Kotlin作用域函数对比:let、also、run、apply、with

文章参考
文章参考
1、作用域函数对比
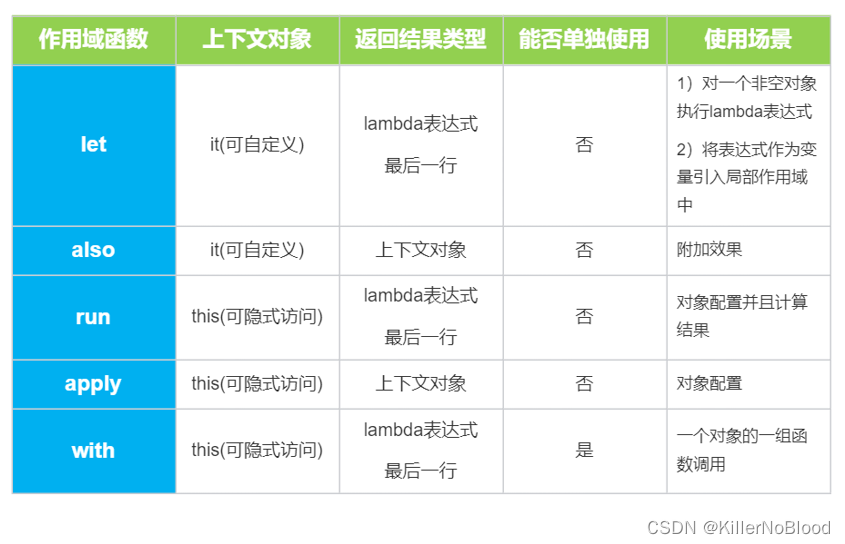
let:返回最后一行
also:与let相似,但返回上下文
with:this隐式访问,返回最后一行
run:let和with的结合体,返回最后一行
apply:与run相似,但返回上下文
注:
尽量避免过度使用作用域函数,会降低代码可读性;
尽量避免嵌套使用作用域函数;
链式调用时注意区分开上下文对象(it或this)
2、使用场景、特点
2.1、 let()函数
- 使用场景:可空变量的操作,无需判空
fun testLet(p: People?) {//返回值为最后一行p?.let {it.name = "leon"it.sex = "man"it.age = "26"it.displayInfo() //name: leon, sex: man, age: 26}p!!.displayInfo() //name: leon, sex: man, age: 26
}
- 特点:
- 返回值为最后一行
2.2、also()函数
- 使用场景:多个扩展函数链式调用
fun testAlso(p: People?) {//返回值上下文p?.also {it.name = "leon"it.sex = "man"it.age = "26"it.displayInfo() //name: leon, sex: man, age: 26}?.displayInfo() //name: leon, sex: man, age: 26p!!.displayInfo() //name: leon, sex: man, age: 26
}
- 特点:
- 与let相似
- 可以做空异常处理
- 返回值为本身,可以做链式调用处理
2.3、with()函数
- 使用场景:用于调用同一个类的多个方法时,如果比较懒连it都不想写,可以省去类名重复,直接调用类的方法就行
fun testWith(p: People?) {//返回最后一行//with无法判空with(p) {this?.name = "leon"this?.sex = "man"this?.age = "26"this?.displayInfo()}//用let判空p?.let {with(it) {name = "leon"sex = "man"age = "26"displayInfo()}}
}
- 特点
- 需要传对象, 用this或省略代表对象本身
- 没有做空异常处理
- 返回值为最后一行
2.4 run()函数
- 使用场景:let和with使用的所有场景。(run结合了let和with两者的特点)
fun testRun(p: People?) {//返回最后一行//【方式一 with】: run(T)run {p?.name = "leon"p?.sex = "man"p?.age = "26"p?.displayInfo()}//【方式二 let】: T.run{}p?.run {name = "leon"sex = "man"age = "26"displayInfo()}
}
- 特点:
- run函数是let和with的结合体, 用this或省略代表对象本身
- 可以做空异常处理
- 返回值为最后一行
2.5、apply()函数
- 使用场景:需要对对象本身做一些操作,然后返回对象本身
- 对象实例初始化,需要对对象属性初始化赋值
- 动态inflate出一个XML的View的时候需要给View绑定数据也会用到
fun testApply(p: People?) {//返回上下文p?.apply {name = "leon"sex = "man"age = "26"displayInfo()}?.displayInfo()
}
- 特点:
- 与run相似,也是this或者省略代表本身
- 可以做空异常处理
- 返回值为本身,可以做链式调用处理
