网络请求实战-实战Fetch和Promise相关的架构

目录
Promise神器(承诺)
Promise+Coding示例
Promise常见用法
简单的promise
Fetch的基本用法
fetch
Fetch基本用法
Fetch+Promise场景举例
小结
Promise神器(承诺)
Promise+Coding示例
- 代表异步求值的过程和结果
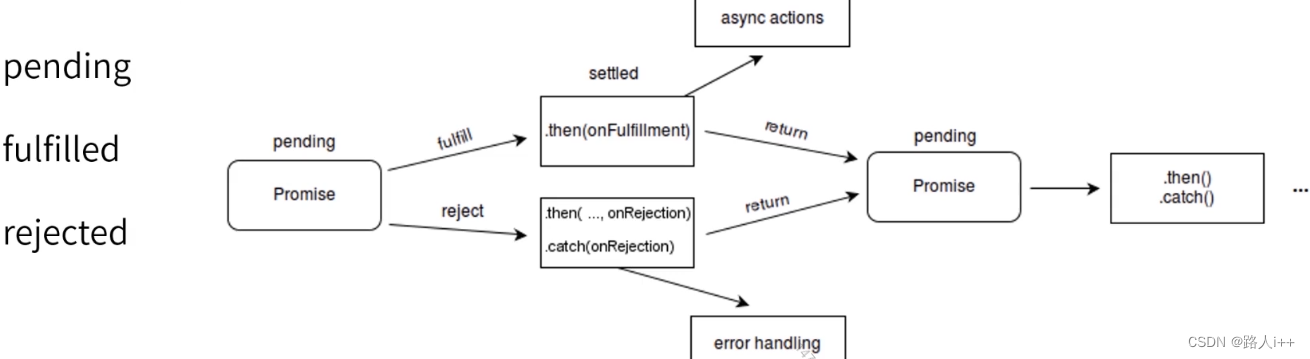
promise链式调用,可以一直promise下去
// example 01
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {resolve(100)
}).then(data => {console.log(data)
})
// 100// example 02
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {resolve(100)
}).then(data => {console.log(data)return 'abc' // 直接返回一个值
})
.then(data => { // 此处不用执行promise了,直接fulfilled了一个'abcconsole.log(data)
})
// 100 abc// example 03
function wait(ms = 1000, data) {return new Promise((resolve) => {setTimeout(() => {resolve(data)}, ms)})
}
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {resolve(100)
}).then(data => {console.log(data) // 100return wait(1000, 'abc') // 等待1s,返'abc'
})
.then(data => {console.log(data) // 等待1000ms,打印'abc'
})// example04
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {reject("some error")
}).then(data => {console.log("1", data) // 不执行
}).catch(ex => {console.error(ex) // some errorreturn "GO"
}).then(data => {console.log(data) // GO
})// example05
function wait(ms = 1000, data){return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {setTimeout(() => {resolve(data)}, ms)})
}
async function foo(){console.log('--begin--')const one = await wait(1000, 1) console.log('--tick 1--') // 等待一秒 const two = await wait(1000, 2)console.log('--tick 2--') // 再等待一秒 console.log(one, two) // 1, 2await Promise.reject('some error')try{await Promise.reject('some error')} catch(ex) {console.log(ex) // some error}
}
foo()// example 6
function wait(ms = 1000, data){return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {setTimeout(() => {resolve(data)}, ms)})
}
// 工厂方法
Promise.all([wait(200, 1), wait(100, 2)]).then(data => {console.log('all', data) // 等2个promise都结束,返回这个数组[1,2]})
Promise.race([wait(200, 1), wait(100, 2)]).then(data => {console.log('race', data) // race是在这个执行promise数组中返回第一个拿到的值})Promise常见用法
- resolve & reject
- Chain (链执行)
- 并发和竞争(all 和 race)
- 异常处理 (try catch)
简单的promise
const PENDING = 1
const FULLFILLED = 2
const REJECTED = 3
class Promise{constructor(executor){this.state = PENDINGconst resolver = (value) => {if(this.state === PENDING) {this.state = FULLFILLED this.value = value }for(let [onFullFill, resolve] of this.fullfills) {const x = onFullFill(this.value)resolve(x)}}const rejector = () => {this.state = REJECTED}this.fullfills = []executor(resolver, rejector)}then(onFullfill) {return new Promise((resolve, rejector) => {switch(this.state) {case FULLFILLED:const x = onFullfill(this.value)resolve(x)breakcase PENDING:this.fullfills.push([onFullfill, resolve])break}})}
}
new Promise((resolve) => {setTimeout(() => {resolve('123')})
}).then(data => {console.log(data) // 123return '456'
}).then(data => {console.log(data) // 456return data
})Fetch的基本用法
fetch
一个让处理http pipeline更容易的工具(MDN)
- 返回Promise
- Resolve发生在网络通信正常(404,500也是resolve)
- Reject发生在网络通信异常
- 默认不接受cookie(需要设置)
存在队头阻塞,服务端负载充足

Fetch基本用法
- GET/POST/PUT/DELETE
- Headers
- Cookie
- 缓存
fetch("/product", {method: "POST",headers : {"Content-Type" : "application/json" },body: JSON.stringify({ name: "123苹果" }),
}).then((resp) => console.log(resp.status))
fetch("/product", {method: "POST",headers : {"Content-Type" : "application/json" },body: JSON.stringify({ name: "".padStart(100000, "A")}),
}).then((resp) => console.log(resp.status))// node端 需要引用实例
const fetch = require('node-fetch')
const promise = fetch('https://www.baidu.com', {method: 'POST',headers: {'Content-Type': "application/json", },credentials: 'include', // 设置之后可以接收服务端的Cookie
})
async function foo() {const resp = await fetch("http://www.baidu.com", {headers: {'user-agent': "Mozillia" } })const text = await resp.text()console.log(text)
}
foo()
// 缓存
fetch("https://www.baidu.com", {cache: 'force-cache'})Fetch+Promise场景举例
1.指数补偿,专门应付移动端频繁网络波动的
按照指数的时间倍数重复发送请求
- 0ms
- 200ms
- 400ms
- 800ms
- 1600ms
- 3200ms
- fail
// 示例程序
const fetch = require('node-fetch')
function request(url){let resolved = falselet t = 1 return new Promise((resolve) => {function doFetch(){if(resolved || t > 16) {return}fetch(url).then((resp) => {return resp.text()}).then(data => {if(!resolved) {resolved = trueresolve(data)console.log('t=', t)}}).catch(ex => {console.error(ex)})setTimeout(() => {doFetch()t *= 2}, t * 100)}doFetch()})
}
request('http://www.baidu.com').then(data => {console.log(data.length)})
setTimeout(() => {
}, 3000)// 有缺陷,所有请求都发送了
function wait(ms, f) {return new Promise((resolve) => {setTimeout(()=> {resolve(f()) }, ms) })
}
function request(url) {Promise.race([fetch(url),wait(100, ()=> fetch(url) ),wait(200, ()=> fetch(url) ),wait(400, ()=> fetch(url) ),wait(800, ()=> fetch(url) ),wait(1600, ()=> fetch(url) ),])
}
request('http://www.baidu.com').then(resp => {console.log(resp)})
setTimeout(() => {
}, 3000)2.并发处理和时间窗口,底层前端请求优化的
多个资源并发请求(Promise.all)
基于时间窗口过滤重复请求
const fetch = require('node-fetch')
function hash(args) {return args.join(',')
}
function window_it(f, time = 50) {let w = {} let flag = false return (...args) => {// 参数传递return new Promise((resolve) => {if (!w[hash(args)]) {w[hash(args)] = {func: f,args,resolvers: [],}}if (!flag) {flag = truesetTimeout(() => {Object.keys(w).forEach((key) => {const { func, args, resolvers } = w[key]const promise = func(...args).then((resp) => resp.text()).then((text) =>resolvers.map((r) => {r(text)}))})flag = false}, time)}console.log(args)w[hash(args)].resolvers.push(resolve)})}
}
const request = window_it(fetch, 20)
request('http://www.baidu.com').then(txt => console.log(txt.length))
request('http://www.baidu.com').then(txt => console.log(txt.length))
request('http://www.baidu.com').then(txt => console.log(txt.length))
request('http://www.zhihu.com').then(txt => console.log(txt.length))
request('http://www.baidu.com').then(txt => console.log(txt.length))
request('http://www.baidu.com').then(txt => console.log(txt.length))小结
- 为什么不教Axios? 因为fetch是浏览器提供的标准
- 优化问题要工程化处理(所有页面的优化,请求优化,页面大小优化,白屏的优化【需要用到算法,数据结构和相关的架构知识,是针对一类问题提供工具】)
