一起读源码 —— Fastjson 的核心方法及其实现原理

源码介绍
Fastjson 是阿里巴巴开源的一个 Java 工具库,它常常被用来完成 Java 的对象与 JSON 格式的字符串的相互转化。
此文读的源码是撰写此文时 Fastjson 的最新的发布版本,即 1.2.83
下载源码
请前去 github 找到 release 最新版下载后解压,地址为:https://github.com/alibaba/fastjson/releases/tag/1.2.83
项目结构
使用 IDEA 打开 fastjson-1.2.83 文件夹,下载相关依赖后,我们再开始阅读源码,接下来我们分别对 JSON 、JSONArray 与 JSONObject。

JSON 实现两个接口
JSON 类是实现两个接口 JSONStreamAware 、JSONAware 的抽象类,即
public abstract class JSON implements JSONStreamAware, JSONAware
我们先介绍这两个接口:
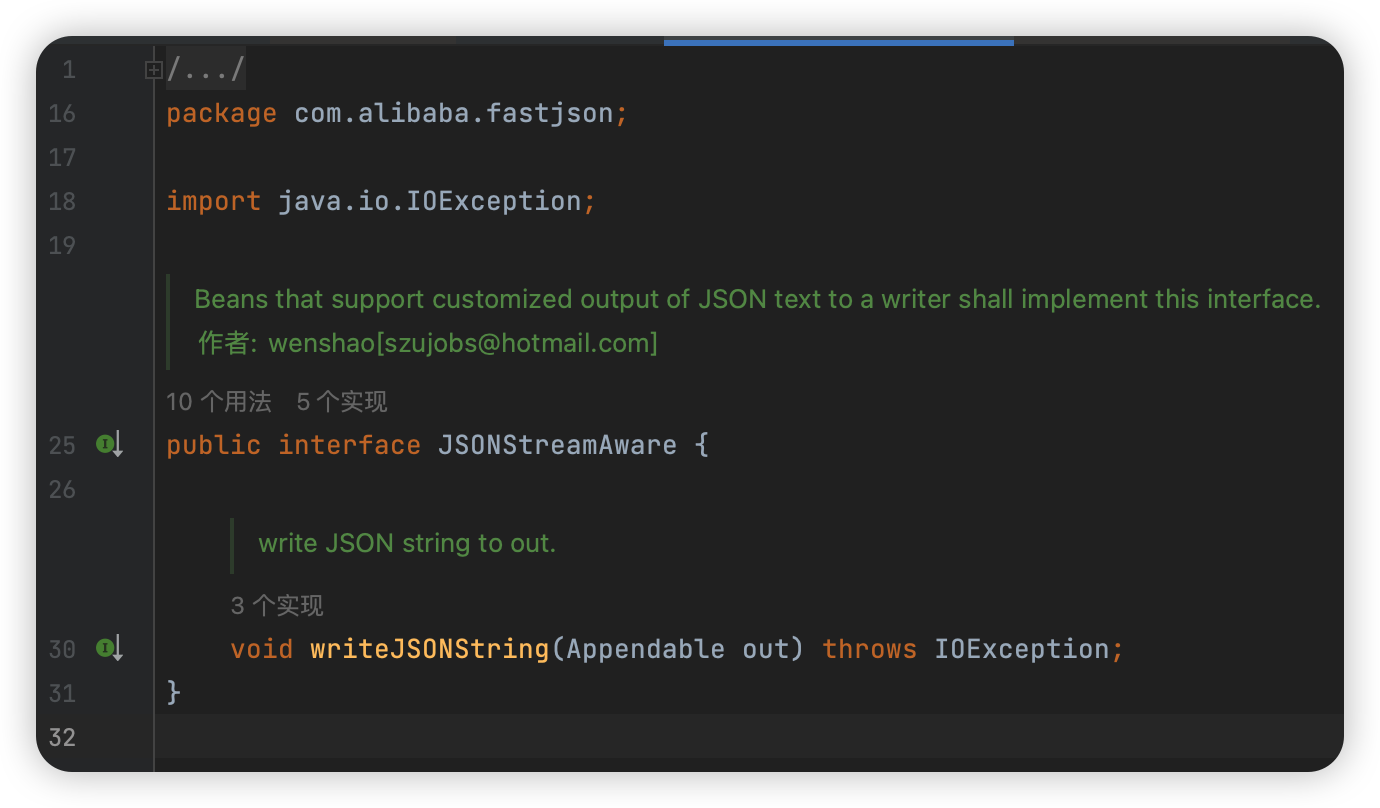
JSONStreamAware
方法 writeJSONString 中的参数 Appendable 也是一个接口,也就是可以附加字符序列和值的对象,这个接口的作用是提供一个输出JSON字符串的方法,以便于其他的方法调用。
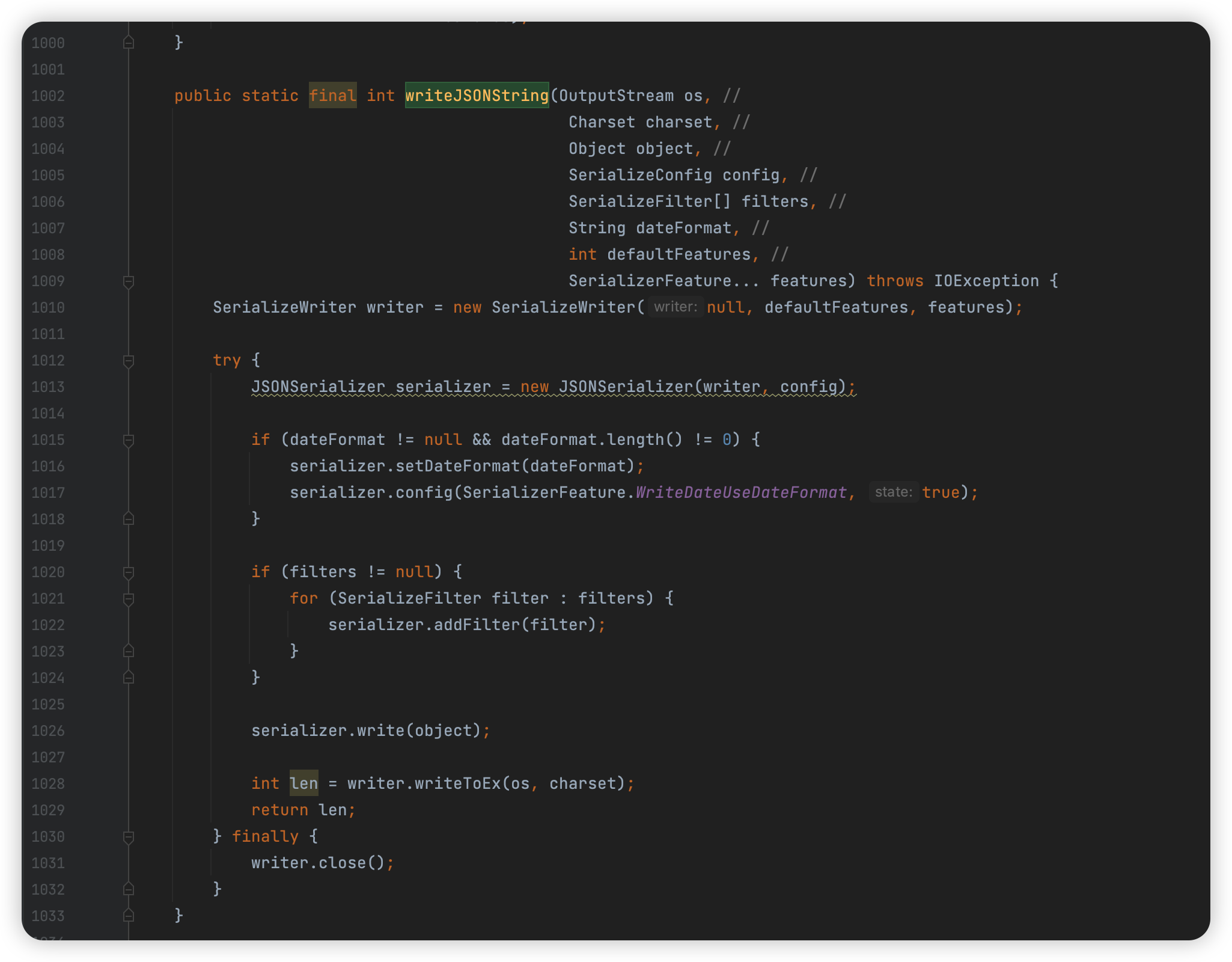
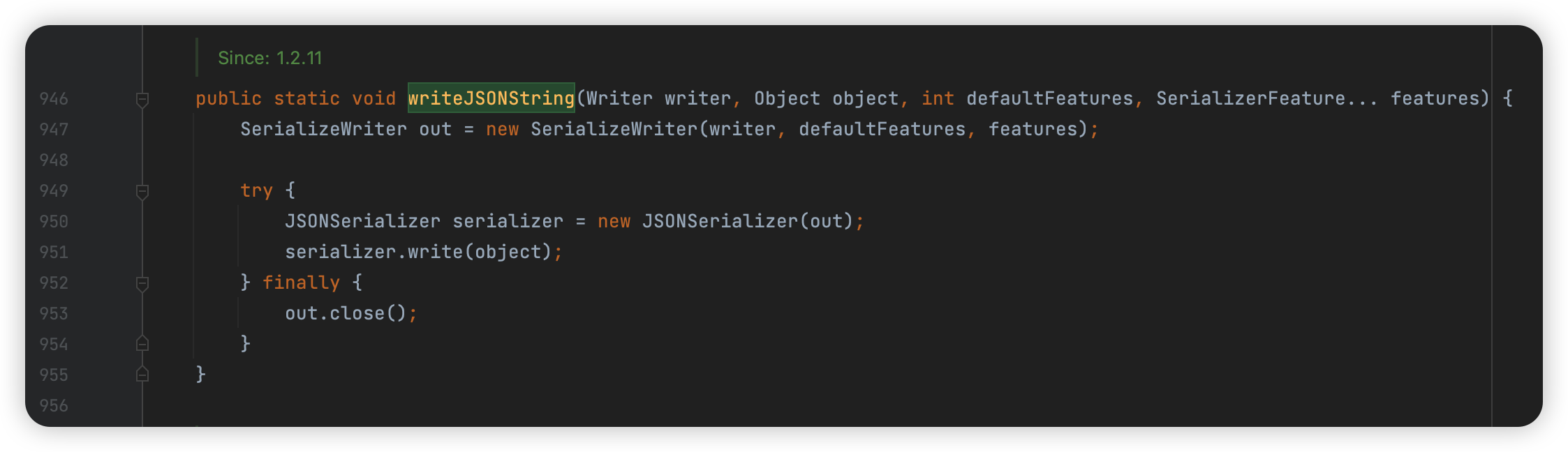
接着我们在 JSON 抽象类中寻找用到这个方法的地方,这里主要截图其中两个具体的实现方法,另外还有几个重载方法是通过调用这两个方法的方法,这里不再列举。
JSONAware
这个接口更加简单了,实现该接口的类即需要实现 toJSONString 的方法即可。
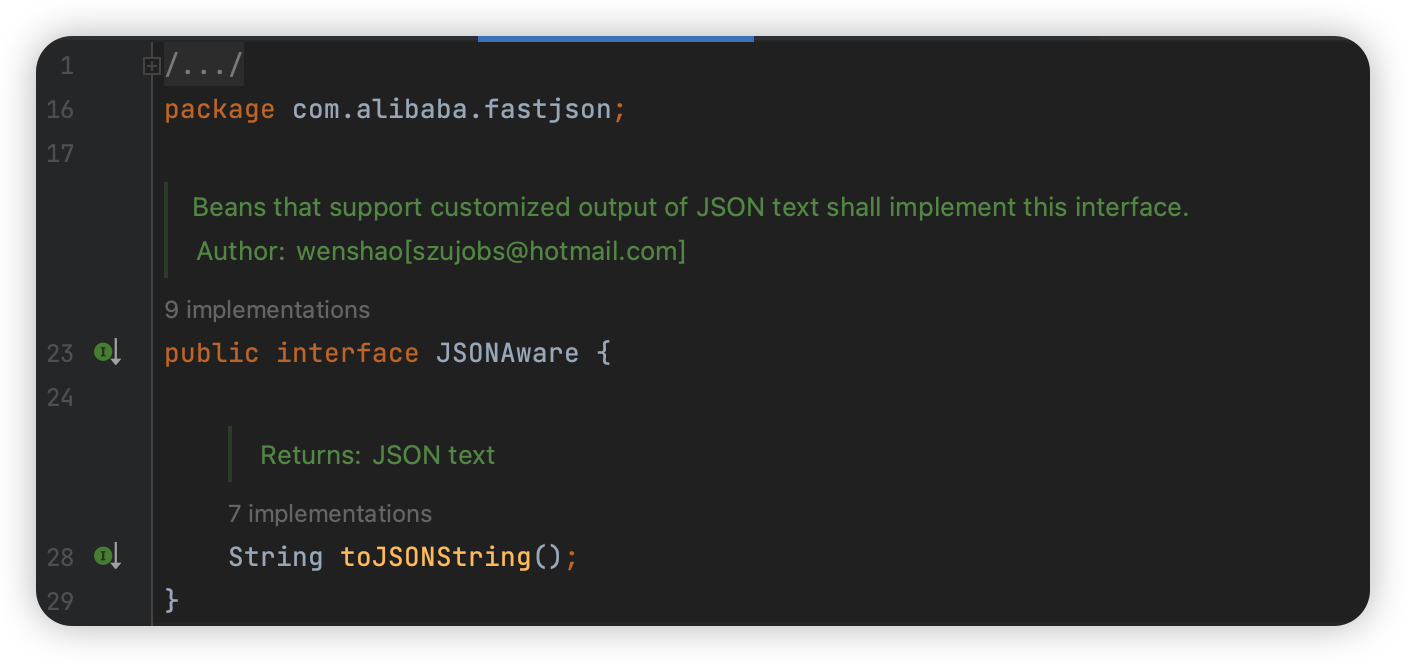
在JSON抽象类中,具体实现为:
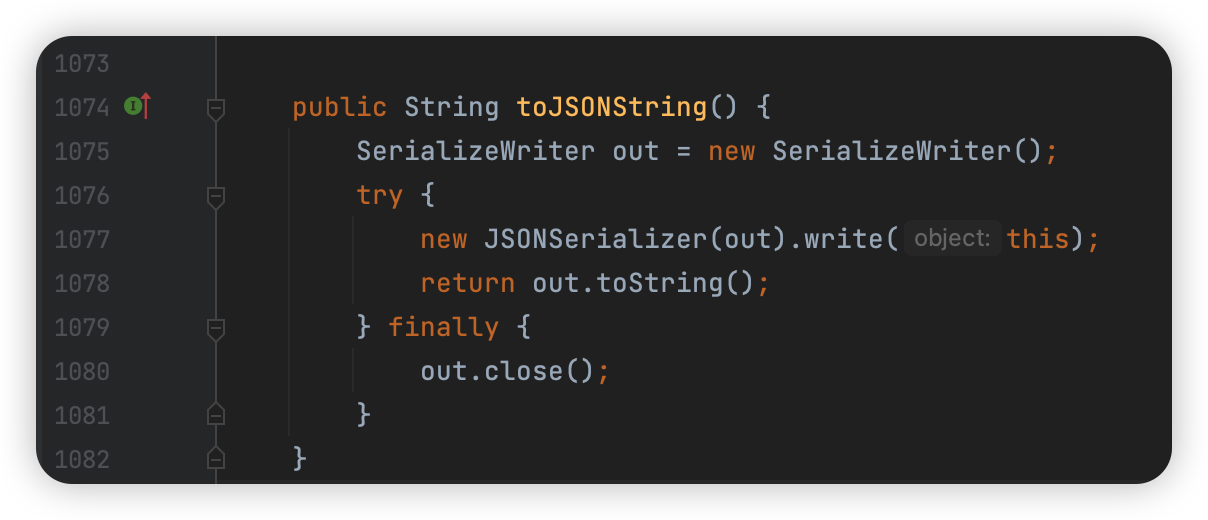
这里调用的是 JSONSerializer 类的对象方法,这里我们在后面介绍这个类的时候进一步介绍。
这个相对于 writeJSONString 更加实用。比如重写 toString 方法。
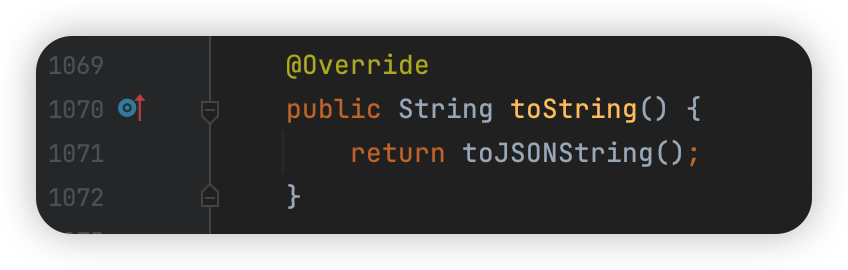
JSON 类的静态方法
我们常常用到这些方法,并且我们在使用 JSONObject 类方法的时候也经常用得到(JSONObject是JSON类的子类)。这里我们介绍我们最最最常用的,并且在 JSONObject 中不再介绍。
JSON.toString / JSON.toJSONString
这个方法前面关于 JSONAware 接口的实现的时候有提到过,这里就不做介绍了。
这里我们看一下 toJSONString 方法的实现原理。源码比较简单,这里就不逐行介绍了。
方法参数介绍
- object: Object 待转换的 Java 对象;
- defaultFeatures: int 后面参数 SerializerFeature 的长度,因为后面是
SerializerFeature...类型的,所以调用时需要指定它的长度; - features: SerializerFeature… 这个地方是指多个 SerializerFeature 类型的对象,调用时可以
toJSONString(obj, 1, feature0)也可以toJSONString(obj, 2, feature0, feature1),也可以toJSONString(obj, 3, feature0, feature1, feature2)等等。
/* @since 1.2.11*/public static String toJSONString(Object object, int defaultFeatures, SerializerFeature... features) {SerializeWriter out = new SerializeWriter((Writer) null, defaultFeatures, features);try {JSONSerializer serializer = new JSONSerializer(out);serializer.write(object);String outString = out.toString();int len = outString.length();if (len > 0&& outString.charAt(len -1) == '.'&& object instanceof Number&& !out.isEnabled(SerializerFeature.WriteClassName)) {return outString.substring(0, len - 1);}return outString;} finally {out.close();}}
源码中用到了 SerializeWriter 对象以及它的方法,这里我们理一下它的作用与用法。
SerializeWriter 构造函数为
public SerializeWriter(Writer writer, int defaultFeatures, SerializerFeature... features){this.writer = writer;buf = bufLocal.get();if (buf != null) {bufLocal.set(null);} else {buf = new char[2048];}int featuresValue = defaultFeatures;for (SerializerFeature feature : features) {featuresValue |= feature.getMask();}this.features = featuresValue;computeFeatures();}
在前面初始化JSONSerializer的时候调用SerializeWriter对象,即 JSONSerializer serializer = new JSONSerializer(out); 这个时候的使用方法是:
这里查看 JSONSerializer 对象的构造函数:
public JSONSerializer(SerializeWriter out){this(out, SerializeConfig.getGlobalInstance());}public JSONSerializer(SerializeWriter out, SerializeConfig config){this.out = out;this.config = config;}
其 write 方法源码为:
public final void write(Object object) {if (object == null) {out.writeNull();return;}Class<?> clazz = object.getClass();ObjectSerializer writer = getObjectWriter(clazz);try {writer.write(this, object, null, null, 0);} catch (IOException e) {throw new JSONException(e.getMessage(), e);}}
JSONObject
相对而言 JSONObject 用得更多,这里需要介绍的也更多。
无参构造函数
其中 DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY 默认等于 16,也就是创建 HashMap 或者 LinkedHashMap 对象的时候默认的 initialCapacity 的值,而 order 参数将会指定创建的 map 对象的类型。
public JSONObject(){this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, false);}public JSONObject(int initialCapacity, boolean ordered){if (ordered) {map = new LinkedHashMap<String, Object>(initialCapacity);} else {map = new HashMap<String, Object>(initialCapacity);}}public JSONObject(boolean ordered){this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, ordered);}public JSONObject(int initialCapacity){this(initialCapacity, false);}有参构函数
public JSONObject(Map<String, Object> map){if (map == null) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("map is null.");}this.map = map;}
这里相对于前面的无参构造函数而言,map 对象在外界创建与初始化,直接传入 JSONObject 中,作为构造函数。这样做使得我们在反序列化、序列化的方法更加灵活,这里我们在后面介绍。
containsKey / containsValue / get / isEmpty / size 方法
这几个方法都是直接调用 成员变量 map 得以实现的,具体实现代码如下:
public int size() {return map.size();}public boolean isEmpty() {return map.isEmpty();}public boolean containsKey(Object key) {boolean result = map.containsKey(key);if (!result) {if (key instanceof Number|| key instanceof Character|| key instanceof Boolean|| key instanceof UUID) {result = map.containsKey(key.toString());}}return result;}public boolean containsValue(Object value) {return map.containsValue(value);}public Object get(Object key) {Object val = map.get(key);if (val == null) {if (key instanceof Number|| key instanceof Character|| key instanceof Boolean|| key instanceof UUID) {val = map.get(key.toString());}}return val;}public Object getOrDefault(Object key, Object defaultValue) {Object v;return ((v = get(key)) != null) ? v : defaultValue;}
反序列化方法
首先出场的是最简单的,将 map 中的某个 key 进行反序列化,一般情况下我们会在 这个 key 对应的是 Object 的时候使用它。比如原始的map 是 {"age": 3, "item" : {"color": "black", "length" : 2}} ,我们在反序列化 item 的时候需要调用这个方法,即 getJSONObject("item") 。
public JSONObject getJSONObject(String key) {Object value = map.get(key);if (value instanceof JSONObject) {return (JSONObject) value;}if (value instanceof Map) {return new JSONObject((Map) value);}if (value instanceof String) {return JSON.parseObject((String) value);}return (JSONObject) toJSON(value);}
类似地如果是 JSON 数组的化,调用 getJSONArray 方法,这里举一个例子为 map 为 {"age": 3, items:[{"color": "red"}, {"color": "black"}]},我们在反序列 items 的时候会调用这个方法。
public JSONArray getJSONArray(String key) {Object value = map.get(key);if (value instanceof JSONArray) {return (JSONArray) value;}if (value instanceof List) {return new JSONArray((List) value);}if (value instanceof String) {return (JSONArray) JSON.parse((String) value);}return (JSONArray) toJSON(value);}
如果不是前面两种,我们需要获取的只是简单的 item 对象,比如 age = 3,那么就调用 getObject 方法即可,注意这里有几个重载方法。
public <T> T getObject(String key, Class<T> clazz) {Object obj = map.get(key);return TypeUtils.castToJavaBean(obj, clazz);}public <T> T getObject(String key, Type type) {Object obj = map.get(key);return TypeUtils.cast(obj, type, ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance());}public <T> T getObject(String key, TypeReference typeReference) {Object obj = map.get(key);if (typeReference == null) {return (T) obj;}return TypeUtils.cast(obj, typeReference.getType(), ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance());}
这个时候我们不得不介绍一下 TypeUtils 类了,毕竟出场率这么高,这里只介绍 cast 与 castToJavaBean 两个静态方法。
private static BiFunction<Object, Class, Object> castFunction = new BiFunction<Object, Class, Object>() {public Object apply(Object obj, Class clazz) {if (clazz == java.sql.Date.class) {return castToSqlDate(obj);}if (clazz == java.sql.Time.class) {return castToSqlTime(obj);}if (clazz == java.sql.Timestamp.class) {return castToTimestamp(obj);}return null;}};
这里实现了接口 BiFunction 的 apply 方法,实现方法也非常简单粗暴,三个 if 对应三个方法 castToSql / castToSqlTime / castToTimestamp 。
这个时候可能大家会疑惑,这个跟 sql 有什么关系?其实确实没什么关系,但是毕竟 java 提供的现有的可用方法,不用白不用,这里也给大家做个广告,这里面的 java.sql.Timestamp 与 java.sql.Time 以及 java.sql.Date 确实很好用,这里以 java.sql.Timestamp 为例,它提供13位时间戳的构造方法 public Timestamp(long time) 以及常用的 compareTo 、before 、after 方法,需要的小伙伴可以自取使用。
而 cast 方法 居然都有 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 标注,着实让人多少有点不放心,难道一定要去使用 Fastjson2 ?
这里我们查看其中一个方法的实现,看完了你大概就会产生一种 “就这?我上我也行” 的感觉:
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public static <T> T cast(Object obj, Type type, ParserConfig mapping) {if (obj == null) {return null;}if (type instanceof Class) {return cast(obj, (Class<T>) type, mapping);}if (type instanceof ParameterizedType) {return (T) cast(obj, (ParameterizedType) type, mapping);}if (obj instanceof String) {String strVal = (String) obj;if (strVal.length() == 0 //|| "null".equals(strVal) //|| "NULL".equals(strVal)) {return null;}}if (type instanceof TypeVariable) {return (T) obj;}throw new JSONException("can not cast to : " + type);}
事实也确实如此,充其量就是用了点反射技术,首先判断数据类型属于哪个小可爱的子类,然后再使用放射和传过来的 clazz 创建对象,而建立其中的映射关系的,就是其中的 mapping 参数对象,仅此而已。
JSON 与 JSONObject 的区别与联系
能够用 JSON 的地方,基本上都能用 JSONObject,不同之处在于一般直接 JSON 的静态方法,因为它是抽象类,不能直接 new 出对象的。而 JSONObject 名字中就强调了 Object 的概念,所以一般直接就用它的对象的方法。
灵活使用 JSONObject
总体来说最经常用到的就是 toString 与 toJSONObject 以及 JSONObject 对象的 getInteger / getLong / getJSONObject 等等方法,这些方法都应该基于 map 联想记忆,都是比较容易理解的。
总结
Fastjson 中存在很多地方都属于让人看了就 “恍然大悟” 之处,也推荐大家去阅读,同时不得不说,阿里巴巴能够有支团队开发并不断完善Fastjson,也是挺值得前去 github 点颗星星。
最后吐槽一下 Fastjson 的实现部分有明显的 “不遵守 《JAVA 规范手册》” 的,请以后的开发人员注意多多参考 Java开发手册(嵩山版) ,多写一些些注释,成为一本与 手册 配套的代码示例,也是非常不错的 ~ 此致,敬上 ~
Smileyan
2023.04.13 00:44


