双端队列 码蹄集

题目来源:码蹄集
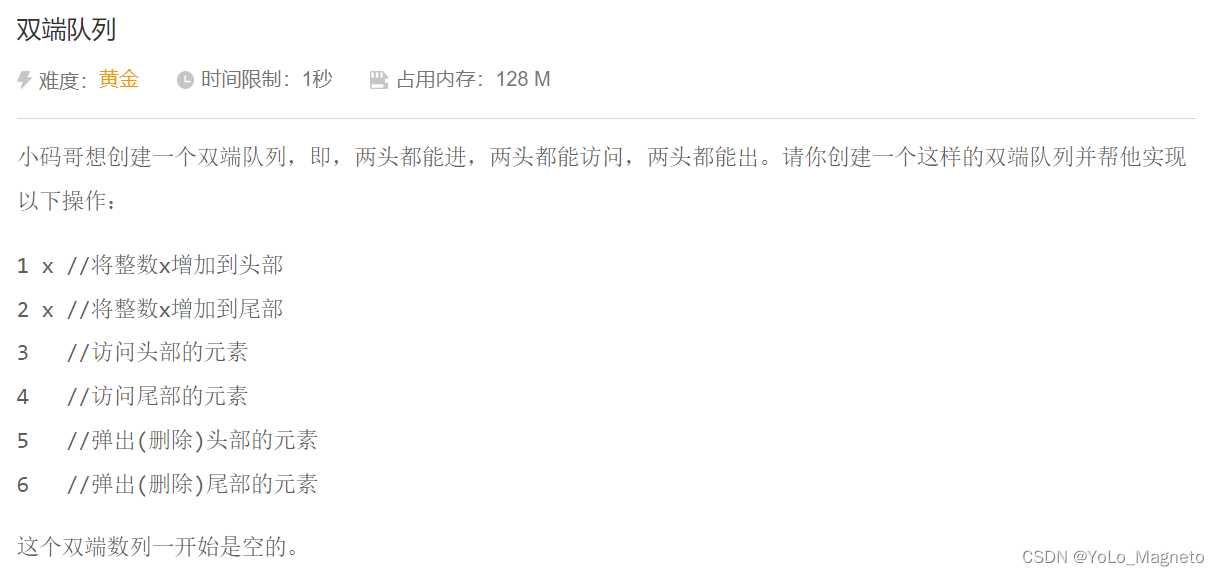
题目描述:


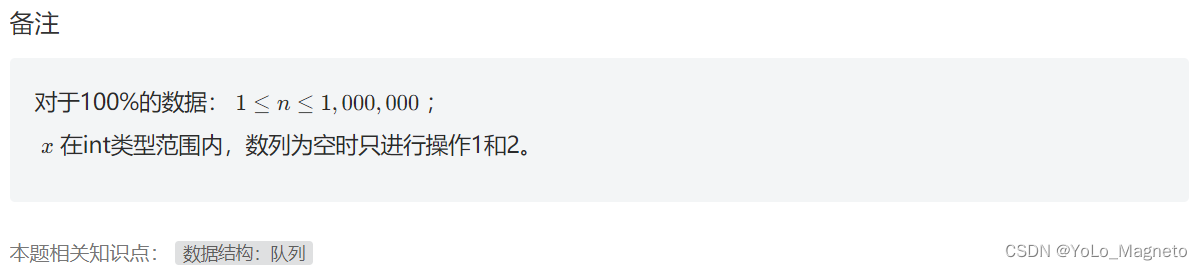
题意分析:
这道题目需要使用到双端队列的数据结构。我们可以借助 STL 中的 deque 来实现这个数据结构。具体来说,我们可以通过 deque 的 push_front 和 push_back 操作在队列的头部和尾部添加元素;通过 front 和 back 操作访问队列的头部和尾部元素;通过 pop_front 和 pop_back 操作删除队列的头部和尾部元素。
具体地,对于每个操作,我们可以按照题意依次执行相应的操作即可:
-
将整数 x 添加到队列的头部,可以使用 deque 的 push_front 操作。
-
将整数 x 添加到队列的尾部,可以使用 deque 的 push_back 操作。
-
访问队列的头部元素,可以使用 deque 的 front 操作。
-
访问队列的尾部元素,可以使用 deque 的 back 操作。
-
删除队列的头部元素,可以使用 deque 的 pop_front 操作。
-
删除队列的尾部元素,可以使用 deque 的 pop_back 操作。
最后,对于每个操作 3 和 4,我们需要输出一行表示答案的整数。
C++代码实现:
原文参考链接:https://betheme.net/dashuju/49396.html?action=onClick
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;int main() {int n, op, x, length;deque<int> ideq;cin >> n;while (n--) {scanf("%d", &op);if (op == 1) {scanf("%d", &x);ideq.push_front(x);} else if (op == 2) {scanf("%d", &x);ideq.push_back(x);} else if (op == 3) {printf("%d\\n", ideq.front());} else if (op == 4) {length = ideq.size();printf("%d\\n", ideq.back());} else if (op == 5) {ideq.pop_front();} else {ideq.pop_back();}}return 0;
}Python代码实现(会超时):
from collections import dequen = int(input())
ideq = deque()for i in range(n):op = list(map(int, input().split()))if op[0] == 1:ideq.appendleft(op[1])elif op[0] == 2:ideq.append(op[1])elif op[0] == 3:print(ideq[0])elif op[0] == 4:print(ideq[-1])elif op[0] == 5:ideq.popleft()else:ideq.pop()Python代码实现(改进):
from collections import deque
import sysn = int(sys.stdin.readline())
ideq = deque()for i in range(n):op = list(map(int, sys.stdin.readline().split()))if op[0] == 1:ideq.appendleft(op[1])elif op[0] == 2:ideq.append(op[1])elif op[0] == 3:if len(ideq) > 0:print(ideq[0])else:print("error")elif op[0] == 4:if len(ideq) > 0:print(ideq[-1])else:print("error")elif op[0] == 5:if len(ideq) > 0:ideq.popleft()else:if len(ideq) > 0:ideq.pop()Java代码实现(会超时):
import java.util.*;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);int n = scan.nextInt();Deque<Integer> ideq = new LinkedList<>();for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {int op = scan.nextInt();if (op == 1) {int x = scan.nextInt();ideq.offerFirst(x);} else if (op == 2) {int x = scan.nextInt();ideq.offerLast(x);} else if (op == 3) {System.out.println(ideq.peekFirst());} else if (op == 4) {System.out.println(ideq.peekLast());} else if (op == 5) {ideq.pollFirst();} else {ideq.pollLast();}}}
}Java代码实现(改进):
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));int n = Integer.parseInt(reader.readLine());Deque<Integer> ideq = new LinkedList<>();for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {String[] line = reader.readLine().split(" ");int op = Integer.parseInt(line[0]);if (op == 1) {int x = Integer.parseInt(line[1]);ideq.offerFirst(x);} else if (op == 2) {int x = Integer.parseInt(line[1]);ideq.offerLast(x);} else if (op == 3) {if (!ideq.isEmpty()) {System.out.println(ideq.peekFirst());} else {System.out.println("error");}} else if (op == 4) {if (!ideq.isEmpty()) {System.out.println(ideq.peekLast());} else {System.out.println("error");}} else if (op == 5) {if (!ideq.isEmpty()) {ideq.pollFirst();}} else {if (!ideq.isEmpty()) {ideq.pollLast();}}}}
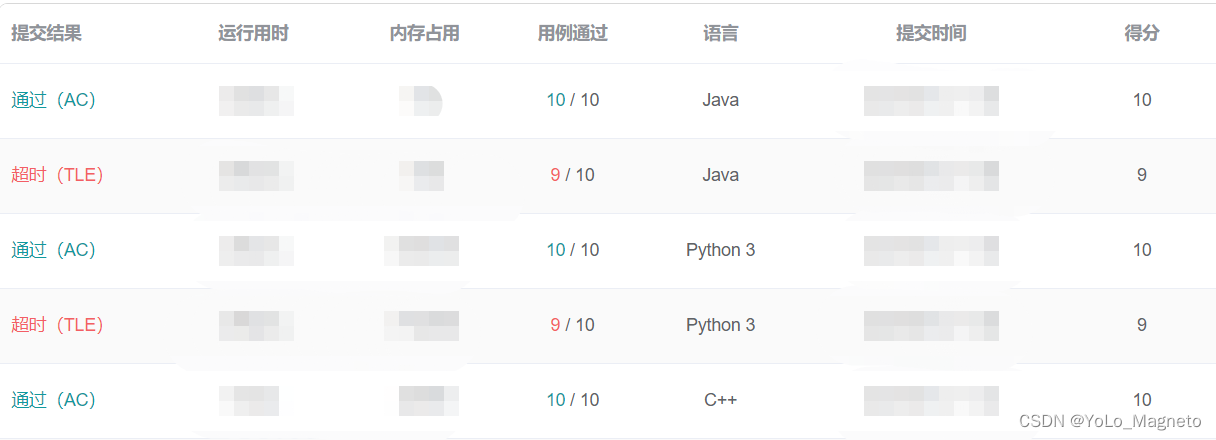
}代码提交测试结果: