用Kotlin 一步步抄作业写一个Redux

前言
我抄的作业
完全理解 redux(从零实现一个 redux) · Issue #22 · brickspert/blog · GitHub
一.架构设计模式
1. mvc>mvp>mvvm->mvi
2.Redux实现类Mvi
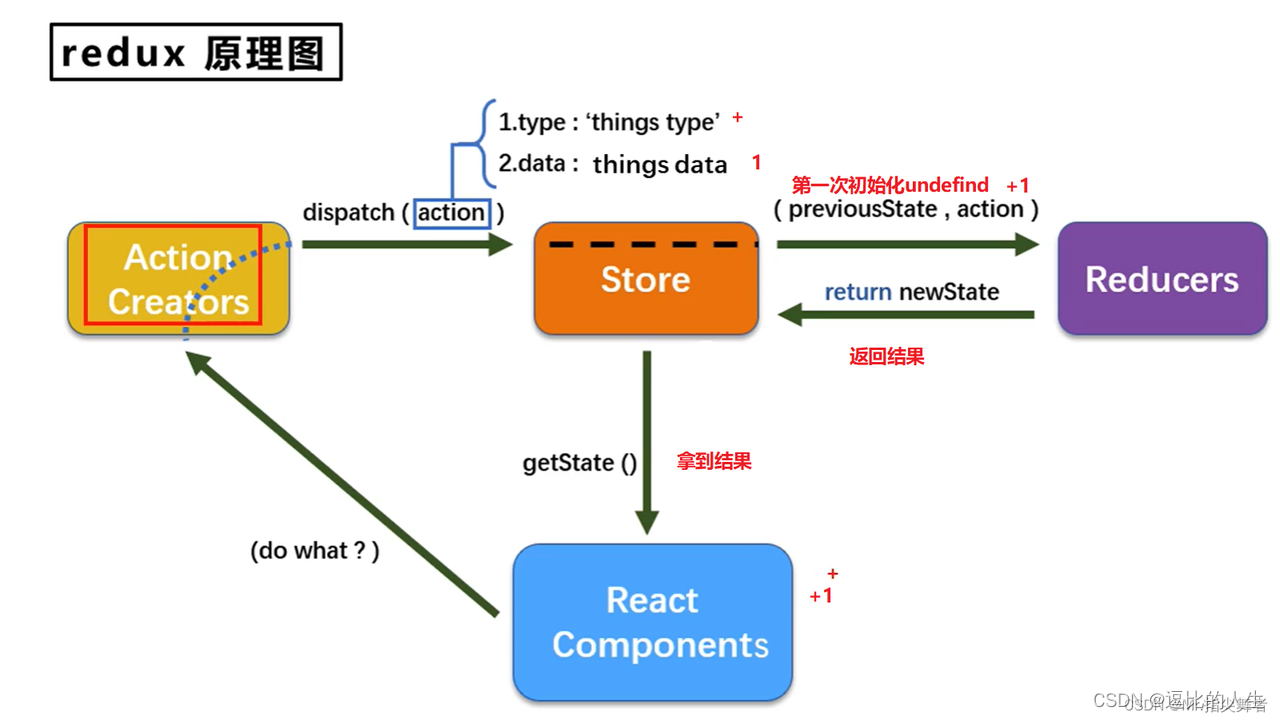
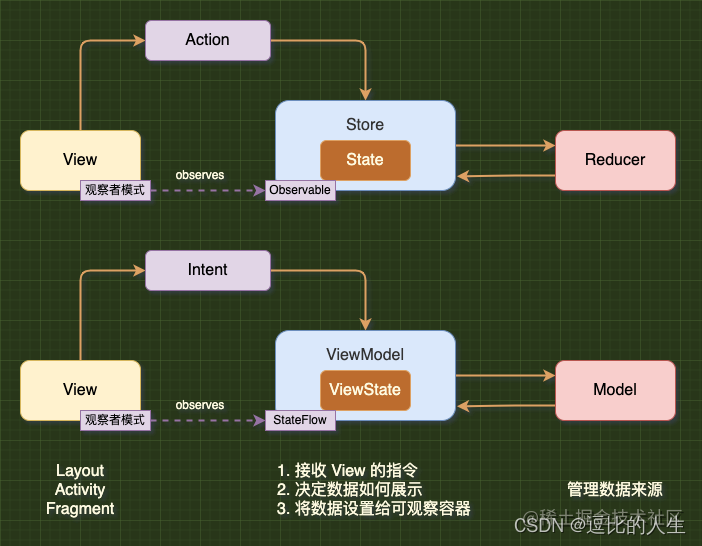
Android Mvi 与Redux对比,思想一致,单向数据流,单一数据源
二.Redux
redux 是一个状态管理器
1.简单的状态管理
redux 是一个状态管理器,那什么是状态呢?状态就是数据,比如计数器中的 count。
data class State(var count:Int=0) val state=State()我们来使用下状态
Log.d("redux",state.count.toString())我们来修改下状态
state.count=2以上就是状态的使用和修改,(很简单这就是redux核心,接下来往下慢慢拓展)
当然上面的有一个很明显的问题:修改 count 之后,使用 count 的地方不能收到通知。我们可以使用发布-订阅模式来解决这个问题。
val state=State(1)
val listeners= mutableListOf<StateLinsenter>()/*订阅*/
fun subscribe(listener:StateLinsenter) {listeners.add(listener)
}fun changeCount(count:Int) {state.count = count;/*当 count 改变的时候,我们要去通知所有的订阅者*/listeners.forEach {it.invoke()}
}我们来尝试使用下这个简单的计数状态管理器
/*来订阅一下,当 count 改变的时候,我要实时输出新的值*/
subscribe{Log.d("redux",state.count.toString());
}/*我们来修改下 state,当然我们不能直接去改 state 了,我们要通过 changeCount 来修改*/
changeCount(2);
changeCount(3);
changeCount(4);现在我们可以看到,我们修改 count 的时候,会输出相应的 count 值。
现在有两个新的问题摆在我们面前
-
这个状态管理器只能管理 count,不通用
-
公共的代码要封装起来
我们尝试来解决这个问题,把公共的代码封装起来
data class Counter(var count:Int)
data class Info(var name:String)
data class State(val counter: Counter?=null,val info: Info?=null)class Store(val subscribe: (listener: StateLinsenter)->Unit,val changeState: (state:State)->Unit,state:State)val createStore = fun(initState:State):Store{var mState=initStateval listeners= mutableListOf<()->Unit>()/*订阅*/val subscribe = fun(listener: ()->Unit) {listeners.add(listener)}val changeState= fun(state:State) {mState=state/*当 count 改变的时候,我们要去通知所有的订阅者*/listeners.forEach {it.invoke()}}return Store(subscribe,changeState, mState)
}进一步简化
typealias StateLinsenter=()->Unit
typealias Subscribe=(listener: StateLinsenter)->Unit
typealias ChangeState=(state:State)->Unitdata class Counter(var count:Int)
data class Info(var name:String)
data class State(val counter: Counter?=null,val info: Info?=null)class Store(val subscribe: Subscribe,val changeState:ChangeState,state:State)val createStore = fun(initState:State):Store{var mState=initStateval listeners= mutableListOf<StateLinsenter>()/*订阅*/val subscribe = fun(listener: StateLinsenter) {listeners.add(listener)}val changeState= fun(state:State) {mState=state/*当 count 改变的时候,我们要去通知所有的订阅者*/listeners.forEach {it.invoke()}}return Store(subscribe,changeState, mState)}我们来使用这个状态管理器管理多个状态 counter 和 info 试试
val initState =State(Counter(1) , Info("gan"))
val store = createStore(initState);store.subscribe{val counter = store.state.counterLog.d("redux","Counter.count=${counter.count}");
}
store.subscribe{val info = store.state.infoLog.d("redux","Info.name=${info.name}");
}store.changeState(store.state.apply { counter.count=2
})
store.changeState(store.state.apply {info.name="redux"
})
到这里就是简单的状态管理器。
这里需要理解的是 createStore,提供了 changeState,getState,subscribe 三个能力。
2.有计划的状态管理器
用上面的状态管理器来实现一个自增,自减的计数器
val initState = State(counter = Counter(1))
val store = createStore(initState);store.subscribe{val counter = store.state.counterLog.d("redux","Counter.count=${counter?.count}");
}
/*自增*/
store.changeState(store.state.apply {counter?.count=counter?.count?:0+1
})
/*自减*/
store.changeState(store.state.apply {counter?.count=counter?.count?:0-1
})
/*我想随便改*/
store.changeState(store.state.apply {counter?.count=100000
})上面可以看到,修改count不仅可以自增自减,同时可以设置成任意数,如果限制只能自增或者自减呢,分步进行
-
制定一个 state 修改计划,告诉 store,我的修改计划是什么。
-
修改 store.changeState 方法,告诉它修改 state 的时候,按照我们的计划修改。
我们来设置一个 plan 函数,接收现在的 state,和一个 action,返回经过改变后的新的 state。
typealias Plan=(state: State, action: Action)->State
val plan = fun(state: State, action: Action): State {when (action.type) {"INCREMENT" ->return state.apply {counter?.count = counter?.count ?: 0 + 1}"DECREMENT" ->return state.apply {counter?.count = counter?.count ?: 0 - 1}else -> return state}
}typealias StateLinsenter = () -> Unit
typealias Subscribe = (listener: StateLinsenter) -> Unit
typealias ChangeState = (action: Action) -> Unitclass Store(val subscribe: Subscribe, val changeState: ChangeState, val state: State)
class Action(val type: String,val data:Any?=null)val createStore = fun(plan:Plan,initState: State): Store {var mState = initStateval mplan=planval listeners = mutableListOf<StateLinsenter>()/*订阅*/val subscribe = fun(listener: StateLinsenter) {listeners.add(listener)}val changeState = fun(action: Action) {mState = mplan(mState,action)/*当 count 改变的时候,我们要去通知所有的订阅者*/listeners.forEach {it()}}return Store(subscribe, changeState, mState)}接下来用新的plan实现自增自减
val plan = fun(state: State, action: Action): State {when (action.type) {"INCREMENT" ->return state.apply {counter?.count = counter?.count ?: 0 + 1}"DECREMENT" ->return state.apply {counter?.count = counter?.count ?: 0 - 1}else -> return state}
}val initState = State(counter = Counter(1))/*把定义好的plan函数传入*/
val store = createStore(plan,initState)
store.subscribe {val counter = store.state.counterLog.d("redux", "Counter.count=${counter?.count}");
}
/*自增*/
store.changeState(Action("INCREMENT"))
/*自减*/
store.changeState(Action("DECREMENT"))
/*我想随便改 计划外的修改是无效的!*/
store.changeState(Action("abc"))以上实现了一个有计划的状态管理器
为了靠近redux,我们给 plan 和 changeState plan 改成 reducer,changeState 改成 dispatch!
typealias StateLinsenter = () -> Unit
typealias Subscribe = (listener: StateLinsenter) -> Unit
typealias Dispatch = (action: Action) -> Unit
typealias Reducer=(state: State, action: Action)->Stateclass Store(val subscribe: Subscribe, val dispatch: Dispatch, val state: State)
class Action(val type: String,val data:Any?=null)val createStore = fun(plan:Reducer,initState: State): Store {var mState = initStateval mplan=planval listeners = mutableListOf<StateLinsenter>()/*订阅*/val subscribe = fun(listener: StateLinsenter) {listeners.add(listener)}val dispatch = fun(action: Action) {mState = mplan(mState,action)/*当 count 改变的时候,我们要去通知所有的订阅者*/listeners.forEach {it()}}return Store(subscribe, dispatch, mState)}3.多文件协作
reducer 的拆分和合并
我们知道 Reducer 是一个计划函数,接收老的 state,按计划返回新的 state,如果我们项目中,有大量的 state,每个 state 都需要计划函数,不可能全部写一起吧
所有的计划写在一个 reducer 函数里面,会导致 reducer 函数及其庞大复杂,我们肯定会按组件维度来拆分出很多个 reducer 函数,然后就需要通过一个函数来把他们合并起来。
上面的reducer只是处理了Counter,那如果同时处理Info呢,就需要两个reducer
val counterReducer = fun(state: State, action: Action): State {when (action.type) {"INCREMENT" ->return state.apply {counter?.count = counter?.count ?: 0 + 1}"DECREMENT" ->return state.apply {counter?.count = counter?.count ?: 0 - 1}else -> return state}
}val InfoReducer= fun(state: State, action: Action): State {when (action.type) {"SET_NAME" ->return state.apply {info?.name = action?.data as String}else -> return state}
}那写个combineReducers 函数来把多个 reducer 函数合并成一个 reducer 函数,输入值需要是一个list
list生成方式随便写
/* 用于合并Reducer*/
fun MutableList<Reducer>.combineReducers(): Reducer {return { state: State, action: Action ->this.fold(initial = state) { acc: State, func: Reducer ->return@fold func(acc, action)}}
}
组合后验证
val counterReducer = fun(state: State, action: Action): State {when (action.type) {"INCREMENT" ->return state.apply {counter?.count = (counter?.count ?: 0) + 1}"DECREMENT" ->return state.apply {counter?.count = (counter?.count ?: 0 )- 1}else -> return state}
}val InfoReducer = fun(state: State, action: Action): State {when (action.type) {"SET_NAME" ->return state.apply {info?.name = action?.data as String}else -> return state}
}val initState = State(counter = Counter(1), info = Info("name"))/*把定义好的plan函数传入*/
val store = createStore(counterReducer.append(InfoReducer).append(InfoReducer).combineReducers(),initState
)store.subscribe {val counter = store.state.counterLog.d("redux====", "Counter.count=${counter?.count}");
}
store.subscribe {val info = store.state.infoLog.d("redux=====", "Counter.info=${info?.name}");
}
/*自增*/
store.changeState(Action("INCREMENT"))
/*自减*/
store.changeState(Action("DECREMENT"))
/*我想随便改 计划外的修改是无效的!*/
store.changeState(Action("abc"))
store.changeState(Action("SET_NAME", "我的新设置的名字"))输出
D/redux====: Counter.count=2D/redux=====: Counter.info=nameD/redux====: Counter.count=1D/redux=====: Counter.info=nameD/redux====: Counter.count=1D/redux=====: Counter.info=nameD/redux====: Counter.count=1D/redux=====: Counter.info=我的新设置的名字redux组合了,但是还有一个问题,state是写在一起的,如何把state也拆开呢
首先改写拆分State为CounterState和InfoState
data class Info(var name: String) : State
data class Counter(var count: Int) : Stateinterface State {fun getTag(): String {return this::class.java.name}fun <T> getData(clazz: Class<T>): T {if (this is StateContainer) {return states[clazz.name] as T} else {return this as T}}
}class StateContainer : State {val states = mutableMapOf<String, State>()companion object {fun allState(): State {return StateContainer()}}
}fun <T : State> T.getState(all: State): T {if (this.getTag() == StateContainer::class.java.name) {return this}if (all is StateContainer) {return all.states[this.getTag()] as T} else {return this}}fun <T : State> T.save(all: State) {if (all is StateContainer) {all.states[this.getTag()] = this}
}
框架代码改造
class IStore {companion object {/* 用于合并Reducer*/fun MutableList<Reducer<out State>>.combineReducers(): CombineReducer {return CombineReducer(StateContainer.allState(), this)}val createStore = fun(plan: Reducer<out State>): Store {var mState: State = StateContainer.allState()if (!(plan is CombineReducer)) {plan.initStatedata.save(mState)} else {mState = plan.initStatedataplan.mutableList.forEach {it.initStatedata.save(mState)}}val listeners = mutableListOf<StateListener>()val subscribe = fun(listener: StateListener): () -> Unit {listeners.add(listener)return fun() {val index = listeners.indexOf(listener)listeners.removeAt(index)}}val dispatch = fun(action: Action) {mState = plan(mState, action)/*当 count 改变的时候,我们要去通知所有的订阅者*/listeners.forEach {it()}}return Store(subscribe, dispatch, mState!!)}}
}
typealias StateListener = () -> Unit
typealias Subscribe = (listener: StateListener) -> Unit
typealias Dispatch = (action: Action) -> Unitabstract class Reducer<T : State>(val initStatedata: T) : InnerReducer {override fun invoke(state: State, action: Action): State {val data = initStatedata.getState()val next = nextState(data, action)next.save()return state}abstract fun nextState(stateData: T, action: Action): T}class CombineReducer(initState: State, val mutableList: MutableList<Reducer<out State>>) :Reducer<State>(initState) {override fun nextState(stateData: State, action: Action): State {mutableList.forEach {val state = it.initStatedata.getState()val next = it.invoke(state, action)next.save()}return stateData}
}
typealias InnerReducer = (state: State, action: Action) -> Statedata class Store(val subscribe: Subscribe, val dispatch: Dispatch, val state: State)
data class Action(val type: String, var data: Any? = null)inline fun <reified T : State> Store.subscribe(crossinline callBack: (state: T) -> Unit): () -> Unit {return this.subscribe {val data = state.getData(T::class.java) as TcallBack(data)}
}自定义reducer
class CounterReducer(initState: Counter) : Reducer<Counter>(initState) {override fun nextState(stateData: Counter, action: Action): Counter {when (action.type) {"INCREMENT" ->return stateData.apply {count = (count ?: 0) + 1}"DECREMENT" ->return stateData.apply {count = (count ?: 0) - 1}else -> return stateData}}}class CounterReducer(initState: Counter) : Reducer<Counter>(initState) {override fun nextState(stateData: Counter, action: Action): Counter {when (action.type) {"INCREMENT" ->return stateData.apply {count = (count ?: 0) + 1}"DECREMENT" ->return stateData.apply {count = (count ?: 0) - 1}else -> return stateData}}}使用测试
fun test() {val counterReducer = CounterReducer(Counter(1))val infoReducer = InfoReducer(Info("name"))/*把定义好的plan函数传入*/val list= mutableListOf<Reducer<out State>>().apply {this.add(counterReducer)this.add(infoReducer)}val store = IStore.createStore(list.combineReducers())//观察所有数据store.subscribe {val counter= store.state.getData(Counter::class.java)Log.d("redux====", "Counter.count=${counter?.count}");}//观察指定类型store.subscribe<Info> {Log.d("redux=====", "Info.name=${it?.name}");}/*自增*/store.dispatch(Action("INCREMENT"))/*自减*/store.dispatch(Action("DECREMENT"))/*我想随便改 计划外的修改是无效的!*/store.dispatch(Action("abc"))store.dispatch(Action("SET_NAME", "我的新设置的名字"))
}4.中间件 middleware
中间件是对 dispatch 的扩展,或者说重写,增强 dispatch 的功能!
记录日志
我现在有一个需求,在每次修改 state 的时候,记录下来 修改前的 state ,为什么修改了,以及修改后的 state。我们可以通过重写 store.dispatch 来实现,直接看代码
val store = IStore.createStore(counterReducer)
val next = store.dispatch
/*重写了store.dispatch*/
store.dispatch = fun(action: Action){Log.d("redux====", store.state.getData(Counter::class.java).toString())Log.d("redux====", action.type.toString())next(action)Log.d("redux====", store.state.getData(Counter::class.java).toString())
}使用下
store.dispatch(Action("INCREMENT"))输出
D/redux====: Counter(count=1)
D/redux====: INCREMENT
D/redux====: Counter(count=2)现在我们已经实现了一个的记录 state.counter 修改日志的功能!
记录异常
我又有一个需求,需要记录每次数据出错的原因,我们扩展下 dispatch
val store = IStore.createStore(counterReducer)
val next = store.dispatch
store.dispatch =fun(action: Action) {try {next(action);} catch (e:Exception) {Log.e("redux====","错误报告: ${e.message}" )}
}这样每次 dispatch 出异常的时候,我们都会记录下来。
多中间件的合作
我现在既需要记录日志,又需要记录异常,怎么办?那就要两个函数合起来
store.dispatch = fun(action: Action) {try {Log.d("redux====", store.state.getData(Counter::class.java).toString())Log.d("redux====", action.type.toString())next(action)Log.d("redux====", store.state.getData(Counter::class.java).toString())} catch (e:Exception) {Log.e("redux====","错误报告: ${e.message}" )}
}如果又来一个需求怎么办?接着改 dispatch 函数?那再来10个需求呢?到时候 dispatch 函数肯定庞大混乱到无法维护了!这个方式不可取呀!如果又来一个需求怎么办?接着改 dispatch 函数?那再来10个需求呢?到时候 dispatch 函数肯定庞大混乱到无法维护了!这个方式不可取呀!
我们需要考虑如何实现扩展性很强的多中间件合作模式。
1.我们把 loggerMiddleware 提取出来
val store = IStore.createStore(counterReducer)
val next = store.dispatchval loggerMiddleware = fun(action: Action){Log.d("redux====", store.state.getData(Counter::class.java).toString())Log.d("redux====", action.type.toString())next(action)Log.d("redux====", store.state.getData(Counter::class.java).toString())
}
store.dispatch =fun(action: Action){try {loggerMiddleware(action);} catch (e:Exception) {Log.e("redux====","错误报告: ${e.message}" )}
}2.我们把 exceptionMiddleware 提取出来
val exceptionMiddleware =fun(action: Action) {try {/*next(action)*/loggerMiddleware(action);} catch (e:Exception) {Log.e("redux====","错误报告: ${e.message}" )}
}3.现在的代码有一个很严重的问题,就是 exceptionMiddleware 里面写死了 loggerMiddleware,我们需要让 next(action)变成动态的,随便哪个中间件都可以
val exceptionMiddleware = fun(next: Dispatch): Dispatch {return fun(action: Action) {try {next(action)} catch (e: Exception) {Log.e("redux====", "错误报告: ${e.message}")}}
}
val logMiddleware = fun(next: Dispatch): Dispatch {return fun(action: Action) {Log.d("redux====", store.state.getData(Counter::class.java).toString())Log.d("redux====", action.type.toString())next(action)Log.d("redux====", store.state.getData(Counter::class.java).toString())}
}这样使用的话,就可以随意嵌套
val next = store.dispatch
/*可以loggerMiddleware 变成参数传进去*/
store.dispatch = exceptionMiddleware(logMiddleware(next))
/*也可以exceptionMiddleware变成参数传进去*/
store.dispatch = logMiddleware(exceptionMiddleware(next))这时候我们开开心心的新建了一个 loggerMiddleware.kt,一个exceptionMiddleware.kt文件,想把两个中间件独立到单独的文件中去。会碰到什么问题吗?如下图。报错
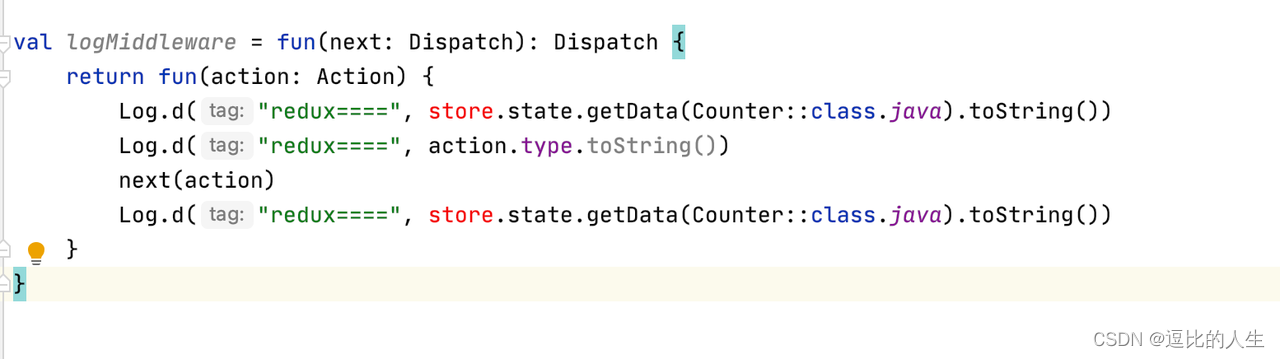
loggerMiddleware 中包含了外部变量 store,导致我们无法把中间件独立出去。那我们把 store 也作为一个参数传进去好了~
val store = IStore.createStore(counterReducer)
val next = store.dispatch
val exceptionMiddleware = fun(store: Store): ((next: Dispatch) -> Dispatch) {return fun(next: Dispatch): Dispatch {return fun(action: Action) {try {next(action)} catch (e: Exception) {Log.e("redux====", "错误报告: ${e.message}")}}}
}
val logMiddleware = fun(store: Store): ((next: Dispatch) -> Dispatch) {return fun(next: Dispatch): Dispatch {return fun(action: Action) {Log.d("redux====", store.state.getData(Counter::class.java).toString())Log.d("redux====", action.type.toString())next(action)Log.d("redux====", store.state.getData(Counter::class.java).toString())}}
}
val exception=exceptionMiddleware(store)
val logger=logMiddleware(store)
/*可以loggerMiddleware 变成参数传进去*/
store.dispatch = logger(exception(next))
/*也可以exceptionMiddleware变成参数传进去*/
store.dispatch = exception(logger(next))到这里为止,实现了两个可以独立的中间件
现在我有一个需求,在打印日志之前输出当前的时间戳。用中间件来实现!
val store = IStore.createStore(counterReducer)
val next = store.dispatch
val exceptionMiddleware = fun(store: Store): ((next: Dispatch) -> Dispatch) {return fun(next: Dispatch): Dispatch {return fun(action: Action) {try {next(action)} catch (e: Exception) {Log.e("redux====", "错误报告: ${e.message}")}}}
}
val logMiddleware = fun(store: Store): ((next: Dispatch) -> Dispatch) {return fun(next: Dispatch): Dispatch {return fun(action: Action) {Log.d("redux====", store.state.getData(Counter::class.java).toString())Log.d("redux====", action.type.toString())next(action)Log.d("redux====", store.state.getData(Counter::class.java).toString())}}
}
val exception=exceptionMiddleware(store)
val logger=logMiddleware(store)
/*可以loggerMiddleware 变成参数传进去*/
store.dispatch = logger(exception(next))
/*也可以exceptionMiddleware变成参数传进去*/
store.dispatch = exception(logger(next))测试一下
val store = IStore.createStore(counterReducer)
val next = store.dispatchval exception = exceptionMiddleware(store)
val logger = logMiddleware(store)
val time = timeMiddleware(store)
/*也可以exceptionMiddleware变成参数传进去*/
store.dispatch = exception(logger(time(next)))================>
D/redux====: Counter(count=1)
D/redux====: INCREMENT
D/redux====: 1669277764203
D/redux====: Counter(count=2)自定义中间件貌似看起来比较难,那就定义两种创建中间件抽象
typealias MiddlewareInner = ((next: Dispatch) -> Dispatch)
typealias Middleware = (store: Store) -> ((next: Dispatch) -> Dispatch)fun registerWrapperMiddleware(before: ((store: Store, action: Action) -> Unit)? = null,after: ((store: Store, action: Action) -> Unit)? = null
): (store: Store) -> MiddlewareInner {return fun(store: Store): MiddlewareInner {return fun(next: Dispatch): Dispatch {return fun(action: Action) {before?.invoke(store, action)next(action)after?.invoke(store, action)}}}
}fun registerAroundMiddleware(around: (store: Store, next: Dispatch, action: Action) -> Unit
): (store: Store) -> MiddlewareInner {return fun(store: Store): MiddlewareInner {return fun(next: Dispatch): Dispatch {return fun(action: Action) {around.invoke(store, next, action)}}}
}上面的两种中间件实现也可以改写成下面的
val logMiddleware = fun(store: Store): MiddlewareInner {return fun(next: Dispatch): Dispatch {return fun(action: Action) {Log.d("redux====修改之前", store.state.getData(Counter::class.java).toString())Log.d("redux====", action.type.toString())next(action)Log.d("redux====修改之后", store.state.getData(Counter::class.java).toString())Log.d("redux===="," \\n")}}
}
等同于下面
val logMiddleware1 = registerWrapperMiddleware({ store, action ->Log.d("redux====修改之前", store.state.getData(Counter::class.java).toString())Log.d("redux====", action.type.toString())
}) { store, action ->Log.d("redux====修改之后", store.state.getData(Counter::class.java).toString())Log.d("redux===="," \\n")
}val timeMiddleware = fun(store: Store): MiddlewareInner {return fun(next: Dispatch): Dispatch {return fun(action: Action) {Log.d("redux====", Date().getTime().toString());next(action);}}
}
等同于下面
val timeMiddleware1 = registerWrapperMiddleware (after = {s, a ->Log.d("redux====", Date().getTime().toString());
})val exceptionMiddleware = fun(store: Store): MiddlewareInner {return fun(next: Dispatch): Dispatch {return fun(action: Action) {try {next(action)} catch (e: Exception) {Log.e("redux====", "错误报告: ${e.message}")}}}
}等同于下面
val exceptionMiddleware1 = registerAroundMiddleware { store, next, action ->try {next(action)} catch (e: java.lang.Exception) {Log.e("redux====", "错误报告: ${e.message}")}
}中间件使用方式优化
上一节我们已经完全实现了正确的中间件,但是中间件的使用方式不是很友好
其实我们只需要知道三个中间件,剩下的细节都可以封装起来!我们通过扩展 createStore 来实现!先看下最终目标
val createStore = IStore.createStore
val newCreateStore = applyMiddleware(exceptionMiddleware, timeMiddleware, logMiddleware)(createStore)
val storeNew = newCreateStore(counterReducer)1.实现 applyMiddleware
typealias RewriteCreateStoreFunc=(oldCreateStore: CreateStore)-> CreateStore
typealias MiddlewareInner =((next: Dispatch) -> Dispatch)
typealias Middleware = (store: Store) -> ((next: Dispatch) -> Dispatch)
typealias CreateStore= (plan: Reducer<out State>) -> Storefun applyMiddleware(vararg middlewares: Middleware):RewriteCreateStoreFunc{return fun(oldCreateStore: CreateStore): CreateStore{return fun(reducer: Reducer<out State>) : Store{val store = oldCreateStore(reducer)var dispatch = store.dispatch/* 实现 exception(time((logger(dispatch))))*/middlewares.reverse()//创建中间件//模拟 val exception = exceptionMiddleware(store)// val logger = logMiddleware(store)// val time = timeMiddleware(store)val chain= mutableListOf<MiddlewareInner>()middlewares.forEach {chain.add(it(store))}//反转一下 实现 exception(time((logger(dispatch))))chain.reverse()chain.forEach {dispatch = it(dispatch);}/*2. 重写 dispatch*/store.dispatch = dispatch;return store}}
}但是现在有个问题,有createStore 和newCreateStore两种创建方式了
val createStore = IStore.createStore
/*没有中间件的 createStore*/
val store = createStore(counterReducer)/*有中间件的 createStore*/
val rewriteCreateStoreFunc = applyMiddleware(exceptionMiddleware,logMiddleware, timeMiddleware )
val newCreateStore = rewriteCreateStoreFunc(createStore)
val store2 = newCreateStore(counterReducer)那就重载一个
fun createStore(middlewares: MutableList<Middleware>,plans:MutableList<Reducer<out State>>): Store {return applyMiddleware(middlewares)(createStore)(plans.combineReducers())}用法
val store = IStore.createStore(counterReducer)val store2= applyMiddleware(mutableListOf(exceptionMiddleware1, timeMiddleware1, logMiddleware1))(IStore.createStore)(list.combineReducers())val store3 = IStore.createStore(mutableListOf(exceptionMiddleware1, timeMiddleware1, logMiddleware1),mutableListOf(counterReducer,infoReducer))
5.退订
typealias Subscribe = (listener: StateListener) -> ()->Unitval subscribe =fun(listener: StateListener):()->Unit{listeners.add(listener)return fun() {val index = listeners.indexOf(listener)listeners.removeAt(index)}
}退订用法
val createStore = IStore.createStore
/*没有中间件的 createStore*/
val store = createStore(counterReducer)val unsubscribe= store.subscribe {val counter= store.state.getData(Counter::class.java)Log.d("redux====", "Counter.count=${counter?.count}");}
/*自增*/
store.dispatch(Action("INCREMENT"))
unsubscribe()
/*自减*/
store.dispatch(Action("DECREMENT"))
/*我想随便改 计划外的修改是无效的!*/
store.dispatch(Action("abc"))
store.dispatch(Action("SET_NAME", "我的新设置的名字"))=============>
D/redux====: Counter.count=2最后放在代码地址
GitHub - 971638267/ReduxByKotlin: 一个kotlin实现的Redux


