软件分析笔记02---Intermediate Representation

整体contents
compiler (source code ——> machine code)
non-trivial非平凡的
经过 语义分析->语法分析->类型检查等各种trivial的分析(前端),生成中间代码IR->进行non-trivial的分析(及静态分析)。
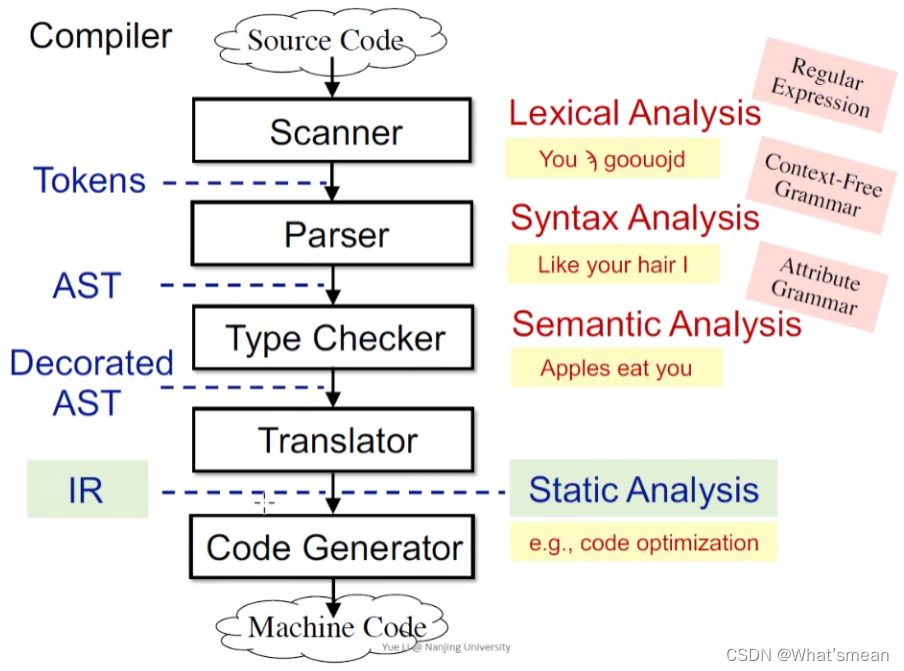
IR介绍
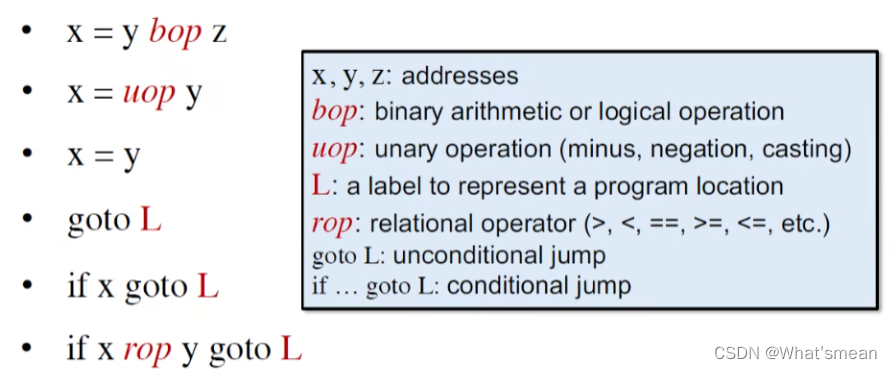
IR为三地址码(3-address)(一个运算符,运算对象1,运算对象2,结果)(因为每个陈述都包含了三个变量,所以它被称为三地址码。)

常用三地址码(简单的)举例:
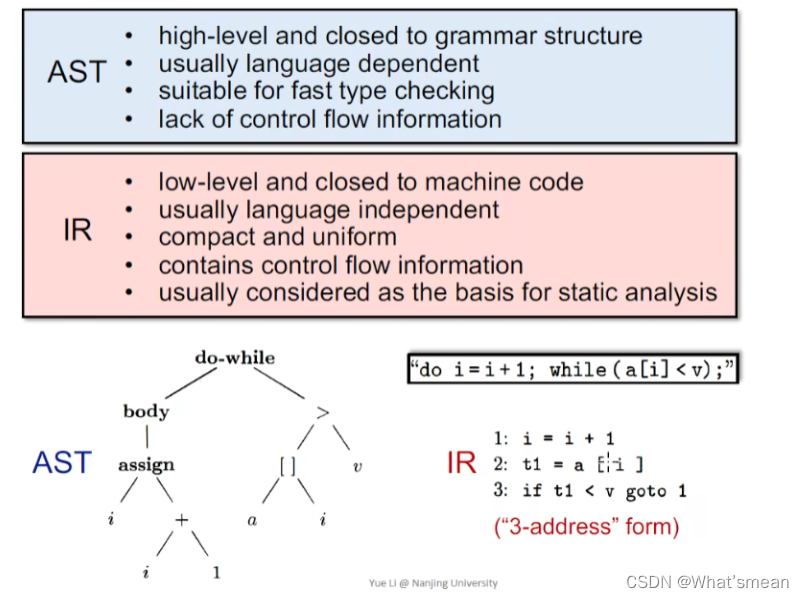
AST vs IR
IR特点:
- 更接近机器语言
- 通常语言都可以转换成IR,对语言无依赖性
- 简洁统一
- 保留了控制流信息
- 有利于进行静态分析
SSA(static single assignment)
给每个definition一个fresh name,如下图

针对最后一条(每个变量只有一个定义)引入的一种function(phi-function 类似于不只一个definition)
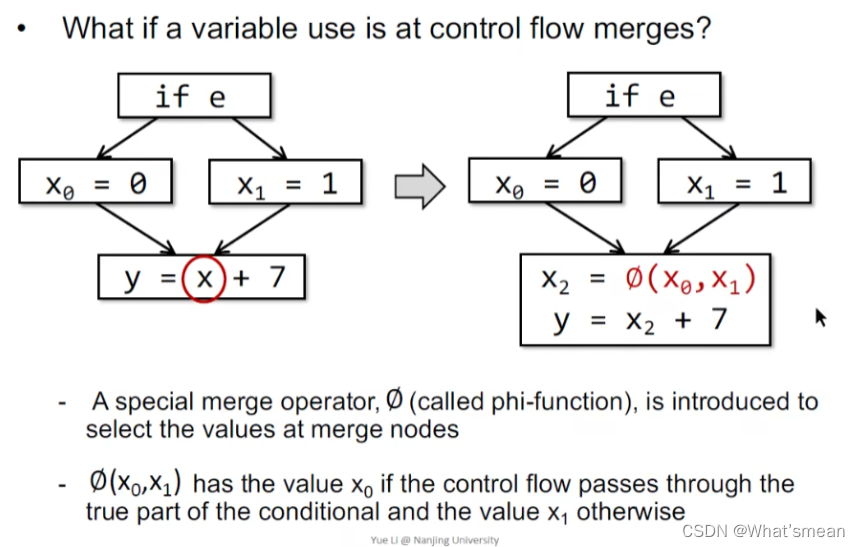
SSA优势:流信息有所保存、定义-使用更明确清楚

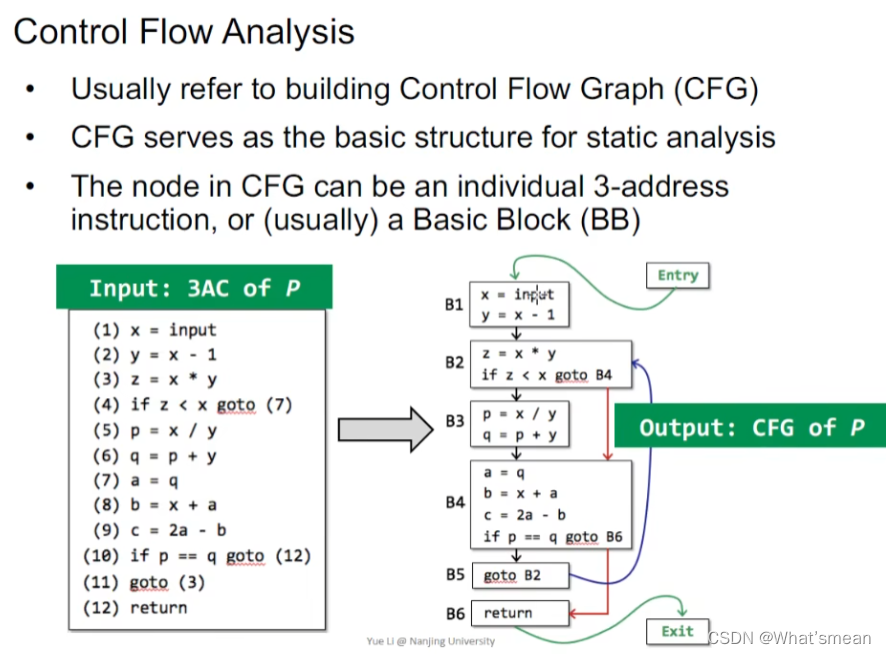
控制流图:
静态分析的基础结构
3AC to CFG
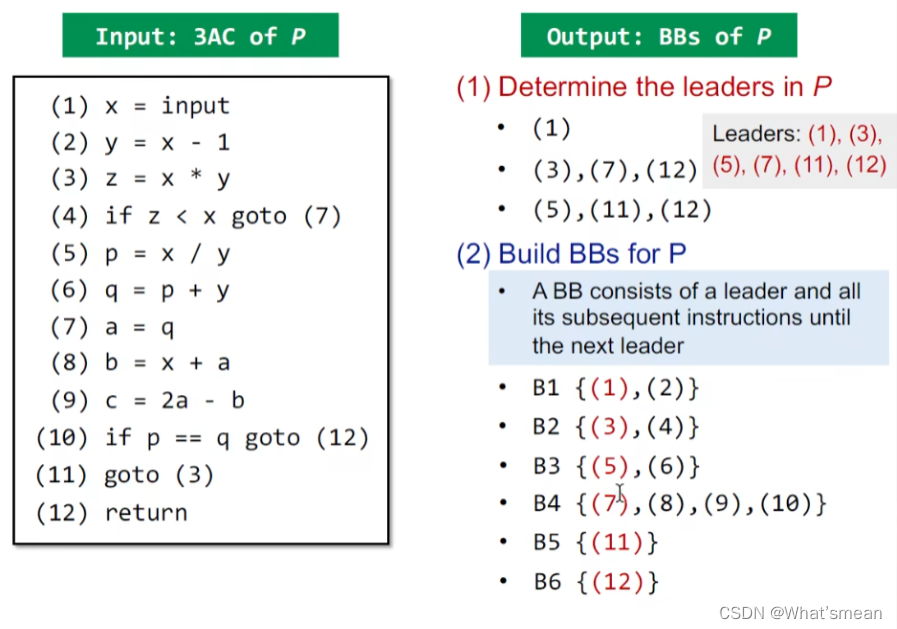
BB块的构建

1.确认leader
- 第一个instruction
- target instruction
- jump之后的第一个instruction
2.构造BB
例子:
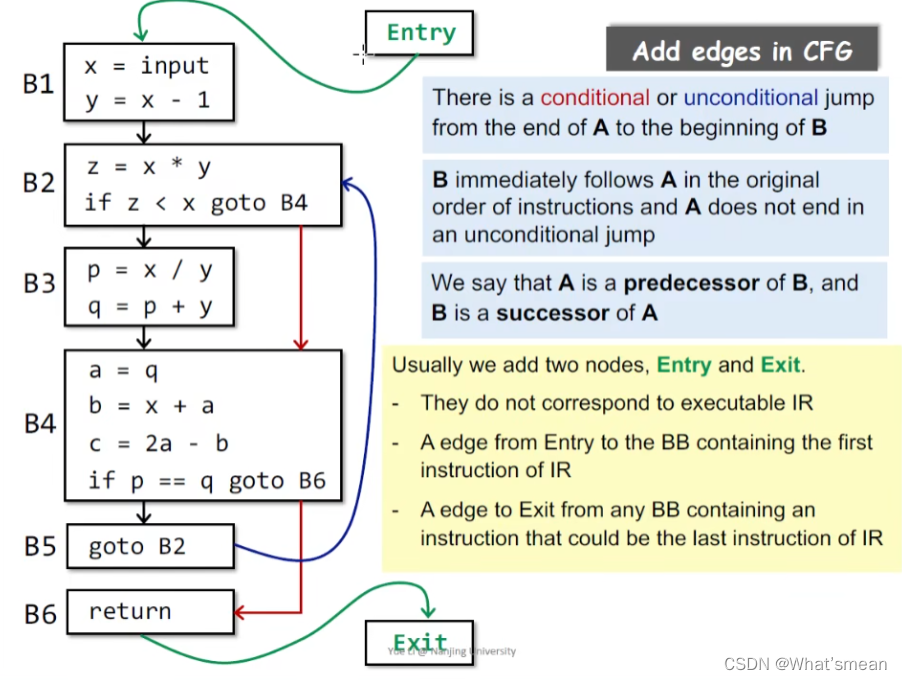
CFG构造:在BB的基础上添加边(哪些需要加,哪些不需要)

PL ---- JVM(方法调用简单介绍)



