第十一章 ThreadLocal全面解析

JUC并发编程系列文章
http://t.csdn.cn/UgzQi
文章目录
- JUC并发编程系列文章
- 前言
- 一、ThreadLocal介绍🍔
- 二、基本使用🥤
-
- 1、常用方法
- 2、使用案例
- 3、ThreadLocal类与synchronized关键字
- 运用案例,两个账户互相转账
- 三、3. ThreadLocal的内部结构🍖
-
- 1、常见的误解(早期的设计)
- 2、现在的设计
- 3、优势
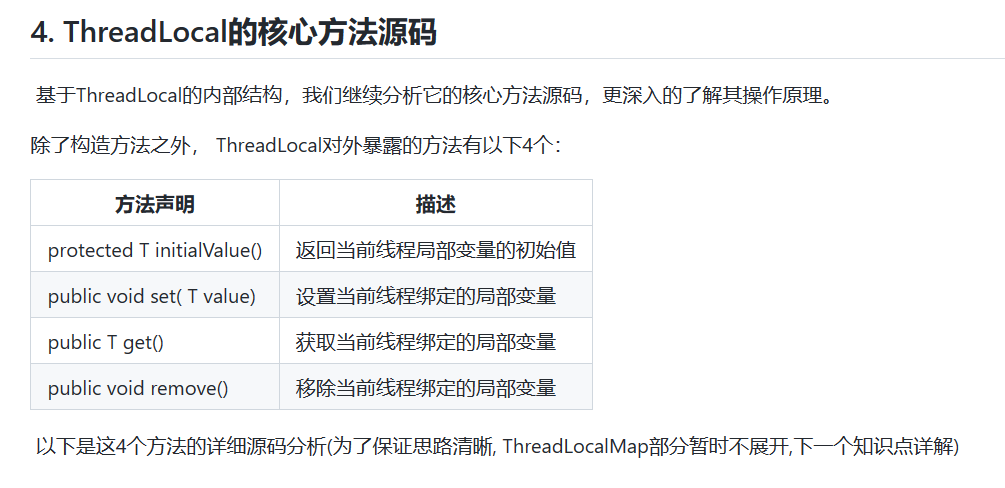
- 四、 ThreadLocal的核心方法源码🍎
-
- 1、set( ) 方法
- 2、get( ) 方法
- 3、remove()方法
- 4、initialValue()方法
- 五、ThreadLocalMap源码分析🥑
前言

一、ThreadLocal介绍🍔

/* This class provides thread-local variables. These variables differ from* their normal counterparts in that each thread that accesses one (via its* {@code get} or {@code set} method) has its own, independently initialized* copy of the variable. {@code ThreadLocal} instances are typically private* static fields in classes that wish to associate state with a thread (e.g.,* a user ID or Transaction ID). <p>For example, the class below generates unique identifiers local to each* thread.* A thread's id is assigned the first time it invokes {@code ThreadId.get()}* and remains unchanged on subsequent calls.* <pre>* import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; public class ThreadId {* // Atomic integer containing the next thread ID to be assigned* private static final AtomicInteger nextId = new AtomicInteger(0); // Thread local variable containing each thread's ID* private static final ThreadLocal<Integer> threadId =* new ThreadLocal<Integer>() {* @Override protected Integer initialValue() {* return nextId.getAndIncrement();* }* }; // Returns the current thread's unique ID, assigning it if necessary* public static int get() {* return threadId.get();* }* }* </pre>* <p>Each thread holds an implicit reference to its copy of a thread-local* variable as long as the thread is alive and the {@code ThreadLocal}* instance is accessible; after a thread goes away, all of its copies of* thread-local instances are subject to garbage collection (unless other* references to these copies exist). @author Josh Bloch and Doug Lea* @since 1.2*/
public class ThreadLocal<T> {...
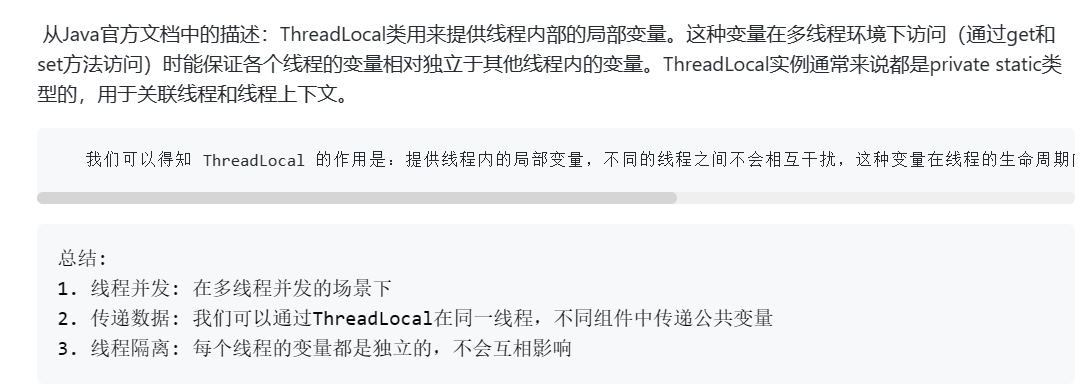
二、基本使用🥤
1、常用方法
2、使用案例

下面根据一个简单的案例,了解 ThreadLocal 的使用场景
public class MyDemo {private String content;private String getContent() {return content;}private void setContent(String content) {this.content = content;}public static void main(String[] args) {MyDemo demo = new MyDemo();for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {demo.setContent(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "的数据");System.out.println("-----------------------");System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--->" + demo.getContent());}});thread.setName("线程" + i);thread.start();}}
}

从结果可以看出多个线程在访问同一个变量的时候出现的异常,线程间的数据没有隔离。下面我们来看下采用 ThreadLocal 的方式来解决这个问题的例子。
使用ThreadLocal 解决上面的问题
public class MyDemo {private static ThreadLocal<String> tl = new ThreadLocal<>();private String content;private String getContent() {return tl.get();}private void setContent(String content) {tl.set(content);}public static void main(String[] args) {MyDemo demo = new MyDemo();for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {demo.setContent(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "的数据");System.out.println("-----------------------");System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--->" + demo.getContent());}});thread.setName("线程" + i);thread.start();}}
}

3、ThreadLocal类与synchronized关键字
public class Demo02 {private String content;public String getContent() {return content;}public void setContent(String content) {this.content = content;}public static void main(String[] args) {Demo02 demo02 = new Demo02();for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {Thread t = new Thread(){@Overridepublic void run() {synchronized (Demo02.class){demo02.setContent(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "的数据");System.out.println("-------------------------------------");String content = demo02.getContent();System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--->" + content);}}};t.setName("线程" + i);t.start();}}
}
使用 Synchronized 关键字也能达到同样的效果,但是却降低了程序的并发性。
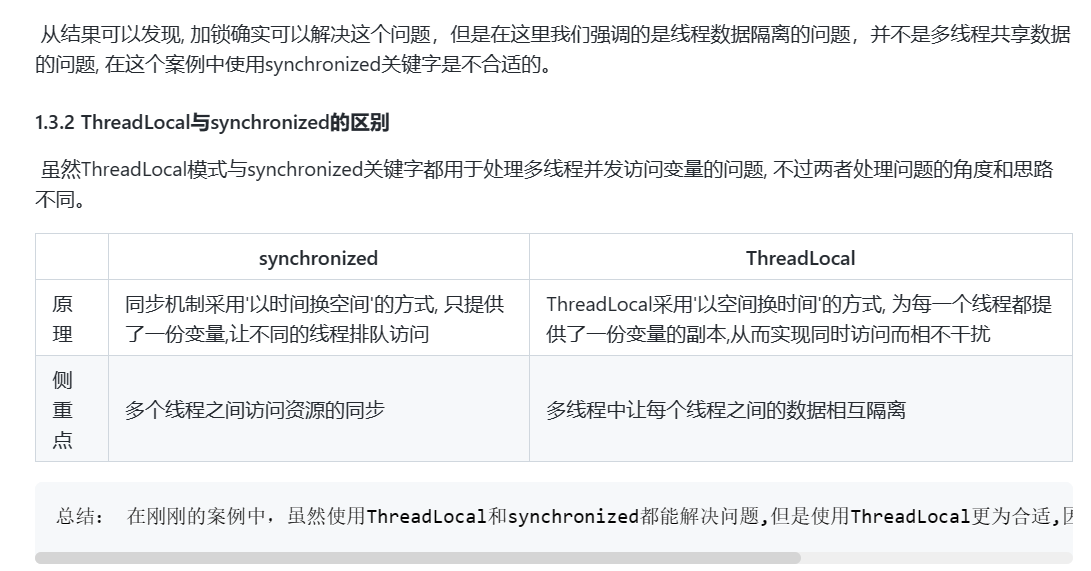
总结:
在刚刚的案例中,虽然使用ThreadLocal和synchronized都能解决问题,但是使用ThreadLocal更为合适,因为这样可以使程序拥有更高的并发性。
运用案例,两个账户互相转账
当两个账户互相转账就需要考虑数据库的事务处理,要么对于两个账户的操作都成功,要么都失败,引入数据库的事务处理,但这样就需要在service层创建一个连接,去提交事务和回滚事务,这时就会出现另外两个问题,dao层也需要和service层的连接使用相同的数据库连接,还要保证多线程情况下每个线程要拿到自己的连接去处理业务,不然多个线程同时去操作同一个数据库连接还是会出现问题。
针对这两个引出的问题,一般的方式就是传参和加锁,将service层的数据库连接传入到dao层,这样可以保证使用的是同一个连接,在service加锁,多线程来操作数据库,排队获取连接,保证数据不被多线程乱窜。但是这样显然是有弊端了,提高了程序的耦合度,加锁也降低了性能。
这时就需要经典的加一层,连解决这两个问题,使用 ThreadLocal ,在使用工具类获取数据库连接时,将数据库连接绑定到当前线程,这样service层和dao层都用过工具类获取连接,由于是同一个线程,获取的连接肯定也是同一个连接。多线程进来获取连接由于 ThreadLocal 是线程隔离的,也不会获取到别的线程绑定的连接。
但是,当前线程绑定数据库连接时也要注意,当前线程第一次来获取连接时,线程并没有绑定连接,需要判断获取的连接是否为空,为空就放一个连接绑定上去,这样后续再获取连接就会获取到同一个连接。当数据库事务提交或者回滚后也要将绑定的连接和当前线程解绑,不然容易造成内存泄漏问题。



package com.itheima.transfer.utils;import com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;public class JdbcUtils {//ThreadLocal对象 : 将connection绑定在当前线程中private static final ThreadLocal<Connection> tl = new ThreadLocal();// c3p0 数据库连接池对象属性private static final ComboPooledDataSource ds = new ComboPooledDataSource();// 获取连接public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {//取出当前线程绑定的connection对象Connection conn = tl.get();if (conn == null) {//如果没有,则从连接池中取出conn = ds.getConnection();//再将connection对象绑定到当前线程中tl.set(conn);}return conn;}//释放资源public static void release(AutoCloseable... ios) {for (AutoCloseable io : ios) {if (io != null) {try {io.close();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}public static void commitAndClose() {try {Connection conn = getConnection();//提交事务conn.commit();//解除绑定tl.remove();//释放连接conn.close();} catch (SQLException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}public static void rollbackAndClose() {try {Connection conn = getConnection();//回滚事务conn.rollback();//解除绑定tl.remove();//释放连接conn.close();} catch (SQLException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}
package com.itheima.transfer.service;import com.itheima.transfer.dao.AccountDao;
import com.itheima.transfer.utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;public class AccountService {public boolean transfer(String outUser, String inUser, int money) {AccountDao ad = new AccountDao();try {Connection conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();//开启事务conn.setAutoCommit(false);// 转出 : 这里不需要传参了 !ad.out(outUser, money);// 模拟转账过程中的异常
// int i = 1 / 0;// 转入ad.in(inUser, money);//事务提交JdbcUtils.commitAndClose();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();//事务回滚JdbcUtils.rollbackAndClose();return false;}return true;}
}
package com.itheima.transfer.dao;import com.itheima.transfer.utils.JdbcUtils;import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;public class AccountDao {public void out(String outUser, int money) throws SQLException {String sql = "update account set money = money - ? where name = ?";Connection conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();PreparedStatement pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql);pstm.setInt(1,money);pstm.setString(2,outUser);pstm.executeUpdate();//照常使用
// JdbcUtils.release(pstm,conn);JdbcUtils.release(pstm);}public void in(String inUser, int money) throws SQLException {String sql = "update account set money = money + ? where name = ?";Connection conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();PreparedStatement pstm = conn.prepareStatement(sql);pstm.setInt(1,money);pstm.setString(2,inUser);pstm.executeUpdate();
// JdbcUtils.release(pstm,conn);JdbcUtils.release(pstm);}
}
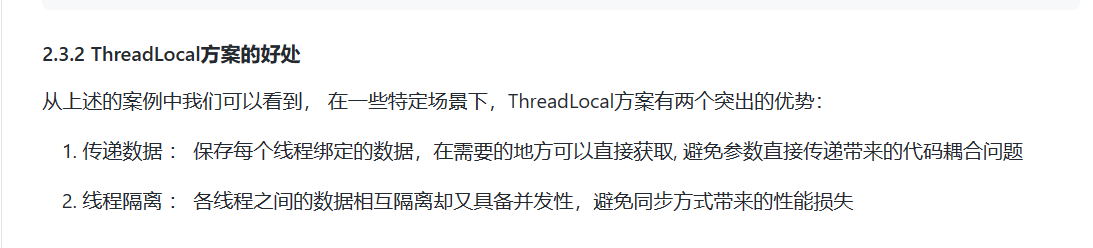
三、3. ThreadLocal的内部结构🍖
1、常见的误解(早期的设计)

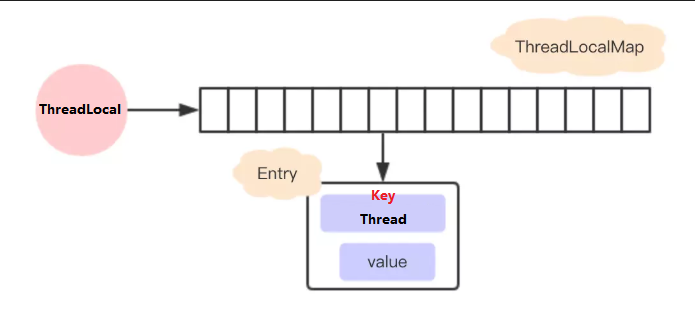
2、现在的设计

3、优势
四、 ThreadLocal的核心方法源码🍎
1、set( ) 方法
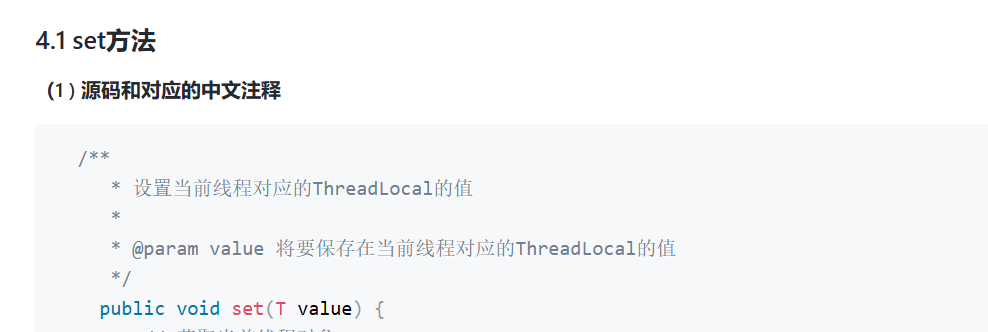
/* 设置当前线程对应的ThreadLocal的值 @param value 将要保存在当前线程对应的ThreadLocal的值*/public void set(T value) {// 获取当前线程对象Thread t = Thread.currentThread();// 获取此线程对象中维护的ThreadLocalMap对象ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);// 判断map是否存在if (map != null)// 存在则调用map.set设置此实体entrymap.set(this, value);else// 1)当前线程Thread 不存在ThreadLocalMap对象// 2)则调用createMap进行ThreadLocalMap对象的初始化// 3)并将 t(当前线程)和value(t对应的值)作为第一个entry存放至ThreadLocalMap中createMap(t, value);}/* 获取当前线程Thread对应维护的ThreadLocalMap * * @param t the current thread 当前线程* @return the map 对应维护的ThreadLocalMap */ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {return t.threadLocals;}/*创建当前线程Thread对应维护的ThreadLocalMap @param t 当前线程* @param firstValue 存放到map中第一个entry的值*/void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {//这里的this是调用此方法的threadLocalt.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);}

2、get( ) 方法
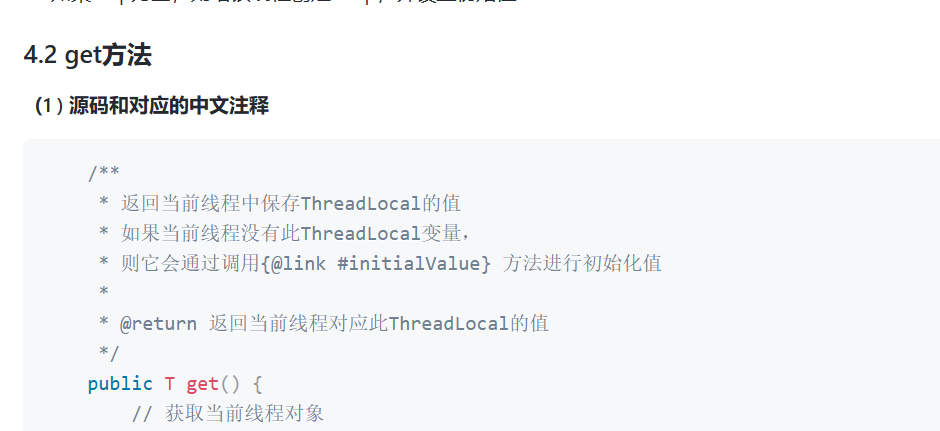
/* 返回当前线程中保存ThreadLocal的值* 如果当前线程没有此ThreadLocal变量,* 则它会通过调用{@link #initialValue} 方法进行初始化值 @return 返回当前线程对应此ThreadLocal的值*/public T get() {// 获取当前线程对象Thread t = Thread.currentThread();// 获取此线程对象中维护的ThreadLocalMap对象ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);// 如果此map存在if (map != null) {// 以当前的ThreadLocal 为 key,调用getEntry获取对应的存储实体eThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);// 对e进行判空 if (e != null) {@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")// 获取存储实体 e 对应的 value值// 即为我们想要的当前线程对应此ThreadLocal的值T result = (T)e.value;return result;}}/*初始化 : 有两种情况有执行当前代码第一种情况: map不存在,表示此线程没有维护的ThreadLocalMap对象第二种情况: map存在, 但是没有与当前ThreadLocal关联的entry*/return setInitialValue();}/* 初始化 @return the initial value 初始化后的值*/private T setInitialValue() {// 调用initialValue获取初始化的值// 此方法可以被子类重写, 如果不重写默认返回nullT value = initialValue();// 获取当前线程对象Thread t = Thread.currentThread();// 获取此线程对象中维护的ThreadLocalMap对象ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);// 判断map是否存在if (map != null)// 存在则调用map.set设置此实体entrymap.set(this, value);else// 1)当前线程Thread 不存在ThreadLocalMap对象// 2)则调用createMap进行ThreadLocalMap对象的初始化// 3)并将 t(当前线程)和value(t对应的值)作为第一个entry存放至ThreadLocalMap中createMap(t, value);// 返回设置的值valuereturn value;}

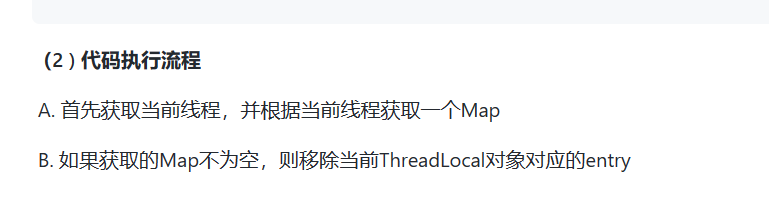
3、remove()方法

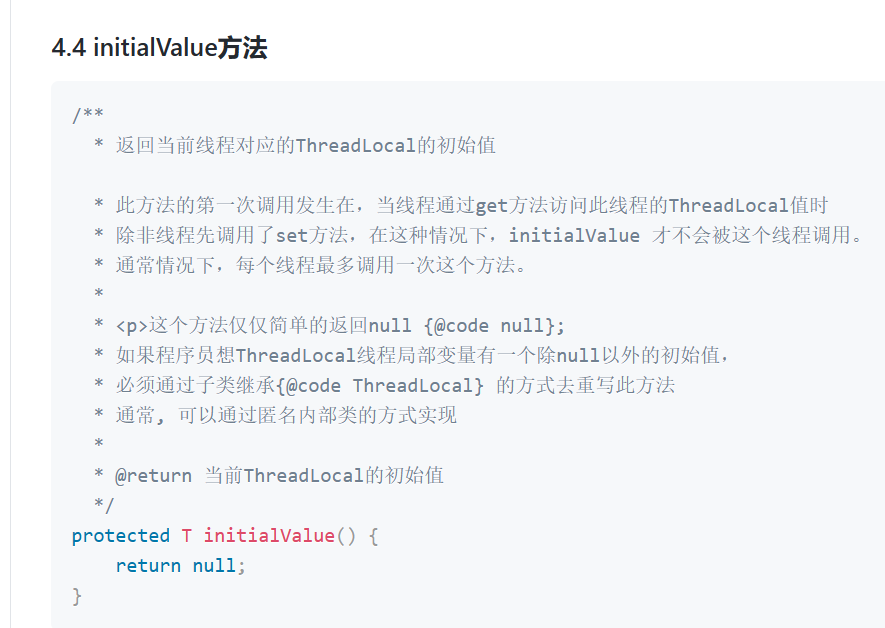
4、initialValue()方法

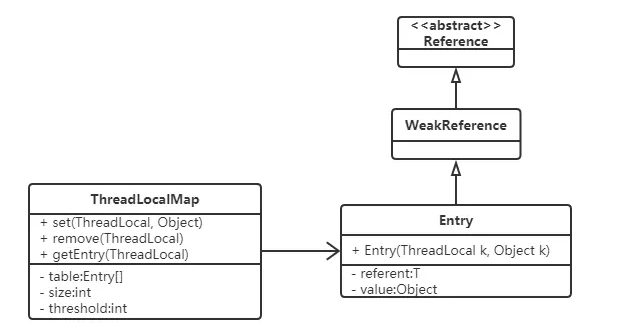
五、ThreadLocalMap源码分析🥑


链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/acfd2239c9f4



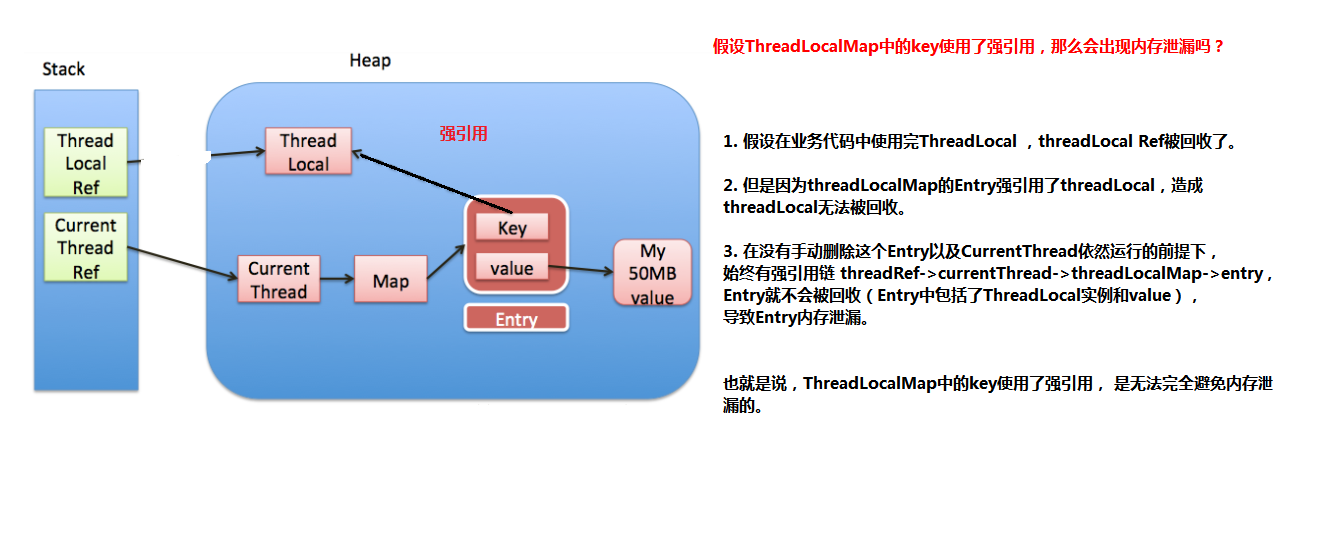
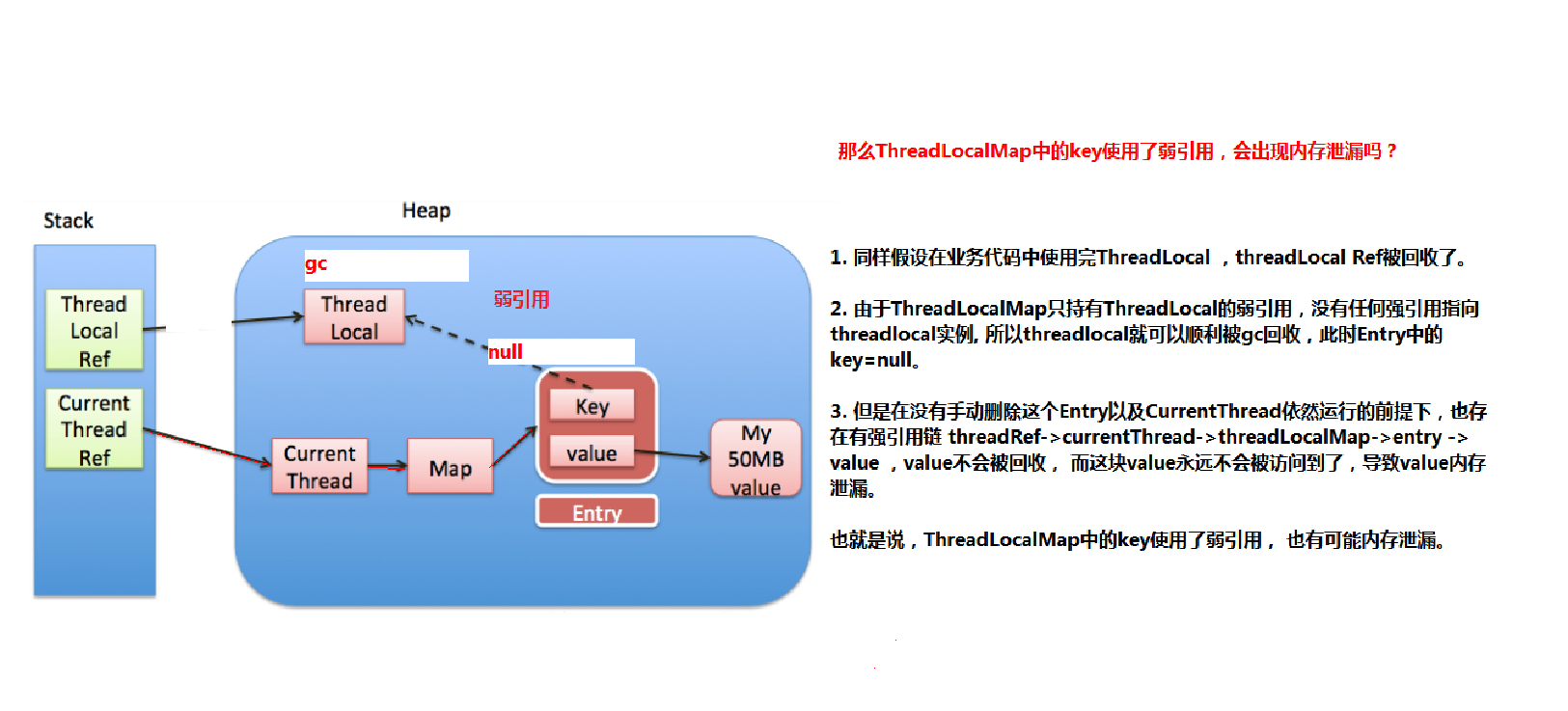
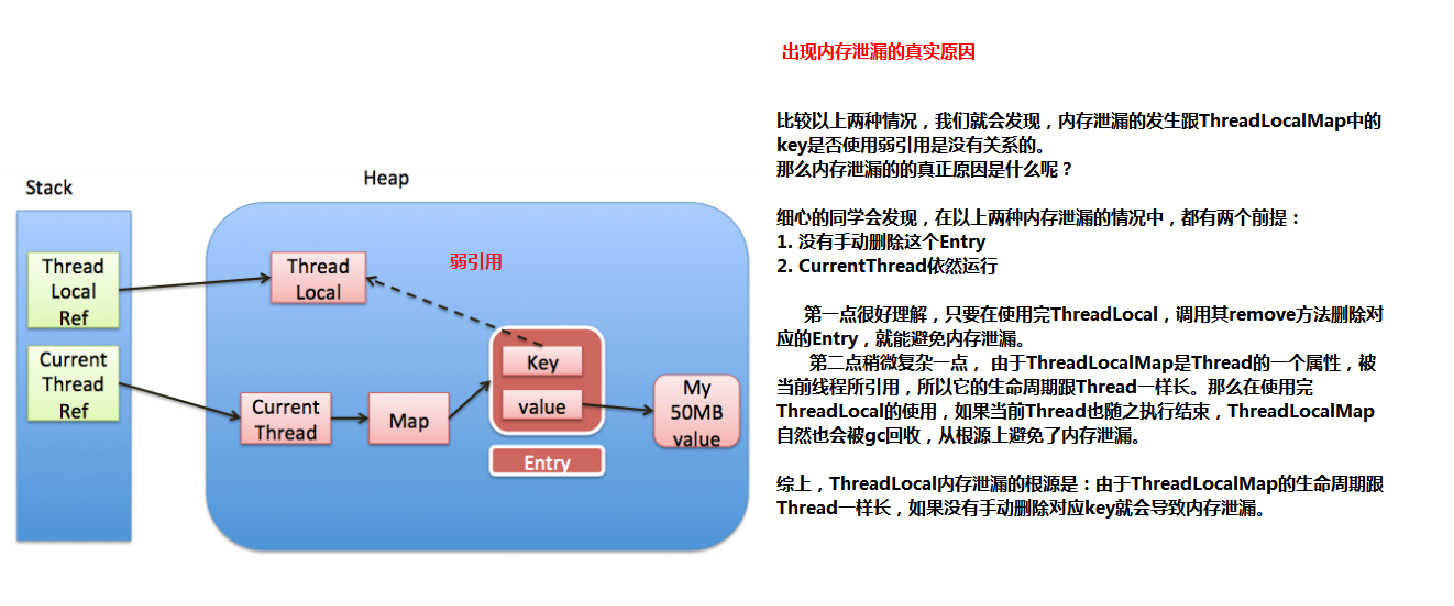







private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap.Entry[] tab = table;int len = tab.length;//计算索引(重点代码,刚才分析过了)int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);/* 使用线性探测法查找元素(重点代码)*/for (ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = tab[i];e != null;e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();//ThreadLocal 对应的 key 存在,直接覆盖之前的值if (k == key) {e.value = value;return;}// key为 null,但是值不为 null,说明之前的 ThreadLocal 对象已经被回收了,// 当前数组中的 Entry 是一个陈旧(stale)的元素if (k == null) {//用新元素替换陈旧的元素,这个方法进行了不少的垃圾清理动作,防止内存泄漏replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);return;}}//ThreadLocal对应的key不存在并且没有找到陈旧的元素,则在空元素的位置创建一个新的Entry。tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);int sz = ++size;/* cleanSomeSlots用于清除那些e.get()==null的元素,* 这种数据key关联的对象已经被回收,所以这个Entry(table[index])可以被置null。* 如果没有清除任何entry,并且当前使用量达到了负载因子所定义(长度的2/3),那么进行 * rehash(执行一次全表的扫描清理工作)*/if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)rehash();
}/* 获取环形数组的下一个索引*/private static int nextIndex(int i, int len) {return ((i + 1 < len) ? i + 1 : 0);}



