day-004-链表-两两交换链表中的节点、删除链表的倒数第N个节点、链表相交、环形链表II

两两交换链表中的节点
题目建议:用虚拟头结点,这样会方便很多。
题目链接/文章讲解/视频讲解
/* Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {if ( head == NULL ) return head;if ( head->next == NULL ) return head;ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode();dummyHead->next = head;ListNode* cur = dummyHead;while (cur->next) {if (cur->next->next) {ListNode* temp = cur->next;cur->next = temp->next;temp->next = temp->next->next;cur->next->next = temp;cur = temp;}else {cur = cur->next;}}head = dummyHead->next;delete dummyHead;return head;}
};
思路
没有太多难度,按自己的习惯可能更喜欢建立四个指针变量保存所有涉及到的结点。
时间复杂度O(n)
空间复杂度O(1)
注意
无
19.删除链表的倒数第N个节点
双指针的操作,要注意,删除第N个节点,那么我们当前遍历的指针一定要指向 第N个节点的前一个节点,建议先看视频。
题目链接/文章讲解/视频讲解
/* Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/class Solution {
public:ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0);dummyHead->next = head;ListNode* slow = dummyHead;ListNode* fast = dummyHead;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {fast = fast->next;}while (fast->next) {fast = fast->next;slow = slow->next;}ListNode* temp = slow->next;slow->next = temp->next;delete temp;head = dummyHead->next;delete dummyHead;return head;}
};
思路
二刷还是有印象双指针的,还是挺快的。
时间复杂度O(n)
空间复杂度O(1)
注意
由于有dummyHead,slow本身就在dummyHead开始,所以快指针先走n个,不需要多走一个,slow就在需要删除的结点的前一个了。
面试题 02.07. 链表相交
本题没有视频讲解,大家注意 数值相同,不代表指针相同。
题目链接/文章讲解/视频讲解
/* Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
private:int getListSize(ListNode* head) {int size = 0;ListNode* cur = head;while (cur) {size++;cur = cur->next;}return size;}public:ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {int size_a, size_b;size_a = getListSize(headA);size_b = getListSize(headB);if (size_a < size_b) {swap(size_a, size_b);swap(headA, headB);}ListNode* cur = headA;for (int i = 0; i < size_a - size_b; i++) {cur = cur->next;}ListNode* cur_b = headB;for (int i = 0; i < size_b; i++) {if (cur == cur_b) return cur;cur = cur->next;cur_b = cur_b->next;}return NULL;}
};
思路
相同指针有相同地址,后续的节点都相同,所以可以从后往前想。在相交节点之后他们一定有相同的节点数量。
时间复杂度O(n)
空间复杂度O(1)
注意
注意要对长链表和短链表做适合代码逻辑的交换,以统一代码内容。
交换用swap()
142.环形链表II
算是链表比较有难度的题目,需要多花点时间理解 确定环和找环入口,建议先看视频。
题目链接/文章讲解/视频讲解
/* Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {ListNode* slow = head;ListNode* fast = head;while (fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;if (slow == fast) {// x + y + n (y + z) = 2 (x +y)// n (y + z) = x +y// 当 n 取 1:z = xslow = head;while (slow != fast) {slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next;}return slow;}}return NULL;}
};
思路
这题还是需要最好画个图来做的,一开始总是默认想着在相交点相遇,不太清醒。画个图,在环中间相遇,就很清晰。
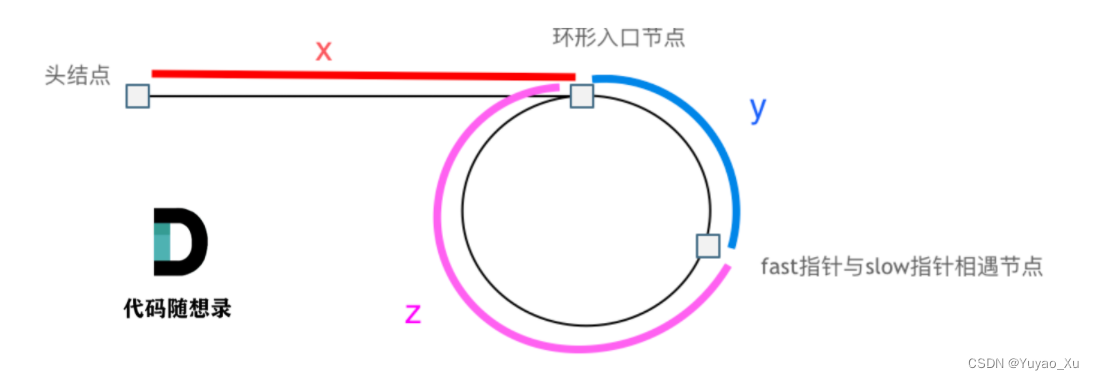
// x + y + n (y + z) = 2 (x +y)
// n (y + z) = x +y
// 当 n 取 1:z = x
时间复杂度O(n)
空间复杂度O(1)
注意
要多画图,多数学公式推导。
