Java文件IO

目录
1.1 绝对路径
1.2 相对路径
二 . 文件操作
2.1 File类
2.2 字符流 Reader/Writer
2.3 字节流 InputStream/OutputStream
三. 实现一个文件的搜索功能
一. 文件路径
1.1 绝对路径
从盘符开始,一层一层往下找,得到的路径是绝对路径;
1.2 相对路径
从给定的某个目录触发,一层一层往下找,得到的路径是相对路径;
假设给定一个这样的路径:
从给定个目录开始找:
假设我们要去找 src 这个文件夹,就可以表示成这样:
./20221030/src../表示返回上一层
二 . 文件操作
因为文件是存储在硬盘上的,直接通过代码去操作硬盘,不太方便,所以我们一般在内存里进行操作,我们在内存中创建一个对应的对象,通过操作这个对象,就可以间接的影响到硬盘里的文件情况了,Java为我们提供File这个类,来方便我们对文件的操作;
2.1 File类
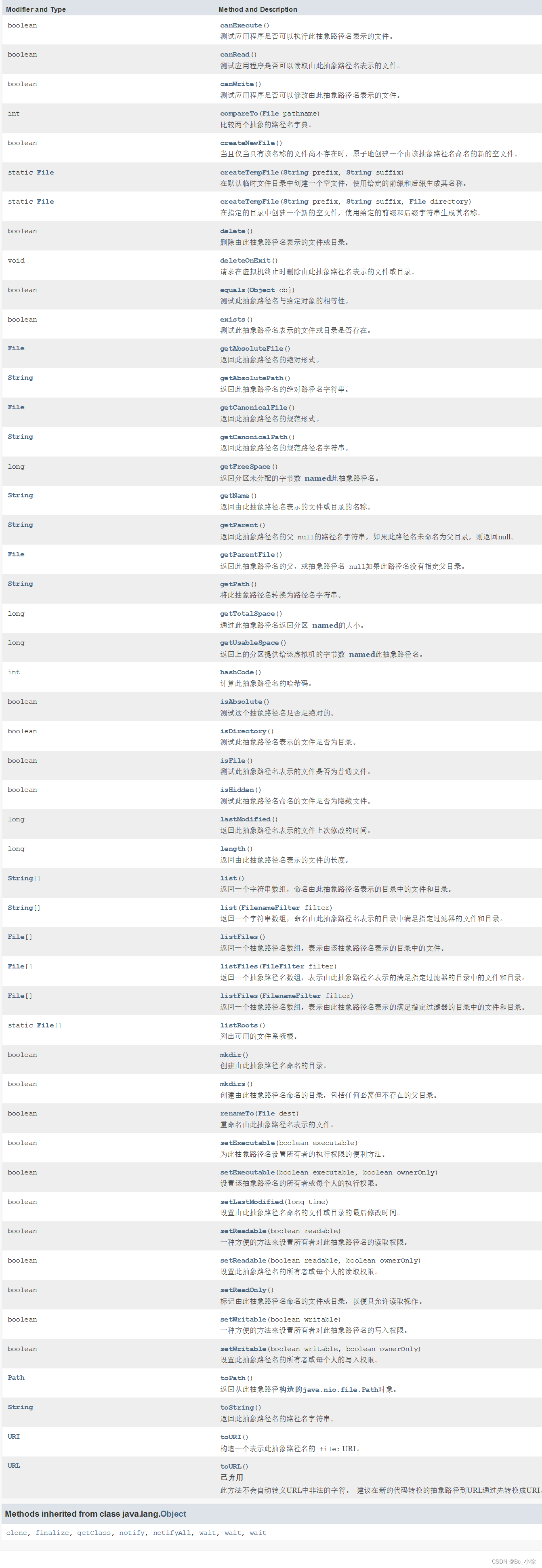
java给我们提供了文件操作的许多API,里面的很多方法都可以帮助我们去解决很多问题:
还是拿这个路径来说,绝对路径表示:
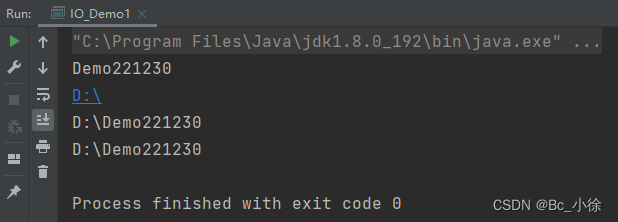
public class IO_Demo1 {public static void main(String[] args) {//绝对路径表示File file = new File("D:/Demo221230");//获取文件名System.out.println(file.getName());//获取父目录文件路径System.out.println(file.getParent());//获取文件的路径System.out.println(file.getPath());//获取文件的绝对路径System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());}}运行结果:
相对路径表示:
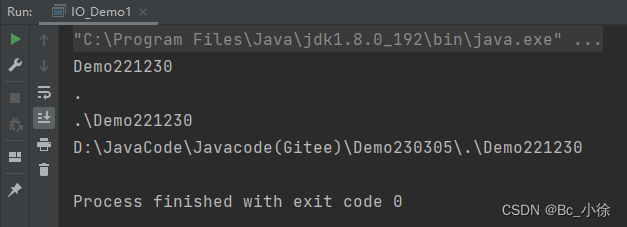
public class IO_Demo1 {public static void main(String[] args) {//相对路径表示File file = new File("./Demo221230");//获取文件名System.out.println(file.getName());//获取父目录文件路径System.out.println(file.getParent());//获取文件的路径System.out.println(file.getPath());//获取文件的绝对路径System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());}}运行结果:
创建文件
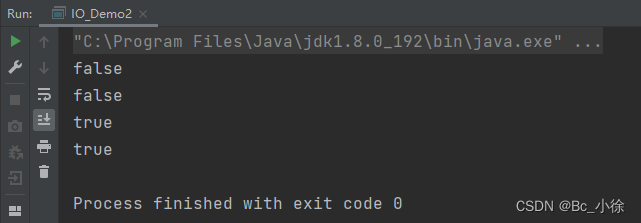
public class IO_Demo2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {File file = new File("Demo.txt");System.out.println(file.exists());System.out.println(file.isFile());//创建文件file.createNewFile();System.out.println(file.exists());System.out.println(file.isFile());} }
在File的构造方法里写了一个“Demo.txt”文件,但是这个文件并不存在,通过createNewFile()方法可以创建一个文件,这个文件的存放位置在项目的所属的根目录下;
2.2 字符流 Reader/Writer
该流用于从文件读取数据,它的对象可以用关键字 new 来创建:
public class IO_Demo3 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 1.写法一,需要手动去close//打开文件//InputStream inputStream =new FileInputStream("d:/test.txt");//关闭文件//inputStream.close();//2. 写法二,try操作会在代码块执行结束后,自动执行close操作try (InputStream inputStream =new FileInputStream("d:/test.txt");){//读文件while (true){int n = inputStream.read();//强转成字符char c =(char)n;if(n == -1){break;}System.out.println(c);}}}
}2.3 字节流 InputStream/OutputStream
该类用来创建一个文件并向文件中写数据:
public class IO_Demo4 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {try (OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("d:/test.txt")){//数字代表对于的字符outputStream.write(97);outputStream.write(98);outputStream.write(99);outputStream.write(100);}}
}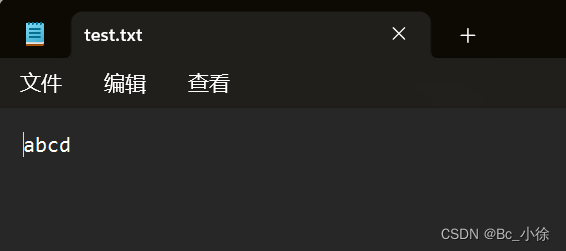
这样就写入数据了
三. 实现一个文件的搜索功能
package 文件IO;import java.io.*;
import java.util.Scanner;/* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.* Description:* User: Snk* Date: 2023-04-07* Time: 22:02*/
public class IO_Demo5 {public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);// 1.让用户输入一个搜索的根目录System.out.println("请输入一个要搜索的根目录: ");File root = new File(scan.next());//判断是否是根目录if (!root.isDirectory()) {System.out.println("输入有误,输入的目录不存在!");return;}// 2.让用户输入一个要查询的词System.out.println("请输入要搜素的词: ");String word = scan.next();// 3.使用递归对文件或者目录进行遍历traverse(root, word);}private static void traverse(File root, String word) throws FileNotFoundException {//列出当前 root 中的内容,如果没有,直接结束程序File[] files = root.listFiles();if (files == null) {return;}//如果目录有内容,就进行递归for (File x : files) {//如果是普通文件if (x.isFile()) {//打开文件,读取内容,看看word是否包含在文件里String content = readFile(x);if (content.contains(word)) {System.out.println(x.getAbsolutePath() + "包含要查找的word");}}//如果是目录else if (x.isDirectory()) {//进行递归traverse(x, word);} else {continue;}}}private static String readFile(File x) throws FileNotFoundException {//读取内容StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();try (Reader reader = new FileReader(x)) {//一次读取一个字符,把读到的结果拼装到 StringBuilder 里面,统一转成Stringwhile (true) {int c = reader.read();if (c == -1) {break;}stringBuilder.append((char) c);}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return stringBuilder.toString();}
}