2023-04-15 算法面试中常见的链表问题

2023-04-15 算法面试中常见的链表问题
本章的两个基础类如下
链表的节点类。toString()在debug时实时查看链表很有用
/ @Description : 链表的节点* @author : 梁山广(Liang Shan Guang)* @date : 2020/1/17 22:13* @email : liangshanguang2@gmail.com*/
package Chapter05LinkedList;public class ListNode {public int val;public ListNode next;public ListNode(int x) {val = x;}@Overridepublic String toString() {StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();ListNode cur = this;while (cur != null) {sb.append(cur.val).append(" -> ");cur = cur.next;}sb.append("NULL");return sb.toString();}
}
链表的显示工具类。create用于从数据创建链表,show用于把head作为头结点的链表表示成一个字符串的形式
/ @Description : 链表的显示工具类* @author : 梁山广(Liang Shan Guang)* @date : 2020/1/17 22:14* @email : liangshanguang2@gmail.com*/
package Chapter05LinkedList;class LinkedListTool {/* 根据数组创建链表 @param nums 数组* @return 创建的链表的头节点*/public static ListNode create(int[] nums) {if (nums.length == 0) {return null;}ListNode head = new ListNode(nums[0]);ListNode curr = head;for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {curr.next = new ListNode(nums[i]);curr = curr.next;}return head;}public static void show(ListNode head) {ListNode curr = head;while (curr != null) {System.out.print(curr.val + " -> ");curr = curr.next;}System.out.println("NULL");}
}
1~2 题目206 反转列表
反转一个单链表。示例:输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
代码实现分两步:
- 1.初始化
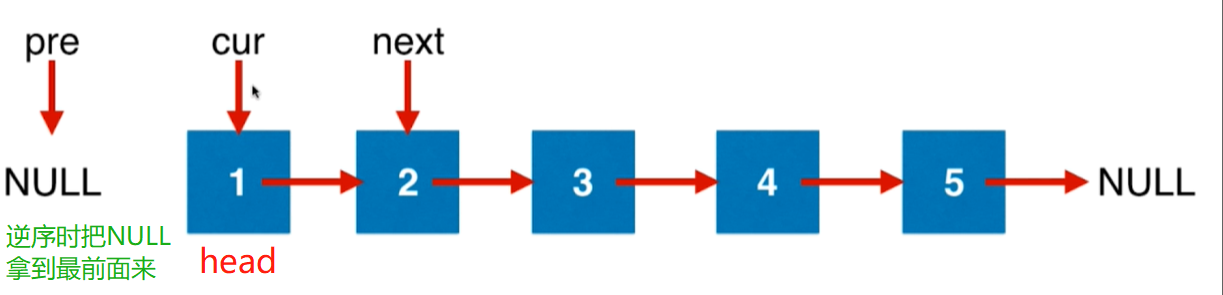
- 2.指针移动
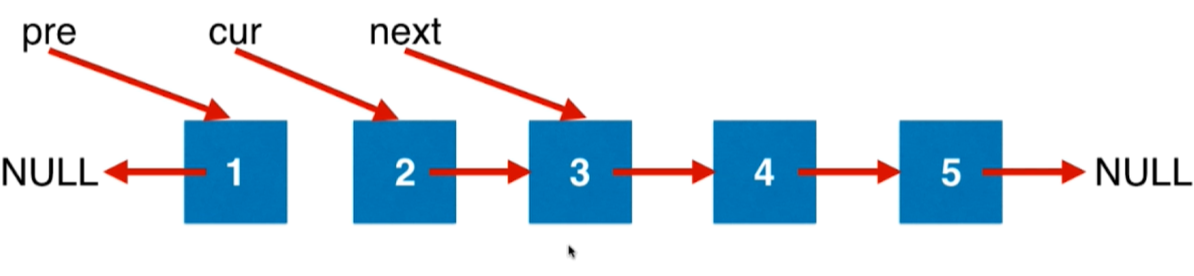
public class Solution {public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {// 当前节点的上一个节点,初始化为null,是因为所有所有的链表最后一个元素都可以看为nullListNode prev = null;// 当前节点ListNode curr = head;// 当前节点的下一个节点while (curr != null) {// 当当前节点的下一个节点不为空时ListNode next = curr.next;// 翻转当前节点,指向上一个节点curr.next = prev;// 上一个节点后移动一位prev = curr;// 当前节点后移动一位curr = next;}// 遍历到最后,pre指向了最后一个节点return prev;}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] nums = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};ListNode head = LinkedListTool.create(nums);LinkedListTool.show(head);ListNode headReverse = new Solution().reverseList(head);LinkedListTool.show(headReverse);}
}/* 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> NULL* 5 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> NULL*/
类似的题目还有92. 反转部分链表 II
反转从位置 m 到 n 的链表。请使用一趟扫描完成反转。说明:
1 ≤ m ≤ n ≤ 链表长度。示例:输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, m = 2, n = 4
输出: 1->4->3->2->5->NULL
- 第一步:找到待反转节点的前一个节点。
- 第二步:反转m到n这部分。
- 第三步:将反转的起点的next指向反转的后面一部分。
- 第四步:将第一步找到的节点指向反转以后的头节点。
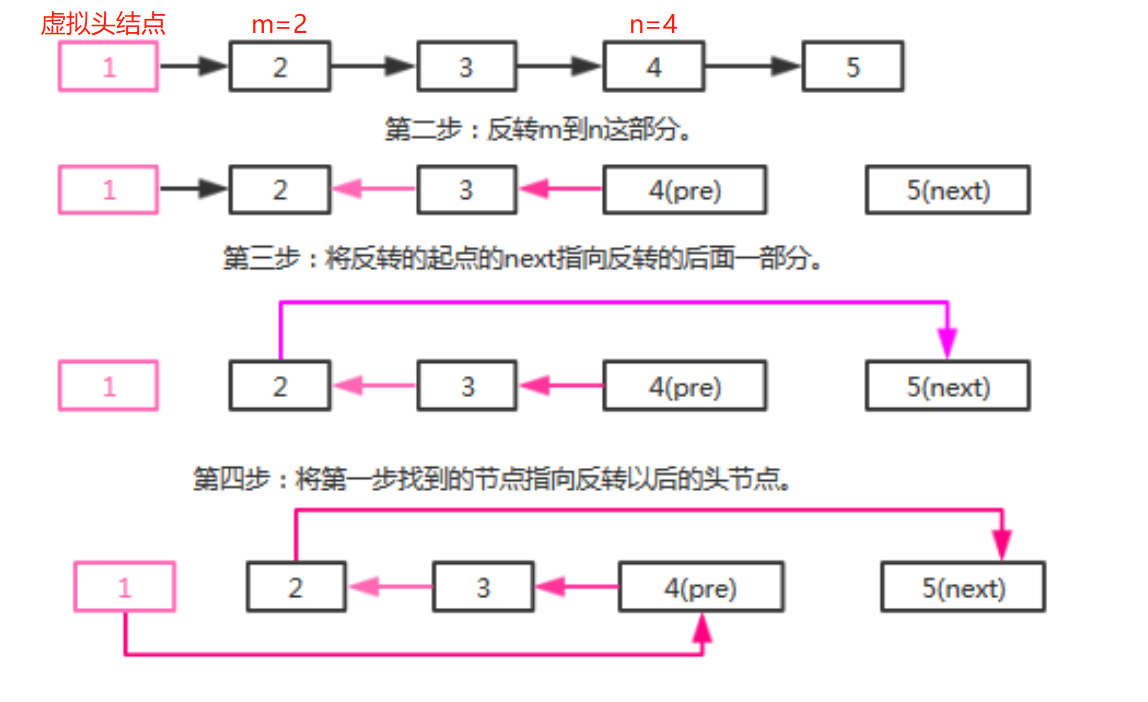
/ @Description : 反转链表的m~n的链表* @author : 梁山广(Liang Shan Guang)* @date : 2020/1/17 23:20* @email : liangshanguang2@gmail.com*/
package Chapter05LinkedList.LeetCode92ReverseLinkedListPart;import Chapter05LinkedList.LinkedListTool;
import Chapter05LinkedList.ListNode;class Solution {public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) {// 创建虚拟头结点,防止一些null导致的问题ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);dummyHead.next = head;ListNode cur = dummyHead;for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {// 找到了m的上一个节点cur = cur.next;}// node.next就是要翻转的起点,mHead表示开始翻转的起点ListNode mHead = cur.next;ListNode next = null;ListNode pre = null;// 翻转m到n这一段,起点是mHead,参考206题for (int i = m; i <= n; i++) {next = mHead.next;mHead.next = pre;pre = mHead;mHead = next;}// m位置的节点指向n位置的下一个节点cur.next.next = next;// m前一个节点指向n位置处的节点cur.next = pre;// 返回虚拟头结点的下一个节点即新的头结点return dummyHead.next;}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] nums = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};ListNode head = LinkedListTool.create(nums);LinkedListTool.show(head);// 返回新链表的deadListNode headNew = new Solution().reverseBetween(head, 2, 4);LinkedListTool.show(headNew);}
}
/* 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> NULL* 1 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 5 -> NULL*/
还有83、86、328、2、445号问题也是链表相关的问题
83.删除排序链表中的重复元素
class Solution {public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {if (cur.next != null && cur.val == cur.next.val) {cur.next = cur.next.next;}else {cur = cur.next;}}return head;}/* 1->1->2 ==> 1->2* [] -> []* [1,1,1,1] ==> [1]* {1,1,2,3,3} ==> [1, 2, 3]*/public static void main(String[] args) {int[] nums = {1,1,2,3,3};ListNode head = LinkedListTool.create(nums);LinkedListTool.show(head);ListNode newHead = new Solution().deleteDuplicates(head);LinkedListTool.show(head);}
}
86.分隔链表
核心思想是把小于x的节点和大于等于x的节点拆成两个链表,最后把后者连接到前者形成一条新的链表就是满足题目的链表
// 核心思想是把小于x的节点和大于等于x的节点拆成两个链表,最后把后者连接到前者形成一条新的链表就是满足题目的链表
class Solution {public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {// 存储所有大于等于x的节点的链表的虚拟头结点ListNode bigHead = new ListNode(0);// 存储所有小于x的节点的链表的虚拟头结点ListNode smallHead = new ListNode(0);// 上面两个链表的指针,用于插入元素ListNode big = bigHead;ListNode small = smallHead;while(head != null){if(head.val < x){// 插入节点到小元素链表small.next = head;// 指针往后移动small = small.next;}else {// 插入节点到大元素链表big.next = head;big = big.next;}head = head.next;}// 把大元素连接到小元素链表后面small.next = bigHead.next;// 大元素链表的尾部要清空下,防止还连着些乱七八糟的节点big.next = null;// 返回小元素链表的头结点,即虚拟头结点的下一个节点return smallHead.next;}
}
328.奇偶链表
和上面的第86号问题非常类似,区别在于这里是按照奇数编号和偶数编号分成了两个链表,除了if逻辑不通,其他地方完全相同
/ @Description : 新建两个不同的链表,遍历一遍原链表后,分别存储奇数编号节点和偶数编号节点,最后把奇数链表连接到偶数链表即可* 和LeetCode第86号问题按照边界分成两个链表的思路基本一致* @author : 梁山广(Liang Shan Guang)* @date : 2020/1/18 18:24* @email : liangshanguang2@gmail.com*/
package Chapter05LinkedList.LeetCode382OddEvenLinkedList;import Chapter05LinkedList.ListNode;class Solution {public ListNode oddEvenList(ListNode head) {// 奇数链表的虚拟头结点ListNode oddHead = new ListNode(0);// 偶数链表的虚拟头结点ListNode evenHead = new ListNode(0);// 上面两个链表的移动指针ListNode odd = oddHead;ListNode even = evenHead;int index = 0;while(head != null){if(index % 2 == 1){ // 奇数编号节点// 插入节点到奇数链表odd.next = head;// 移动指针往后一位odd = odd.next;}else { // 偶数编号节点even.next = head;even = even.next;}head = head.next;index++;}// 奇数链表连接到偶数链表后面even.next = oddHead.next;// 奇数链表的最后清空下,防止连接些乱七八糟的节点odd.next = null;return evenHead.next;}
}
2.两数相加
涉及到大数相加~~需要用到BigDecimal
/* Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }* }*/
import java.math.BigDecimal;
class Solution {private String add2Sum(String s1, String s2) {BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(s1);BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(s2);return b1.add(b2).toString();}/* 两个数相加,要考虑大数相加的情况,所以数字都以字符串的形式来存储*/public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {// 用字符串来存储两个数StringBuilder num1 = new StringBuilder();StringBuilder num2 = new StringBuilder();while (l1 != null) {num1.append(l1.val);l1 = l1.next;}while (l2 != null) {num2.append(l2.val);l2 = l2.next;}String sum = add2Sum(num1.reverse().toString(), num2.reverse().toString());ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);ListNode cur = dummyHead;for (int i = sum.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {cur.next = new ListNode(Integer.parseInt(sum.charAt(i) + ""));cur = cur.next;}return dummyHead.next;}
}
445.两数相加 II
和上面的第2题类似,甚至更简单点,因为不用再逆序了
import java.math.BigDecimal;
class Solution {private String add2Sum(String s1, String s2) {BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal(s1);BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal(s2);return b1.add(b2).toString();}/* 两个数相加,要考虑大数相加的情况,所以数字都以字符串的形式来存储*/public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {// 用字符串来存储两个数StringBuilder num1 = new StringBuilder();StringBuilder num2 = new StringBuilder();while (l1 != null) {num1.append(l1.val);l1 = l1.next;}while (l2 != null) {num2.append(l2.val);l2 = l2.next;}String sum = add2Sum(num1.toString(), num2.toString());ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);ListNode cur = dummyHead;for (int i = 0; i < sum.length(); i++) {cur.next = new ListNode(Integer.parseInt(sum.charAt(i) + ""));cur = cur.next;}return dummyHead.next;}
}
3 设立链表的虚拟头节点DummyHead可以大大简化代码逻辑
LeetCode203号问题 Remove Linked List Elements
删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点。示例:输入: 1->2->6->3->4->5->6, val = 6
输出: 1->2->3->4->5
不设置虚拟头结点时,需要对头结点作各种异常判断
package Chapter05LinkedList.RemoveElements;/ 反转一个单链表。 示例: 输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL* 输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL @note : 创建pre、cur和next三个节点指针,不断移动节点来达到目的* @author : l00379880 梁山广* @version : V1.0 at 2019/8/21 15:23*/
public class Solution {public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {// 每次都要更新headwhile (head != null && head.val == val) {// 头结点的val就是想找的val,那么就要删除头节点head = head.next;}// 最后的head仍然可能为空if (head == null) {// 需要对头结点判空return null;}ListNode curr = head;while (curr.next != null) {if (curr.next.val == val) {// 把current.next这个节点释放掉curr.next = curr.next.next;} else {// 没有找到符合的节点就继续向下找curr = curr.next;}}return head;}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] nums = {1, 2, 3, 6, 4, 5, 6};int val = 6;ListNode head = LinkedListTool.create(nums);LinkedListTool.show(head);ListNode headRemove = new Solution().removeElements(head, val);LinkedListTool.show(headRemove);}
}/* 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> NULL* 5 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> NULL*/
引入虚拟头结点后,算法就简化多了
虚拟头节点,可以避免head为空的各种情况,代码逻辑可以大大简化
class Solution {public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {// 虚拟头节点,可以避免head为空的各种情况,代码逻辑可以大大简化 ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);dummyHead.next = head;// 所有节点的操作都统一了ListNode curr = dummyHead;while (curr.next != null) {if (curr.next.val == val) {// 把current.next这个节点释放掉curr.next = curr.next.next;} else {// 没有找到符合的节点就继续向下找curr = curr.next;}}// 虚拟头结点后面的点才是真正的头结点return dummyHead.next;}
}
更简化的实现:递归
class Solution {public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {if (head == null) {return null;}head.next = removeElements(head.next, val);// head节点要删除就直接跳过head节点,否则就返回原来的return head.val == val ? head.next : head;}
}
本节的练习题:82、21
82.删除排序链表中的重复元素 II
注意这里是要删除
所有相等的元素~~
/ @Description : 删除所有重复的节点* @author : 梁山广(Liang Shan Guang)* @date : 2020/1/18 20:21* @email : liangshanguang2@gmail.com*/
package Chapter05LinkedList.LeetCode82RemoveDuplicatesII;import Chapter05LinkedList.LinkedListTool;
import Chapter05LinkedList.ListNode;class Solution {public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {if (head == null) {return null;}ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);dummyHead.next = head;ListNode cur = dummyHead;while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null) {if (cur.next.val == cur.next.next.val) {// 重复元素的起点ListNode del = cur.next;while (del.next != null && del.val == del.next.val) {del = del.next;}// while退出时,del走到了最后一个重复元素的位置,在这里设置下cur.next = del.next;} else {cur = cur.next;}}return dummyHead.next;}/* 特殊用例:* [] ==> []* [1] ==> [1]* [1, 1] ==> [] 这个是 while (cur.next!=null)的来源* * [1,2,3,3,4,4,5] ==> [1, 2, 5]*/public static void main(String[] args) {int[] nums = {1, 1};ListNode head = LinkedListTool.create(nums);ListNode newHead = new Solution().deleteDuplicates(head);LinkedListTool.show(newHead);}
}
21.合并两个有序链表
创建个新链表,一次比较存储两个链表的元素即可
class Solution {public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {// 合并后的链表ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);// 链表的移动指针ListNode cur = dummyHead;while(l1 != null && l2 != null){if(l1.val < l2.val){cur.next = l1;l1 = l1.next;}else {cur.next = l2;l2 = l2.next;}cur = cur.next;}// 一个链表遍历完了另一个可能还有元素没遍历,把还没遍历完的链表直接挂到cur后面即可if(l1 == null){cur.next = l2;}else{cur.next = l1;}return dummyHead.next;}
}
4 第24号问题:Swap Nodes in Pairs
给定一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后的链表。你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
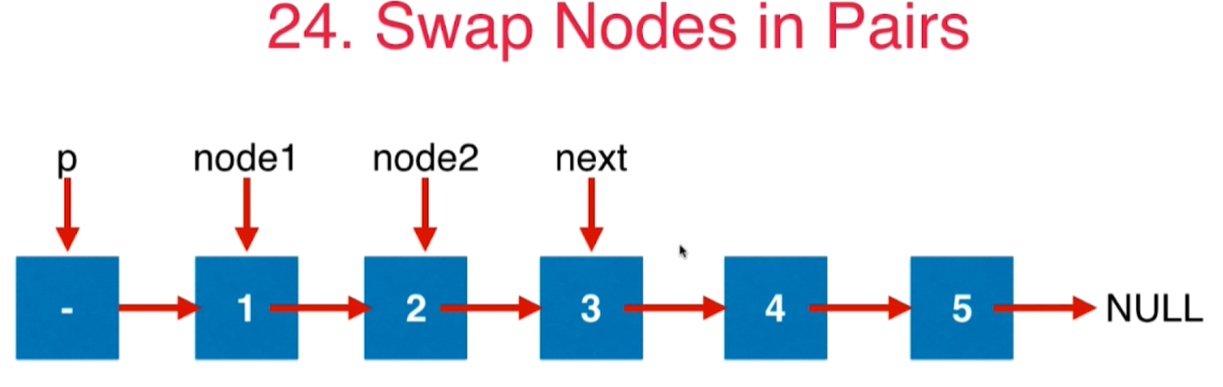
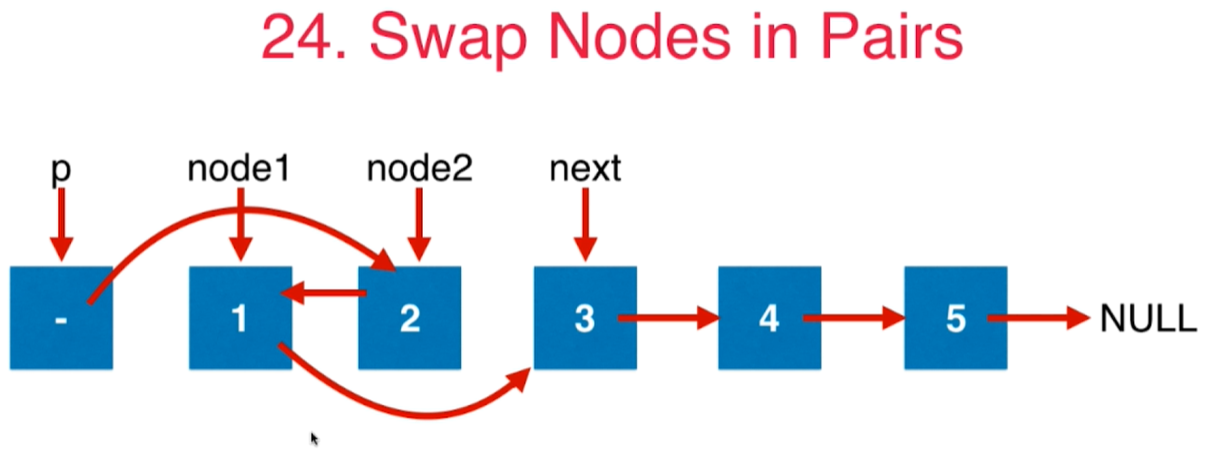
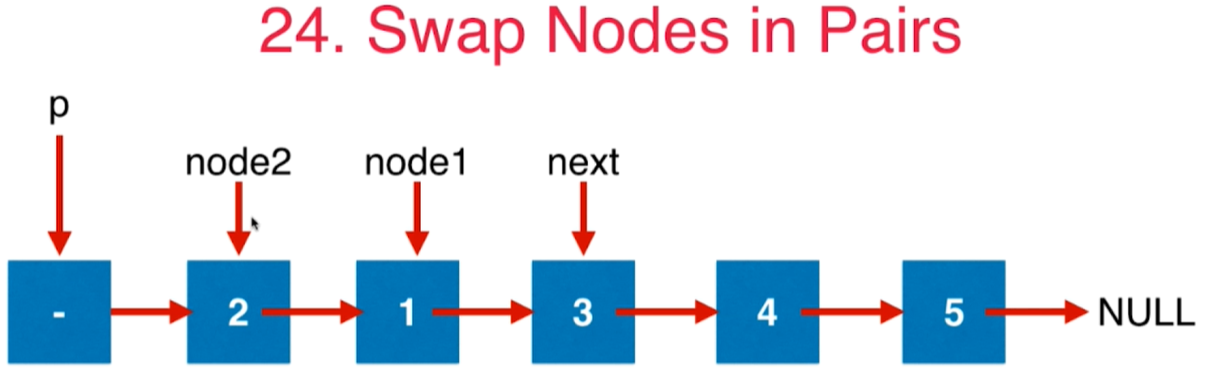
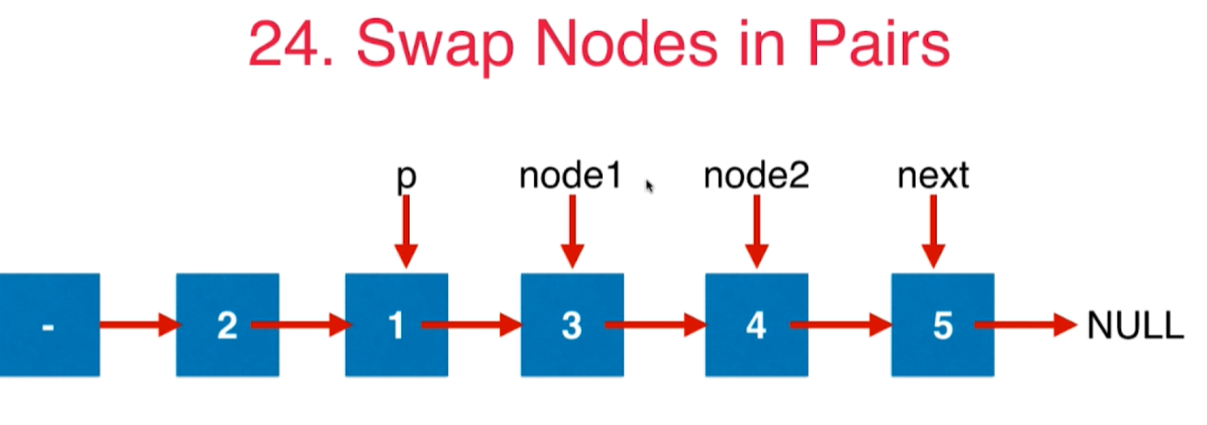
class Solution {public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {// 至少要有两个点,否则直接返回if(head == null || head.next == null){return head;}ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);dummyHead.next = head;// 正在挪动的点对的前面那个元素ListNode pre = dummyHead;while(pre.next!= null && pre.next.next != null){// 更新node1和node2ListNode node1 = pre.next;ListNode node2 = pre.next.next;// 旋转两个点pre.next = node2;node1.next = node2.next;node2.next = node1;// p变成交换后靠后的那个元素pre = node1;}return dummyHead.next;}
}
LeetCode上面类似的题目:25、147、148
25.K个一组翻转链表
困难级别的题目,实际很简单,利用下92题_翻转部分列表的函数即可
/* Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }* }*/
class Solution {/* 参考 92. 反转部分链表 II,把第m个元素到第n个元素及之间的元素逆序*/public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) {// 创建虚拟头结点,防止一些null导致的问题ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);dummyHead.next = head;ListNode cur = dummyHead;for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {// 找到了m的上一个节点cur = cur.next;}// node.next就是要翻转的起点,mHead表示开始翻转的起点ListNode mHead = cur.next;ListNode next = null;ListNode pre = null;// 翻转m到n这一段,起点是mHead,参考206题for (int i = m; i <= n; i++) {next = mHead.next;mHead.next = pre;pre = mHead;mHead = next;}// m位置的节点指向n位置的下一个节点cur.next.next = next;// m前一个节点指向n位置处的节点cur.next = pre;// 返回虚拟头结点的下一个节点即新的头结点return dummyHead.next;}public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {if(head == null){return null;}// 链表节点的个数int len = 1;ListNode cur = head;while (cur.next != null) {cur = cur.next;len++;}// 累计要进行多少轮翻转int cnt = len / k;for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {int m = 1 + k * i;int n = 1 + k * (i + 1);head = reverseBetween(head, m, n - 1);}return head;}
}
147.对链表进行插入排序
class Solution {public ListNode insertionSortList(ListNode head) {// 初始化虚拟头结点为最小节点ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(Integer.MIN_VALUE);dummyHead.next = head;ListNode cur = dummyHead;while (cur.next != null) {// pre记录需要插入位置的前面的节点ListNode pre = dummyHead;boolean swap = false;// 遍历cur之前的节点,找到cur所指的节点应该插入的位置while (pre != cur) {if (pre.next.val > cur.next.val) {// 存储要进行插入的节点ListNode tmp = cur.next;// 移除cur.next节点cur.next = cur.next.next;// 下面3行是把cur.next移动到合适位置ListNode tmp2 = pre.next;pre.next = tmp;tmp.next = tmp2;// 是否经过了元素插入swap = true;// 插入完毕,提前退出break;}pre = pre.next;}if (!swap) {// 如果没有经过元素置换,cur是不需要移动cur = cur.next;}}return dummyHead.next;}
}
148.排序链表
直接用上一题的代码即可
class Solution {// 直接用147的插入排序public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {// 初始化虚拟头结点为最小节点ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(Integer.MIN_VALUE);dummyHead.next = head;ListNode cur = dummyHead;while (cur.next != null) {// pre记录需要插入位置的前面的节点ListNode pre = dummyHead;boolean swap = false;// 遍历cur之前的节点,找到cur所指的节点应该插入的位置while (pre != cur) {if (pre.next.val > cur.next.val) {// 存储要进行插入的节点ListNode tmp = cur.next;// 移除cur.next节点cur.next = cur.next.next;// 下面3行是把cur.next移动到合适位置ListNode tmp2 = pre.next;pre.next = tmp;tmp.next = tmp2;// 是否经过了元素插入swap = true;// 插入完毕,提前退出break;}pre = pre.next;}if (!swap) {// 如果没有经过元素置换,cur是不需要移动cur = cur.next;}}return dummyHead.next;}
}
5 LeetCode237:删除链表中的节点
只给出了当前节点,可以通过把当前节点的值改成当前节点的下一个节点的值,然后删除下一个节点即可
删除链表中指定节点步骤:
- 1.将该节点下一个节点的值复制给当前节点。
- 2.删除该节点的下一个节点
class Solution {public void deleteNode(ListNode node) {// 相当于删除当前节点,因为不知道当前节点的上一个节点,所以把当前节点的下一个节点的val复制到当前节点并释放下一个节点即可node.val = node.next.val;node.next = node.next.next;}
}
6 双指针法:LeetCode第19号问题:删除链表的倒数第N个节点
一般的解法:遍历两遍

更优的算法:遍历一遍
使用间距为n的两个点p和q从起始点开始往后移动,当q到达最后一个节点时,p所在的节点就是导数第n个节点
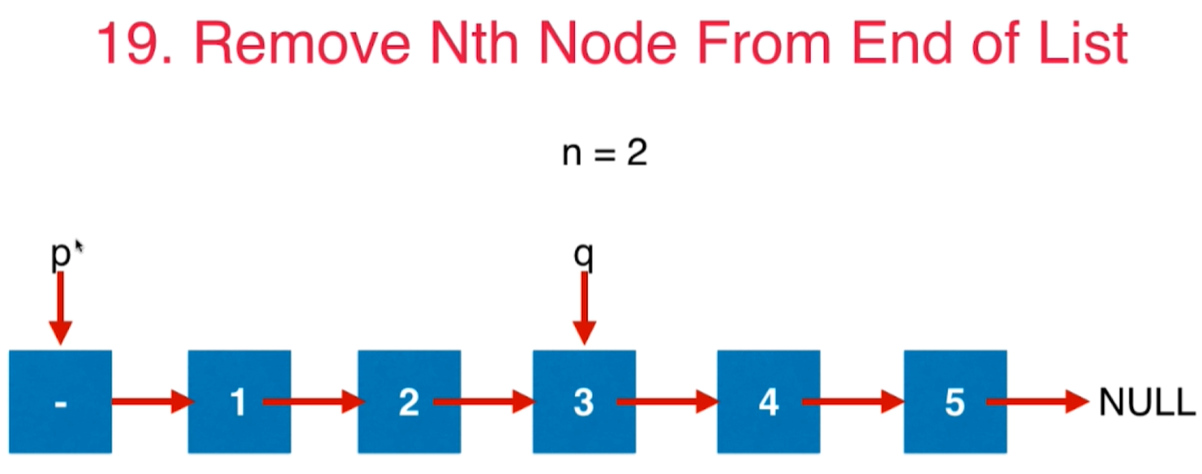
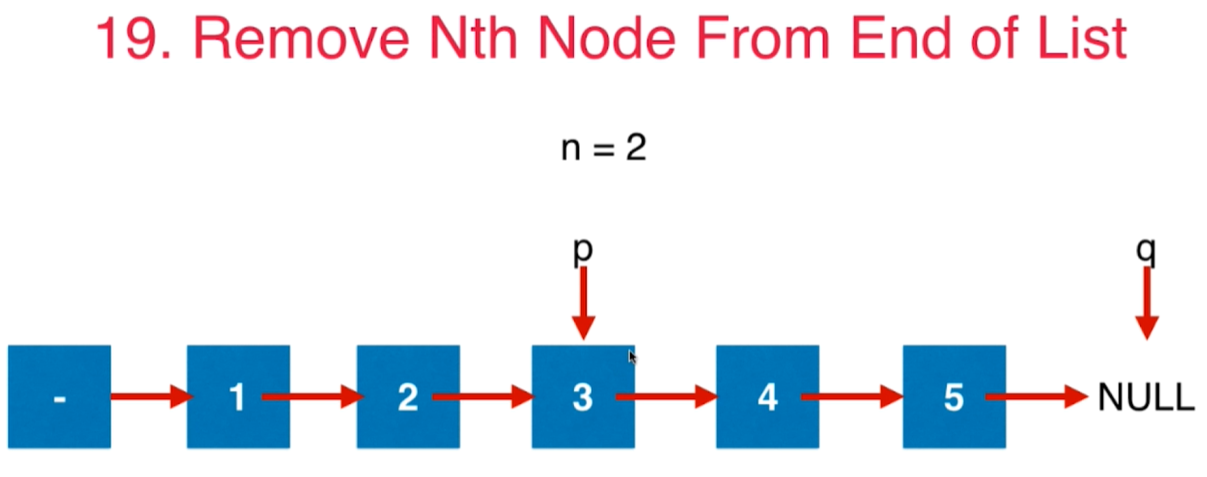
class Solution {public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);dummyHead.next = head;// p和q初始化为dummyHead可以防止很多null的异常ListNode p = dummyHead;ListNode q = dummyHead;for(int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++){// q移动到和p间距为n的地方q = q.next;}// p和q一直往后移动直到q移动到链表结尾while(q != null){p = p.next;q = q.next;}// q到达null了,此时p就是要删除的节点的上一个节点p.next = p.next.next;return dummyHead.next;}
}
双指针法的其他题目:61、143、234
61.旋转链表
class Solution {public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) {if (head == null || k == 0) {return head;}ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);dummyHead.next = head;// 链表的元素个数int cnt = 0;ListNode cur = dummyHead;// 找到链表的最后节点while (cur.next != null) {cur = cur.next;cnt++;}// 只要把链表最后k个元素移动到最前面就达到目标啦int n = k % cnt;// p和q初始化为dummyHead可以防止很多null的异常ListNode p = dummyHead;ListNode q = dummyHead;for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) {// q移动到和p间距为n的地方q = q.next;}// p和q一直往后移动直到q移动到链表结尾while (q != null) {p = p.next;q = q.next;}dummyHead.next = p.next;p.next = null;cur = dummyHead;while (cur.next != null) {cur = cur.next;}cur.next = head;return dummyHead.next;}
}
143.重排链表
在中间把链表后一半逆序,然后隔一个把后一半对应的元素插入到前一半
class Solution {/* 参考 92. 反转部分链表 II*/public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) {// 创建虚拟头结点,防止一些null导致的问题ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);dummyHead.next = head;ListNode cur = dummyHead;for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {// 找到了m的上一个节点cur = cur.next;}// node.next就是要翻转的起点,mHead表示开始翻转的起点ListNode mHead = cur.next;ListNode next = null;ListNode pre = null;// 翻转m到n这一段,起点是mHead,参考206题for (int i = m; i <= n; i++) {next = mHead.next;mHead.next = pre;pre = mHead;mHead = next;}// m位置的节点指向n位置的下一个节点cur.next.next = next;// m前一个节点指向n位置处的节点cur.next = pre;// 返回虚拟头结点的下一个节点即新的头结点return dummyHead.next;}public void reorderList(ListNode head) {if (head == null || head.next == null) {return;}ListNode cur = head;// n是链表的节点总数int m, n = 1;while (cur.next != null) {cur = cur.next;n++;}if (n % 2 == 0) { // 偶数个节点m = n / 2 + 1;} else { // 奇数个节点m = n / 2 + 2;}// 反转第m个节点到第n个节点之间的链表,包含第m个和第n个,反转后的链表刷新下headhead = reverseBetween(head, m, n);// 下面利用双指针法进行二次连接ListNode preM = head;for (int i = 2; i < m; i++) {// for循环结束,mNodePre就是第m个节点前一个节点的位置preM = preM.next;}// 要和m节点进行位置交换的节点ListNode pre = head;// pre != preM是为了防止偶数的最后一对,这一对不用交换while (preM.next != null && pre != preM) {// 下面对调链表中的两个节点,参考 第24号问题:Swap Nodes in Pairs// 1.更新两个要进行交换的节点,各自的前面那个节点分别是pre和preMListNode node1 = pre.next;ListNode node2 = preM.next;// 把node2插入到node1前面preM.next = node2.next;pre.next = node2;node2.next = node1;// preM不用换,还可以用之前的?// pre变成交换后的node2的下一个节点,直接后面就是要进行交换的另一个节点pre = node2.next;}}
}
234.回文链表
基本上和上面的143号问题相同,先逆序后一半,然后用双指针判断前后两半部分对应的节点值是否相等即可
/* Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }* }*/// 和143号问题类似,先逆转后一半的链表,然后用双指针法逐个判断是否相等即可
class Solution {/* 参考 92. 反转部分链表 II*/public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) {// 创建虚拟头结点,防止一些null导致的问题ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);dummyHead.next = head;ListNode cur = dummyHead;for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {// 找到了m的上一个节点cur = cur.next;}// node.next就是要翻转的起点,mHead表示开始翻转的起点ListNode mHead = cur.next;ListNode next = null;ListNode pre = null;// 翻转m到n这一段,起点是mHead,参考206题for (int i = m; i <= n; i++) {next = mHead.next;mHead.next = pre;pre = mHead;mHead = next;}// m位置的节点指向n位置的下一个节点cur.next.next = next;// m前一个节点指向n位置处的节点cur.next = pre;// 返回虚拟头结点的下一个节点即新的头结点return dummyHead.next;}public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {if (head == null || head.next == null) {return true;}ListNode cur = head;// n是链表的节点总数int m, n = 1;while (cur.next != null) {cur = cur.next;n++;}if (n % 2 == 0) { // 偶数个节点m = n / 2 + 1;} else { // 奇数个节点m = n / 2 + 2;}// 反转第m个节点到第n个节点之间的链表,包含第m个和第n个,反转后的链表刷新下headhead = reverseBetween(head, m, n);// 下面利用双指针法进行二次连接ListNode node2 = head;for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {// for循环结束,node2就是第m个节点前一个节点的位置node2 = node2.next;}// 比较前后两半部分对应的节点值是否相等ListNode node1 = head;while (node2 != null) {if(node1.val != node2.val){return false;}node1 = node1.next;node2 = node2.next;}return true;}
}
