虚假评论检测可视化系统的实现

菜鸟一枚,大佬勿喷,主要是想分享,希望能帮到像我一样的人。
主要代码是参考:https://github.com/SoulDGXu/NLPVisualizationSystem/tree/master/frontend
他这个代码实现了词云、摘要生成等功能吧。因为我做的是虚假评论检测系统,就没有使用他这个里面的功能,参考了他的思路和使用 了他的前端界面。
前端是Bootstrap框架完成的,后端是用的Flask和tensorflow框架。tensorflow框架就是自己算法的主体啦。这里的算法是BERT-whitening+LR实现的,准确率也可以的。通过LR_xitong()进行的调用。
主要的功能有:登录注册、单条文本检测、批量文本检测、网页评论爬取。
还是有不足的地方,例如爬取只爬取了一页的内容。
1.app.py
这个代码就是Flask的整个逻辑实现的地方啦,通过路由规则到达指定的页面,然后通过get方式得到页面输入的内容,通过post方式返回内容给前端页面。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""服务:-自动生成词云图:
1. 根据用户输入指定网址,通过采集该网址文本进行处理。
2. 根据用户输入文本字符串进行处理。
3. 根据用户输入载入本地文本进行处理,用户将所需要处理文本文件放入text文本夹中,指定文件名进行处理。-文本关键信息提取
-文本情感分析
-用户评价分析
-用户画像后台设计:
1. 服务接口设计
1.1 页面请求设计
1.2 数据请求设计
2. 异常请求设计"""import os
from src import config
from src.exe import LR_xitong
from src.exe import file
from src.exe import yelp_clawfrom flask import Flask, render_template,send_from_directory
from flask import Flask, render_template, request, redirect, url_for
from flask import request, redirect, json, url_for
from werkzeug.utils import secure_filename
import requests
import json
from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemy
from sqlalchemy import and_# from src.exe import exe_02
# from src.exe import exe_03
# from src.exe import exe_05
# from src.exe import exe_06# from src.exe import exe_01, exe_02, exe_03, exe_05, exe_06## =================================== 路由配置 ===================================#
print(LR_xitong.predict_review())
## Part 1 ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++#==================================================================
#登录,连接数据库
app = Flask(__name__, template_folder=config.template_dir,static_folder=config.static_dir)
HOSTNAME = "127.0.0.1"
PORT = 3306
USERNAME = "root"
PASSWORD = "root"
DATABASE = "database_learn"
app.config['SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI'] = \\f"mysql+pymysql://{USERNAME}:{PASSWORD}@{HOSTNAME}:{PORT}/{DATABASE}?charset=utf8mb4"
app.config['SQLALCHEMY_TRACK_MODIFICATIONS'] = True
db = SQLAlchemy(app)@app.route("/")
def index():return render_template("register.html")
class User(db.Model):__tablename__ = 'user_list1' #(设置表名)id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True) #(设置主键)username = db.Column(db.String(255), unique=True)password = db.Column(db.String(255), unique=True)
# 返回一个可以用来表示对象的可打印字符串:(相当于java的toString)def __repr__(self):return '<User 用户名:%r 密码:%r>' % (self.username, self.password)# 操作数据库
#增
def add_object(user):db.session.add(user)db.session.commit()print("添加 % r 完成" % user.__repr__)
with app.app_context():user = User()user = db.session.merge(user) # 将未绑定的实例或对象合并到会话中# user.username = 'li三'# user.password = '123456'# add_object(user)# 查 (用到and的时候需要导入库from sqlalchemy import and_)
# def query_object(user, query_condition_u, query_condition_p):
# result = user.query.filter(and_(user.username == query_condition_u, user.password == query_condition_p))
# print("查询 % r 完成" % user.__repr__)
# return result
# 删
# def delete_object(user):
# result = user.query.filter(user.username == '11111').all()
# db.session.delete(result)
# db.session.commit()
# #改
# def update_object(user):
# result = user.query.filter(user.username == '111111').all()
# result.title = 'success2018'@app.route("/login",methods=['POST'])
def login():username1=request.form.get("username")password1 = request.form.get("password")if user.query.filter_by(username =username1,password =password1).all()!=[]:# print(user.username,username1,user.password,password1)print("登录成功")return render_template("text_classification1.html")else:print("失败")print(username1,password1)return render_template("register.html")#===========================================================
#注册:
@app.route("/register",methods=['POST'])
def register():username1=request.form.get("username")password1 = request.form.get("password")#判断是否在表中,如果不在,则增加,如果在,则返回已经存在的错误提示if user.query.filter_by(username=username1, password=password1).all() == []:user.username = username1user.password = password1add_object(user)return render_template("login.html")else:print("已经注册过了")message="已经注册过了"return render_template("register.html",message=message)## Part 2 自动生成词云图 ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
def read_file(filepath):"""Read the local file and transform to text.Parameters----------filepath : TYPE-strDESCRIPTION: the text file path.Returns-------content : TYPE-strDESCRIPTION:The preprocessed news text."""f = open(filepath,'r',encoding='utf-8')content = f.read()f.close()return content def save_to_file(filepath, content):f = open(filepath, 'w', encoding='utf-8') f.write(content)f.close()def check_url(url):"""Check if the URL can be accessed normally.Open a simulated browser and visit.If the access is normal, the output is normal, and the error is output.Parameters----------url : TYPE-strDESCRIPTION: the URL.Returns-------content : TYPE-strDESCRIPTION:The preprocessed news text."""import urllibimport timeopener = urllib.request.build_opener()opener.addheaders = [('User-agent', 'Mozilla/49.0.2')] #Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64; rv:6.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/6.0url = url.replace('\\n','').strip()try:opener.open(url)print(url + ' successfully accessed.')return Trueexcept urllib.error.HTTPError:print(url + ' = Error when accessing the page.')time.sleep(2)except urllib.error.URLError:print(url + " = Error when accessing the page.")time.sleep(2)time.sleep(0.1)return False##
## Part 3 文本预处理
## Part 3.2 文本关键信息提取--多文本分析--主题分析### Part 4 文本分类
#/classification_1是单文本
#英文
@app.route("/classification_1",methods=['GET'])
def review_classification_home():return render_template("text_classification1.html")@app.route("/classification_1",methods=['POST'])
def review_classification_input():text=request.form.get('inputtext')text1=text #将输入的文本储存到text1中if not text.isascii(): #如果不是英文url = 'http://fanyi.youdao.com/translate?smartresult=dict&smartresult=rule'data = {'i': text,'from': 'AUTO','to': 'AUTO','smartresult': 'dict','client': 'fanyideskweb','salt': '16071715461327','sign': 'f5d5d5c129878e8e36558fb321b16f85','ts': '1607171546132','bv': 'd943a2cf8cbe86fb2d1ff7fcd59a6a8c','doctype': 'json','version': '2.1','keyfrom': 'fanyi.web','action': 'FY_BY_REALTlME','typoResult': 'false'}# 发送POST请求并获取响应数据response = requests.post(url, data=data)result = json.loads(response.text)# 解析翻译结果并输出translate_result = result['translateResult'][0][0]['tgt']print("翻译结果:", translate_result)text = translate_resulttry:if text!=None:save_to_file(config.classificaion_input_text_path,text) #英文文本save_to_file(config.classificaion_input_text1_path,text1) #输入的中文文本print(text)return redirect('/download_classification')except:return render_template("text_classification1.html")
#
# 文本分类结果
@app.route('/download_classification', methods=['GET'])
def review_classification():cur = LR_xitong.predict_review()print("要返回结果啦")return render_template("classification.html", curinput=cur)# 文本分类结果,下载输出结果
@app.route('/download_classification', methods=['POST'])
def download_review_classification():file_dir, filename = os.path.split(config.download_classification_input_text_save_path)print("要保存啦")return send_from_directory(file_dir, filename, as_attachment=True)
##
#批量文本处理
@app.route("/classification_2",methods=['GET'])
def pilialng():return render_template("text_classification2.html")@app.route('/classification_2', methods=['POST'])
def get_import_file():userfile = request.files.get('loadfile')if userfile:filename = secure_filename(userfile.filename)types = ['xlsx', 'csv', 'xls']if filename.split('.')[-1] in types:uploadpath = os.path.join(config.save_dir, filename)userfile.save(uploadpath)save_to_file(config.wc_input_file_save_path, uploadpath)print('文件上传成功')return redirect('/download_classification_2')else:return render_template("text_classification2.html")#=============================
#批量文本下载
@app.route('/download_classification_2', methods=['GET'])
def rt_keyinfo_import_file():filepath=read_file(config.wc_input_file_save_path)cur = file.predict(filepath) #这里就要把列表的东西返回return render_template("classification2.html", curinput=cur)# 03 tab3关键信息生成-下载输出结果
@app.route('/download_classification_2', methods=['POST'])
def download_keyinfo_3():file.save()return 0#
#输入URL
@app.route("/classification_3", methods=['GET'])
def keyinfo_home_1():return render_template("text_classification3.html")# 01 tab1关键信息提取构建-获取前端输入数据
@app.route('/classification_3', methods=['POST'])
def get_keyinfo_url():url = request.form.get('texturl')[25:]try:save_to_file(config.keyinfo_input_url_path, url)# if check_url(url):# save_to_file(config.keyinfo_input_url_path, url)# print('add URL: ' + url)return redirect('/download_classification_3')except:return render_template("text_classification3.html")# 01 tab1关键信息生成-数据请求@app.route('/download_classification_3', methods=['GET'])
def rt_keyinfo_url():res_name=read_file(config.keyinfo_input_url_path) #这是读的餐厅名字#然后进行爬取,存储到另一个路径yelp_claw.claw(res_name)cur = file.predict('yelp_reviews.csv')return render_template("classification3.html", curinput=cur)# 01 tab1关键信息生成-下载输出结果
@app.route('/download_classification_3', methods=['POST'])
def download_keyinfo_1():file_dir, filename = os.path.split(config.download_keyinfo_input_url_save_path)return send_from_directory(file_dir, filename, as_attachment=True)## ## 异常处理
# 403错误
@app.errorhandler(403)
def miss(e):return render_template('error-403.html'), 403# 404错误
@app.errorhandler(404)
def error404(e):return render_template('error-404.html'), 404# 405错误
@app.errorhandler(405)
def erro405r(e):return render_template('error-405.html'), 405# 500错误
@app.errorhandler(500)
def error500(e):return render_template('error-500.html'), 500# 主函数
if __name__ == "__main__":app.run() - LR_xitong.py
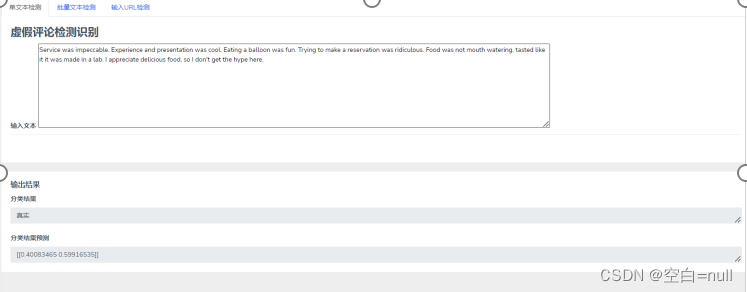
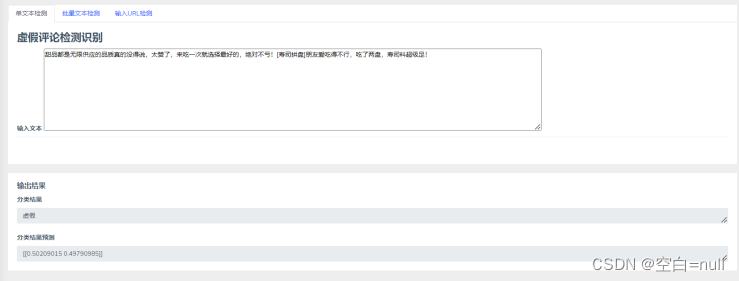
这部分代码就是单条文本检测的实现了,先将数据集进行训练,保存LR模型参数,然后使LR对新得到的句子向量进行判断。
## 基础函数库
import numpy as np## 导入逻辑回归模型函数
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
import pandas as pd
from sklearn import linear_model
from src.exe import Singlesentence
from Singlesentence import *
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras##Demo演示LogisticRegression分类## 构造数据集
train_data_features=pd.read_csv(r'D:\\BaiduNetdiskDownload\\yelp\\new\\BHAN+W\\res.csv') #需要加一行数组标
file_name = r'D:\\BaiduNetdiskDownload\\yelp\\yelp_rzj\\label.csv' #键入训练数据名
label_name = 'label1' #键入标签列标题
#提取评论标签
def getLabel():df_data=pd.read_csv(file_name, encoding='utf-8')data = list(df_data[label_name])return data
label = getLabel()
x_fearures = train_data_features
y_label = label## 调用逻辑回归模型
lr_clf = LogisticRegression()## 用逻辑回归模型拟合构造的数据集
lr_clf = lr_clf.fit(x_fearures, y_label)def predict_review():x_fearures_new1=[vec()]##在训练集和测试集上分布利用训练好的模型进行预测y_label_new1_predict=lr_clf.predict(x_fearures_new1)if y_label_new1_predict[0] == 1:a='真实'else:a='虚假'print('The New point 1 predict class:\\n',a)##由于逻辑回归模型是概率预测模型(前文介绍的p = p(y=1|x,\\theta)),所有我们可以利用predict_proba函数预测其概率y_label_new1_predict_proba=lr_clf.predict_proba(x_fearures_new1)print('The New point 1 predict Probability of each class:\\n',y_label_new1_predict_proba)a1=read_file(config.classificaion_input_text_path) #b=read_file(config.classificaion_input_text1_path)if a1==b:inputtext=a1else:inputtext=bcurinput={'inputtext':inputtext,'a':a,'proba':y_label_new1_predict_proba}return curinput
- singleSentence.py
这部分就是对文本通过BERT-whitening模型进行向量化。
#! -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# 简单的线性变换(白化)操作,就可以达到甚至超过BERT-flow的效果。from utils import *
import os, sys
import numpy as np
import xlsxwriter
import re
from src import config
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
def save_to_file(filepath, content):"""Write the text to the local file.Parameters----------filepath : TYPE-strDESCRIPTION: the file save path.Returns-------content : TYPE-strDESCRIPTION: the text."""f = open(filepath, 'w', encoding='utf-8')f.write(content)f.close()def read_file(filepath):"""Read the local file and transform to text.Parameters----------filepath : TYPE-strDESCRIPTION: the text file path.Returns-------content : TYPE-strDESCRIPTION:The preprocessed news text."""f = open(filepath,'r',encoding='utf-8')content = f.read()f.close()return content
def load_mnli_train_data1(filename):df = pd.read_csv(filename, encoding='gbk')# 划分data与labeldata = df['comment_text']D = []with open(filename, encoding='gbk') as f:for i, l in enumerate(f):if i > 0:l = l.strip().split(',')pattern = r'\\.|\\?|\\~|!|。|、|;|‘|’|【|】|·|!|…|(|)'result_list = re.split(pattern, data[i-1])for text in result_list:D.append((text, l[-1]))return D
def convert_to_ids1(data, tokenizer, maxlen=64):"""转换文本数据为id形式"""a_token_ids= []for d in tqdm(data):token_ids = tokenizer.encode(d, maxlen=maxlen)[0]a_token_ids.append(token_ids)a_token_ids = sequence_padding(a_token_ids)return a_token_idsdef convert_to_vecs1(data, tokenizer, encoder, maxlen=64):"""转换文本数据为向量形式"""a_token_ids = convert_to_ids1(data, tokenizer, maxlen)with session.as_default():with session.graph.as_default():a_vecs = encoder.predict([a_token_ids,np.zeros_like(a_token_ids)],verbose=True)return a_vecsconfig1 = tf.ConfigProto(device_count={'CPU': 1},intra_op_parallelism_threads=1,allow_soft_placement=True
)
session = tf.Session(config=config1)
keras.backend.set_session(session)
#BERT配置config_path = r'D:\\HomeWork\\Paper\\ZhangRong\\BERT\\BERT\\GLUE\\BERT_BASE_DIR\\uncased_L-12_H-768_A-12\\bert_config.json'
checkpoint_path =r'D:\\HomeWork\\Paper\\ZhangRong\\BERT\\BERT\\GLUE\\BERT_BASE_DIR\\uncased_L-12_H-768_A-12\\bert_model.ckpt'
dict_path = r'D:\\HomeWork\\Paper\\ZhangRong\\BERT\\BERT\\GLUE\\BERT_BASE_DIR\\uncased_L-12_H-768_A-12\\vocab.txt'# 建立分词器
tokenizer = get_tokenizer(dict_path)# 建立模型
encoder = get_encoder(config_path, checkpoint_path)# 加载NLI预训练权重encoder.load_weights('D:\\downloads\\BERT-whitening-main\\BERT-whitening-main\\eng\\weights\\_res200.weights')def vec():data=read_file(config.classificaion_input_text_path)print("在vec函数内的",data)# pattern = r'\\.|\\?|\\~|!|。|、|;|‘|’|【|】|·|!|…|(|)'# result_list = re.split(pattern, data)# D1=[]# for text in result_list:# D1.append(text)# nli_data = D1nli_data = data#在这里增加对不符合正常逻辑的句子的判断?还是去除停用词比较好呢?nli_a_vecs= convert_to_vecs1(nli_data, tokenizer, encoder)# nli_a_vecs=nli_a_vecs.reshape((2,384))#得到白化后的向量kernel, bias = compute_kernel_bias([nli_a_vecs],n_components=200)# np.save('weights/hotel.kernel.bias' , [kernel, bias])kernel = kernel[:, :768]a_vecs = transform_and_normalize(nli_a_vecs, kernel, bias) #shape=[8000,768]#需要在这里将[句子数量,768]变成[1,768]a=[0]*200#200是这个最后的向量维度for i in a_vecs:a=a+ioutput = a/len(a_vecs)return output
- 批量文本的处理
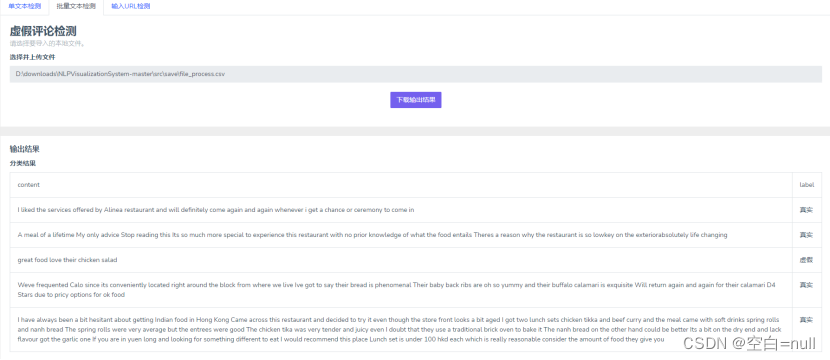
这部分代码和上面单条文本的很像,不同之处就是在predict()函数那里增加了读取文件的操作,将对单文本进行文本向量化变成了对多文本进行文本向量化。
#! -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# 简单的线性变换(白化)操作,就可以达到甚至超过BERT-flow的效果。from utils import *
import os, sys
import numpy as np
import xlsxwriter
import re
from src import config
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
def save_to_file(filepath, content):"""Write the text to the local file.Parameters----------filepath : TYPE-strDESCRIPTION: the file save path.Returns-------content : TYPE-strDESCRIPTION: the text."""f = open(filepath, 'w', encoding='utf-8')f.write(content)f.close()def read_file(filepath):"""Read the local file and transform to text.Parameters----------filepath : TYPE-strDESCRIPTION: the text file path.Returns-------content : TYPE-strDESCRIPTION:The preprocessed news text."""f = open(filepath,'r',encoding='utf-8')content = f.read()f.close()return content
def load_mnli_train_data2(filename):# df = pd.read_csv(filename, encoding='gbk')# 划分data与label# data = df['comment_text']D = []with open(filename, encoding='gbk') as f:for i, l in enumerate(f):if i > 0:D.append(l)return D
def load_mnli_train_data3(filename):df = pd.read_csv(filename, encoding='gbk')data = df['comment_text']D = []for d in data:D.append(d)return D
def convert_to_ids1(data, tokenizer, maxlen=64):"""转换文本数据为id形式"""a_token_ids= []for d in tqdm(data):token_ids = tokenizer.encode(d, maxlen=maxlen)[0]a_token_ids.append(token_ids)a_token_ids = sequence_padding(a_token_ids)return a_token_idsdef convert_to_vecs1(data, tokenizer, encoder, maxlen=64):"""转换文本数据为向量形式"""a_token_ids = convert_to_ids1(data, tokenizer, maxlen)with session.as_default():with session.graph.as_default():a_vecs = encoder.predict([a_token_ids,np.zeros_like(a_token_ids)],verbose=True)return a_vecsconfig1 = tf.ConfigProto(device_count={'CPU': 1},intra_op_parallelism_threads=1,allow_soft_placement=True
)
session = tf.Session(config=config1)
keras.backend.set_session(session)
#BERT配置config_path = r'D:\\HomeWork\\Paper\\ZhangRong\\BERT\\BERT\\GLUE\\BERT_BASE_DIR\\uncased_L-12_H-768_A-12\\bert_config.json'
checkpoint_path =r'D:\\HomeWork\\Paper\\ZhangRong\\BERT\\BERT\\GLUE\\BERT_BASE_DIR\\uncased_L-12_H-768_A-12\\bert_model.ckpt'
dict_path = r'D:\\HomeWork\\Paper\\ZhangRong\\BERT\\BERT\\GLUE\\BERT_BASE_DIR\\uncased_L-12_H-768_A-12\\vocab.txt'# 建立分词器
tokenizer = get_tokenizer(dict_path)# 建立模型
encoder = get_encoder(config_path, checkpoint_path)# 加载NLI预训练权重encoder.load_weights('D:\\downloads\\BERT-whitening-main\\BERT-whitening-main\\eng\\weights\\_res200.weights')# 得到向量
def vec1(nli_data):# 在这里增加对不符合正常逻辑的句子的判断?还是去除停用词比较好呢?# nli_data = preProcess(nli_data) #先将网页那些去除nli_a_vecs = convert_to_vecs1(nli_data, tokenizer, encoder)# 得到白化后的向量kernel, bias = compute_kernel_bias([nli_a_vecs], n_components=200)# np.save('weights/hotel.kernel.bias' , [kernel, bias])kernel = kernel[:, :768]a_vecs = transform_and_normalize(nli_a_vecs, kernel, bias) # shape=[8000,768]# 需要在这里将[句子数量,768]变成[1,768]a = [0] * 200 # 200是这个最后的向量维度for i in a_vecs:a = a + ioutput = a / len(a_vecs)return output## 导入逻辑回归模型函数
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
import pandas as pd
from sklearn import linear_model
from src.exe import Singlesentence
from Singlesentence import *
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras##Demo演示LogisticRegression分类## 构造数据集
train_data_features=pd.read_csv(r'D:\\BaiduNetdiskDownload\\yelp\\new\\BHAN+W\\res.csv') #需要加一行数组标
file_name = r'D:\\BaiduNetdiskDownload\\yelp\\yelp_rzj\\label.csv' #键入训练数据名
label_name = 'label1' #键入标签列标题
#提取评论标签
def getLabel():df_data=pd.read_csv(file_name, encoding='utf-8')data = list(df_data[label_name])return data
label = getLabel()
x_fearures = train_data_features
y_label = label## 调用逻辑回归模型
lr_clf = LogisticRegression()## 用逻辑回归模型拟合构造的数据集
lr_clf = lr_clf.fit(x_fearures, y_label)def predict(filepath):Data = []#开始预测data = load_mnli_train_data3(filepath)for input_text in data:#进行预处理,去掉<br>和索引号input_text = re.sub(r"'", "", input_text)input_text = re.sub(r"[^a-zA-Z0-9\\s]", "", input_text)predict=lr_clf.predict([vec1(input_text)])if predict[0] == 1:a = '真实'Data.append([input_text,a])else:b = '虚假'Data.append([input_text,b])curinput={'Data':Data,'filename':filepath,'url':read_file(config.keyinfo_input_url_path) }print(Data)return curinput
# predict()# def save():
# # 将data内容写到表格中
# dd=pd.DataFrame(predict().Data,columns=['comment','label'])
# file='D:\\downloads\\predict_file.csv'
# dd.to_csv(file)
# return file
#- 爬取网页代码
import requests
import csv# 设置 API 访问密钥和 API 端点 URL
# API_KEY = 'GET https://api.yelp.com/v3/businesses/north-india-restaurant-san-francisco/reviews'
# API_HOST = 'https://api.yelp.com/v3'
# REVIEWS_PATH = '/businesses/{}/reviews'
#
# # 设置餐厅ID和请求头
# business_id = 'NORTH-INDIA-RESTAURANT-SAN-FRANCISCO'
# headers = {'Authorization': 'Bearer %s' % API_KEY}
#
# # 发送评论请求获取餐厅评论
# url = API_HOST + REVIEWS_PATH.format(business_id)#通过请求分析得到店铺的评论接口,然后进行爬取解析Json对象得到想要的内容和特征
def claw(res_name):# businessid=res_namei=0print(res_name+"这是店铺名称")response = requests.get('https://www.yelp.com/biz/{}/review_feed?start={}'.format(res_name,i))reviews = response.json()['reviews']# 将评论数据写入 CSV 文件with open('yelp_reviews.csv', mode='w', encoding='utf-8', newline='') as file:writer = csv.writer(file)writer.writerow(['User Name', 'User_URL', 'Review Data', 'Rating', 'comment_text', 'Review Count'])for review in reviews:user_name = review['user']['altText'] # 用户IDuser_link = review['user']['link'][21:] # 用户个人地址review_count = review['user']['reviewCount'] # 用户评论数量rating = review['rating'] # 评论评分text = review['comment']['text'] # 评论data = review['localizedDate'] # 拿的评论日期writer.writerow([user_name, user_link, data, rating, text, review_count])主要代码好像就这么多了。接下来是可视化界面: