c++11 标准模板(STL)(std::unordered_set)(九)

定义于头文件 <unordered_set>
| template<
class Key, > class unordered_set; |
(1) | (C++11 起) |
| namespace pmr {
template <class Key, } |
(2) | (C++17 起) |
查找
返回匹配特定键的元素数量
std::unordered_set<Key,Hash,KeyEqual,Allocator>::count|
size_type count( const Key& key ) const; |
(1) | (C++11 起) |
|
template< class K > |
(2) | (C++20 起) |
1) 返回拥有比较等于指定参数 key 的关键的元素数,因为此容器不允许重复故为 1 或 0 。
2) 返回键比较等价于指定参数 x 的元素数。此重载仅若有限定 Hash::transparent_key_equal 合法并指代类型才参与重载决议。这假设能用 K 和 Key 类型一起调用这种 Hash ,还有其 key_equal 是通透的,进而允许不用构造 Key 的实例就调用此函数。
参数
| key | - | 要计量等价元素数的键值 |
| x | - | 能通透地与键比较的任何类型值 |
返回值
1) 拥有关键 key 的元素数,即 1 或 0 。
2) 键比较等价于 x 的元素数。
复杂度
平均为常数,最坏情况与容器大小成线性。
寻找带有特定键的元素
std::unordered_set<Key,Hash,KeyEqual,Allocator>::find|
iterator find( const Key& key ); |
(1) | |
|
const_iterator find( const Key& key ) const; |
(2) | |
|
template< class K > iterator find( const K& x ); |
(3) | (C++20 起) |
|
template< class K > const_iterator find( const K& x ) const; |
(4) | (C++20 起) |
1,2) 寻找键等于 key 的的元素。
3,4) 寻找键比较等价于值 x 的元素。此重载仅若有限定 Hash::transparent_key_equal 合法并指代类型才参与重载决议。这假设能用 K 和 Key 类型一起调用这种 Hash ,还有其 key_equal 是通透的,进而允许不用构造 Key 的实例就调用此函数。
参数
| key | - | 要搜索的元素键值 |
| x | - | 能通透地与键比较的任何类型值 |
返回值
指向键等于 key 的元素的迭代器。若找不到这种元素,则返回尾后(见 end() )迭代器。
复杂度
平均为常数,最坏情况与容器大小成线性。
返回匹配特定键的元素范围
std::unordered_set<Key,Hash,KeyEqual,Allocator>::equal_range|
std::pair<iterator,iterator> equal_range( const Key& key ); |
(1) | (C++11 起) |
|
std::pair<const_iterator,const_iterator> equal_range( const Key& key ) const; |
(2) | (C++11 起) |
|
template< class K > |
(3) | (C++20 起) |
|
template< class K > |
(4) | (C++20 起) |
1,2) 返回容器中所有键等于 key 的元素范围。范围以二个迭代器定义,第一个指向所需范围的首元素,而第二个指向范围的尾后一位元素。
3,4) 返回含有容器中所有键等价于 x 的元素的范围。此重载仅若有限定 Hash::transparent_key_equal 合法并指代类型才参与重载决议。这假设能用 K 和 Key 类型一起调用这种 Hash ,还有其 key_equal 是通透的,进而允许不用构造 Key 的实例就调用此函数。
参数
| key | - | 要与元素比较的键值 |
| x | - | 任何能与键通透比较的类型的值 |
返回值
含一对定义所需范围的迭代器的 std::pair 。若无这种元素,则将尾后(见 end() )迭代器作为 pair 的两个元素返回。
复杂度
平均情况与带关键 key 的元素数成线性,最坏情况与容器大小成线性。
调用示例
#include <iostream>
#include <forward_list>
#include <string>
#include <iterator>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <time.h>using namespace std;struct Cell
{int x;int y;Cell() = default;Cell(int a, int b): x(a), y(b) {}Cell &operator +=(const Cell &cell){x += cell.x;y += cell.y;return *this;}Cell &operator +(const Cell &cell){x += cell.x;y += cell.y;return *this;}Cell &operator *(const Cell &cell){x *= cell.x;y *= cell.y;return *this;}Cell &operator ++(){x += 1;y += 1;return *this;}bool operator <(const Cell &cell) const{if (x == cell.x){return y < cell.y;}else{return x < cell.x;}}bool operator >(const Cell &cell) const{if (x == cell.x){return y > cell.y;}else{return x > cell.x;}}bool operator ==(const Cell &cell) const{return x == cell.x && y == cell.y;}
};struct myCompare
{bool operator()(const int &a, const int &b){return a < b;}
};std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Cell &cell)
{os << "{" << cell.x << "," << cell.y << "}";return os;
}std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const std::pair<const int, Cell> &pCell)
{os << pCell.first << "-" << pCell.second;return os;
}struct CHash
{size_t operator()(const Cell& cell) const{size_t thash = std::hash<int>()(cell.x) | std::hash<int>()(cell.y);
// std::cout << "CHash: " << thash << std::endl;return thash;}
};struct CEqual
{bool operator()(const Cell &a, const Cell &b) const{return a.x == b.x && a.y == b.y;}
};int main()
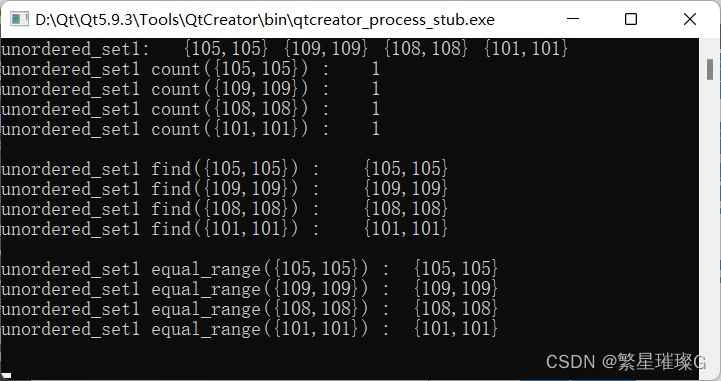
{std::cout << std::boolalpha;std::mt19937 g{std::random_device{}()};srand((unsigned)time(NULL));auto generate = [](){int n = std::rand() % 10 + 100;Cell cell{n, n};return cell;};std::unordered_set<Cell, CHash, CEqual> unordered_set1;//6) 插入来自 initializer_list ilist 的元素。若范围中的多个元素拥有比较等价的关键,则插入哪个元素是未指定的unordered_set1.insert({generate(), generate(), generate(), generate(), generate(), generate()});std::cout << "unordered_set1: ";std::copy(unordered_set1.begin(), unordered_set1.end(), std::ostream_iterator<Cell>(std::cout, " "));std::cout << std::endl;for (std::unordered_set<Cell, CHash, CEqual>::const_iterator cit =unordered_set1.cbegin(); cit != unordered_set1.end(); cit++){//1) 返回拥有比较等于指定参数 key 的关键的元素数,因为此容器不允许重复故为 1 或 0 。std::cout << "unordered_set1 count(" << *cit << ") : "<< unordered_set1.count(*cit) << std::endl;}std::cout << std::endl;for (std::unordered_set<Cell, CHash, CEqual>::const_iterator cit =unordered_set1.cbegin(); cit != unordered_set1.end(); cit++){//1,2) 寻找键等于 key 的的元素。std::unordered_set<Cell, CHash, CEqual>::const_iterator fit = unordered_set1.find(*cit);std::cout << "unordered_set1 find(" << *cit << ") : " << *fit << std::endl;}std::cout << std::endl;for (std::unordered_set<Cell, CHash, CEqual>::const_iterator cit =unordered_set1.cbegin(); cit != unordered_set1.end(); cit++){//1,2) 返回容器中所有键等于 key 的元素范围。//范围以二个迭代器定义,第一个指向所需范围的首元素,而第二个指向范围的尾后一位元素。std::pair<std::unordered_set<Cell, CHash, CEqual>::const_iterator,std::unordered_set<Cell, CHash, CEqual>::const_iterator> pit = unordered_set1.equal_range(*cit);std::cout << "unordered_set1 equal_range(" << *cit << ") : ";for (std::unordered_set<Cell, CHash, CEqual>::const_iterator it = pit.first; it != pit.second; it++){std::cout << *it << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;}std::cout << std::endl;return 0;
}输出