when the user hosts a internal storage with self signed certificate.
# ca_bundle:# # storage backend, default is filesystem, options include filesystem, azure, gcs, s3, swift and oss
# # for more info about this configuration please refer https://docs.docker.com/registry/configuration/
# filesystem:
# maxthreads: 100
# # set disable to true when you want to disable registry redirect
# redirect:
# disabled: false# Clair configuration
clair:# The interval of clair updaters, the unit is hour, set to 0 to disable the updaters.updaters_interval: 12jobservice:# Maximum number of job workers in job servicemax_job_workers: 10notification:# Maximum retry count for webhook jobwebhook_job_max_retry: 10chart:# Change the value of absolute_url to enabled can enable absolute url in chartabsolute_url: disabled# Log configurations
log:# options are debug, info, warning, error, fatallevel: info# configs for logs in local storagelocal:# Log files are rotated log_rotate_count times before being removed. If count is 0, old versions are removed rather than rotated.rotate_count: 50# Log files are rotated only if they grow bigger than log_rotate_size bytes. If size is followed by k, the size is assumed to be in kilobytes.# If the M is used, the size is in megabytes, and if G is used, the size is in gigabytes. So size 100, size 100k, size 100M and size 100G# are all valid.rotate_size: 200M# The directory on your host that store loglocation: /var/log/harbor# Uncomment following lines to enable external syslog endpoint.# external_endpoint:# # protocol used to transmit log to external endpoint, options is tcp or udp# protocol: tcp# # The host of external endpoint# host: localhost# # Port of external endpoint# port: 5140#This attribute is for migrator to detect the version of the .cfg file, DO NOT MODIFY!
_version: 1.10.0# Uncomment external_database if using external database.
external_database:harbor:host: 192.168.194.134port: 5432db_name: harbor_dbusername: adminpassword: 123456ssl_mode: disablemax_idle_conns: 2max_open_conns: 0
# clair:
# host: clair_db_host
# port: clair_db_port
# db_name: clair_db_name
# username: clair_db_username
# password: clair_db_password
# ssl_mode: disable
# notary_signer:
# host: notary_signer_db_host
# port: notary_signer_db_port
# db_name: notary_signer_db_name
# username: notary_signer_db_username
# password: notary_signer_db_password
# ssl_mode: disable
# notary_server:
# host: notary_server_db_host
# port: notary_server_db_port
# db_name: notary_server_db_name
# username: notary_server_db_username
# password: notary_server_db_password
# ssl_mode: disable# Uncomment external_redis if using external Redis server
external_redis:host: 192.168.194.134port: 6379password: 123456
# # db_index 0 is for core, it's unchangeableregistry_db_index: 1jobservice_db_index: 2chartmuseum_db_index: 3clair_db_index: 4# Uncomment uaa for trusting the certificate of uaa instance that is hosted via self-signed cert.
# uaa:
# ca_file: /path/to/ca# Global proxy
# Config http proxy for components, e.g. http://my.proxy.com:3128
# Components doesn't need to connect to each others via http proxy.
# Remove component from `components` array if want disable proxy
# for it. If you want use proxy for replication, MUST enable proxy
# for core and jobservice, and set `http_proxy` and `https_proxy`.
# Add domain to the `no_proxy` field, when you want disable proxy
# for some special registry.
proxy:http_proxy:https_proxy:# no_proxy endpoints will appended to 127.0.0.1,localhost,.local,.internal,log,db,redis,nginx,core,portal,postgresql,jobservice,registry,registryctl,clair,chartmuseum,notary-serverno_proxy:components:- core- jobservice- clair
[root@harbor02 harbor]#
- harbor02
[root@harbor02 harbor]# cat harbor.yml
# Configuration file of Harbor# The IP address or hostname to access admin UI and registry service.
# DO NOT use localhost or 127.0.0.1, because Harbor needs to be accessed by external clients.
hostname: 192.168.194.130# http related config
http:# port for http, default is 80. If https enabled, this port will redirect to https portport: 80# https related config
#https:# https port for harbor, default is 443
# port: 443# The path of cert and key files for nginx
# certificate: /your/certificate/path
# private_key: /your/private/key/path# Uncomment external_url if you want to enable external proxy
# And when it enabled the hostname will no longer used
# external_url: https://reg.mydomain.com:8433# The initial password of Harbor admin
# It only works in first time to install harbor
# Remember Change the admin password from UI after launching Harbor.
harbor_admin_password: Harbor12345# Harbor DB configuration
#database:# The password for the root user of Harbor DB. Change this before any production use.
# password: root123# The maximum number of connections in the idle connection pool. If it <=0, no idle connections are retained.
# max_idle_conns: 50# The maximum number of open connections to the database. If it <= 0, then there is no limit on the number of open connections.# Note: the default number of connections is 100 for postgres.
# max_open_conns: 100# The default data volume
data_volume: /data# Harbor Storage settings by default is using /data dir on local filesystem
# Uncomment storage_service setting If you want to using external storage
# storage_service:
# # ca_bundle is the path to the custom root ca certificate, which will be injected into the truststore
# # of registry's and chart repository's containers. This is usually needed when the user hosts a internal storage with self signed certificate.
# ca_bundle:# # storage backend, default is filesystem, options include filesystem, azure, gcs, s3, swift and oss
# # for more info about this configuration please refer https://docs.docker.com/registry/configuration/
# filesystem:
# maxthreads: 100
# # set disable to true when you want to disable registry redirect
# redirect:
# disabled: false# Clair configuration
clair:# The interval of clair updaters, the unit is hour, set to 0 to disable the updaters.updaters_interval: 12jobservice:# Maximum number of job workers in job servicemax_job_workers: 10notification:# Maximum retry count for webhook jobwebhook_job_max_retry: 10chart:# Change the value of absolute_url to enabled can enable absolute url in chartabsolute_url: disabled# Log configurations
log:# options are debug, info, warning, error, fatallevel: info# configs for logs in local storagelocal:# Log files are rotated log_rotate_count times before being removed. If count is 0, old versions are removed rather than rotated.rotate_count: 50# Log files are rotated only if they grow bigger than log_rotate_size bytes. If size is followed by k, the size is assumed to be in kilobytes.# If the M is used, the size is in megabytes, and if G is used, the size is in gigabytes. So size 100, size 100k, size 100M and size 100G# are all valid.rotate_size: 200M# The directory on your host that store loglocation: /var/log/harbor# Uncomment following lines to enable external syslog endpoint.# external_endpoint:# # protocol used to transmit log to external endpoint, options is tcp or udp# protocol: tcp# # The host of external endpoint# host: localhost# # Port of external endpoint# port: 5140#This attribute is for migrator to detect the version of the .cfg file, DO NOT MODIFY!
_version: 1.10.0# Uncomment external_database if using external database.
external_database:harbor:host: 192.168.194.134port: 5432db_name: harbor_dbusername: adminpassword: 123456ssl_mode: disablemax_idle_conns: 2max_open_conns: 0
# clair:
# host: clair_db_host
# port: clair_db_port
# db_name: clair_db_name
# username: clair_db_username
# password: clair_db_password
# ssl_mode: disable
# notary_signer:
# host: notary_signer_db_host
# port: notary_signer_db_port
# db_name: notary_signer_db_name
# username: notary_signer_db_username
# password: notary_signer_db_password
# ssl_mode: disable
# notary_server:
# host: notary_server_db_host
# port: notary_server_db_port
# db_name: notary_server_db_name
# username: notary_server_db_username
# password: notary_server_db_password
# ssl_mode: disable# Uncomment external_redis if using external Redis server
external_redis:host: 192.168.194.134port: 6379password: 123456
# # db_index 0 is for core, it's unchangeableregistry_db_index: 1jobservice_db_index: 2chartmuseum_db_index: 3clair_db_index: 4# Uncomment uaa for trusting the certificate of uaa instance that is hosted via self-signed cert.
# uaa:
# ca_file: /path/to/ca# Global proxy
# Config http proxy for components, e.g. http://my.proxy.com:3128
# Components doesn't need to connect to each others via http proxy.
# Remove component from `components` array if want disable proxy
# for it. If you want use proxy for replication, MUST enable proxy
# for core and jobservice, and set `http_proxy` and `https_proxy`.
# Add domain to the `no_proxy` field, when you want disable proxy
# for some special registry.
proxy:http_proxy:https_proxy:# no_proxy endpoints will appended to 127.0.0.1,localhost,.local,.internal,log,db,redis,nginx,core,portal,postgresql,jobservice,registry,registryctl,clair,chartmuseum,notary-serverno_proxy:components:- core- jobservice- clair
[root@harbor02 harbor]#
- 与单节点配置相比,主要修改为:
- 注释database配置项,启用external_database;
- 启用external_redis
external_database:harbor:host: 192.168.194.134port: 5432db_name: harbor_dbusername: adminpassword: 123456ssl_mode: disablemax_idle_conns: 2max_open_conns: 0external_redis:host: 192.168.194.134port: 6379password: 123456 # # db_index 0 is for core, it's unchangeableregistry_db_index: 1jobservice_db_index: 2chartmuseum_db_index: 3clair_db_index: 4
配置nginx
[root@lvs-2 nginx]# cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
user nginx;
worker_processes auto;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
pid /run/nginx.pid;# Load dynamic modules. See /usr/share/doc/nginx/README.dynamic.
include /usr/share/nginx/modules/*.conf;events {worker_connections 1024;
}http {log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ''$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ''"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for" "$host" "backend:$upstream_addr"';access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;sendfile on;tcp_nopush on;tcp_nodelay on;keepalive_timeout 65;types_hash_max_size 4096;include /etc/nginx/mime.types;default_type application/octet-stream;# Load modular configuration files from the /etc/nginx/conf.d directory.# See http://nginx.org/en/docs/ngx_core_module.html#include# for more information.include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;upstream harbor_backend {server 192.168.194.128:80;server 192.168.194.130:80;}server {listen 80;server_name 192.168.194.131;location / {proxy_pass http://harbor_backend;proxy_set_header Host $host;proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;}}}
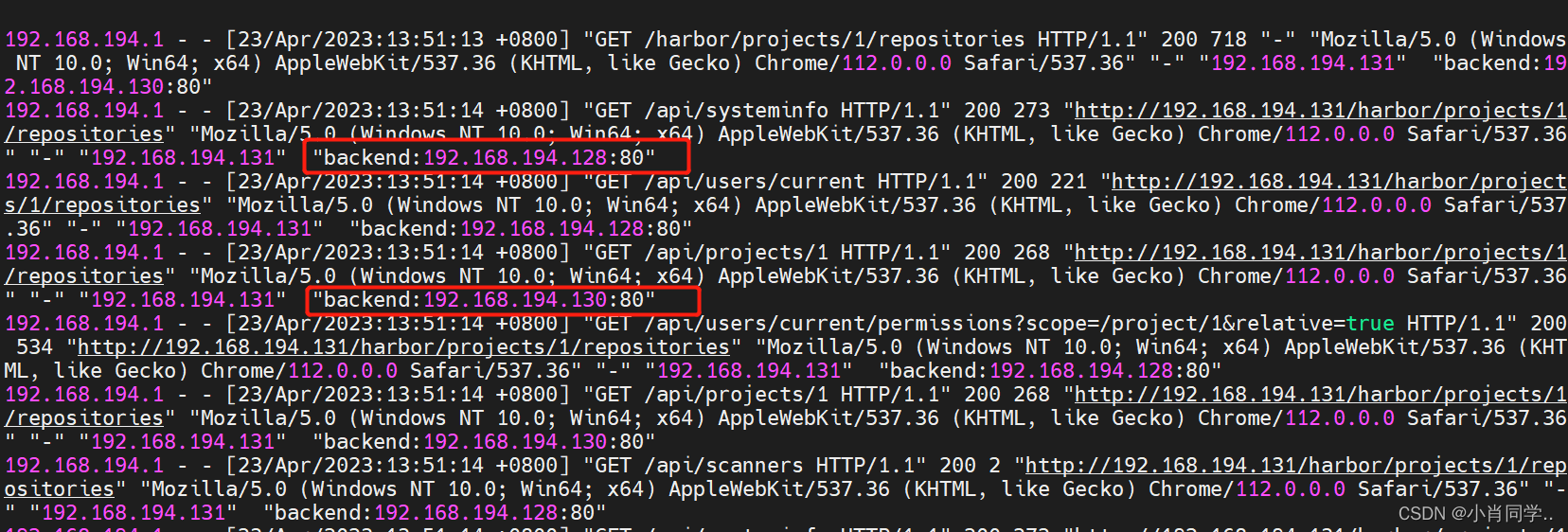
"$http_x_forwarded_for":HTTP 头中X-Forwarded-For字段的值,它通常包含了请求经过的代理服务器的 IP 地址列表,如果没有经过代理,它将包含客户端的 IP 地址。"$host":HTTP 头中Host字段的值,它表示客户端请求的主机名或 IP 地址。"backend:$upstream_addr":backend是一个自定义的字符串,用于标识使用哪个负载均衡组;$upstream_addr表示代理到的后端服务器的 IP 地址和端口号,格式为IP:端口号。
访问测试
- 通过192.168.194.131访问harbor
- 多次刷新页面,查看代理情况
总结
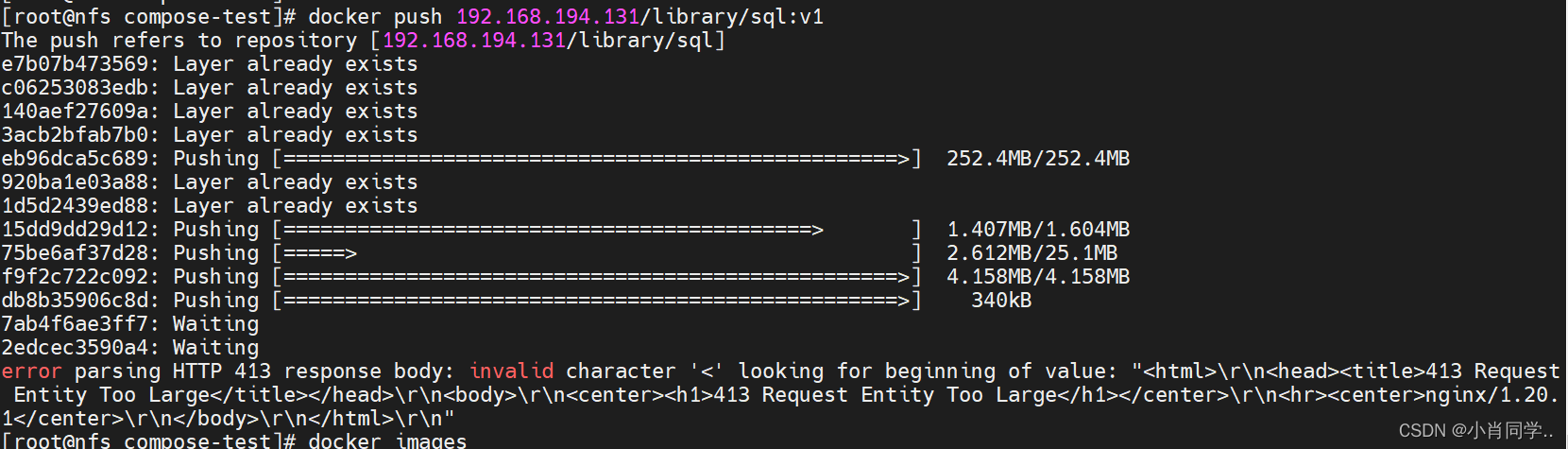
- 在镜像打tag和上传的时候,此时tag需要指定nginx的ip或者域名
[root@nfs compose-test]# docker tag busybox:latest 192.168.194.131/library/sy:v1 [root@nfs compose-test]# docker push 192.168.194.131/library/sy:v1 The push refers to repository [192.168.194.131/library/sy] 01fd6df81c8e: Retrying in 2 seconds 01fd6df81c8e: Retrying in 8 seconds 01fd6df81c8e: Pushed v1: digest: sha256:62ffc2ed7554e4c6d360bce40bbcf196573dd27c4ce080641a2c59867e732dee size: 527 [root@nfs compose-test]#
- 前端配置nginx的复制之后,在push打镜像的时候,可以会提示如下错误:
个错误提示表明您的请求实体太大,已经超过了 Nginx 的限制。默认情况下,Nginx 的 client_max_body_size 指令设置为 1MB,即它限制了可以上传到服务器的文件大小。要解决这个问题,您可以在 Nginx 配置中增加 client_max_body_size 指令的值。http {...client_max_body_size 100M;... }
- 使用nginx等负载均衡时
如果 Harbor 在代理或弹性负载平衡后运行nginx,请打开文件common/config/nginx/nginx.conf并搜索以下行。
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
如果代理已经有类似的设置,请将其从除location /,location /v2/然后location /service/中删除
如果在 Harbor 运行在代理或弹性负载平衡后的 Nginx 上,并且 Harbor 的 Nginx 配置文件中也设置了
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme,而代理的设置与 Harbor 的设置不一致,可能会导致镜像删除失败。这是因为当您尝试删除一个镜像时,Harbor 会检查请求的协议和主机信息,以确保它们与镜像存储库的 URL 匹配。如果请求的协议和主机信息与存储库的 URL 不匹配,Harbor 将拒绝删除请求,并返回一个错误消息。
在 Harbor 运行在代理或弹性负载平衡后的 Nginx 上时,代理通常会添加一些 HTTP 头信息,以便将请求正确地转发到 Harbor 的后端服务器上。其中,
X-Forwarded-Proto头信息用于指示请求的协议,X-Forwarded-Host头信息用于指示请求的主机名。如果代理已经设置了
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme,则将请求的协议设置为$scheme。而如果 Harbor 的 Nginx 配置文件中也设置了proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme,则可能会导致协议信息不一致,从而导致镜像删除失败。
t_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
如果代理已经有类似的设置,请将其从除location /,location /v2/然后location /service/中删除