【机器学习】 多维kd-tree的python实现

一、说明
本篇主要介绍一个用python实现kd-tree的代码,以及围绕代码实现的kd-tree原理。期望能够为读者打开另一个视角,看待kd-tree的好处。
二、什么是K维树?
K-D 树(也称为 K 维树)是一种二叉搜索树,其中每个节点中的数据是空间中的 K 维点。简而言之,它是一种空间划分(详见下文)数据结构,用于在K维空间中组织点。 K-D树中的一个非叶节点将空间分成两部分,称为半空间。该空间左侧的点由该节点的左子树表示,空间右侧的点由右子树表示。我们很快就会解释如何划分空间和形成树的概念。为了简单起见,让我们通过一个例子来理解二维树。 root 将有一个 x 对齐的平面,root 的子级都有 y 对齐的平面,root 的孙级都有 x 对齐的平面,root 的曾孙级都有 y 对齐的平面,依此类推。
概括:让我们将平面编号为 0、1、2、...(K – 1)。从上面的示例中,很明显深度 D 处的点(节点)将有一个对齐的平面,其中 A 的计算公式为:A = D mod K
如何判断一个点是在左子树还是在右子树?如果根节点在平面 A 中对齐,则左子树将包含在该平面中坐标小于根节点坐标的所有点。类似地,右子树将包含其在该平面中的坐标大于等于根节点坐标的所有点。
三、如何创建Kd-tree
创建二维树:考虑二维平面中的以下点:(3, 6), (17, 15), (13, 15), (6, 12), (9, 1), (2 , 7), (10, 19)
- Insert(3, 6):因为树是空的,所以把它作为根节点。
- Insert(17, 15):与根节点比较。由于根节点是 X 对齐的,因此将比较 X 坐标值以确定它是在右子树中还是在左子树中。该点将 Y 对齐。
- Insert (13, 15):该点的X值大于根节点中点的X值。所以,这将位于 (3, 6) 的右子树中。再次比较此点的 Y 值与点 (17, 15) 的 Y 值(为什么?)。因为,它们是相等的,所以该点将位于 (17, 15) 的右子树中。该点将 X 对齐。
- Insert (6, 12):该点的X值大于根节点中点的X值。所以,这将位于 (3, 6) 的右子树中。再次比较此点的 Y 值与点 (17, 15) 的 Y 值(为什么?)。因为,12 < 15,这个点将位于 (17, 15) 的左子树中。该点将 X 对齐。
- Insert (9, 1):同样,该点将位于(6, 12)的右侧。
- Insert (2, 7):同样,这个点会在(3, 6)的左边。
- Insert (10, 19):同样,该点将位于 (13, 15) 的左侧。

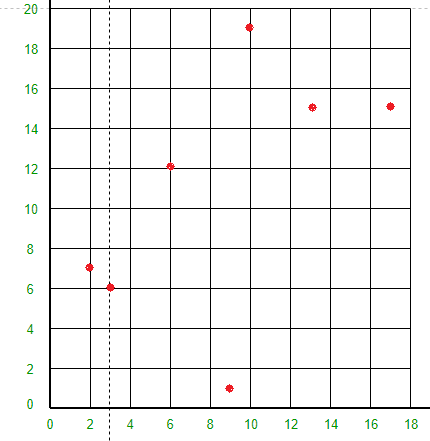
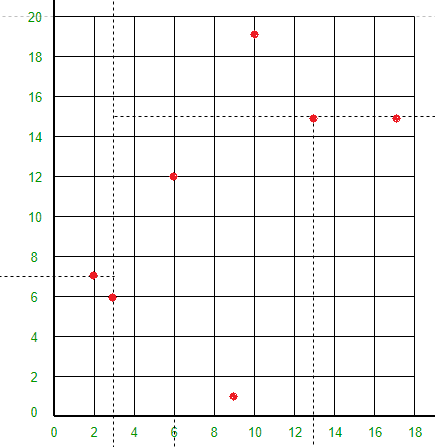
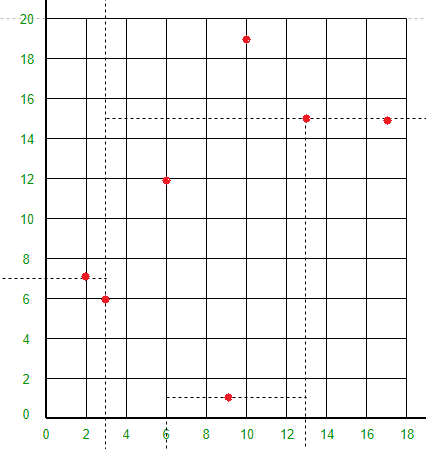
空间是如何划分的?所有 7 个点都将绘制在 X-Y 平面中,如下所示:
-
点 (3, 6) 会将空间分成两部分:画线 X = 3。
-
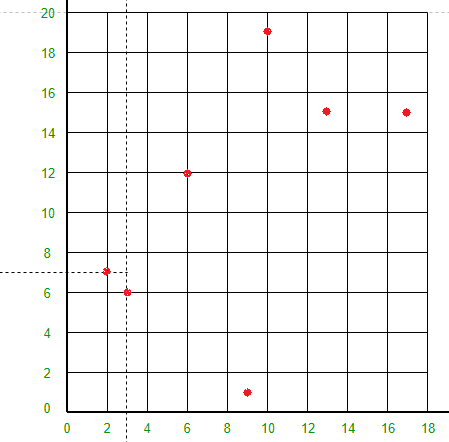
点 (2, 7) 将线 X = 3 左侧的空间水平分成两部分。在 X = 3 的左侧绘制 Y = 7 线。
-
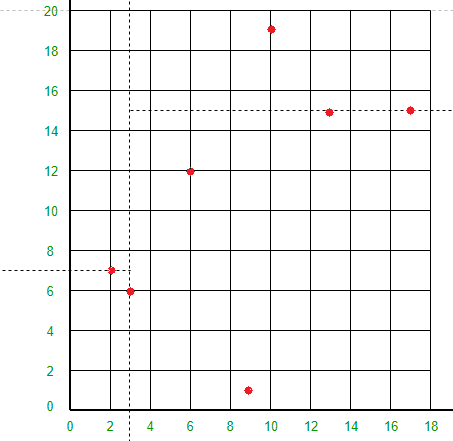
点 (17, 15) 会将直线 X = 3 右侧的空间水平分成两部分。在 X = 3 的右侧绘制 Y = 15 线。
-
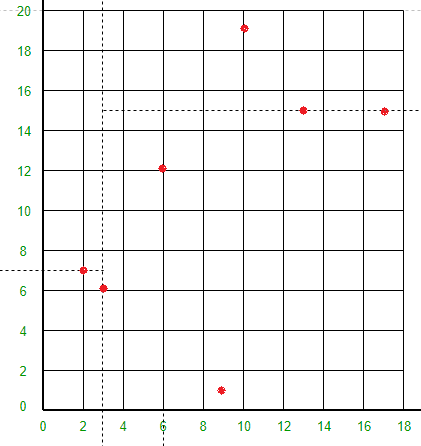
点 (6, 12) 将线 Y = 15 下方和线 X = 3 右侧的空间分成两部分。在 X = 3 线的右侧和 Y = 15 线的下方绘制线 X = 6。
-
点 (13, 15) 会将 Y = 15 线下方和 X = 6 线右侧的空间分成两部分。在 X = 6 线的右侧和 Y = 15 线的下方绘制线 X = 13。
-
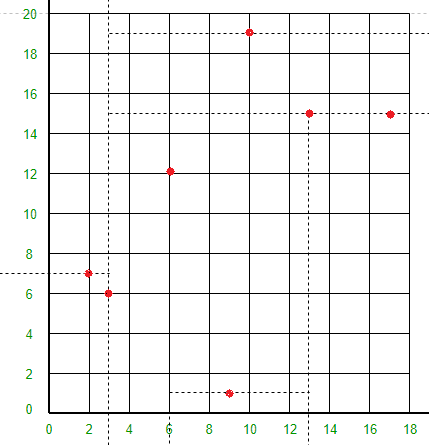
点 (9, 1) 将线 X = 3、X = 6 和 Y = 15 之间的空间分成两部分。在 X = 3 和 X = 13 之间绘制 Y = 1 线。
-
点 (10, 19) 会将 X = 3 行右侧和 Y = 15 行上方的空间分成两部分。在 X = 3 行的右侧和 Y = 15 行的上方绘制 Y = 19 行。
四、对应的python代码
|
|
Output:
Found
Not Found
五、后记
K-d树作为数据结构有几个优点:
- 高效搜索:K-d 树在 k 维空间中有效地搜索点,例如最近邻搜索或范围搜索。
- 降维:K-d 树可用于降低问题的维数,从而缩短搜索时间并降低数据结构的内存需求。
- 多功能性:K-d 树可用于广泛的应用,例如数据挖掘、计算机图形学和科学计算。
- 平衡:K-d 树是自平衡的,这确保树即使在插入或删除数据时也能保持高效。
- 增量构建:K-d 树可以增量构建,这意味着可以在结构中添加或删除数据,而无需重建整棵树。
- 易于实现:K-d 树相对容易实现,可以用多种编程语言实现。
- 本文由 Aashish Barnwal 编译。如果您发现任何不正确的地方,或者您想分享有关上述主题的更多信息,请发表评论。


