带头单向链表源码及相关练习

目录
移除链表元素
链表的中间节点
链表倒数第k个节点
合并两个有序链表
相交链表
环形链表
环形链表2
分割链表
回文链表
public class MySingleList {//内部类的使用class ListNode {public int val;public ListNode next;public ListNode(int val) {this.val = val;}}public ListNode head;//永远指向我的头节点public void createTree() {ListNode A = new ListNode(13);ListNode B = new ListNode(14);ListNode C = new ListNode(19);A.next = B;B.next = C;this.head = A;}public void show() {//定义一个引用变量//只有new的时候才是定义了一个节点ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {//因为最后一个地址是空System.out.println(cur.val + " ");cur = cur.next;}}public int size() {ListNode cur = head;int count = 0;while (cur != null) {count++;cur = cur.next;}return count;}public boolean contains(int key) {ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {//如果是引用类型呢?,用.equals()来比较if (cur.val == key) {return true;}cur = cur.next;}return false;}public void addVal(int index, int val) {//判断index的合法性if (index < 0 || index > size()) {throw new RuntimeException("越界了");}if (index == 0) {insertList(val);return;}if (index == size() - 1) {addTail(val);return;}ListNode node = new ListNode(val);ListNode cur = head;while (index - 1 != 0) {cur = cur.next;index--;}node.next = cur.next;cur.next = node;}public void remove(int key) {if (head == null) return;if (head.val == key) {head = head.next;}ListNode prev = searchPrev(key);if (prev == null) {return;}prev.next = prev.next.next;}public ListNode searchPrev(int key) {ListNode prev = head;while (prev != null) {if (prev.next.val == key) {return prev;} else {prev = prev.next;}}return null;}public void insertList(int val) {ListNode node = new ListNode(val);//才开始没有节点也行node.next = head;head = node;}//找index-1位置的节点public ListNode findIndex(int index) {ListNode cur = head;while (index - 1 != 0) {cur = cur.next;index--;}return cur;}public void addTail(int val) {ListNode node = new ListNode(val);ListNode cur = head;if (head == null) {//空指针异常head = node;return;}while (cur.next != null) {cur = cur.next;}cur.next = node;}public void delete(int val) {if (head == null) return;ListNode cur = head;while (cur.val != val) {}}public static void main(String[] args) {MySingleList m = new MySingleList();m.createTree();//System.out.println(m.size());// System.out.println(m.contains(14));// m.insertList(m.new ListNode(99));// m.addTail(100);// m.show();// m.addTail(11);m.addVal(1, 111);m.show();}public void clear() {}/ 要求遍历链表一遍,删除所有值为key的节点* 双指针* cur节点代表当前要删除节点,prev是要删除节点的上一个节点 /public void deleteAllKey(int key) {if (head == null) {return;}ListNode prev = head;ListNode cur = prev.next;while (cur != null) {//遍历完了if (cur.val == key) {prev.next = cur.next;cur = cur.next;//先别急着走prev,因为可能有连着好几个的要删除的值} else {prev = cur;cur = cur.next;}}if(head.val==key){head=head.next;}}//cur!=null,while循环结束走到最后一个节点的位置,//cur.next!=null,while循环结束走到最后一个节点后面的位置}203. 移除链表元素
移除链表元素
难度简单1217
给你一个链表的头节点
head和一个整数val,请你删除链表中所有满足Node.val == val的节点,并返回 新的头节点 。
示例 1:
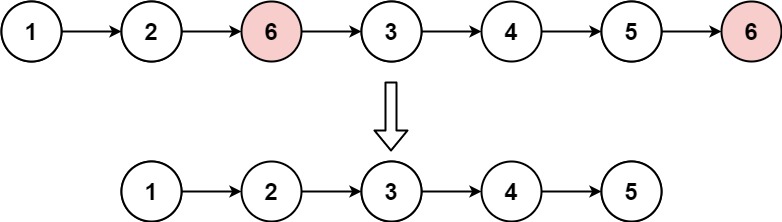
输入:head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6 输出:[1,2,3,4,5]示例 2:
输入:head = [], val = 1 输出:[]示例 3:
输入:head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7 输出:[]class Solution {public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {if (head == null) {return null;}ListNode prev = head;ListNode cur = prev.next;while (cur != null) {//遍历完了if (cur.val == val) {prev.next = cur.next;cur = cur.next;//先别急着走prev,因为可能有连着好几个的要删除的值} else {prev = cur;cur = cur.next;}}if(head.val==val){head=head.next;}return head;} }链表的中间节点
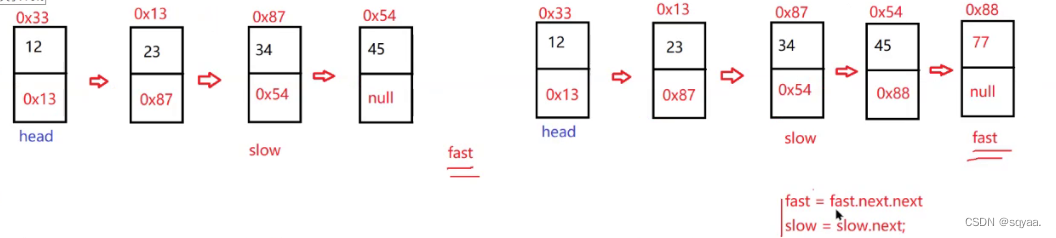
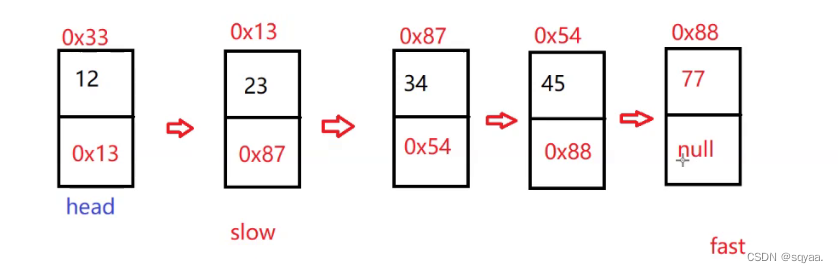
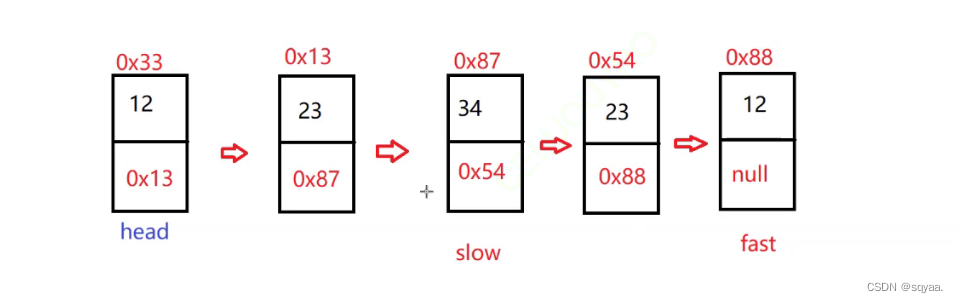
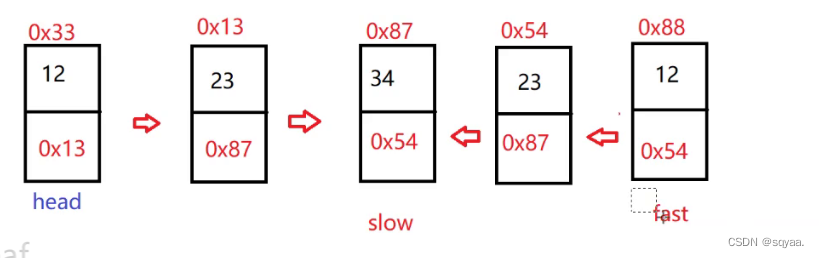
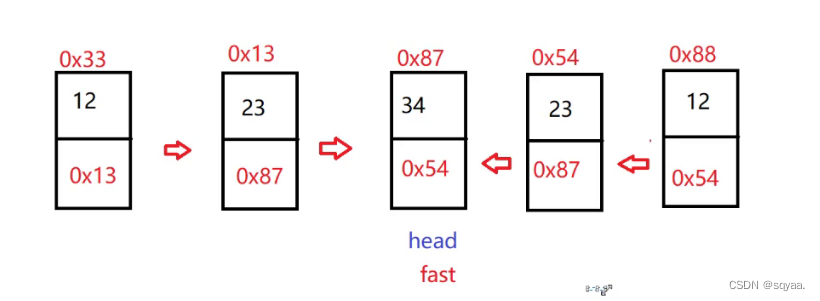
class Solution {public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {if(head==null) return null;if(head.next==null) return head;//使用快慢指针ListNode fast=head;ListNode slow=head;while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){//考虑这个判断的先后顺序//考虑是||还是&&//为了避免空指针异常slow=slow.next;fast=fast.next.next;}return slow;} }链表倒数第k个节点
输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个节点。为了符合大多数人的习惯,本题从1开始计数,即链表的尾节点是倒数第1个节点。
例如,一个链表有
6个节点,从头节点开始,它们的值依次是1、2、3、4、5、6。这个链表的倒数第3个节点是值为4的节点。
示例:
给定一个链表: 1->2->3->4->5, 和 k = 2.返回链表 4->5.
让fast先走k-1步数,然后俩指针同时走
class Solution {public ListNode getKthFromEnd(ListNode head, int k) {ListNode fast=head;ListNode slow=head;while(k!=0){fast=fast.next;k--;}while(fast!=null){fast=fast.next;slow=slow.next;}return slow;} }合并两个有序链表
/* Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/ class Solution {public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {// ListNode newHead=new ListNode();// ListNode tempH=newHead;// while(list1!=null&&list2!=null){// if(list2.val<list1.val){// tempH.next=list2;// tempH=tempH.next;// list2=list2.next;// }else{// tempH.next=list1;// tempH=tempH.next;// list2=list2.next;// }// }// if(list1!=null){// tempH.next=list1;// }// if(list2!=null){// tempH.next=list2;// }// return newHead.next;// 类似归并排序中的合并过程ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);ListNode cur = dummyHead;while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {if (l1.val < l2.val) {cur.next = l1;cur = cur.next;l1 = l1.next;} else {cur.next = l2;cur = cur.next;l2 = l2.next;}}// 任一为空,直接连接另一条链表if (l1 == null) {cur.next = l2;} else {cur.next = l1;}return dummyHead.next;} }相交链表
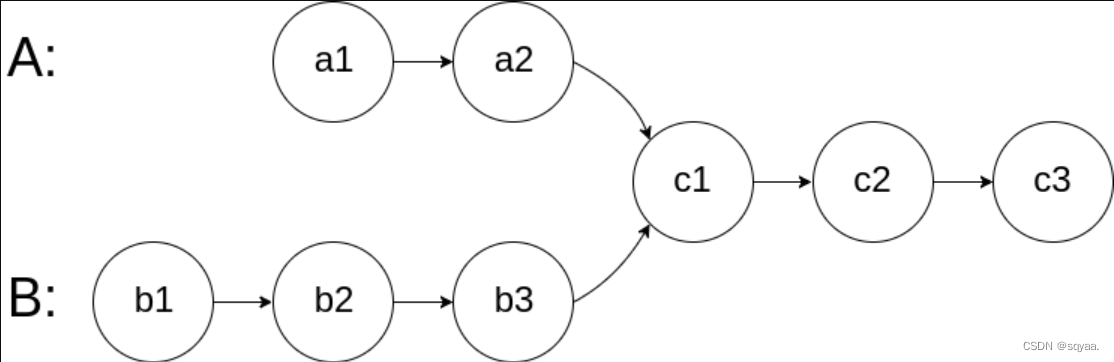
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表不存在相交节点,返回 null 。
图示两个链表在节点 c1 开始相交:
题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。
public class Solution {public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {//1.计算长度查ListNode plong=headA;ListNode pshort=headB;int lenA=0;int lenB=0;while(plong!=null){lenA++;plong=plong.next;}while(pshort!=null){lenB++;pshort=pshort.next;}plong=headA;pshort=headB;int len=lenA-lenB;//2.保证长链表是plong,短链表是pshortif(len<0){plong=headB;pshort=headA;len=lenB-lenA;}//3.长链表先走差值步while(len!=0){plong=plong.next;len--;}//4.一起走直到相遇while(plong!=pshort){plong=plong.next;pshort=pshort.next;}return plong;} }//如何说明相交//val值相同并且next值相同//从相交节点开始后,长度就是一样的了//从头往后走,长度差的地方就是相交节点之前//此时复杂度接近O(N)public class Solution {public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {if (headA == null || headB == null) {return null;}ListNode pA = headA, pB = headB;while (pA != pB) {pA = pA == null ? headB : pA.next;pB = pB == null ? headA : pB.next;}return pA;} }环形链表
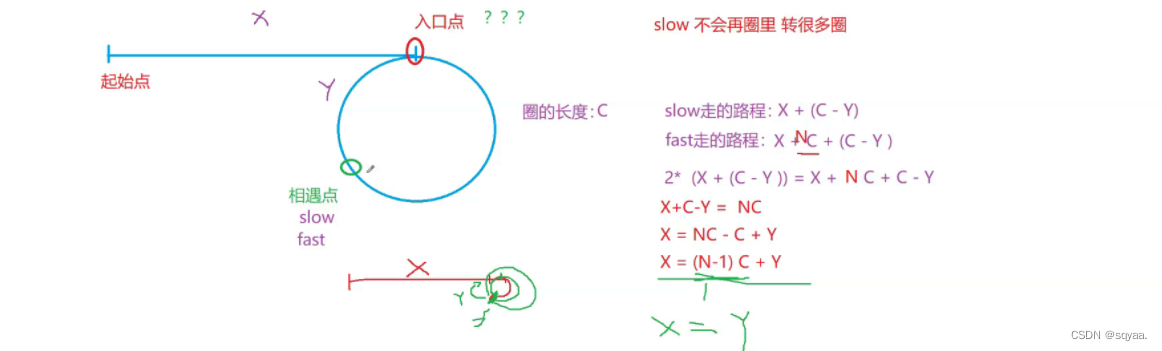
* 1.如果存在环,,那么当两个引用速度不一样时,一定会在环里相遇 * fast走2,slow走1 * 那为啥是这种速度差? * fast走3,slow走1,不可以!比如:环形链表中只有2个节点 * 上述情况就可能错过或者很晚相遇。 *2.扩充 如何找到入口点一个指针从相遇点开始走,另一个从头开始,遇见就是入口点 * */结论:转一圈的情况下,起始点到入口点和 相遇点到入口点的距离时一样的
so速度一样,路程一样,一个指针从相遇点开始走,另一个从头开始,遇见就是入口点
*/ public class Solution {public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {if(head==null) return false;ListNode fast=head;ListNode slow=head;while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){//避免空指针fast=fast.next.next;slow=slow.next;if(fast==slow){return true;}}return false;} }环形链表2
给定一个链表的头节点 head ,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
不允许修改 链表。
示例 1:
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:返回索引为 1 的链表节点
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
public class Solution {public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head){if(head==null) return null;ListNode fast=head;ListNode slow=head;while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){fast=fast.next.next;slow=slow.next;if(fast==slow){//说明找到相遇点了break;}}//万一根本就没有相遇的点呢//就是上一个循环的结束条件不是因为break//而是因为上面找不到,if(fast==null||fast.next==null){return null;}fast=head;while(fast!=slow){fast=fast.next;slow=slow.next;}//此时就相遇了//找到入口点了return slow;} }分割链表
class Solution {public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {ListNode as=null;ListNode ae=null;ListNode bs=null;ListNode be=null;ListNode cur=head;while(cur!=null){if(cur.val<x){if(bs==null){bs=cur;be=cur;}else{be.next=cur;be=cur;}}else if(cur.val>=x){if(as==null){as=cur;ae=cur;}else{as.next=cur;ae=cur;}}cur=cur.next;}//考虑两个段都有数据码if(bs==null){return as;}be.next=as;if(as!=null){ae.next=null;}return bs;} }回文链表
对于奇数个节点的链表,1.先找中间节点,2.反转中间节点后面的链表,3.两指针分别从后从前遍历直到两者相遇。
class Solution {public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {if(head==null) return true;//1.先找中间节点ListNode fast=head;ListNode slow=head;while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){fast=fast.next.next;slow=slow.next;}//此时slow就在中间节点了//2.翻转中间节点后的节点ListNode cur=slow.next;while(cur!=null){//结束后cur为空,也就是最后一个节点的后一个位置ListNode curNext=cur.next;cur.next=slow;slow=cur;cur=curNext;}//翻转完后slow再最后一个节点了//判断是否是回文//考虑奇数偶数,奇数的fast指针刚好走到最后一个节点,但是偶数的fast指针走到最后一个节点的后一个while(head!=slow){if(head.val!=slow.val){return false;}//专门针对偶数再写一个回文if(head.next==slow){return true;}head=head.next;slow=slow.next;}return true;} }
public class SingleLinkedList{static class ListNode {public int val;//数值域public ListNode next;//存储下一个节点的地址public ListNode(int val) {this.val = val;}}public ListNode head;//代表单链表的头结点的引用/* 这里只是简单的进行,链表的构造。*/public void createList() {ListNode listNode1 = new ListNode(12);ListNode listNode2 = new ListNode(23);ListNode listNode3 = new ListNode(34);ListNode listNode4 = new ListNode(45);ListNode listNode5 = new ListNode(56);listNode1.next = listNode2;listNode2.next = listNode3;listNode3.next = listNode4;listNode4.next = listNode5;this.head = listNode1;}public void display() {ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {System.out.print(cur.val+" ");cur = cur.next;}System.out.println();}/* 从指定的节点开始答应* @param newHead*/public void display(ListNode newHead) {ListNode cur = newHead;while (cur != null) {System.out.print(cur.val+" ");cur = cur.next;}System.out.println();}/* 头插法* OaddLast*/public void addFirst(int data){ListNode node = new ListNode(data);/*if(this.head == null) {this.head = node;}else {node.next = this.head;this.head = node;}*/node.next = this.head;this.head = node;}//尾插法 O(n)public void addLast(int data) {ListNode node = new ListNode(data);if(head == null) {head = node;}else {ListNode cur = head;while (cur.next != null) {cur = cur.next;}//cur.next == null;cur.next = node;}}/* 任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标* 指定位置插入*/public void addIndex(int index,int data) throws MySingleListIndexOutOfException{checkIndexAdd(index);if(index == 0) {addFirst(data);return;}if(index == size()) {addLast(data);return;}ListNode node = new ListNode(data);ListNode cur = findIndexSubOne(index);node.next = cur.next;cur.next = node;}/* 找到index-1位置的节点* @param index* @return 该节点的地址*/private ListNode findIndexSubOne(int index) {ListNode cur = this.head;while (index-1 != 0) {cur = cur.next;index--;}return cur;}private void checkIndexAdd(int index) {if(index < 0 || index > size()) {throw new MySingleListIndexOutOfException("任意位置插入的时候,index不合法!");}}//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中 314public boolean contains(int key) {//head == nullListNode cur = this.head;//cur != null 说明 没有遍历完 链表while (cur != null) {if(cur.val == key) {return true;}cur = cur.next;}return false;}//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点public void remove(int key){if(this.head == null) {System.out.println("此时链表为空,不能进行删除!");return;}if(this.head.val == key) {//判断 第一个节点是不是等于我要删除的节点this.head = this.head.next;return;}ListNode cur = this.head;while (cur.next != null) {if(cur.next.val == key) {//进行删除了ListNode del = cur.next;cur.next = del.next;return;}cur = cur.next;}}//删除所有值为key的节点public void removeAllKey(int key){if(this.head == null) {return;}ListNode cur = this.head.next;ListNode prev = this.head;while (cur != null) {if(cur.val == key) {prev.next = cur.next;cur = cur.next;}else {prev = cur;cur = cur.next;}}//单独处理了头节点if(this.head.val == key) {head = head.next;}}//得到单链表的长度public int size(){int count = 0;ListNode cur = this.head;while (cur != null) {count++;cur = cur.next;}return count;}/* 当我们 执行clear这个函数的时候,会将这个链表当中的所有的节点回收*/public void clear(){//this.head = null;//这种做法 比较粗暴!ListNode cur = this.head;ListNode curNext = null;while (cur != null) {curNext = cur.next;cur.next = null;cur = curNext;}head = null;}
}