剑指offer:关于二叉树的汇总(c++)

1、重建二叉树:
输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请重建出该二叉树。假设输入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果中都不含重复的数字。例如输入前序遍历序列{1,2,4,7,3,5,6,8}和中序遍历序列{4,7,2,1,5,3,8,6},则重建二叉树并返回。
2、树的子结构:
输入两棵二叉树A和B,判断B是不是A的子结构。如图:A中有一部分子树的结构和B是一样的,因此B是A的子结构
#include<stdio.h>using namespace std;struct Node
{int value;//根节点BinaryTreeNode* m_pLeft;//左孩子BinaryTreeNode* m_pRight;//右孩子
}//判断二叉树A是否包含二叉树B
//1->A;2->B
bool DoseTree1HaveTree2(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot1, BinaryTreeNode* pRoot2)
{//如果二叉树B节点全部遍历完,返回falseif(pRoot2 == NULL)return false;//如果遍历完二叉树A的全部结点,并且二叉树2未遍历结束,返回falseif(pRoot1 == NULL)return false;//如果遍历过程中有二叉树的结点不相同,遍历结束,返回falseif(pRoot1->value != pRoot2->value)return false;//递归遍历二叉树的所有左右子树return DoseTree1HaveTree2(pRoot1->m_pLeft, pRoot2->m_pLeft)&&DoseTree1HaveTree2(pRoot1->m_pRight, pRoot2->m_pRight);
}//判断两棵树的根结点是否相同
bool HasSubtree(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot1, BinaryTreeNode* pRoot2)
{bool result = false;if(pRoot1 != NULL && pRoot2 != NULL){//如果两个根节点相同,就是找到了if(pRoot1 ->value == pRoot2 ->value)result = DoseTree1HaveTree2(pRoot1,pRoot2);//如果未找到,则从左子树开始寻找if(!result) return = HasSubtree(pRoot1->m_pRight,pRoot2);//如果未找到,从右子树中查找if (!result)result = HasSubtree(pRoot1->m_pRight, pRoot2);}return result;
}3、二叉树的镜像
请完成一个函数,输入一个二叉树,该函数输出它的镜像。如图,右边的二叉树就是左边的树的镜像。
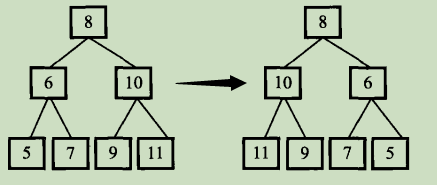
#include <iostream>struct BinaryTreeNode
{int m_nValue;BinaryTreeNode* m_pLeft;BinaryTreeNode* m_pRight;
};// 生成二叉树镜像
void MirrorRecursively (BinaryTreeNode *pNode)
{// 如果结点为空,停止递归if (pNode == nullptr)return;// 交换左右子树std::swap(pNode->m_pLeft,pNode->m_pRight);// 当左子树非空时,递归生成左子树镜像if (pNode->m_pLeft)MirrorRecursively(pNode->m_pLeft);// 当右子树非空时,递归生成右子树镜像if (pNode->m_pRight)MirrorRecursively(pNode->m_pRight);
}int main()
{return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
4、从上往下打印二叉树
从上往下打印出二叉树的每个结点,同一层的结点按照从左到右的顺序打印。
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;struct BinaryTreeNode
{int value;BinaryTreeNode*m_pLeft;BinaryTreeNode*m_pRight;
};//从上往下打印
void PrintTree(BinaryTreeNode *pTreeRoot)
{if(pTreeRoot != NULL)return;queue<BinaryTreeNode *> queNode;queNode.push(pTreeRoot);while (!queNode.empty()){BinaryTreeNode *pNode =queNode.front();queNode.pop();cout << pNode->value << " ";if (pNode->p_left)queNode.push(pNode->p_left);if (pNode->p_right)queNode.push(pNode->p_right);}}int main()
{queue<BinaryTreeNode>data;BinaryTreeNode n1{5, nullptr, nullptr};BinaryTreeNode n2{7, nullptr, nullptr};BinaryTreeNode n3{9, nullptr, nullptr};BinaryTreeNode n4{11, nullptr, nullptr};BinaryTreeNode n5{6, &n1, &n2};BinaryTreeNode n6{10, &n3, &n4};BinaryTreeNode n7{8, &n5, &n6};PrintTree(&n7);return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}5、二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
输入一个整数数组,判断该数组是不是某二叉搜索树的后序遍历的结果。假设输入的数组的任意两个数字都互不相同
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;bool VerifySequenceOfBST(int sequence[], int length)
{if(sequence == NULL || length <= 0)return false;int root = length - 1;int i = 0;for(;i<length-1;++i){if(sequence[i] > root)break;}int j = i;for(;j<length-1;++j){if(sequence[j] < root)return false;}//只有当两个结点都为真才可以bool left = true;if (i > 0)left = VerifySequenceOfBST(sequence, i);bool right = true;if (i < length - 1)right = VerifySequenceOfBST(sequence + i, length - i - 1);return (left && right);
}int main()
{int binary_sort_tree[] = {5,7,6,9,11,10,8};cout << "The result is "<< VerifySequenceOfBST(binary_sort_tree, sizeof(binary_sort_tree)/ sizeof(int)) << endl;return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}6、二叉树中和为某一值的路径
class Soultion
{puclic:vector<vector<int>>result;vector<int>tmp;vector<vector<int> > FindPath(TreeNode* root,int sum){if(root == NULL)return NULL;tmp.push_back(root->val);if(root->left == NULL && root->right && sum->root->val ==0)result.push_back(tmp);//如果不是父节点就是子节点FindPath(root->left,sum->root->val);FindPath(root->right,sum->root->val);if(tmp.size()>0)temp.pop_back();return result;}
};
7、二叉搜索树与双向链表
8、二叉树的深度
输入一棵二叉树的根结点,求该树的深度
思路:如果一棵树只有一个结点,它的深度为1。如果根结点只有左子树,那么树的深度应该是该其左子树的深度加1;同样如果根结点只有右子树而没有左子树,那么树的深度是其右子树的深度加1。如果既有右子树又有左子树,那该树的深度就是其左、右子树的深度较大值再加1。
头文件:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;struct BinaryTreeNode
{int m_nValue;BinaryTreeNode* m_pLeft;BinaryTreeNode* m_pRight;
};算法内容:
int TreeDepth(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot)
{if(pRoot == NULL)return;int nLeft = TreeDepth(pRoot->m_pLeft);int nRight = TreeDepth(pRoot->m_pRight);return (nLeft > nRight) ? (nLeft + 1) : (nRight + 1);
}主函数:
int main()
{BinaryTreeNode n8{8, nullptr, nullptr};BinaryTreeNode n7{7, nullptr, nullptr};BinaryTreeNode n6{6, nullptr, nullptr};BinaryTreeNode n5{5, nullptr, nullptr};BinaryTreeNode n4{4, &n8, nullptr};BinaryTreeNode n3{3, &n6, &n7};BinaryTreeNode n2{2, &n4, &n5};BinaryTreeNode n1{1, &n2, &n3};int depth = 0;cout << "The depth is: " << TreeDepth(&n1) << endl<< "Is a Balance Tree ? : " << IsBalanced(&n1, &depth) << endl;return 0;
}
9、平衡二叉树
题目:输入一棵二叉树,判断该二叉树是否是平衡二叉树
思想:如果某二叉树中任意节点的左右子树的深度相差不超过1,那么它就是一棵平衡二叉树。
class Solution
{
public:
bool IsBalanced_Solution(TreeNode* pRoot)
{if(pRoot == NULL)return true;int depth = 0;return IsBalanced(pRoot, &depth);
}private:
bool IsBalanced(TreeNode *pRoot, int *depth)
{if(pRoot == NULL){*depth =0;return true;}int left,right;if(IsBalanced(pRoot->left, &left) && IsBalanced(pRoot->right, &right)){int diff = left - right;if(diff <= 1 && diff >= -1){*depth = left>right?(left+1):(right+1);return true;}}return false;
}
};10、二叉树的下一个结点
*/
/*分析二叉树的下一个节点,一共有以下情况:
1.二叉树为空,则返回空;
2.节点右孩子存在,则设置一个指针从该节点的右孩子出发,一直沿着指向左子结点的指针找到的叶子节点即为下一个节点;
3.节点不是根节点。如果该节点是其父节点的左孩子,则返回父节点;否则继续向上遍历其父节点的父节点,重复之前的判断,返回结果*/
class Solution {
public:TreeLinkNode* GetNext(TreeLinkNode* pNode){if(pNode==NULL)return NULL;if(pNode->right!=NULL){pNode = pNode->right;while(pNode->left){pNode = pNode->left;}return pNode;}while(pNode->next!=NULL){TreeLinkNode* proot = pNode->next;if(proot->left == pNode)return proot;pNode=pNode->next;}return NULL;}
};11、对称的二叉树
题目:请实现一个函数,用来判断一颗二叉树是不是对称的。注意,如果一个二叉树同此二叉树的镜像是同样的,定义其为对称的
思路:递归判断:R1->left与R2->right比较,R2->left与R1->right比较
struct TreeNode
{int val;struct TreeNode *left;struct TreeNode *right;TreeNode(int x) :val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};class Solution
{
public:
bool isSymmetrical(TreeNode* pRoot)
{return isSymmetrical(pRoot,pRoot);
}
private:
bool isSymmetrical(TreeNode *pRoot1, TreeNode *pRoot2)
{if(pRoot1 == NULL && pRoot2 == NULL){return true;}if(pRoot1 == NULL || pRoot2 == NULL){return false;}if(pRoot1->val != pRoot2->val){return false;}return isSymmetrical(pRoot->left, &right) && isSymmetrical(pRoot->right,&left);
}
};12、按之字形顺序打印二叉树
请实现一个函数按照之字形打印二叉树,即第一行按照从左到右的顺序打印,第二层按照从右至左的顺序打印,第三行按照从左到右的顺序打印,其他行以此类推。
13、把二叉树打印成多行
struct TreeNode
{int val;struct TreeNode*left;struct TreeNode*right;TreeNode(int x):val(x),left(NULL),right(NULL);{}
};class Solution
{public:vector<vector<int> > Print(TreeNode* pRoot){vector<vector<int>>ans;if(pRoot == NULL)return ans;queue<TreeNode*>q;q.push(pRoot);while(q.empty()){int size = q.size();//读取每一层的元素的数量vector<TreeNode*>q1;while(size--){TreeNode*front = q.front();q.pop();q1.push_back(front ->val);if(front->left!=NULL) return front->left;if(front->right!=NULL) return front->right;}ans.push_back(q1);}return ans;}
};14、序列化二叉树
15、二叉搜索树的第k个结点
//中序遍历
TreeNode* KthNode(TreeNode* pRoot, unsigned int k)
{TreeNode *cur = root;int count = 0;stack<TreeNode*>s;while(s.empty() || cur){if(cur != NULL){s.push(cur);cur = cur->left;}else{cur = s.top();s.pop();count++;if(num == k)return cur->val;cur = cur->right;}}return 0;
}

