3.12、生成者消费者模型

1.生产者消费者模型介绍
-
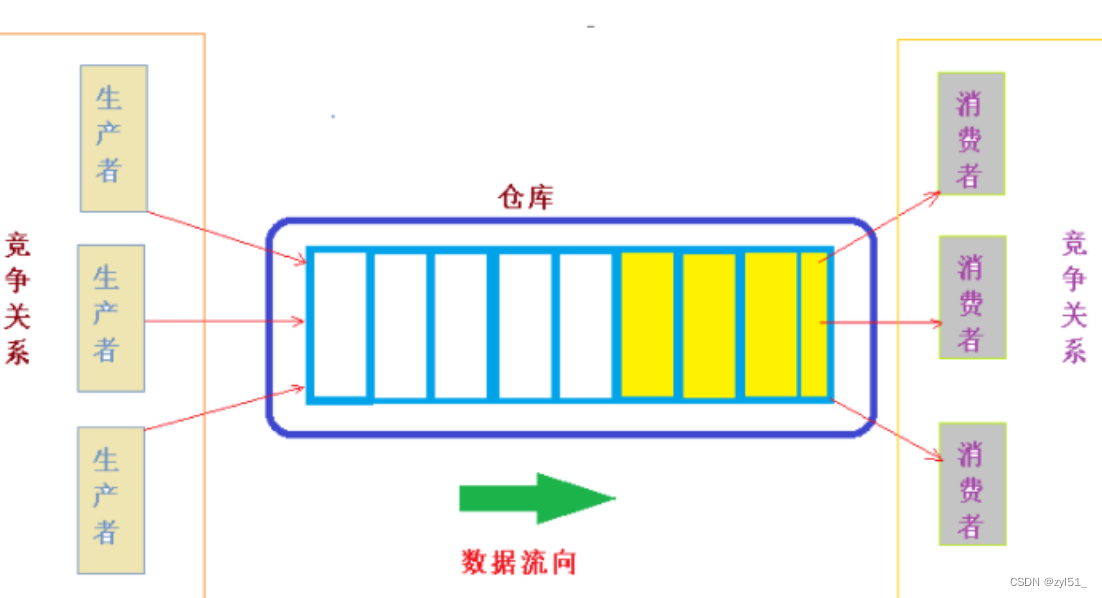
生产者消费者模型是一种多线程的设计模式,用于解决生产者和消费者之间的同步和协作问题。
-
在生产者消费者模型中,生产者和消费者通过共享一个缓冲区来交换信息。生产者向缓冲区中放置数据,消费者从缓冲区中取出数据。但是由于缓冲区是有限的,当生产者向缓冲区放置数据时,如果缓冲区已经满了,那么生产者就必须等待消费者从缓冲区中取出一些数据,以便为新数据腾出空间。同样的,当消费者从缓冲区中取出数据时,如果缓冲区为空,那么消费者就必须等待生产者向缓冲区中放置一些数据,以便取出。
-
在生产者消费者模型中,线程间通信非常重要。为了保证数据的安全和正确性,需要使用同步和互斥机制来控制对共享缓冲区的访问。一般使用信号量或互斥锁来实现线程的同步和互斥。
2.一个没有实现线程同步的生产者消费者模型
/*实现生产者消费者模型- 不考虑容量大小会满- 不考虑消费者会消费完产品因此这是一个错误的生产者消费者模型
*/#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <cstring>
#include <unistd.h>using namespace std;struct Node
{int num;struct Node * next;
};struct Node * head = nullptr;void * producer(void * arg)
{while (1){struct Node * newNode = (struct Node *) malloc(sizeof (struct Node));newNode->num = rand() % 1000;newNode->next = head;head = newNode;printf("add: newNode->num: %d, tid: %ld\\n", newNode->num, pthread_self());usleep(100);}pthread_exit(NULL);
}void * customer(void * arg)
{while (1){struct Node * Num = head;head = head->next;printf("del: Num->num: %d, tid: %ld\\n", Num->num, pthread_self());free(Num);usleep(100);}pthread_exit(NULL);
}int main()
{pthread_t ptid[5], ctid[5];for (int i = 0; i < 5; i ++ ){pthread_create(&ptid[i], NULL, producer, NULL);pthread_create(&ctid[i], NULL, customer, NULL);}for (int i = 0; i < 5; i ++ ){pthread_detach(ptid[i]);pthread_detach(ctid[i]);}while (1){sleep(10);}pthread_exit(NULL);return 0;
}
