( “树” 之 BST) 538. 把二叉搜索树转换为累加树 ——【Leetcode每日一题】
.jpg)
538. 把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
给出二叉 搜索 树的根节点,该树的节点值各不相同,请你将其转换为累加树(Greater Sum Tree),使每个节点 node 的新值等于原树中大于或等于 node.val 的值之和。
提醒一下,二叉搜索树满足下列约束条件:
- 节点的左子树仅包含键 小于 节点键的节点。
- 节点的右子树仅包含键 大于 节点键的节点。
- 左右子树也必须是二叉搜索树。
注意:本题和 1038: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-search-tree-to-greater-sum-tree/ 相同
示例 1:
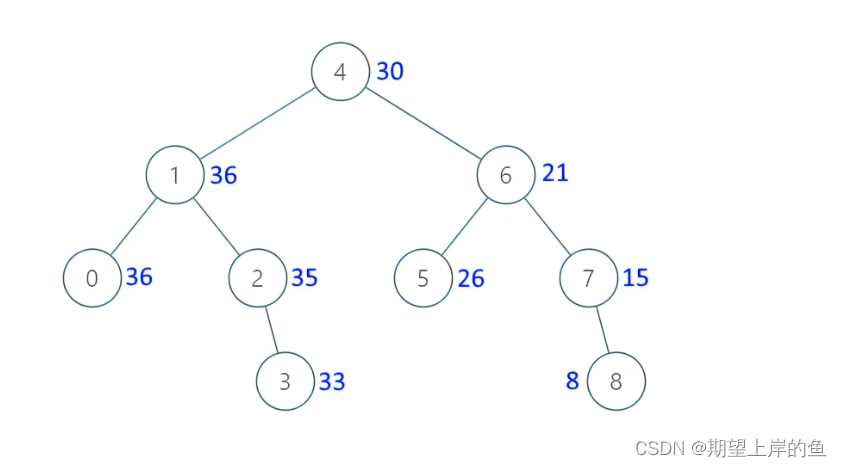
输入:[4,1,6,0,2,5,7,null,null,null,3,null,null,null,8]
输出:[30,36,21,36,35,26,15,null,null,null,33,null,null,null,8]
示例 2:
输入:root = [0,null,1]
输出:[1,null,1]
示例 3:
输入:root = [1,0,2]
输出:[3,3,2]
示例 4:
输入:root = [3,2,4,1]
输出:[7,9,4,10]
提示:
- 树中的节点数介于 0 和 1 0 4 10^4 104 之间。
- 每个节点的值介于 -104 和 1 0 4 10^4 104 之间。
- 树中的所有值 互不相同 。
- 给定的树为二叉搜索树。
思路:反序中序遍历
二叉搜索树中序遍历就是有序的,所以中序遍历该树,大于或等于 node.val 的值即是当前节点遍历值及其后面的值。
- 由于求大于或等于
node.val的值之和,所以采用右、中、左的遍历顺序,即可得到逆序的序列; - 定义一个全局变量
sum,记录已经遍历节点的和,当遍历到node节点时,只需再加上sum,即为该节点的替换值。
法一:递归、法二:迭代
略,具体思路请看:94. 二叉树的中序遍历
代码:(Java、C++)
法一:递归
Java
/* Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/
class Solution {private int sum = 0;public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {dfs(root);return root;}public void dfs(TreeNode root){if(root == null) return;if(root.right != null) dfs(root.right);root.val += sum;sum = root.val;if(root.left != null) dfs(root.left);}
}
C++
/* Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:int sum = 0;TreeNode* convertBST(TreeNode* root) {dfs(root);return root;}void dfs(TreeNode* root){if(root == nullptr) return;if(root->right != nullptr) dfs(root->right);root->val += sum;sum = root->val;if(root->left != nullptr) dfs(root->left);}
};
法二:迭代
Java
class Solution {public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {Stack<TreeNode> stk = new Stack();int sum = 0;if(root == null) return root;TreeNode cur = root;while(cur != null || !stk.isEmpty()){while(cur != null){stk.push(cur);cur = cur.right;}cur = stk.pop();cur.val += sum;sum = cur.val;cur = cur.left;}return root;}
}
C++
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* convertBST(TreeNode* root) {stack<TreeNode*> stk;int sum = 0;if(root == nullptr) return root;TreeNode* cur = root;while(cur != nullptr || !stk.empty()){while(cur != nullptr){stk.push(cur);cur = cur->right;}cur = stk.top();stk.pop();cur->val += sum;sum = cur->val;cur = cur->left;}return root;}
};
运行结果:
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n),其中
n是二叉搜索树的节点数。每一个节点恰好被遍历一次。 - 空间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n),为递归过程中栈的开销,平均情况下为 O ( l o g n ) O(logn) O(logn),最坏情况下树呈现链状,为 O ( n ) O(n) O(n)。
题目来源:力扣。
放弃一件事很容易,每天能坚持一件事一定很酷,一起每日一题吧!
关注我 leetCode专栏,每日更新!


