【Spring Security】 入门实战

文章目录
一、基本概念
单点登录
- 什么叫做单点登录呢。就是在一个多应用系统中,只要在其中一个系统上登录之后,不需要在其它系统上登录也可以访问其内容。
- 举个例子,京东那么复杂的系统肯定不会是单体结构,必然是微服务架构,比如订单功能是一个系统,交易是一个系统…那么我在下订单的时候登录了,付钱难道还需要再登录一次吗,如果是这样,用户体验也太差了吧。
- 实现的流程就是我在下单的时候系统发现我没登录就让我登录,登录完了之后系统返回给我一个Token,就类似于身份证的东西;然后我想去付钱的时候就把Token再传到交易系统中,然后交易系统验证一下Token就知道是谁了,就不需要再让我登录一次。
JWT(JSON Web Token)
Token的生成与解密
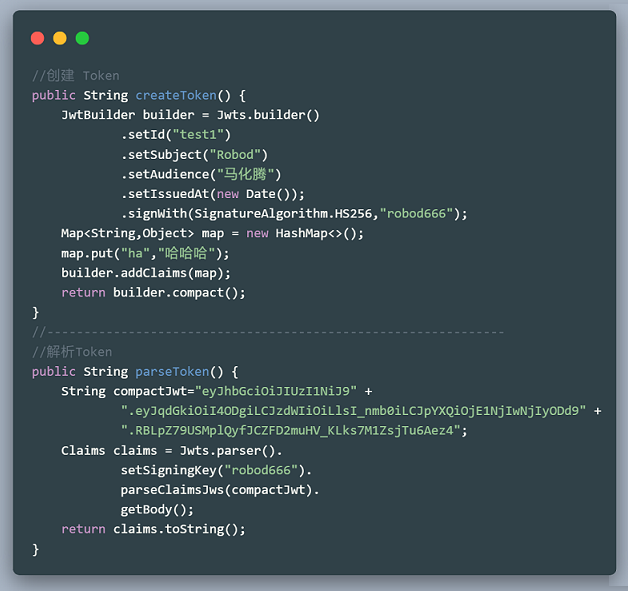
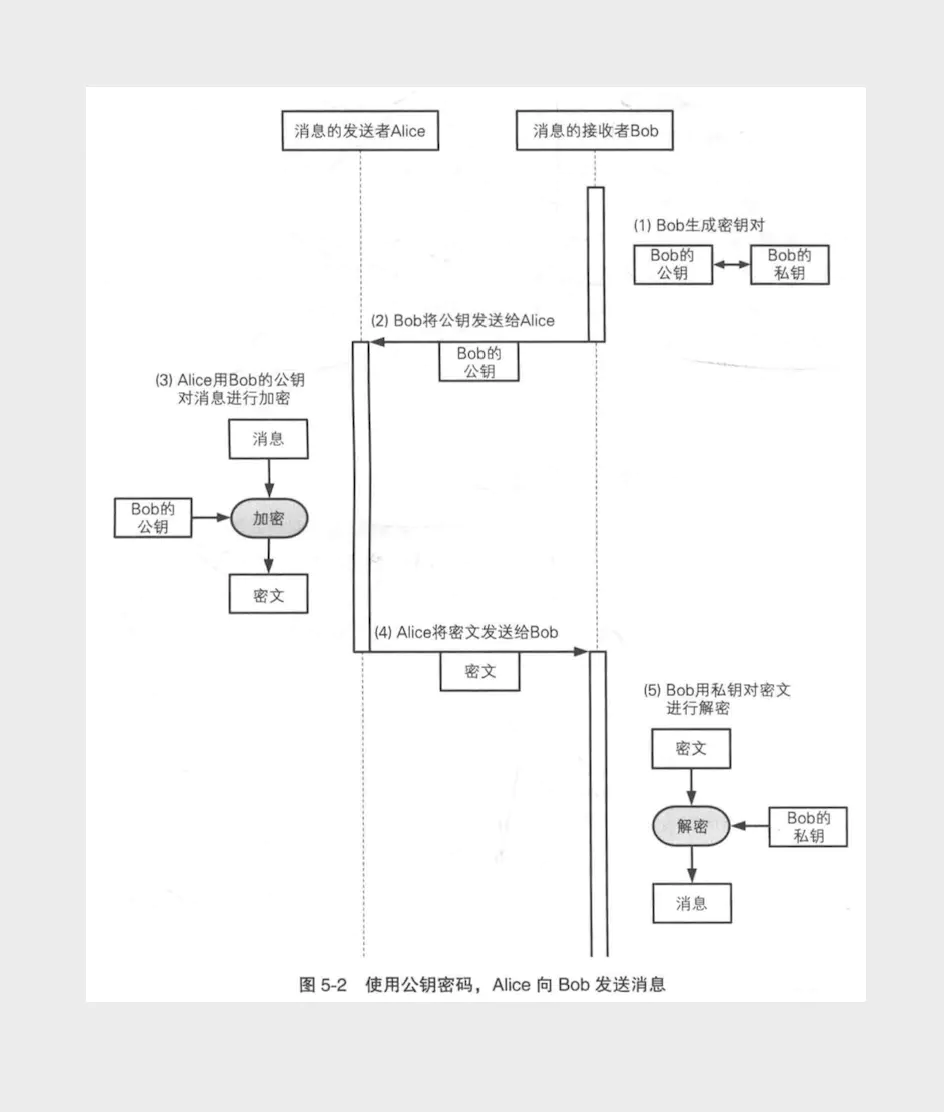
RSA(非对称加密算法)
从上面的例子中可以看出,JWT在加密解密的时候都用到了同一个密钥 “ robod666 ”,这将会带来一个弊端,如果被黑客知道了密钥的内容,那么他就可以去伪造Token了。所以为了安全,我们可以使用非对称加密算法RSA。
二、Spring Security第一个程序
Spring Security导入依赖就能生效了。
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId></dependency>
查看Controller层结果
@RestController
public class UserController {@AutowiredUserMapper userMapper;@RequestMapping("/user/select/{id}")public User list(@PathVariable("id") int id){return userMapper.queryUserById(id);}
}
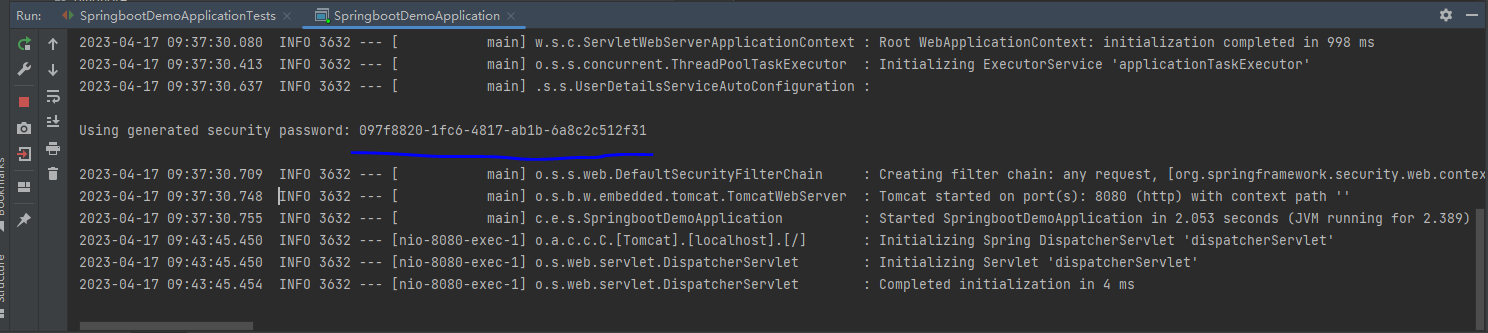
启动项目,默认账号是user,密码在输出控制信息中
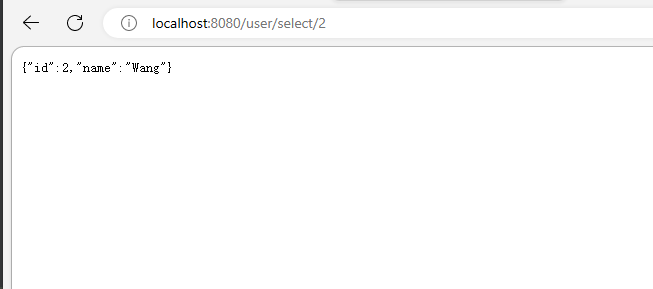
在浏览器中访问localhost:8080/user/selet/2,会自动跳转到localhost:8080/login
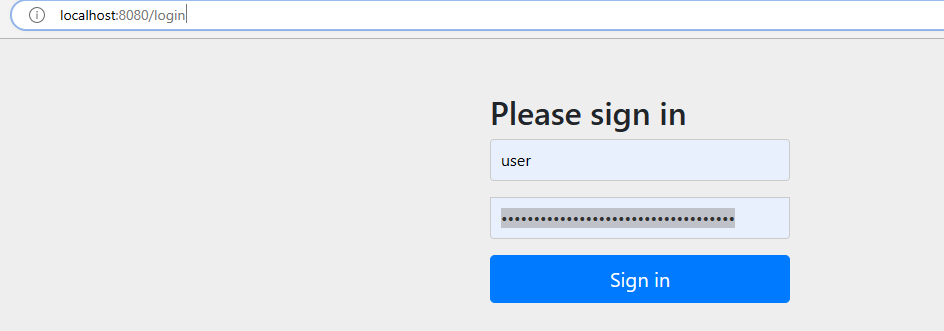
输入账号密码,跳转到我们原来请求的内容localhost:8080/user/selet/2
三、Spring Security没有生效
Spring Security在导入依赖之后就能生效,并且会使用一些默认配置。但是有时候导入依赖之后访问页面,也没有跳转到指定验证页面,这就是Spring Security没有生效。
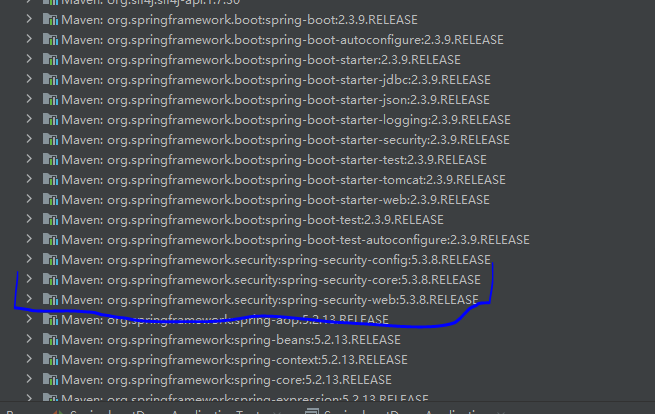
这是因为,你在pom.xml中导入了依赖包,等于告诉maven要导入Spring Security依赖,但是不等于已经导入了Spring Securtiy,因为maven可能还没来得及导入,你就已经启动项目了。我们可以通过查看External Libraries这里,看看Spring Security是否已经导入成功。
四、修改默认账号密码(appliction.yml)
在application.yml配置文件中修改默认账号密码
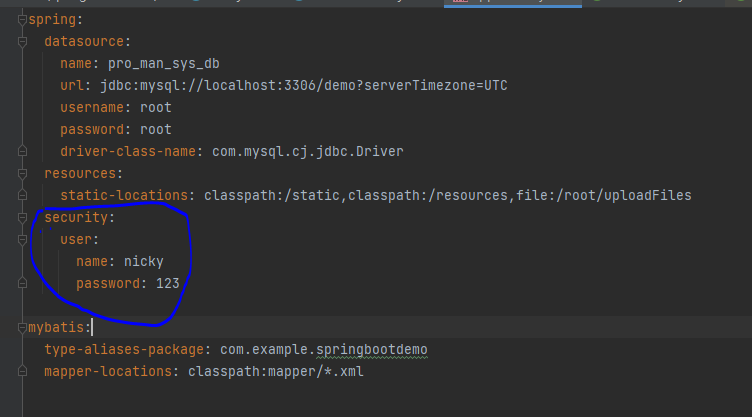
启动项目,在浏览器中访问localhost:8080/user/selet/2,会自动跳转到localhost:8080/login,账号是nicky,密码在123
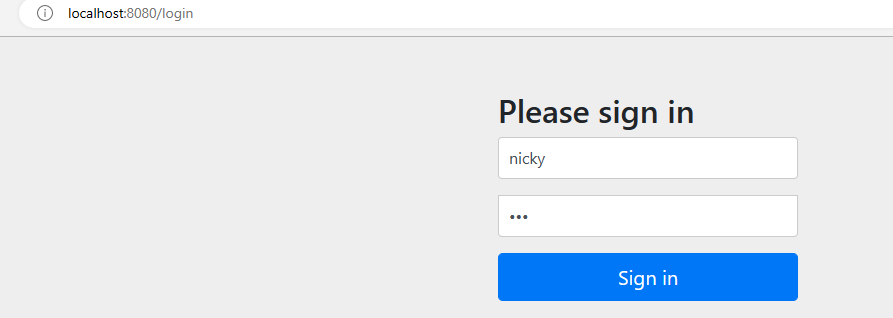
输入账号密码,跳转到我们原来请求的内容localhost:8080/user/selet/2

五、修改默认账号密码(配置类)
也可以新建Spring Security配置类,注意Spring Security5.2.1版本,配置密码要用BCryptPasswordEncoder加密,不过登录还是明文,Spring Security不同版本各有差别,详情配置还是参考官方文档
@Configuration // 设置为配置类,变成Spring Bean
public class SecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {@Overrideprotected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { //auth.inMemoryAuthentication()auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("nicky").password(bcryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456")).roles("admin").and().withUser("rocky").password(bcryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456")).roles("admin");}@Beanpublic PasswordEncoder bcryptPasswordEncoder() {return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();}
}
启动项目,在浏览器中访问localhost:8080/user/selet/2,会自动跳转到localhost:8080/login,账号是nicky,密码在123

输入账号密码,跳转到我们原来请求的内容localhost:8080/user/selet/2

六、Spring Security的三个configure方法
Spring Security通过继承WebSecurityConfigurationAdapter这个类,可以选择实现该类中的三个重载的configure方法
configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth):用来记录账号,密码,角色信息。
AuthenticationManagerBuilder allows public void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) {auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("user").password("password").roles("USER").and().withUser("admin").password("password").roles("ADMIN","USER");
}
configure(HttpSecurity http):(授权)配置 URL 访问权限,对应用户的权限
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {http//任何请求都必须经过身份验证.authorizeUrls().antMatchers("/admin/").hasRole("ADMIN").anyRequest().authenticated();
configure(WebSecurity):一般用于配置忽略掉的 URL 地址,一般用于js,css,图片等静态资源
public void configure(WebSecurity web) throws Exception {web//web.ignoring() 用来配置忽略掉的 URL 地址,一般用于静态文件.ignoring().antMatchers("/resources/");
}
七、Spring Security的三种身份的验证
1. 默认身份验证
在pom.xml文件映入SpringSecutrity依赖启动器,启动项目,访问文章列表页面时,出现默认的登录页,需要用默认用户名:user,密码源于控制台输出,也就是最基础的登录
2. 内存身份验证
自定义用户名和密码(用户名和密码是写在代码内,不好维护)
@Configuration // 设置为配置类,变成Spring Bean
public class SecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {@Overrideprotected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("nicky").password(bcryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456")).roles("admin").and().withUser("rocky").password(bcryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456")).roles("admin");}@Beanpublic PasswordEncoder bcryptPasswordEncoder() {return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();}@Overrideprotected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {http.headers().frameOptions().disable();//开启运行iframe嵌套页面//任何请求都必须经过身份验证http.authorizeRequests().anyRequest().authenticated();http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/vip/vip0/").hasRole("vip0").antMatchers("/vip/vip1/").hasRole("vip1").antMatchers("/vip/vip2/").hasRole("vip2").antMatchers("/vip/vip3/").hasRole("vip3");//开启表单验证http.formLogin().and().formLogin()//开启表单验证.loginPage("/toLogin")//跳转到自定义的登录页面.usernameParameter("name")//自定义表单的用户名的name,默认为username.passwordParameter("pwd")//自定义表单的密码的name,默认为password.loginProcessingUrl("/doLogin")//表单请求的地址,一般与form的action属性一致.successForwardUrl("/index")//登录成功后跳转的页面(重定向).failureForwardUrl("/toLogin")//登录失败后跳转的页面(重定向).and().logout()//开启注销功能.logoutSuccessUrl("/toLogin")//注销后跳转到哪一个页面.logoutUrl("/logout") // 配置注销登录请求URL为"/logout"(默认也就是 /logout).clearAuthentication(true) // 清除身份认证信息.invalidateHttpSession(true) //使Http会话无效.permitAll() // 允许访问登录表单、登录接口.and().csrf().disable(); // 关闭csrf}
}
3. 数据库方式校验
实现WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter类:将身份校验方式改变为数据库方式校验,即使用UserDetailsService
/*开启安全管理配置*/
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {@AutowiredUserDetailsServiceImpl userDetailsService;/*自定义身份认证*/@Overrideprotected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {/*1. 密码编译器*/BCryptPasswordEncoder encoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder();/*2.使用UserDetails进行身份认证*/auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService).passwordEncoder(encoder);}/*自定义用户权限*/@Overrideprotected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/").permitAll() // 表示放行“/”访问.antMatchers("/admin/").hasAuthority("admin") // 表示admin才能访问/admin/.antMatchers("/common/").hasAuthority("common") // 表示common可以访问/commom/.and().formLogin();}
}
实现UserDetailsService类:该类只有 loadUserByUsername 一个接口方法, 用于通过用户名获取用户数据. 返回 UserDetails 对象, 表示用户的核心信息 (用户名, 用户密码, 权限等信息).
注意:其实UserDetailsService就是一个Service层的类,没有大不了的,我们也可以用UserService继承UserDetailsService
@Service
public class UserDetailsServiceImpl implements UserDetailsService {@AutowiredUserMapper userMapper;@AutowiredAuthorityMapper authorityMapper;/*根据前端登录页面传入的用户名,查询出数据库对应的用户信息和用户权限,把用户信息和权限封装成UserDetails对象,交给SpringSecurity进行身份认证*/@Overridepublic UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String s) throws UsernameNotFoundException {BCryptPasswordEncoder encoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder();/*根据用户名查询用户信息*/User user = userMapper.selectUserByUserName(s);/*根据用户名查询权限信息*/List<Authority> authorities = authorityMapper.selectAuthorityByUserName(s);/*遍历封装用户权限*/List<SimpleGrantedAuthority> authorityList = new ArrayList<>();for (int i=0; i<authorities.size(); i++){authorityList.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority(authorities.get(i).getAuthority()));}// 如果用户不存在if(user!=null){/*将用户名、密码、用户权限封装成UserDetails对象*/UserDetails userDetails = new User(user.getUsername(),encoder.encode(user.getPassword()),authorityList);return userDetails;}else {throw new UsernameNotFoundException("用户不存在");}}
}
编写UserMapper类:这里仅仅编写了Mapper层逻辑,至于domain与数据库sql就不再赘述了
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {/*根据用户名去查询用户讯息*/
@Select("select * from t_user where username=#{username}")public TUser selectUserByUserName(String username);
}
@Mapper
public interface AuthorityMapper {/*根据用户名去查询用户权限*/@Select(" select a.* from t_user u,t_authority a,user_authority au where u.id=au.uid and a.id=au.aid and u.username=#{username}")
public List<Authority> selectAuthorityByUserName(String username);
}


