LinkedList-源码解读

简介
LinkedList 的特点:

LinkedList 的底层操作机制
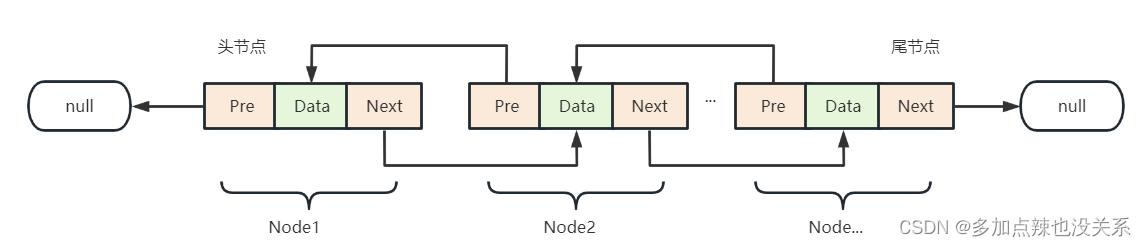
- LinkedList 底层维护了一个双向链表
- LinkedList 中维护了两个属性 first 和 last 分别指向首节点和尾节点
- 每个节点(Node对象),里面又维护了 prev、next、item三个属性,其中通过 prev 指向前一个,通过 next 指向后一个节点,最终实现双向链表
- 所以 LinkedList 的元素的添加和删除,不是通过数组完成的,相对来说效率较高
关于双向链表不太理解的可转至:Java-双向链表的实现
源码解读
首先可以先看一下 LinkedList 类的结构
public class LinkedList<E>extends AbstractSequentialList<E>implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{// 集合大小transient int size = 0;// 头节点transient Node<E> first;// 尾节点transient Node<E> last;// 修改次数protected transient int modCount = 0;//内部类:节点对象private static class Node<E> {// 节点数据E item;// 下一个节点Node<E> next;// 上一个节点Node<E> prev;Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {this.item = element;this.next = next;this.prev = prev;}} // 方法...
}
可以看到 LinkedList 类有一个内部类 Node,它是链表中的节点对象,数据保存在节点对象的 item 属性中,每个节点都会记录它的上一个节点 prev和下一个节点 next。 LinkedList 类也有两个比较关键的属性就是头节点 first 和尾节点last,其次就是用 size 来记录集合的大小。
值得注意的是这里面的属性都被 transient 关键字修饰,表示瞬时的,不可序列化,关于这个关键字的用途可跳转至:Java中transient关键字的详细总结
这里我大概分析以下三个方法:
- boolean add(E e) 方法
- void add(int index, E element) 方法
- E remove() 方法
无参构造方法
/* Constructs an empty list.*/public LinkedList() {}
可以看到在 LinkedList 的无参构造方法中并没有做什么事情,只是一个初始化,然后它的成员变量赋上默认值,比如:
- first =
null - last =
null
boolean add(E e) 方法
该方法就是往集合的末端添加元素,源码如下:
public boolean add(E e) {// 向链表的尾部添加元素linkLast(e);return true;}
可以看到该方法中实际上是调用了 linkLast() 方法
/* Links e as last element.*/void linkLast(E e) {// l 指向 last,即 l 表示链表的原尾节点final Node<E> l = last;// 创建一个新的节点 newNode// 在新的节点 newNode 中,它的上一个节点 prev 指向原尾节点 l,item 保存元素 efinal Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);// 移动链表的尾节点指向新创建的节点 newNodelast = newNode;// 判断原尾节点是否为空if (l == null)// 为空则表示之前的集合为空,这种情况下头节点就是尾节点first = newNode;else// 不为空,则将原尾节点的下一个节点 next 指向新节点 newNodel.next = newNode;// 集合大小+1size++;// 修改次数+1modCount++;}
往链表的尾部插入数据可分为两种情况:
-
链表为空时,即当前插入的元素为链表的第一个元素
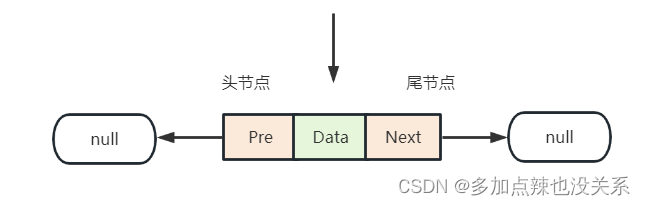
这种情况下新创建的节点不仅是链表的头节点也是链表的尾节点,新节点的前驱节点prev和后驱节点next都指向null -
链表不为空时
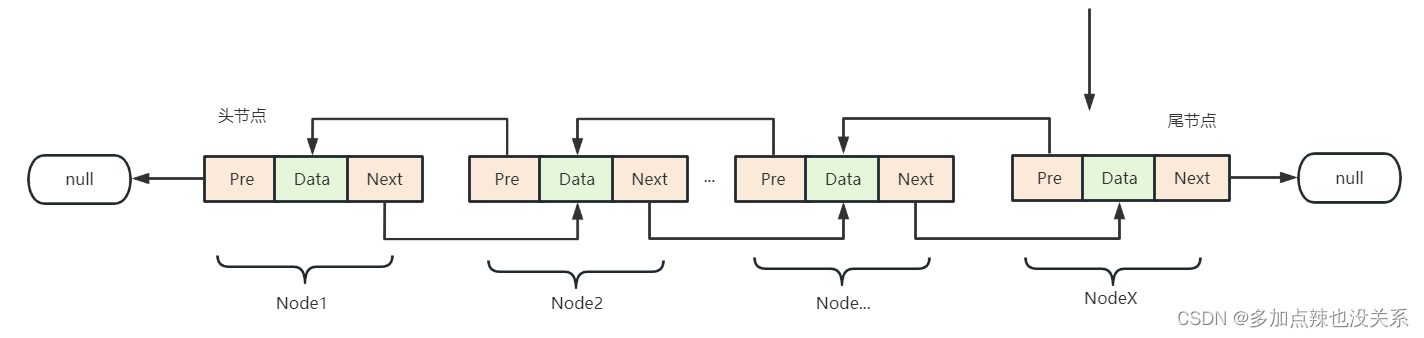
新插入的节点NodeX成为链表的尾节点,新节点的前驱节点prev指向原链表的尾节点Node...,原链表的尾节点Node...的后驱节点next指向新插入的节点NodeX
所以 linkLast() 方法的逻辑大概就是:
- 新增一个节点
newNode,将数据保存在新节点的item属性中,新节点的prev指向原尾节点 - 移动链表的尾节点,指向新创建的节点
newNode - 判断原尾节点是否为
null- 为
null表示此时新增的节点是链表的第一个节点,故头节点也是新创建的节点newNode - 不为
null,则需要将原尾节点的后驱节点next指向新节点newNode
- 为
- 集合长度
+1,集合修改次数+1
还有一点值得注意的是,l 和 newNode 都被 final 关键字修饰,关于 final 关键字的用法可跳转至:java final 关键字
void add(int index, E element) 方法
该方法作用为在指定索引位置上添加元素,源码如下:
/* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list.* Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and any* subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices). @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted* @param element element to be inserted* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}*/public void add(int index, E element) {// 校验指定索引是否合法checkPositionIndex(index);// 判断索引是否等于集合大小if (index == size)// 是,在尾端插入元素linkLast(element);else// 不是,则为从指定位置插入元素linkBefore(element, node(index));}
以上代码大概逻辑:
- checkPositionIndex() 校验指定索引是否合法
- 判断索引是否等于集合大小
- 是, 在尾端插入元素,方法 linkLast()
- 不是
- 先获取指定索引的节点,方法 node()
- 从指定节点插入元素,方法 linkBefore()
checkPositionIndex() 方法如下:
private void checkPositionIndex(int index) {if (!isPositionIndex(index))throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));}
/* Tells if the argument is the index of a valid position for an* iterator or an add operation.*/private boolean isPositionIndex(int index) {return index >= 0 && index <= size;}
node() 方法如下:
/* Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index.*/Node<E> node(int index) {// assert isElementIndex(index);// 这段代码是通过二分法来获取指定索引位置上的节点if (index < (size >> 1)) { // 右移1位 ==> size/2Node<E> x = first;for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)x = x.next;return x;} else {Node<E> x = last;for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)x = x.prev;return x;}}
此方法是通过二分法来回去指定索引位置上的节点,不多做赘述了~~
linkBefore() 方法如下:
/* Inserts element e before non-null Node succ.*/void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {// assert succ != null;// 获取指定节点的前驱节点 predfinal Node<E> pred = succ.prev;// 新建节点 newNode// item 保存元素 e// prev 保存指定节点的前驱节点 pred// next 保存指定节点final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);// 指定节点的前驱节点 prev 指向新节点 newNodesucc.prev = newNode;// 判断指定节点的前驱节点是否为 nullif (pred == null)// 是,表明在链表的第一个位置插入元素,则设置新节点为链表的头节点first = newNode;else// 指定节点的前驱节点 next 指向新节点pred.next = newNode;// 集合大小+1size++;// 修改次数+1modCount++;}
往链表的指定位置插入数据(排除尾插)可分为两种情况:
- 在第一个位置上插入元素
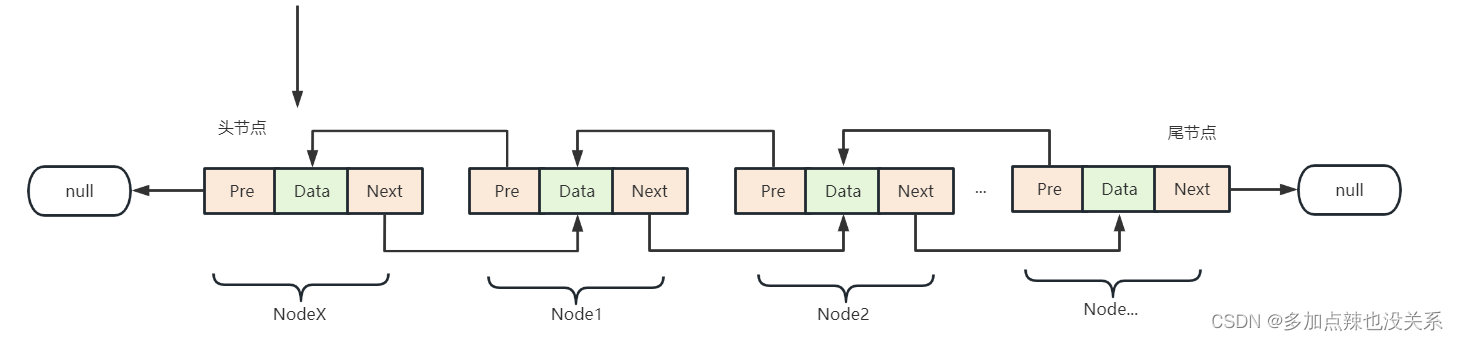
这种情况下,新插入的节点NodeX变成了头节点,所以NodeX的Next要指向原头节点Node1,NodeX的Pre为null - 在中间位置上插入元素
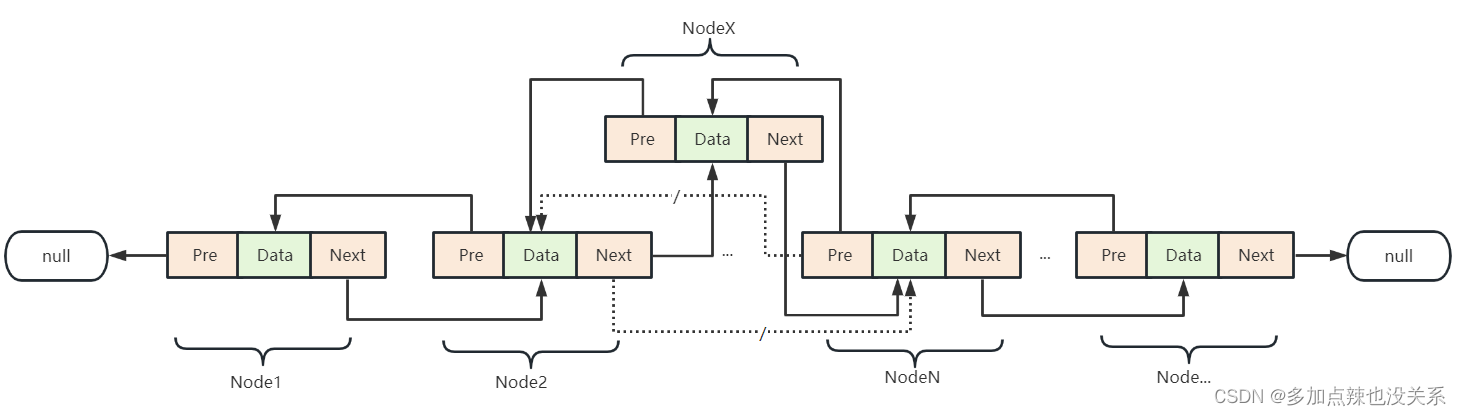
这种情况下,新插入的节点NodeX的前驱节点为原指定节点的前驱节点,原指定位置上的节点变成了新插入节点的后驱节点了
E remove() 方法
该方法会删除 LinkedList 集合中第一个元素,源码如下:
/* Retrieves and removes the head (first element) of this list. @return the head of this list* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty* @since 1.5*/public E remove() {// 移除第一个元素return removeFirst();}
跟进removeFirst() 方法:
/* Removes and returns the first element from this list. @return the first element from this list* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty*/public E removeFirst() {// 获取头节点final Node<E> f = first;// 判断头节点是否为 nullif (f == null)// 为 null 表示当前集合为空,抛出异常throw new NoSuchElementException();// 删除第一个元素return unlinkFirst(f);}
看到这里面会先对集合进行一个非空校验,然后进入 unlinkFirst() 方法,跟进:
/* Unlinks non-null first node f.*/private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {// assert f == first && f != null;// 获取原头节点的数据final E element = f.item;// 获取原头节点的后驱节点final Node<E> next = f.next;// 将原头节点的 item 置为 nullf.item = null;// 将原头节点中的 next 设置为 null f.next = null; // help GC:原头节点没有引用关系之后会被 GC 掉// 移动头节点为原头节点的下一个节点first = next;// 判断集合此前是否只有一个节点,即头节点的后驱节点为 nullif (next == null)// 如果是,删除该节点后,链表无节点,尾节点也需要设置为 nulllast = null;else// 如果不是,那么现在的头节点的前驱节点需要设置为 nullnext.prev = null;// 集合大小-1size--;// 修改次数+1modCount++;// 返回被删除的元素return element;}
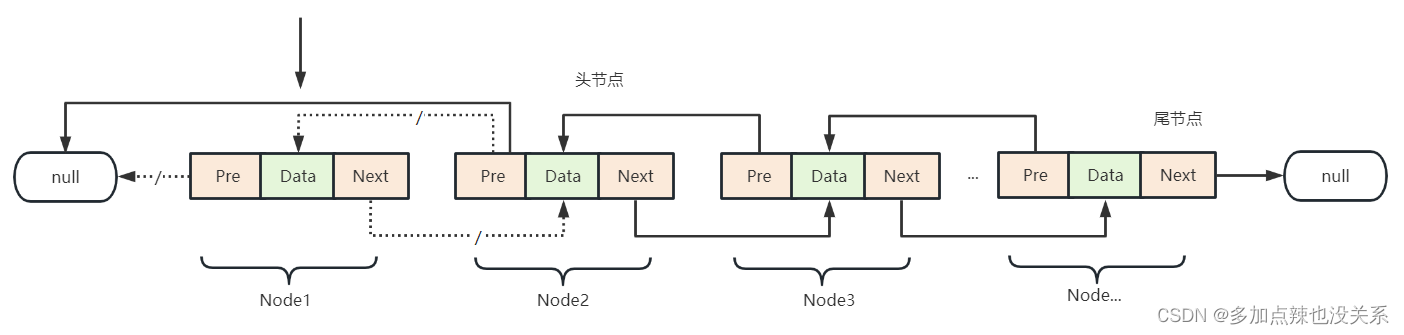
删除链表头部节点也需要分为两种情况去看待:
- 集合大小
= 1时,此时删除第一个节点之后,链表就没有节点了,所以链表的头节点和尾节点都需要设置为null - 集合大小
> 1时,原头节点Node1的后驱节点Next指向null,而它的下一个节点Node2变成头节点,Node2的 前驱节点Pre指向null
所以 unlinkFirst() 方法的逻辑大概就是:
- 获取原头节点的元素值
- 将原头节点的
item和next属性设置为null - 移动头节点到原头节点的后驱节点上
- 判断此前集合是否只有一个节点
- 是,链表的尾节点也需要设置为
null - 不是,则当前头节点的
prev需要设置为null
- 是,链表的尾节点也需要设置为
- 集合大小
-1,修改次数+1 - 返回原头节点的元素值


