C++之模拟实现map和set

文章目录
- 前言
- 一、迭代器
-
- 1.begin()和end()
- 2.operator++()
- 二、改造红黑树
- 三、map的模拟实现
- 四、set的模拟实现
- 总结
前言
基于之前的红黑树和map、set的相关知识,本节我们使用红黑树来模拟实现STL中的map和set。
一、迭代器
使用迭代器可以方便我们对数据结构进行遍历,它使数据结构的底层实与用户的使用分离(封装了底层实现),因此我们要给红黑树增加一个迭代器。
1.begin()和end()
STL中明确规定,begin()和end()代表的是一段前闭后开的区间。我们知道对红黑树进行中序遍历可以得到一个有序的序列,因此begin()可以放置在红黑树的最小节点处(即,最左节点),end()应该放置在红黑树最大节点的下一个位置。但是最大结点的下一个位置是什么呢?这个位置是nullptr吗?答案是不能是nullptr,因为对end()位置进行–操作要能找到最后一个元素,如果设置为nullptr就找不到最后一个结点了。
我们可以给红黑树增加一个header结点,让最大结点的next指向它
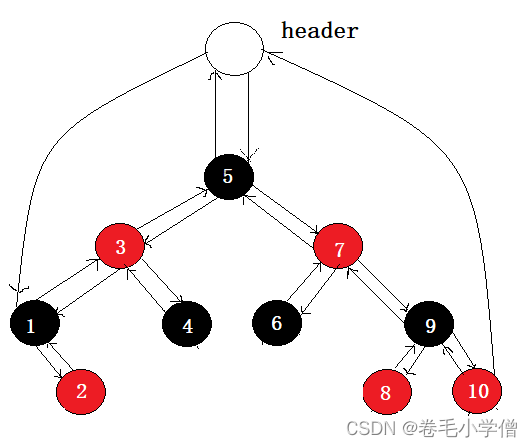
但是我们只是对它进行模拟,理解它的底层原理即可,为了不要让代码太过复杂,我们本次模拟实现就不设定header结点,直接让end()为nullptr即可(不实现–)。
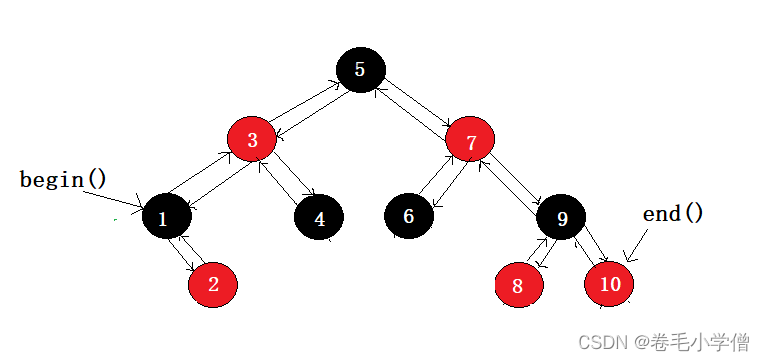
2.operator++()
找迭代器的下一个结点(它的值一定比当前结点的值大)
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>struct __RBTreeIterator{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;typedef __RBTreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;typedef __RBTreeIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;Node* _node;__RBTreeIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}Self& operator++(){if (_node->_right){Node* min = _node->_right;while (min->_left){min = min->_left;}_node = min;}else{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = _node->_parent;while (parent && cur == parent->_right){cur = cur->_parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;}bool operator!=(const Self& s){return _node != s._node;}bool operator==(const Self& s){return _node == s._node;}};
二、改造红黑树
namespace Jinger
{enum Colour//结点颜色{RED,BLACK,};template<class K,class V>struct RBTreeNode//红黑树结点{pair<K, V> _kv;typedef RBTreeNode<K, V> Node;RBTreeNode(const pair<K,V>& kv):_kv(kv), _parent(nullptr), _left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _colour(RED){}Node* _parent;Node* _left;Node* _right;Colour _colour;};template<class K, class V>struct __RBTreeIterator//迭代器{typedef RBTreeNode<K,V> Node;typedef __RBTreeIterator<K,V> Self;Node* _node;__RBTreeIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}pair<K,V>& operator*(){return _node->_kv;}pair<K, V>* operator->(){return &_node->_kv;}Self& operator++(){if (_node->_right){_node = _node->_right;}else{Node* parent = _node->_parent;if (_node == parent->_left){_node = parent;}else{while (parent && _node == parent->_right){_node = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent;}}return *this;}bool operator!=(const Self& s){return _node != s._node;}};template<class K,class V>struct RBTree{typedef RBTreeNode<K,V> Node;typedef __RBTreeIterator<K,V> iterator;RBTree():_root(nullptr){}//左旋void RotateL(Node* parent){Node* SubR = parent->_right;Node* SubRL = SubR->_left;parent->_right = SubRL;if (SubRL){SubRL->_parent = parent;}Node* Grandpa = parent->_parent;SubR->_left = parent;parent->_parent = SubR;if (!Grandpa){_root = SubR;SubR->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (parent == Grandpa->_left){Grandpa->_left = SubR;}else{Grandpa->_right = SubR;}}SubR->_parent = Grandpa;}//右旋void RotateR(Node* parent){Node* SubL = parent->_left;Node* SubLR = SubL->_right;Node* Grandpa = parent->_parent;parent->_parent = SubL;parent->_left = SubLR;if (SubLR){SubLR->_parent = parent;}if (!Grandpa){_root = SubL;SubL->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (parent == Grandpa->_left){Grandpa->_left = SubL;}else{Grandpa->_right = SubL;}}SubL->_right = parent;}iterator begin(){Node* cur = _root;while (cur && cur->_left){cur = cur->_left;}return iterator(cur);}iterator end(){return iterator(nullptr);}bool insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){Node* newnode = new Node(kv);if (!_root)//空树{_root = newnode;_root->_colour = BLACK;}else{Node* parent = _root;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){parent = cur;if (cur->_kv.first > kv.first){cur = cur->_left;}else if (cur->_kv.first < kv.first){cur = cur->_right;}else{return false;}}if (parent->_kv.first > kv.first){parent->_left = newnode;}else{parent->_right = newnode;}newnode->_parent = parent;cur = newnode;parent = cur->_parent;if (parent->_colour == BLACK)//如果父亲的结点为黑色{return true;}while (parent && parent->_colour == RED)//如果parent为空,说明此时cur为根节点(如果调整到父节点为黑色就不需要再调整了){Node* g = parent->_parent;//祖父Node* u = nullptr;//叔叔结点if (parent == g->_left)//如果父亲是祖父的左孩子,那么叔叔是祖父的右孩子{u = g->_right;}else{u = g->_left;}if (u && u->_colour == RED){g->_colour = RED;u->_colour = parent->_colour = BLACK;cur = g;parent = cur->_parent;}else//叔叔不存在/叔叔的结点为黑色{//parent是g的右孩子,cur是parent的右孩子(左单旋)if (parent == g->_right && cur == parent->_right){RotateL(g);parent->_colour = BLACK;g->_colour = RED;}//parent是g的左孩子,cur是parent的左孩子(右单旋)else if (parent == g->_left && cur == parent->_left){RotateR(g);parent->_colour = BLACK;g->_colour = RED;}//parent是g的左孩子,cur是parent的右孩子(左右双旋)else if (parent == g->_left && cur == parent->_right){RotateL(parent);RotateR(g);cur->_colour = BLACK;g->_colour = RED;}//parent是g的右孩子,cur是parent的左孩子(右左双旋)else if (parent == g->_right && cur == parent->_left){RotateR(parent);RotateL(g);cur->_colour = BLACK;g->_colour = RED;}break;}}}_root->_colour = BLACK;//性质2要求根节点的颜色为黑色return true;}void inoder(){_inorder(_root);}void _inorder(Node* root){if (!root) return;_inorder(root->_left);cout << root->_kv.first << ":" << root->_kv.second<< " ";_inorder(root->_right);}bool _isbalance(Node* root, int count, const int& leftcount){if (root == nullptr){if (count != leftcount){cout << "每条路径黑色结点数不相同,违反了性质4" << endl;return false;}else{return true;}}if (root->_colour == RED && root->_parent->_colour == RED){cout << "父亲结点和cur都是红色,违反了性质3" << endl;return false;}if (root->_colour == BLACK){count++;}bool left = _isbalance(root->_left, count, leftcount);bool right = _isbalance(root->_right, count, leftcount);return left && right;}bool isBalance(){if (_root == nullptr){return true;}if (_root->_colour == RED){cout << "根节点为红色,违反了性质2" << endl;return false;}int leftcount = 0;Node* cur = _root;while (cur->_left){if (cur->_colour == BLACK){leftcount++;}cur = cur->_left;}cout << leftcount << endl;return _isbalance(_root, 0, leftcount);}private:Node* _root;};
}
三、map的模拟实现
map的底层结构就是一个红黑树,因此在map中直接封装一个红黑树,然后包装一下它的借口即可。
namespace Jinger
{template<class K, class V>class Map{struct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<const K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};public:typedef typename RBTree<K, pair< const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;iterator begin(){return _t.begin();}iterator end(){return _t.end();}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<const K, V>& kv){return _t.insert(kv);}V& operator[](const K& k){pair<iterator, bool> ret = _t.insert(make_pair(k, V()));return ret.first->second;}iterator& find(const K& k){_t.find(k);}private:Jinger::RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;};
}
四、set的模拟实现
set的底层结构就是一个红黑树,因此在map中直接封装一个红黑树,然后包装一下它的借口即可。
namespace Jinger
{template<class K>class set{struct SetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};public:typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;iterator begin() const{return _t.begin();}iterator end() const{return _t.end();}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key){pair<typename RBTree<K,K,SetKeyOfT>::iterator,bool> ret = _t.insert(key);return pair<iterator, bool>(ret.first, ret.second);}private:RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;};
}
总结
以上就是今天要讲的内容,本文介绍了如何用红黑树模拟实现map和set的相关概念。本文作者目前也是正在学习C++相关的知识,如果文章中的内容有错误或者不严谨的部分,欢迎大家在评论区指出,也欢迎大家在评论区提问、交流。
最后,如果本篇文章对你有所启发的话,希望可以多多支持作者,谢谢大家!


