【JavaEE】sychronized总结

1.synchronized的特性
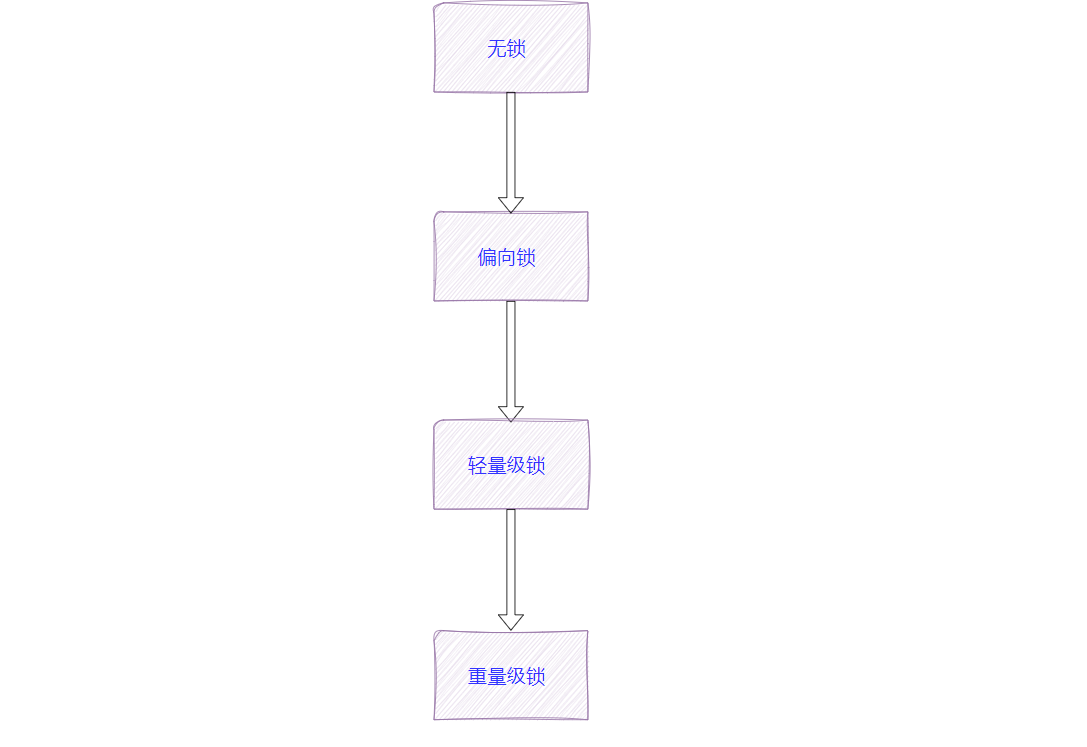
- 开始是乐观锁,如果锁冲突频繁,即很多线程竞争同一把锁,会转为悲观锁。
- 开始是轻量级锁(基于自旋锁实现),如果锁被持有的时间较长,会变为重量级锁
- 是不公平锁
- 是可重入锁
- 不是读写锁,只有加锁和解锁两个操作。
2.synchronized的使用
2.1synchronized修饰代码块
语法为:
synchronized (锁对象){}
例如:
synchronized (this) {
}
示例:
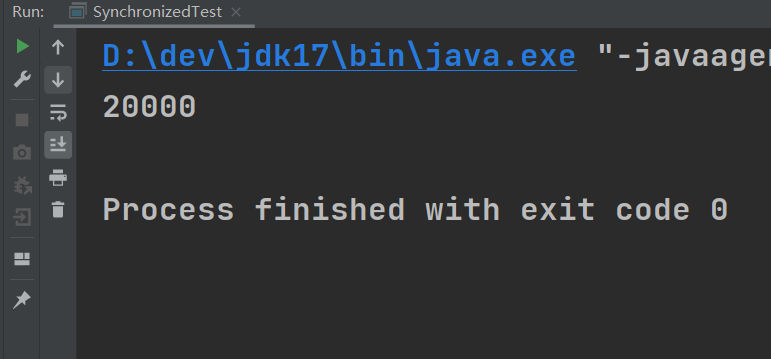
public class SynchronizedTest1 {public static Object lock = new Object();public static int count = 0;public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {//线程t1,执行count++ 10000次Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {synchronized(lock) {count++;}}});//线程t2,执行count++ 10000次Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {synchronized (lock) {count++;}}});t1.start();t2.start();//等t1和t2执行完Thread.sleep(1000);System.out.println(count);}
}
执行结果:
2.2synchronized修饰普通方法
synchronized修饰普通方法时,锁的对象等同于this对象。
示例:
public synchronized void countIncrement() {count++;
}
Demo类
Demo类中有count属性和countIncrement方法。
countIncrement方法由synchronized修饰,锁的对象是this,即Demo对象本身。
class Demo {public int count = 0;public synchronized void countIncrement() {count++;}
}测试类
创建t1和t2线程,每个线程调用500000次countIncrement()方法
最后打印count变量
public class SynchronizedTest2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Demo demo = new Demo();Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0; i < 500000; i++) {demo.countIncrement();}});Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0; i < 500000; i++) {demo.countIncrement();}});t1.start();t2.start();Thread.sleep(1000);System.out.println(demo.count);}
}
2.3synchronized修饰静态方法
用synchronized修饰静态方法时,锁的对象是类对象。
比如类名为Test,那么锁对象就为Test.class。
Demo2类
countIncrement方法由synchronized修饰,锁的对象是Demo2.class。
class Demo2 {public static int count = 0;public static synchronized void countIncrement() {count++;}
}
测试类
创建t1和t2线程,每个线程调用500000次countIncrement()方法
最后打印count变量
public class SynchronizedTest3 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0; i < 500000; i++) {Demo2.countIncrement();}});Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{for (int i = 0; i < 500000; i++) {Demo2.countIncrement();}});t1.start();t2.start();Thread.sleep(1000);System.out.println(Demo2.count);}
}
3.synchronized的锁机制
JVM会根据锁的竞争激烈程度对synchronized进行锁升级。
如图: